当前位置:网站首页>Unit test of boot
Unit test of boot
2022-06-26 18:49:00 【51CTO】
1、JUnit5 The change of
- Spring Boot 2.2.0 Version introduction JUnit 5 As the default library for unit tests
- As the latest version of JUnit frame ,JUnit5 With the previous version of Junit The framework is very different . It consists of several different modules of three different subprojects .
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
- JUnit Platform: Junit Platform Is in JVM Start the Foundation of test framework , Not only support Junit Home made test engine , Other test engines can also be accessed .
- JUnit Jupiter: JUnit Jupiter Provides JUnit5 New programming model , yes JUnit5 The core of the new features . Inside Contains a Test engine , Used in Junit Platform Up operation .
- JUnit Vintage: because JUint It has developed for many years , in order to Compatible with old projects ,JUnit Vintage Provides compatibility JUnit4.x,Junit3.x The test engine .

- Be careful :
- SpringBoot 2.4 The above version removes the default pair Vintage Dependence . If you need compatibility junit4 It needs to be introduced by itself ( Out of commission junit4 The function of @Test)
- JUnit 5’s Vintage Engine Removed from
spring-boot-starter-test, If you need to continue compatibility junit4 It needs to be introduced by itself vintage
introduce junit Scene launcher
add to vintage engine , For continued compatibility junit4
<
dependency
>
<
groupId
>org.junit.vintage
</
groupId
>
<
artifactId
>junit-vintage-engine
</
artifactId
>
<
scope
>test
</
scope
>
<
exclusions
>
<
exclusion
>
<
groupId
>org.hamcrest
</
groupId
>
<
artifactId
>hamcrest-core
</
artifactId
>
</
exclusion
>
</
exclusions
>
</
dependency
>
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
Now the version :
- before :
- SpringBoot Integrate Junit5 in the future .
- @SpringBootTest Yes spring Some automatic injection and other functions
- Write test methods :@Test mark ( Pay attention to the need to use junit5 Comments on the version )
- Junit Class has Spring The function of ,@Autowired、 such as @Transactional Mark the test method , Automatically roll back after the test is completed
2、JUnit5 Commonly used annotations
JUnit5 The comments and JUnit4 The annotation of has changed
Official documents : https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests-annotations
- @Test : The representation method is the test method . But with the JUnit4 Of @Test Different , His duties are very single and cannot declare any attributes , The extended test will be conducted by Jupiter Provide additional testing
- @ParameterizedTest : The representation method is parametric testing , There will be a detailed introduction below
- @RepeatedTest : The representation method is repeatable , There will be a detailed introduction below
- @DisplayName : Set the display name for the test class or test method
- @BeforeEach : Means to execute before each unit test
- @AfterEach : Means to execute after each unit test
- @BeforeAll : Means to execute before all unit tests
- @AfterAll : Means to execute after all unit tests
- @Tag : Represents the unit test category , Be similar to JUnit4 Medium @Categories
- @Disabled : Indicates that the test class or test method does not execute , Be similar to JUnit4 Medium @Ignore
- @Timeout : Indicates that the test method will return an error if it exceeds the specified time
- @ExtendWith : Provide extension class references for test classes or test methods
// Join in springboot The function of , load springboot Whole
(
"junit5 unit testing ")
public
class
junit5Text1 {
UserServiceImpl
userServiceImpl;
(
" Test method 1 ")
public
void
text(){
System.
out.
println(
" ha-ha ");
}
(
" Test method 2 ")
// Disable this method , Will not run
public
void
text1(){
System.
out.
println(
" ha-ha ");
}
// Each unit test method is run before
void
text2(){
System.
out.
println(
" The test is about to begin !!");
}
// After each unit test method is completed, it will run
void
text3() {
System.
out.
println(
" The test is over !!");
}
// All unit tests will be run before
// Static method
// When running a unit test , Front and back runs
static
void
text4() {
System.
out.
printf(
" All the tests started !!");
}
// Run after all unit tests are completed
static
void
text5() {
System.
out.
println(
" All tests are over !!");
}
// If the specified time is exceeded, a timeout exception error will be returned
(
value
=
500,
unit
=
TimeUnit.
MILLISECONDS)
//value Is the value ,unit In units of
void
text6() {
try {
Thread.
sleep(
600);
}
catch (
InterruptedException
e) {
e.
printStackTrace();
}
}
void
text7() {
System.
out.
println(
userServiceImpl);
}
// Repeat test notes
(
5)
// Repeat the number
void
text8() {
System.
out.
println(
"a");
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
3、 Assertion (assertions)
- Assertion (assertions) Is the core part of the test method , It is used to verify the conditions that the test needs to meet .
- Check whether the data returned by the business logic is reasonable .
- After all the test runs , There will be a detailed test report ;
- The previous assertion failed , Later assertions will not execute
- These assertion methods are org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions Static method of .
- JUnit 5 Built in assertions can be divided into the following categories :
- Simple assertion 、 Combine assertions 、 Array assertion 、 Exception assertion 、 Assertion timeout 、 Fast failure
1、 Simple assertion
Used for simple validation of a single value . Such as :
Method | explain |
assertEquals | Determine whether two objects or two primitive types are equal |
assertNotEquals | Determine whether two objects or two primitive types are not equal |
assertSame | Determine whether two object references point to the same object |
assertNotSame | Judge whether two object references point to different objects |
assertTrue | Determines whether the given Boolean value is true |
assertFalse | Determines whether the given Boolean value is false |
assertNull | Determine whether the given object reference is null |
assertNotNull | Determine whether the given object reference is not null |
(
"simple assertion")
public
void
simple() {
assertEquals(
3,
1
+
2,
"simple math");
assertNotEquals(
3,
1
+
1);
assertNotSame(
new
Object(),
new
Object());
Object
obj
=
new
Object();
assertSame(
obj,
obj);
assertFalse(
1
>
2);
assertTrue(
1
<
2);
assertNull(
null);
assertNotNull(
new
Object());
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
2、 Array assertion
adopt assertArrayEquals Method to determine whether two objects or arrays of primitive types are equal
3、 Combine assertions
assertAll Method accepts multiple org.junit.jupiter.api.Executable An instance of a functional interface as an assertion to verify , Can pass lambda Expressions can easily provide these assertions
4、 Exception assertion
stay JUnit4 period , When you want to test the exception of a method , Need to use @Rule Annotated ExpectedException Variables are still troublesome . and JUnit5 Provides a new assertion method Assertions.assertThrows() , It can be used with functional programming .
5、 Assertion timeout
Junit5 It also provides Assertions.assertTimeout() Set timeout for test method
6、 Fast failure
adopt fail() Method directly causes the test to fail
4、 precondition (assumptions)
- JUnit 5 Preconditions in (assumptions【 hypothesis 】) Similar to assertions ,
- The different assertion is that Unsatisfied assertions will cause the test method to fail , Not satisfied Preconditions only terminate the execution of the test method .
- Preconditions can be regarded as the premise of test method execution , When the premise is not satisfied , There is no need to continue .
(
" precondition ")
public
class
AssumptionsTest {
private
final
String
environment
=
"DEV";
(
"simple")
public
void
simpleAssume() {
assumeTrue(
Objects.
equals(
this.
environment,
"DEV"));
assumeFalse(()
->
Objects.
equals(
this.
environment,
"PROD"));
}
(
"assume then do")
public
void
assumeThenDo() {
assumingThat(
Objects.
equals(
this.
environment,
"DEV"),
()
->
System.
out.
println(
"In DEV")
);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- assumeTrue and assumFalse Ensure that the given condition is true or false, Failure to meet the conditions will cause the test execution to terminate
- assumingThat The parameters of are Boolean values representing conditions and corresponding Executable Interface implementation object .
- Only when the conditions are met ,Executable Object will be executed ; When conditions are not met , Test execution does not terminate .
5、 Nested tests
- JUnit 5 Can pass Java Inner classes in and @Nested Annotations implement nested tests , So we can better organize the relevant test methods together .
- You can use... In inner classes @BeforeEach and @AfterEach annotation , And there is no limit to the level of nesting .
- Method execution outside the inner class , Will not execute inner classes @BeforeEach and @AfterEach Method
- Method execution in inner class , It will drive the outside @BeforeEach and @AfterEach Method , It will also drive the @BeforeEach and @AfterEach Method
(
"A stack")
class
TestingAStackDemo {
Stack
<
Object
>
stack;
(
"is instantiated with new Stack()")
void
isInstantiatedWithNew() {
new
Stack
<>();
}
(
"when new")
class
WhenNew {
void
createNewStack() {
stack
=
new
Stack
<>();
}
(
"is empty")
void
isEmpty() {
assertTrue(
stack.
isEmpty());
}
(
"throws EmptyStackException when popped")
void
throwsExceptionWhenPopped() {
assertThrows(
EmptyStackException.
class,
stack::
pop);
}
(
"throws EmptyStackException when peeked")
void
throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() {
assertThrows(
EmptyStackException.
class,
stack::
peek);
}
(
"after pushing an element")
class
AfterPushing {
String
anElement
=
"an element";
void
pushAnElement() {
stack.
push(
anElement);
}
(
"it is no longer empty")
void
isNotEmpty() {
assertFalse(
stack.
isEmpty());
}
(
"returns the element when popped and is empty")
void
returnElementWhenPopped() {
assertEquals(
anElement,
stack.
pop());
assertTrue(
stack.
isEmpty());
}
(
"returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")
void
returnElementWhenPeeked() {
assertEquals(
anElement,
stack.
peek());
assertFalse(
stack.
isEmpty());
}
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
6、 Parametric testing
- Parametric testing is JUnit5 An important new feature , It makes it possible to run tests multiple times with different parameters , It also brings a lot of convenience to our unit testing .@ParameterizedTest Specifies that the current method is a parameterized method
- utilize @ValueSource Etc , Specify input parameters , We will be able to do multiple unit tests with different parameters , Instead of adding a unit test every time a parameter is added , It saves a lot of redundant code .
- @ValueSource : Specify the input parameter source for parameterized tests , Support eight basic categories and String type ,Class class
- @NullSource : Representation provides a... For parameterized testing null Input
- @EnumSource : Represents an enumeration input parameter for parameterized testing
- @CsvFileSource : Indicates to read the specified CSV File content as parametric test input parameter
- @MethodSource : Read the return value of the specified method as the parameterized test input parameter ( Note that the method return needs to be a stream )
Of course, if the parametric test can only specify ordinary input parameters, it can not reach the point that makes me feel amazing . What makes me really feel his strength is that he can support all kinds of external participation . Such as :CSV,YML,JSON Files and even the return value of a method can be used as input parameters . Just need to realize ArgumentsProvider Interface , Any external file can be its input parameter .
// The current test method is parameterized test
(
strings
= {
"one",
"two",
"three"})
// Parameter passing , Pass a parameter to execute the method once
(
" Parametric testing 1")
public
void
parameterizedTest1(
String
string) {
System.
out.
println(
string);
Assertions.
assertTrue(
StringUtils.
isNotBlank(
string));
}
(
"method")
// Specify the method name
(
" Method source parameter ")
public
void
testWithExplicitLocalMethodSource(
String
name) {
System.
out.
println(
name);
Assertions.
assertNotNull(
name);
}
static
Stream
<
String
>
method() {
return
Stream.
of(
"apple",
"banana");
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
7、 Migration guide
from junit4 The following changes should be noted during migration :
- Annotations in org.junit.jupiter.api In bag , Assertion in org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions Class , The precondition is org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions Class .
- hold @Before and @After Replace with @BeforeEach and @AfterEach.
- hold @BeforeClass and @AfterClass Replace with @BeforeAll and @AfterAll.
- hold @Ignore Replace with @Disabled.
- hold @Category Replace with @Tag.
- hold @RunWith、 @Rule and @ClassRule Replace with @ExtendWith.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Boot的单元测试
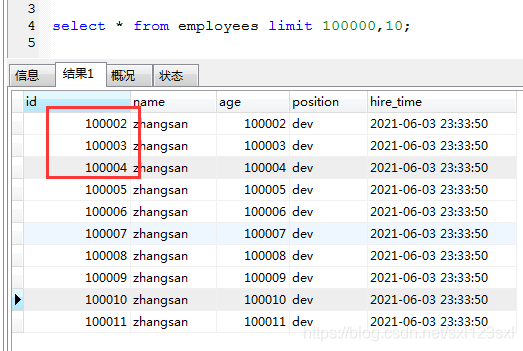
Paging query and join Association query optimization

Basic and necessary common plug-ins of vscade

Redis single sign on system + voting system

(multi threading knowledge points that must be mastered) understand threads, create threads, common methods and properties of using threads, and the meaning of thread state and state transition

Micro service single sign on system (SSO)

Take you to resolve hash conflicts and implement a simple hash table,
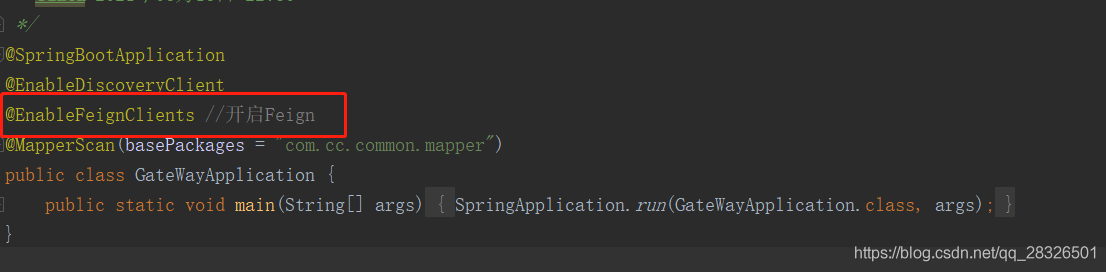
Feign remote call

wm_ Concat() and group_ Concat() function
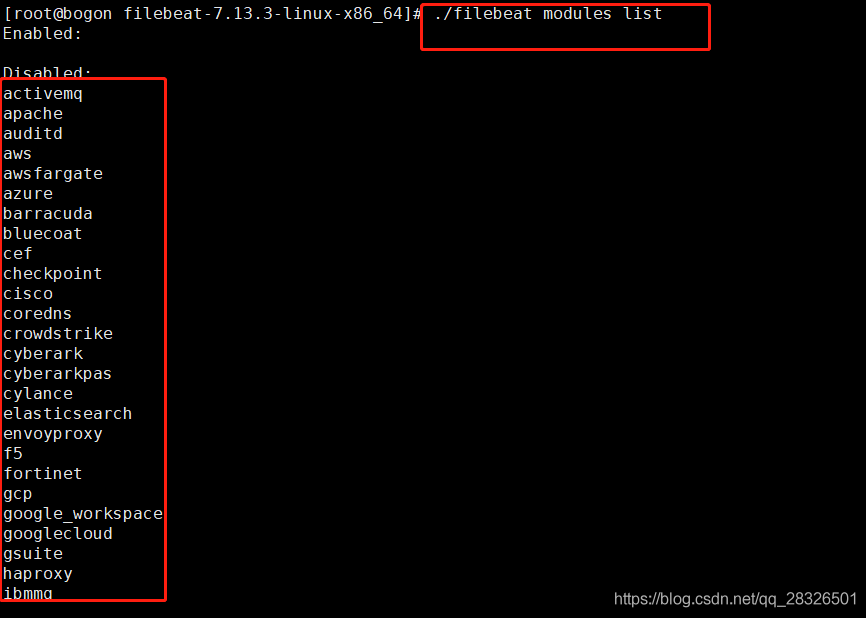
Filebeat安装及使用
随机推荐
Temporarily turn off MySQL cache
ROS的发布消息Publishers和订阅消息Subscribers
项目实战六:分布式事务-Seata
Wechat applet custom pop-up components
JVM entry door (1)
元宇宙链游开发案例版 NFT元宇宙链游系统开发技术分析
Convex hull problem
GDB installation
CD-CompactDisk
Successfully solved the problem of garbled microservice @value obtaining configuration file
Insert string B into string A. how many insertion methods can make the new string a palindrome string
知识点总结
Summary of alter operation in SQL
Chain game development finished product source code chain game system development details
深度学习之Numpy篇
手机影像内卷几时休?
Union, intersection and difference operations in SQL
Current limiting design and Implementation
Basic and necessary common plug-ins of vscade
Feign remote call