当前位置:网站首页>Redis source code and design analysis -- 13. Ordered collection objects
Redis source code and design analysis -- 13. Ordered collection objects
2022-07-23 10:50:00 【JunesFour】
Redis An orderly collection of objects
List of articles
1. The structure of an ordered collection object
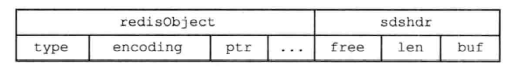
The encoding of an ordered set can be ziplist perhaps skiplist.
When using ziplist When coding , Each collection element uses two packed list nodes next to each other to hold , The first node holds the members of the element , And the second element holds the score of the element , The set elements in the compressed list are sorted from small to large . Elements with small scores are close to the header , Elements with high scores are near the end of the table . Here's the picture :


When using skiplist When coding , Of ordered collection objects ptr The pointer will point to a zset structure , This structure contains both a dictionary and a jump table :
// Ordered set type
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
Pictured :

But why use two data structures , Instead of using jump tables or dictionaries directly ?
When you want to find the score of an ordered set object according to its members , Dictionary will be used to realize , The time complexity is O(1), And if you just use the jump table , This complexity will be O(log(n)).
When an ordered collection object wants to perform a range operation , such as ZRANK、ZRANGE When ordered , We will use jump table to realize , And if we only use dictionary to realize , Each time, the found elements should be reordered , The time complexity of sorting is at least O(NlogN), And the extra O(N) Spatial complexity ( Save sorting results ).
therefore Redis We choose to use dictionary and jump table to realize ordered set . But these two data structures share the members and scores of the same element through pointers , So using jump table and dictionary to save set elements at the same time will not produce any duplicate members or scores , It will not waste extra space .
You can refer to the following structure diagram , For the convenience of display , The members and scores of each element are repeatedly displayed in dictionaries and jump tables , But in practice , Dictionaries and jump tables share members and scores of elements , So it doesn't cause any data duplication , It will not waste any space .

2. Ordered collection object encoding
2.1 Coding rules
When an ordered collection object can satisfy both of the following conditions , Object use ziplist code :
- The ordered set holds less elements than
128individual . - The length of all element members in an ordered set is less than 64 byte .
An ordered collection object that does not satisfy both of the above conditions will use skiplist code .
2.2 Encoding conversion
For the use of ziplist Coded ordered sets of objects , When using ziplist When either of the two conditions required for encoding cannot be satisfied , The object's transcoding operation is performed , All collection elements originally saved in the compressed list are transferred and saved to the zset Inside the structure , The object's encoding will also be from ziplist Turn into skiplist.
3. Introduction to the order collection object command
| command | describe |
|---|---|
| ZADD key score1 member1 [score2 member2] | Add one or more members... To an ordered collection , Or update scores of existing members |
| ZCARD key | Get the number of members of the ordered set |
| ZCOUNT key min max | Calculates the number of members of a specified interval fraction in an ordered set |
| ZINCRBY key increment member | Add the increment... To the score of the specified member in the ordered set increment |
| ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] | Calculates the intersection of a given ordered set or sets and stores the result set in a new ordered set key in |
| ZLEXCOUNT key min max | Computes the number of members in the specified dictionary interval in an ordered collection |
| ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] | Returns an ordered set through an index interval to synthesize members in a specified interval |
| ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count] | Returns the members of an ordered set through a dictionary interval |
| ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT] | Returns the members of an ordered set in a specified interval through scores |
| ZRANK key member | Returns the index of a specified member in an ordered collection |
| ZREM key member [member …] | Remove one or more members of an ordered collection |
| ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max | Remove all members of a given dictionary interval from an ordered set |
| ZREMRANGEBYRANK key start stop | Remove all members of a given rank range from an ordered set |
| ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key min max | Remove all members of a given fraction interval from an ordered set |
| ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] | Returns the members of a specified interval in an ordered set , Through the index , Score from high to the end |
| ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] | Returns the members of the specified score range in an ordered set , Rank scores from high to low |
| ZREVRANK key member | Returns the rank of a specified member in an ordered set , Members of an ordered set are decremented by fractions ( From big to small ) Sort |
| ZSCORE key member | Back to the ordered set , The score of a member |
| ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] | Computes the union of a given ordered set or sets , And store it in the new key in |
| ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] | Iterate over elements in an ordered set ( Include element members and element scores ) |
4. Implementation of the order collection object command
The source code of ordered collection objects is server.h Header files and t_zset.c In the source file .
4.1 How to limit the scope of an ordered set
We can find that ordered sets have three main commands about range operations :
| command | describe |
|---|---|
| ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] | Returns an ordered set through an index interval to synthesize members in a specified interval |
| ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count] | Returns the members of an ordered set through a dictionary interval |
| ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT] | Returns the members of an ordered set in a specified interval through scores |
therefore Redis Ordered sets have three kinds of scope restrictions :
- According to the dictionary interval
- According to the ranking ( Indexes ) Section
- According to the score range
The above three mainly rely on two sorting methods :
- Score sequence
- Dictionary order
The range represented by the above two sorts , Depends on two structures , A specified range and boundary of score order , A scope and boundary that defines the lexicographic order :
The following structures are defined in server.h Header file .
/* Struct to hold a inclusive/exclusive range spec by score comparison. */
typedef struct {
// Min and Max
double min, max;
// minex Indicates whether the minimum value is included in this range ,1 Does not include ,0 Means to contain
// Empathy maxex Represents the maximum value
int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zrangespec;
/* Struct to hold an inclusive/exclusive range spec by lexicographic comparison. */
typedef struct {
robj *min, *max; /* May be set to shared.(minstring|maxstring) */// Min and Max
// minex Indicates whether the minimum value is included in this range ,1 Does not include ,0 Means to contain
// Empathy maxex Represents the maximum value
int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zlexrangespec;
4.2 Range operation of ordered set
4.2.1 ZRANGE
// ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
// ZRANGE Command implementation
void zrangeCommand(client *c) {
zrangeGenericCommand(c,0);
}
// ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
// ZREVRANGE Command implementation
void zrevrangeCommand(client *c) {
zrangeGenericCommand(c,1);
}
Underlying implementation
// ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
// ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES]
// ZRANGE、ZREVRANGE Command bottom implementation
void zrangeGenericCommand(client *c, int reverse) {
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *zobj;
int withscores = 0;
long start;
long end;
int llen;
int rangelen;
// Take out the starting position start And end position end
if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &start, NULL) != C_OK) ||
(getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[3], &end, NULL) != C_OK)) return;
// If there is WITHSCORES Parameters , Set logo
if (c->argc == 5 && !strcasecmp(c->argv[4]->ptr,"withscores")) {
withscores = 1;
// Too many parameters send syntax error message
} else if (c->argc >= 5) {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
return;
}
// Take out with read operation key Order the collection and check the data type of the collection
if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,key,shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL
|| checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET)) return;
/* Sanitize indexes. */
// Get the subscript range of the ordered set
llen = zsetLength(zobj);
// Handle negative Subscripts
if (start < 0) start = llen+start;
if (end < 0) end = llen+end;
if (start < 0) start = 0;
/* Invariant: start >= 0, so this test will be true when end < 0. * The range is empty when start > end or start >= length. */
// Trim adjust subscript
if (start > end || start >= llen) {
addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk);
return;
}
if (end >= llen) end = llen-1;
rangelen = (end-start)+1; // Range length
/* Return the result in form of a multi-bulk reply */
// Send the number of reply lines to client
addReplyMultiBulkLen(c, withscores ? (rangelen*2) : rangelen);
// If it is ziplist
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;
unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
// according to reverse Determine the node address of the traversal head or tail element eptr
if (reverse)
eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,-2-(2*start));
else
eptr = ziplistIndex(zl,2*start);
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL);
// Get the address of the score node
sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);
// Take out rangelen Elements
while (rangelen--) {
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL && sptr != NULL);
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ziplistGet(eptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong)); // The element information is saved in parameters
// The types of elements are different , Send different types of reply messages
if (vstr == NULL)
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,vlong);
else
addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,vstr,vlen);
// Set up withscores, Send score
if (withscores)
addReplyDouble(c,zzlGetScore(sptr));
// according to reverse, The node that points to the next element and score
if (reverse)
zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
else
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
// If it's a jump table
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
zskiplistNode *ln;
robj *ele;
/* Check if starting point is trivial, before doing log(N) lookup. */
// according to reverse decision , The node address of the traversal head or tail element
if (reverse) {
ln = zsl->tail;
if (start > 0)
ln = zslGetElementByRank(zsl,llen-start);
} else {
ln = zsl->header->level[0].forward;
if (start > 0)
ln = zslGetElementByRank(zsl,start+1);
}
// Take out rangelen Elements
while(rangelen--) {
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ln != NULL);
ele = ln->obj;
addReplyBulk(c,ele); // Send element
if (withscores)
addReplyDouble(c,ln->score); // Send score
// Point to next node
ln = reverse ? ln->backward : ln->level[0].forward;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
}
4.2.2 ZRANGEBYSCORE
// ZRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
// ZRANGEBYSCORE Command implementation
void zrangebyscoreCommand(client *c) {
genericZrangebyscoreCommand(c,0);
}
// ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
// ZREVRANGEBYSCORE Command implementation
void zrevrangebyscoreCommand(client *c) {
genericZrangebyscoreCommand(c,1);
}
Underlying implementation
/* This command implements ZRANGEBYSCORE, ZREVRANGEBYSCORE. */
// ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
// ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
// ZRANGEBYSCORE ZREVRANGEBYSCORE The underlying implementation of the command
void genericZrangebyscoreCommand(client *c, int reverse) {
zrangespec range;
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *zobj;
long offset = 0, limit = -1;
int withscores = 0;
unsigned long rangelen = 0;
void *replylen = NULL;
int minidx, maxidx;
/* Parse the range arguments. */
// analysis min and max Subscript of the parameter of the range
if (reverse) {
/* Range is given as [max,min] */
maxidx = 2; minidx = 3;
} else {
/* Range is given as [min,max] */
minidx = 2; maxidx = 3;
}
// analysis min and max Range parameter , Save to zrangespec in , The default is to include [] critical value
if (zslParseRange(c->argv[minidx],c->argv[maxidx],&range) != C_OK) {
addReplyError(c,"min or max is not a float");
return;
}
/* Parse optional extra arguments. Note that ZCOUNT will exactly have * 4 arguments, so we'll never enter the following code path. */
// Parse other parameters
if (c->argc > 4) {
int remaining = c->argc - 4; // Number of other parameters
int pos = 4;
while (remaining) {
// If there is WITHSCORES, Set logo
if (remaining >= 1 && !strcasecmp(c->argv[pos]->ptr,"withscores")) {
pos++; remaining--;
withscores = 1;
// If there is LIMIT, Take out offset and count value Save in offset and limit in
} else if (remaining >= 3 && !strcasecmp(c->argv[pos]->ptr,"limit")) {
if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[pos+1], &offset, NULL) != C_OK) ||
(getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[pos+2], &limit, NULL) != C_OK)) return;
pos += 3; remaining -= 3;
} else {
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
return;
}
}
}
/* Ok, lookup the key and get the range */
// Fetch an ordered collection object with a read operation
if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,key,shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET)) return;
// ziplist
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;
unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
double score;
/* If reversed, get the last node in range as starting point. */
// get range The starting element node address in the range
if (reverse) {
eptr = zzlLastInRange(zl,&range);
} else {
eptr = zzlFirstInRange(zl,&range);
}
/* No "first" element in the specified interval. */
// There are no elements in range in , Send an empty reply
if (eptr == NULL) {
addReply(c, shared.emptymultibulk);
return;
}
/* Get score pointer for the first element. */
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL);
// Score node address
sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);
/* We don't know in advance how many matching elements there are in the * list, so we push this object that will represent the multi-bulk * length in the output buffer, and will "fix" it later */
// Reply length
replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);
/* If there is an offset, just traverse the number of elements without * checking the score because that is done in the next loop. */
// skip offset Set length
while (eptr && offset--) {
if (reverse) {
zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
} else {
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
}
// Traverse all nodes that meet the scope
while (eptr && limit--) {
score = zzlGetScore(sptr); // Get points
/* Abort when the node is no longer in range. */
// Check whether the score meets the score within the range
if (reverse) {
if (!zslValueGteMin(score,&range)) break;
} else {
if (!zslValueLteMax(score,&range)) break;
}
/* We know the element exists, so ziplistGet should always succeed */
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ziplistGet(eptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong)); // Save the value of the current element into the parameter
rangelen++;
// Different element types , Send different types of values to client
if (vstr == NULL) {
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,vlong);
} else {
addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,vstr,vlen);
}
if (withscores) {
addReplyDouble(c,score); // Send score
}
/* Move to next node */
// Point to the next element and score node
if (reverse) {
zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
} else {
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
}
// Skip list
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
zskiplistNode *ln;
/* If reversed, get the last node in range as starting point. */
// get range The starting node address in the range
if (reverse) {
ln = zslLastInRange(zsl,&range);
} else {
ln = zslFirstInRange(zsl,&range);
}
/* No "first" element in the specified interval. */
// No element exists within the specified scope
if (ln == NULL) {
addReply(c, shared.emptymultibulk);
return;
}
/* We don't know in advance how many matching elements there are in the * list, so we push this object that will represent the multi-bulk * length in the output buffer, and will "fix" it later */
// Reply length
replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);
/* If there is an offset, just traverse the number of elements without * checking the score because that is done in the next loop. */
// skip offset Nodes
while (ln && offset--) {
if (reverse) {
ln = ln->backward;
} else {
ln = ln->level[0].forward;
}
}
// Traverse all nodes that meet the scope
while (ln && limit--) {
/* Abort when the node is no longer in range. */
// Check whether the score meets
if (reverse) {
if (!zslValueGteMin(ln->score,&range)) break;
} else {
if (!zslValueLteMax(ln->score,&range)) break;
}
rangelen++;
addReplyBulk(c,ln->obj); // Send element
if (withscores) {
addReplyDouble(c,ln->score); // Send score
}
/* Move to next node */
// Point to next node
if (reverse) {
ln = ln->backward;
} else {
ln = ln->level[0].forward;
}
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
if (withscores) {
// Update reply length
rangelen *= 2;
}
setDeferredMultiBulkLength(c, replylen, rangelen); // The length of the sending range
}
4.2.3 ZRANGEBYLEX
// ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
// ZRANGEBYLEX Command implementation
void zrangebylexCommand(client *c) {
genericZrangebylexCommand(c,0);
}
// ZREVRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
// ZREVRANGEBYLEX Command implementation
void zrevrangebylexCommand(client *c) {
genericZrangebylexCommand(c,1);
}
Underlying implementation
/* This command implements ZRANGEBYLEX, ZREVRANGEBYLEX. */
// ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
// ZRANGEBYLEX Command implementation
void genericZrangebylexCommand(client *c, int reverse) {
zlexrangespec range;
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *zobj;
long offset = 0, limit = -1;
unsigned long rangelen = 0;
void *replylen = NULL;
int minidx, maxidx;
/* Parse the range arguments. */
// analysis min and max Subscript of the parameter of the range
if (reverse) {
/* Range is given as [max,min] */
maxidx = 2; minidx = 3;
} else {
/* Range is given as [min,max] */
minidx = 2; maxidx = 3;
}
// analysis min and max Parameters of the range , Save to range
if (zslParseLexRange(c->argv[minidx],c->argv[maxidx],&range) != C_OK) {
addReplyError(c,"min or max not valid string range item");
return;
}
/* Parse optional extra arguments. Note that ZCOUNT will exactly have * 4 arguments, so we'll never enter the following code path. */
// Parse other parameters
if (c->argc > 4) {
int remaining = c->argc - 4; // Number of other parameters
int pos = 4;
while (remaining) {
// If there is LIMIT, Take out offset and count Save in offset and limit
if (remaining >= 3 && !strcasecmp(c->argv[pos]->ptr,"limit")) {
if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[pos+1], &offset, NULL) != C_OK) ||
(getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[pos+2], &limit, NULL) != C_OK)) return;
pos += 3; remaining -= 3;
} else {
zslFreeLexRange(&range);
addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);
return;
}
}
}
/* Ok, lookup the key and get the range */
// Fetch an ordered collection object with a read operation
if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,key,shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL ||
checkType(c,zobj,OBJ_ZSET))
{
zslFreeLexRange(&range);
return;
}
// ziplist
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
unsigned char *zl = zobj->ptr;
unsigned char *eptr, *sptr;
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
/* If reversed, get the last node in range as starting point. */
// get range The starting element node address in the range
if (reverse) {
eptr = zzlLastInLexRange(zl,&range);
} else {
eptr = zzlFirstInLexRange(zl,&range);
}
/* No "first" element in the specified interval. */
// No element is in scope
if (eptr == NULL) {
addReply(c, shared.emptymultibulk);
zslFreeLexRange(&range);
return;
}
/* Get score pointer for the first element. */
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,eptr != NULL);
// The address of the score node
sptr = ziplistNext(zl,eptr);
/* We don't know in advance how many matching elements there are in the * list, so we push this object that will represent the multi-bulk * length in the output buffer, and will "fix" it later */
// Reply length
replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);
/* If there is an offset, just traverse the number of elements without * checking the score because that is done in the next loop. */
// skip offset Set length
while (eptr && offset--) {
if (reverse) {
zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
} else {
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
}
// Traverse all nodes that meet the scope
while (eptr && limit--) {
/* Abort when the node is no longer in range. */
// Check whether the score meets the score within the range
if (reverse) {
if (!zzlLexValueGteMin(eptr,&range)) break;
} else {
if (!zzlLexValueLteMax(eptr,&range)) break;
}
/* We know the element exists, so ziplistGet should always * succeed. */
serverAssertWithInfo(c,zobj,ziplistGet(eptr,&vstr,&vlen,&vlong)); // Save the value of the current element into the parameter
rangelen++;
// Different element value types , Send different types of values client
if (vstr == NULL) {
addReplyBulkLongLong(c,vlong);
} else {
addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,vstr,vlen);
}
/* Move to next node */
// Point to the next element and score node
if (reverse) {
zzlPrev(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
} else {
zzlNext(zl,&eptr,&sptr);
}
}
// skiplist
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
zskiplistNode *ln;
/* If reversed, get the last node in range as starting point. */
// get range The starting node address in the range
if (reverse) {
ln = zslLastInLexRange(zsl,&range);
} else {
ln = zslFirstInLexRange(zsl,&range);
}
/* No "first" element in the specified interval. */
// No nodes meet the scope
if (ln == NULL) {
addReply(c, shared.emptymultibulk);
zslFreeLexRange(&range);
return;
}
/* We don't know in advance how many matching elements there are in the * list, so we push this object that will represent the multi-bulk * length in the output buffer, and will "fix" it later */
// Reply length
replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);
/* If there is an offset, just traverse the number of elements without * checking the score because that is done in the next loop. */
// skip offset Nodes
while (ln && offset--) {
if (reverse) {
ln = ln->backward;
} else {
ln = ln->level[0].forward;
}
}
// Traverse all nodes that meet the scope
while (ln && limit--) {
/* Abort when the node is no longer in range. */
if (reverse) {
// Check whether the score meets
if (!zslLexValueGteMin(ln->obj,&range)) break;
} else {
if (!zslLexValueLteMax(ln->obj,&range)) break;
}
rangelen++;
addReplyBulk(c,ln->obj); // Send element
/* Move to next node */
// Point to next node
if (reverse) {
ln = ln->backward;
} else {
ln = ln->level[0].forward;
}
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown sorted set encoding");
}
zslFreeLexRange(&range); // Release dictionary order range
setDeferredMultiBulkLength(c, replylen, rangelen); // Send reply length value
}
Reference material :
《Redis Design and implementation 》
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

《Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks》论文阅读

Response object

IO应知应会
PyQt5_ Qlistwidget paging multiple selection control

赫克Hurco工控机维修WinMax数控机床控制器维修

Add trust list
Redis源码与设计剖析 -- 9.字符串对象

3dMax先蒙皮刷权重,再附加合并

PXE remote installation and kickstart unattended installation technical documents

SQLZOO——SELECT from WORLD Tutorial
随机推荐
When flutter runs flutter pub get, it reports an error: "the client does not have the required privileges“
Add trust list
Chapter 3 Standard Input
UNITY VFX syntax error: unexpected token ‘#‘ at kernel CSMain
A case study on the collaborative management of medical enterprise suppliers, hospitals, patients and other parties by building a low code platform
【无标题】
TZC 1283: 简单排序 —— 堆排序
Ultra Fast Deep Lane Detection with Hybrid Anchor Driven Ordinal Classification论文解读
Leetcode skimming -- bit by bit record 022
第一章概述-------第一节--1.2互联网概述
nacos限流查询的脚本
toco生成tflite模型
0 basic career change software test, the necessary skills with a monthly salary of 6000 and 11000 are quite different
NOTIFIER诺帝菲尔消防主机电源维修及日常维护
Wechat applet package wx.request
交换机Exchanges
部署storageclass踩坑记录
MGRE环境下实现私网互通综合实验
C language explanation series - understanding of functions (1) library functions, user-defined functions
20.有效的括号