当前位置:网站首页>Machine learning Basics - decision tree-12
Machine learning Basics - decision tree-12
2022-07-28 12:56:00 【gemoumou】
Decision tree Decision Tree












Decision tree - Example
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn import preprocessing
import csv
# Read in the data
Dtree = open(r'AllElectronics.csv', 'r')
reader = csv.reader(Dtree)
# Get the first row of data
headers = reader.__next__()
print(headers)
# Define two lists
featureList = []
labelList = []
#
for row in reader:
# hold label Deposit in list
labelList.append(row[-1])
rowDict = {
}
for i in range(1, len(row)-1):
# Build a data dictionary
rowDict[headers[i]] = row[i]
# Store the data dictionary in list
featureList.append(rowDict)
print(featureList)

# Convert data into 01 Express
vec = DictVectorizer()
x_data = vec.fit_transform(featureList).toarray()
print("x_data: " + str(x_data))
# Print attribute name
print(vec.get_feature_names())
# Print labels
print("labelList: " + str(labelList))
# Convert labels into 01 Express
lb = preprocessing.LabelBinarizer()
y_data = lb.fit_transform(labelList)
print("y_data: " + str(y_data))

# Create a decision tree model
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
# Input data to build model
model.fit(x_data, y_data)

# test
x_test = x_data[0]
print("x_test: " + str(x_test))
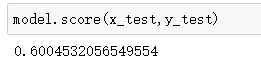
predict = model.predict(x_test.reshape(1,-1))
print("predict: " + str(predict))












Decision tree -CART
from sklearn import tree
import numpy as np
# Load data
data = np.genfromtxt("cart.csv", delimiter=",")
x_data = data[1:,1:-1]
y_data = data[1:,-1]
# Create a decision tree model
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# Input data to build model
model.fit(x_data, y_data)

# Export decision tree
import graphviz # http://www.graphviz.org/
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model,
out_file = None,
feature_names = ['house_yes','house_no','single','married','divorced','income'],
class_names = ['no','yes'],
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)
graph.render('cart')


Decision tree - Linear dichotomy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import tree
# Load data
data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv", delimiter=",")
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
plt.scatter(x_data[:,0],x_data[:,1],c=y_data)
plt.show()

# Create a decision tree model
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# Input data to build model
model.fit(x_data, y_data)

# Export decision tree
import graphviz # http://www.graphviz.org/
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model,
out_file = None,
feature_names = ['x','y'],
class_names = ['label0','label1'],
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)

# Get the range of data values
x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1
# Generate grid matrix
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])# ravel And flatten similar , Multidimensional data to one dimension .flatten Will not change the original data ,ravel Will change the original data
z = z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Contour map
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z)
# Sample scatter plot
plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], c=y_data)
plt.show()

predictions = model.predict(x_data)
print(classification_report(predictions,y_data))

Decision tree - Nonlinear dichotomy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Load data
data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet2.txt", delimiter=",")
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
plt.scatter(x_data[:,0],x_data[:,1],c=y_data)
plt.show()

# Split data
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data)
# Create a decision tree model
# max_depth, Depth of tree
# min_samples_split Minimum number of samples required for internal node subdivision
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=7,min_samples_split=4)
# Input data to build model
model.fit(x_train, y_train)

# Export decision tree
import graphviz # http://www.graphviz.org/
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model,
out_file = None,
feature_names = ['x','y'],
class_names = ['label0','label1'],
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)

# Get the range of data values
x_min, x_max = x_data[:, 0].min() - 1, x_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_data[:, 1].min() - 1, x_data[:, 1].max() + 1
# Generate grid matrix
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])# ravel And flatten similar , Multidimensional data to one dimension .flatten Will not change the original data ,ravel Will change the original data
z = z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Contour map
cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, z)
# Sample scatter plot
plt.scatter(x_data[:, 0], x_data[:, 1], c=y_data)
plt.show()

predictions = model.predict(x_train)
print(classification_report(predictions,y_train))

predictions = model.predict(x_test)
print(classification_report(predictions,y_test))


Back to the tree
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
# Load data
data = np.genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",")
x_data = data[:,0,np.newaxis]
y_data = data[:,1,np.newaxis]
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data)
plt.show()

model = tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
model.fit(x_data, y_data)

x_test = np.linspace(20,80,100)
x_test = x_test[:,np.newaxis]
# drawing
plt.plot(x_data, y_data, 'b.')
plt.plot(x_test, model.predict(x_test), 'r')
plt.show()

# Export decision tree
import graphviz # http://www.graphviz.org/
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model,
out_file = None,
feature_names = ['x','y'],
class_names = ['label0','label1'],
filled = True,
rounded = True,
special_characters = True)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)

Back to the tree - Forecast house prices
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.datasets.california_housing import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
housing = fetch_california_housing()
print(housing.DESCR)

housing.data.shape

housing.data[0]

housing.target[0]

x_data = housing.data
y_data = housing.target
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data)
model = tree.DecisionTreeRegressor()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)

边栏推荐
- LeetCode 移除元素&移动零
- Fundamentals of machine learning - principal component analysis pca-16
- [graduation design teaching] ultrasonic ranging system based on single chip microcomputer - Internet of things embedded stm32
- Hongjiu fruit passed the hearing: five month operating profit of 900million Ali and China agricultural reclamation are shareholders
- 05 pyechars 基本图表(示例代码+效果图)
- CCF201912-2 回收站选址
- Merge sort
- 非标自动化设备企业如何借助ERP系统,做好产品质量管理?
- STM32F103 几个特殊引脚做普通io使用注意事项以及备份寄存器丢失数据问题1,2
- Leetcode remove element & move zero
猜你喜欢

01 introduction to pyechars features, version and installation

Cloud native - runtime environment

How to add PDF virtual printer in win11

Design a thread pool

Introduction to border border attribute

Science heavyweight: AI design protein has made another breakthrough, and it can design specific functional proteins

机器学习实战-决策树-22

LeetCode 42.接雨水

Linear classifier (ccf20200901)

VS1003调试例程
随机推荐
DART 三维辐射传输模型申请及下载
Initialization examples of several modes of mma8452q
Leetcode: array
Which big model is better? Openbmb releases bmlist to give you the answer!
1331. Array sequence number conversion: simple simulation question
Solution to using json.tojsonstring to display question marks in Chinese in Servlet
MySQL总是安装不成功,这样处理就好啦
Machine learning practice - decision tree-22
How to view win11 system and reserved space?
How can non-standard automation equipment enterprises do well in product quality management with the help of ERP system?
A brief introduction to the for loop. Some of the code involves arrays
Machine learning practice - logistic regression-19
SuperMap game engine license module division
力扣315计算右侧小于当前元素的个数
SQL most commonly used basic operation syntax
leetcode 376. Wiggle Subsequence
线性分类器(CCF20200901)
Rolling update strategy of deployment.
LeetCode394 字符串解码
Fundamentals of machine learning - principal component analysis pca-16