当前位置:网站首页>Multithreading (4) -- no lock (2) -- Atomic related atomic classes
Multithreading (4) -- no lock (2) -- Atomic related atomic classes
2022-06-12 06:20:00 【leo_ messi94】
Preface
java.util.concurrent.atomic It also provides some concurrent tool classes , Here it is divided into five categories :
- Update the basic types using atoms
- AtomicInteger: Integer atom class
- AtomicLong: Long integer atom class
- AtomicBoolean : Boolean atom class
- Atomic reference
- An array of atoms
- Field updater
- Atomic accumulator
1. Atomic integer
With AtomicInteger As an example, discuss its api Interface : By observing the source code, we can find that ,AtomicInteger The interior is all through cas Based on the principle of !
relevant api:
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
// Get and auto increment (i = 0, result i = 1, return 0), Be similar to i++
System.out.println(i.getAndIncrement());
// Self increase and gain (i = 1, result i = 2, return 2), Be similar to ++i
System.out.println(i.incrementAndGet());
// Self subtraction and acquisition (i = 2, result i = 1, return 1), Be similar to --i
System.out.println(i.decrementAndGet());
// Get and subtract (i = 1, result i = 0, return 1), Be similar to i--
System.out.println(i.getAndDecrement());
// Get and add value (i = 0, result i = 5, return 0)
System.out.println(i.getAndAdd(5));
// Add value and get (i = 5, result i = 0, return 0)
System.out.println(i.addAndGet(-5));
// Get and update (i = 0, p by i The current value of the , result i = -2, return 0)
// Functional programming interface , The operation in the function can ensure that the atom , But the function needs to have no side effects
System.out.println(i.getAndUpdate(p -> p - 2));
// Update and get (i = -2, p by i The current value of the , result i = 0, return 0)
// Functional programming interface , The operation in the function can ensure that the atom , But the function needs to have no side effects
System.out.println(i.updateAndGet(p -> p + 2));
// Get and calculate (i = 0, p by i The current value of the , x Is the parameter 1, result i = 10, return 0)
// Functional programming interface , The operation in the function can ensure that the atom , But the function needs to have no side effects
// getAndUpdate If in lambda External local variables are referenced in , Ensure that the local variable is final Of
// getAndAccumulate Can pass Parameters 1 To reference external local variables , But because it's not here lambda So it doesn't have to be final
System.out.println(i.getAndAccumulate(10, (p, x) -> p + x));
// Calculate and get (i = 10, p by i The current value of the , x Is the parameter 1 value , result i = 0, return 0)
// Functional programming interface , The operation in the function can ensure that the atom , But the function needs to have no side effects
System.out.println(i.accumulateAndGet(-10, (p, x) -> p + x));
}
AtomicInteger Source code :
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
/* * This class intended to be implemented using VarHandles, but there * are unresolved cyclic startup dependencies. */
private static final jdk.internal.misc.Unsafe U = jdk.internal.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long VALUE = U.objectFieldOffset(AtomicInteger.class, "value");
private volatile int value;
Unsafe yes CAS The core of the class ,Java No direct access to underlying operating system , But through local (native) Method to access . But that's all ,JVM Or a back door :Unsafe, It provides hardware level atomic operations . It is used to call some native Method .
VALUE Offset address in memory for variable value ,unsafe The original value of data is obtained by offset address .
value Current value , Use volatile modification , Make sure that you see the same in a multithreaded environment .
We'll take AtomicInteger Of addAndGet() How to explain , Look at the source code :
addAndGet Source code :
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, delta) + delta;
}
public final int getAndAddInt(Object o, long offset, int delta) {
int v;
// spinlocks , Until it can be replaced
do {
// Get the value in the memory address
v = getIntVolatile(o, offset);
} while (!weakCompareAndSetInt(o, offset, v, v + delta));
return v;
}
// If the value in the memory address offset It is the same as the value I passed on
// Assign the value in the current memory to x
public final boolean weakCompareAndSetInt(Object o, long offset,
int expected,
int x) {
return compareAndSetInt(o, offset, expected, x);
}
// Four parameters , Represent the : object 、 Address of the object 、 Expected value 、 Modified value
public final native boolean compareAndSetInt(Object o, long offset,
int expected,
int x);
2. Atomic reference
Why atomic reference types are needed ? Ensure that shared variables of reference types are thread safe ( Make sure that this atomic reference does not refer to anyone else ).
A primitive type atomic class can only update one variable , If you need atoms to update multiple variables , You need to use the reference type atomic class .
- AtomicReference: Reference type atomic class
- AtomicStampedReference: Atomic update reference type with version number . This class associates integer values with references , It can be used to solve the update data of atoms and the version number of data , It can solve the problem of using CAS What may occur when atomic updates are made ABA problem .
- AtomicMarkableReference : Atom update reference types with tags . This class will boolean Tags are associated with references , It can also solve the problem of using CAS What may occur when atomic updates are made ABA problem .
Use atomic references to implement BigDecimal Thread safety of deposit and withdrawal
The following is an unsafe implementation process :
class DecimalAccountUnsafe implements DecimalAccount {
BigDecimal balance;
public DecimalAccountUnsafe(BigDecimal balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public BigDecimal getBalance() {
return balance;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {
BigDecimal balance = this.getBalance();
this.balance = balance.subtract(amount);
}
}
The solution code is as follows : stay AtomicReference Class , There is one. value Variable of type , Save pairs BigDecimal References to objects .
class DecimalAccountCas implements DecimalAccount{
//private BigDecimal balance;
private AtomicReference<BigDecimal> balance ;
public DecimalAccountCas(BigDecimal balance) {
this.balance = new AtomicReference<>(balance);
}
@Override
public BigDecimal getBalance() {
return balance.get();
}
@Override
public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {
while(true){
BigDecimal pre = balance.get();
// Be careful : there balance What is returned is a new object , namely pre!=next
BigDecimal next = pre.subtract(amount);
if (balance.compareAndSet(pre,next)){
break;
}
}
}
}
ABA problem :
The following procedure shows , Although again other There are two threads in the method that modify the shared variable , But after modification, it becomes the original value ,main This is not visible in the thread , This operation has no effect on the business code :
static AtomicReference<String> ref = new AtomicReference<>("A");
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("main start");
// Get value A
String prev = ref.get();
other();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("A -> C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "A"));
}
private static void other() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("A -> B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "B"));
}, "t1").start();
Thread.sleep(500);
new Thread(() -> {
// Be careful : If you use log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), new String("A")));
// So in this experiment log.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C"));
// What's printed is false, because new String("A") The reference of the returned object and "A" The reference of the returned object is different !
log.debug("B -> A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "A"));
}, "t2").start();
}
result :
13:49:06.903 [main] DEBUG aba - main start
13:49:06.909 [t1] DEBUG aba - A -> B true
13:49:07.415 [t2] DEBUG aba - B -> A true
13:49:08.425 [main] DEBUG aba - A -> C true
The main thread can only judge the value of the shared variable from the initial value A Are they the same? , Can't perceive this from A Change it to B And back to A The situation of , If the main thread wants : As long as there are other threads 【 I've moved 】 Shared variables , So own cas Even if it fails , At this time , Just comparing values is not enough , You need to add another version number . Use AtomicStampedReference To solve .
ABA Problem solving :AtomicStampedReference
Java Provides AtomicStampedReference To solve .AtomicStampedReference By packing [E,Integer] Tuples to label the object with a version stamp stamp, To avoid ABA problem .
AtomicStampedReference Of compareAndSet() The method is defined as follows :
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&
expectedStamp == current.stamp &&
((newReference == current.reference &&
newStamp == current.stamp) ||
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newStamp)));
}
compareAndSet There are four parameters , respectively : Expected quote 、 Updated references 、 Expected sign 、 Updated logo .
If the updated reference and flag are equal to the current reference and flag, it directly returns true, Otherwise, by Pair Make a new one pair Object and current pair CAS Replace .Pair by AtomicStampedReference The inner class of , It is mainly used to record reference and version stamp information ( identification ), The definition is as follows :
private static class Pair<T> {
final T reference;
final int stamp;
private Pair(T reference, int stamp) {
this.reference = reference;
this.stamp = stamp;
}
static <T> Pair<T> of(T reference, int stamp) {
return new Pair<T>(reference, stamp);
}
}
private volatile Pair<V> pair;
Pair Record the reference and version stamp of the object , The version stamp is int type , Keep increasing . meanwhile Pair It's an immutable object , All of its properties are defined as final, Provide a of Method , This method returns a new Pari object .pair Object defined as volatile, Ensure visibility in a multithreaded environment . stay AtomicStampedReference in , Most methods are by calling Pair Of of Method to generate a new Pair object , And then assign it to the variable pair. Such as set Method :
public void set(V newReference, int newStamp) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
if (newReference != current.reference || newStamp != current.stamp)
this.pair = Pair.of(newReference, newStamp);
}
Use AtomicStampedReference solve aba problem :
static AtomicStampedReference<String> ref = new AtomicStampedReference<>("A",0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("main start...");
// Get value A
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("main stamp:{}",stamp);
String prev = ref.getReference();
other();
Thread.sleep(1000);
// Try to change to C
log.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C",stamp,stamp+1));
}
private static void other() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("t1 stamp:{}",stamp);
log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "B",stamp,stamp+1));
}, "t1").start();
Thread.sleep(500);
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("t2 stamp:{}",stamp);
log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "A",stamp,stamp+1));
}, "t2").start();
}
result :
14:13:48.082 [main] DEBUG aba - main start...
14:13:48.086 [main] INFO aba - main stamp:0
14:13:48.089 [t1] INFO aba - t1 stamp:0
14:13:48.090 [t1] DEBUG aba - change A->B true
14:13:48.603 [t2] INFO aba - t2 stamp:1
14:13:48.603 [t2] DEBUG aba - change B->A true
14:13:49.617 [main] DEBUG aba - change A->C false
compare The comparison is the address :
meanwhile , From above compareAndSet We see the source code of compare The comparison method is to use the double equal sign , That is, the reference address is compared , If using Integer type ,1000= =1000 Our judgment is false, For other objects , Only one new The objects that come out are equal .
Code example :
static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> ref = new AtomicStampedReference<>(200,0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.debug("main start...");
// Get value A
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("main stamp:{}",stamp);
Integer prev = ref.getReference();
other();
Thread.sleep(1000);
// Try to change to C
log.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, 400,stamp,stamp+1));
}
private static void other() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("t1 stamp:{}",stamp);
log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(200, 300,stamp,stamp+1));
}, "t1").start();
Thread.sleep(500);
new Thread(() -> {
int stamp = ref.getStamp();
log.info("t2 stamp:{}",stamp);
log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(300, 200,stamp,stamp+1));
}, "t2").start();
}

Solution :
// Get when comparing , Or the value is less than 128
log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), 300,stamp,stamp+1));
AtomicMarkableReference
AtomicStampedReference You can add version numbers to atomic references , Track the whole process of atomic reference , Such as :A -> B -> A ->C, adopt AtomicStampedReference, We can know , The reference variable was changed several times in the middle of the way .
But sometimes , I don't care how many times the reference variable has changed , Just care about whether it has been changed , So there it is AtomicMarkableReference
Source code :
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
boolean expectedMark,
boolean newMark) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&
expectedMark == current.mark &&
((newReference == current.reference &&
newMark == current.mark) ||
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newMark)));
}
adopt AtomicMarkableReference We can see the source code of , His logo is Boolean , in other words , We don't need to worry about updating a few times , We only care about whether there are updates .
3. An array of atoms
Update an element in an array by using atoms , There are mainly three :
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
For functional programming, see : Four functional interfaces
Code demonstration :
public class TestAtomicArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestAtomicArray.demo(
()->new AtomicIntegerArray(10),
(array)-> array.length(),
(array,index)-> array.getAndIncrement(index),
(array)->System.out.println(array)
);
TestAtomicArray.demo(
()->new int[10],
(array)-> array.length,
(array,index)-> array[index]++,
(array)->System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array))
);
}
/** Parameters 1, Provide arrays 、 It can be a thread unsafe array or a thread safe array Parameters 2, Method to get the length of the array Parameters 3, Self increasing method , Pass on array, index Two parameters array Is an array ,index The subscript of the element for each increment of the array element Parameters 4, How to print an array */
// supplier Provider Out of thin air ()-> result
// function function One parameter, one result ( Parameters )-> result , BiFunction ( Parameters 1, Parameters 2)-> result
// consumer consumer A parameter has no result ( Parameters )->void, BiConsumer ( Parameters 1, Parameters 2)->
public static <T> void demo(
Supplier<T> arraySupplier,
Function<T,Integer> lengthFun,
BiConsumer<T,Integer> putConsumer,
Consumer<T> printConsumer){
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();
T array = arraySupplier.get();
Integer length = lengthFun.apply(array);
for (int i = 0;i<length;i++){
ts.add(new Thread(()->{
for (int j=0;j<10000;j++){
putConsumer.accept(array,j%length);
}
}));
}
ts.forEach(t->t.start());
ts.forEach(t->{
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
printConsumer.accept(array);
}
}
result :
[10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000]
[6857, 6840, 6815, 6802, 6825, 6847, 6845, 6850, 6824, 6768]
You can see the use of atomic Initialized array , Output the result correctly
4. Field updater
Update attributes in an object atomically , It mainly includes three categories :
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater // The field type is integer
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater // The field type is long
Be careful , The attribute must use volatile To modify
The field updater uses :
public class TestAtomicField {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater u = AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Student.class, String.class, "name");
System.out.println(u.compareAndSet(student, null, " Zhang San "));
}
}
@Data
class Student {
// Pay attention to the need to use volatile Embellishments ensure visibility
volatile String name;
}
result :
true
5. Atomic accumulator
seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Atomic accumulator , Is to accumulate the numbers ;
stay jdk8 after ,jdk We have added several classes for accumulation :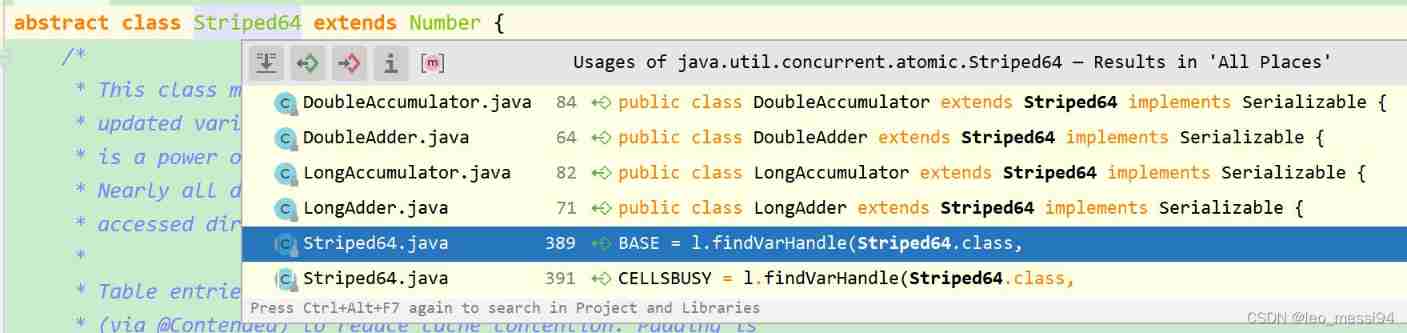
Code display :
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
demo(() -> new LongAdder(), adder -> adder.increment());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
demo(() -> new AtomicLong(), adder -> adder.getAndIncrement());
}
}
private static <T> void demo(Supplier<T> adderSupplier, Consumer<T> action) {
T adder = adderSupplier.get();
long start = System.nanoTime();
List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>();
// 4 Threads , Everyone adds up 50 ten thousand
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ts.add(new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 500000; j++) {
action.accept(adder);
}
}));
}
ts.forEach(t -> t.start());
ts.forEach(t -> {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(adder + " cost:" + (end - start)/1000_000);
}
result :
20000000 cost:91
20000000 cost:72
20000000 cost:43
20000000 cost:45
20000000 cost:51
20000000 cost:558
20000000 cost:551
20000000 cost:579
20000000 cost:514
20000000 cost:503
It can be seen that ,LongAdder Is almost ten times as efficient as AtomicInteger Self - increment method .
The reason for the performance improvement is simple , It's when there's competition , Set multiple accumulation units ( But not more than cpu The number of core ),Therad-0 Add up Cell[0], and Thread-1 Add up Cell[1],Thread-2 Add up Cell[0]… Finally, summarize the results . In this way, they operate differently when accumulating Cell Variable , Therefore, it is reduced CAS Retry fail , To improve performance .
边栏推荐
- Redis data structure (VIII) -- Geo
- About why GPU early-z reduces overdraw
- 前台展示LED数字(计算器上数字类型)
- Unity3d display FPS script
- English语法_副词_有无ly,意义不同
- Word vector training based on nnlm
- 468. verifying the IP address
- Modifying theme styles in typora
- Single channel picture reading
- Leetcode-1043. Separate arrays for maximum sum
猜你喜欢

QT--实现TCP通信

线程有哪些状态?
![How to increase heap size of JVM [duplicate] - how to increase heap size of JVM [duplicate]](/img/65/a214d137e230b1a1190feb03660f2c.jpg)
How to increase heap size of JVM [duplicate] - how to increase heap size of JVM [duplicate]

Summary of some problems in sensor bring up

数据库为什么不使用hash表?
Leetcode-1535. Find the winner of the array game

Analysis of memory management mechanism of (UE4 4.26) UE4 uobject

MNIST handwritten data recognition by RNN

C2w model - language model

sqlite交叉編譯動態庫
随机推荐
Overview of camera image quality
Performance optimization metrics and tools
Leetcode-93. Restore IP address
SQL注入——联合查询union
Univariate linear regression model
Bert Chinese classification model training + reasoning + deployment
sqlite交叉编译动态库
Redis data structure (VIII) -- Geo
Storing texture2d to hard disk JPG file with script under unity3d
Word2Vec
Directx11 advanced tutorial PBR (1) summary of physical phenomena of light
How do I get the date and time from the Internet- How to get DateTime from the internet?
Summary of some problems in sensor bring up
OverFeat: Integrated Recognition, Localization and Detection using Convolutional Networks
Nodemon cannot load the file c:\users\administrator\appdata\roaming\npm\nodemon PS1, because script execution is prohibited in this system
Why doesn't the database use binary tree, red black tree, B tree and hash table? Instead, a b+ tree is used
. Net core - pass Net core will Net to cross platform
Single channel picture reading
摄像头拍摄运动物体,产生运动模糊/拖影的原因分析
Directx11 advanced tutorial cluster based deffered shading