当前位置:网站首页>Cache design in Web services (error allowed, error not allowed)
Cache design in Web services (error allowed, error not allowed)
2022-07-25 07:42:00 【Langlang Lang】
stay Web Server Used in Cache, Basically, it can be divided into two categories , Allow errors and do not allow errors . The main body of this article will also expand according to these two parts .
On the other hand , The data is divided into Source and Cache .Source and Cache Usually different storage media 、 data structure 、 Software , such as Cache Usually stored in memory , Use Redis、Mencache、ES、 even to the extent that MongoDB Such as software .Source Usually MySQL、PostgreSQL、MongoDB Wait software .
cache , It usually means more efficient queries , Therefore, it is usually used K/V This simple data model ( The difference in SQL This complex relational model ). meanwhile ,Cache The data and Source The data of sometimes have different formats , The most common scenario :Cache There is SQL Of SELECT COUNT(1) FROM TABLE; Result ,Cache The data in is a number , and Source The data in is N Bar record .
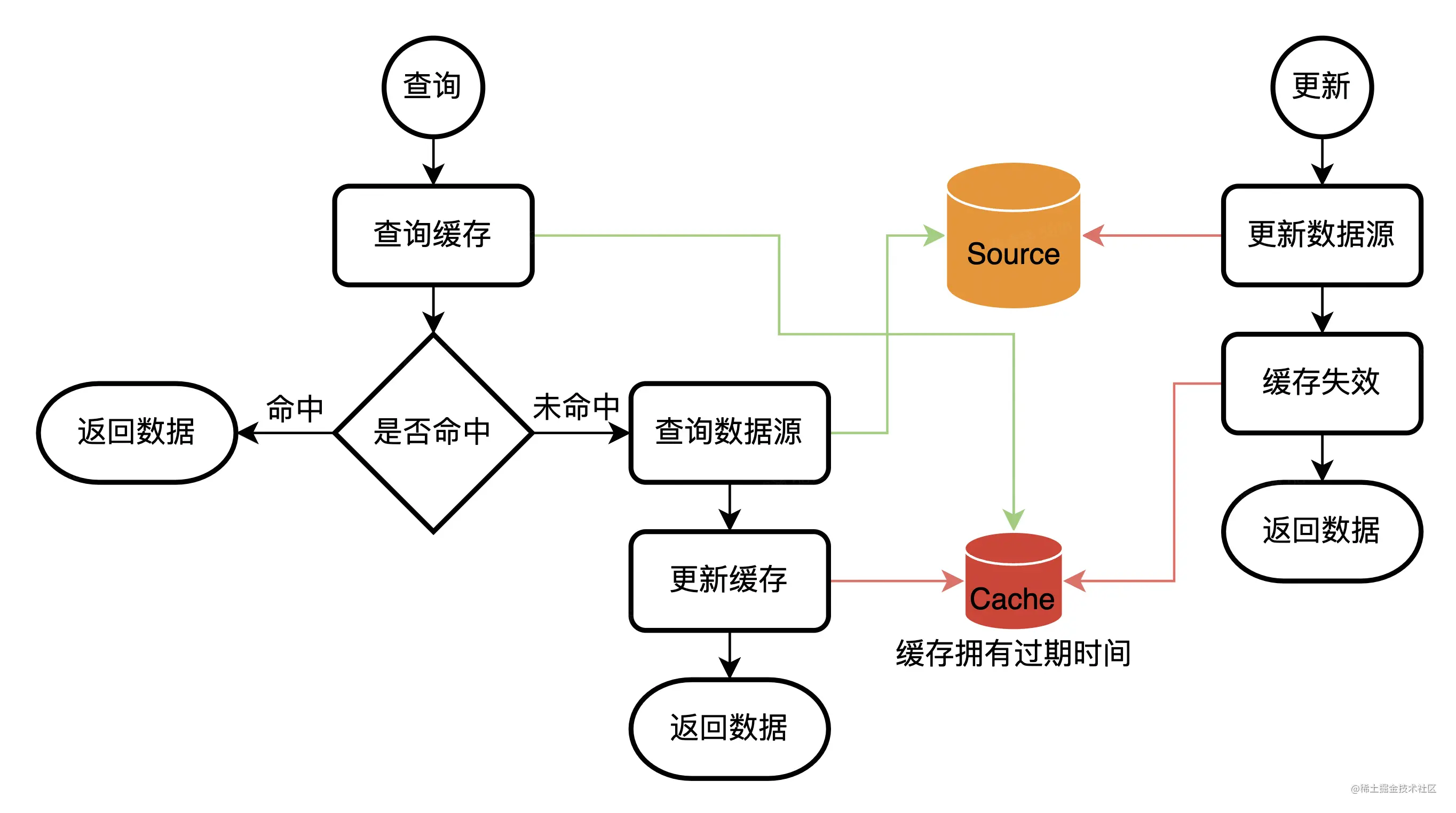
Caching process - Allow errors
Allow wrong caching schemes , Generally, there will be cache expiration time .
The basic flow
Why not update the database and cache at the same time ?
It's easy to make mistakes - From the perspective of distributed transactions
First , Updating cache and updating database are two independent operations ( Or two things ), There is no way to submit at the same time .(2PC、3PC Sure , But trouble ) So either of the two operations failed , Will lead to inconsistent data .
Update the data source first , Update the cache again
Update cache first , Update the data source
It's easy to make mistakes - Concurrent write angle
Some people say , Under normal circumstances , database 、redis The connection of is generally quite stable , Rarely will the operation fail . Let's look at another concurrency scenario :
Update cache first , Update the database Write A Write B At the same time , Update cached writes first A But then update the database .
Update the database first , Update the cache again Write A Write B At the same time , First update the database write A Then update the cache .
Other reasons
First , Data is updated , It doesn't mean that the data will be read immediately ( Depending on the specific scenario )( Data lazy loading principle ).
secondly , Cache of data , It is not necessarily consistent with the original structure of the data ( For example, caching is a count(*) Cache of operations ).
Last , Because the database itself has some logic ( For example, the default value 、on update current_timestamp(6)、 Incremental value 、 Random values, etc ), therefore , Only the read data , Is the real data .
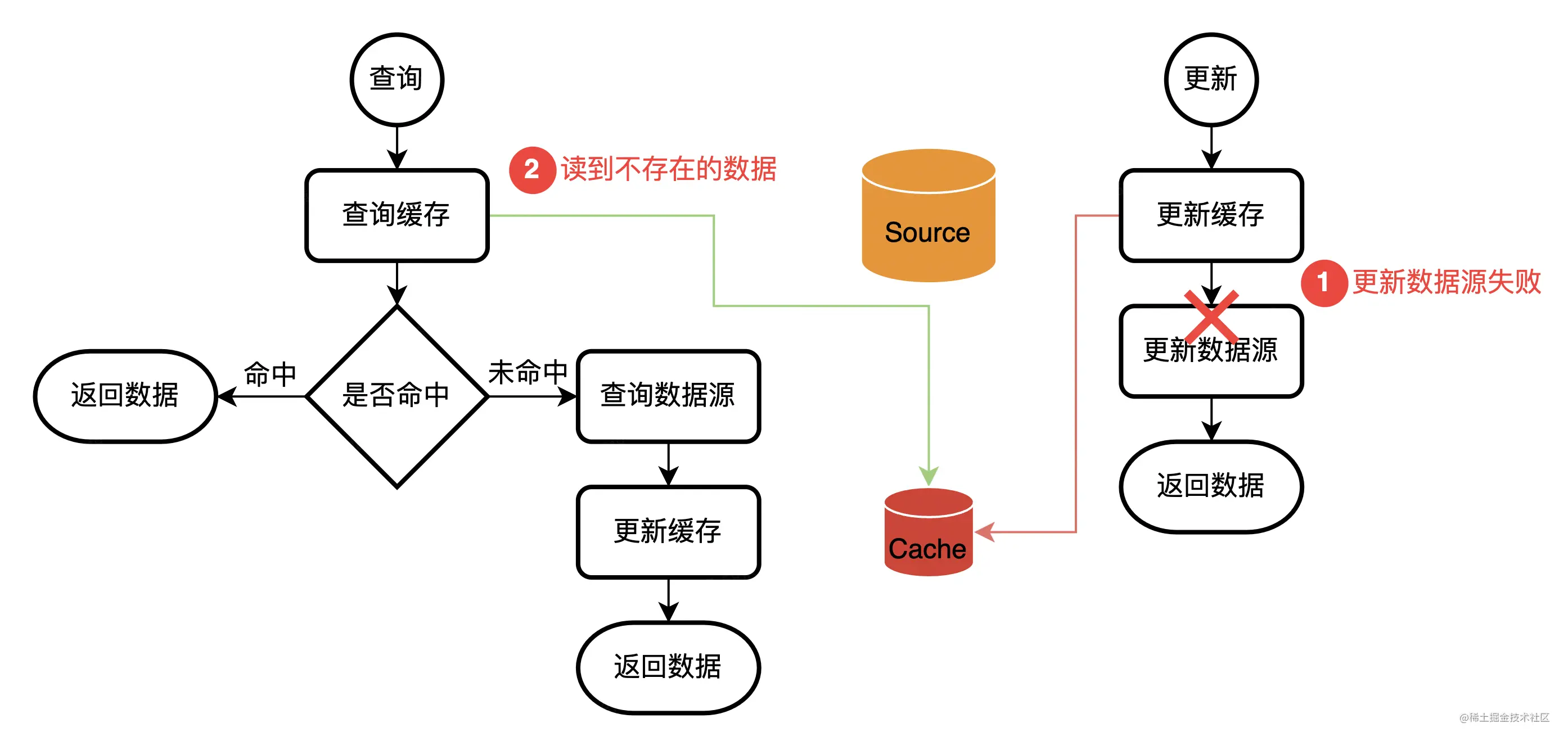
Twitter The choice of :trade off
Twitter Choose to update the database first , And then invalidate the cache . Just like this picture :
Although this way does not guarantee 100% correct , But it can avoid what we mentioned above Concurrent write problems .(Twitter It is considered that the probability of operation cache failure is very small , To some extent, it ignores Distributed transaction problems ). This approach has its own problems , and Concurrent write problems Similar but different :
Explain it. 1 The reason for the non existence of moderate delay , It may be because there is no cache , Maybe the cache timeout has expired , It could be in 1 Followed by a write request , Deleted the cache .
Although the errors shown in the figure may occur , But the probability of error is very small , It must meet two conditions :
- The cache has expired in advance ( Active deletion of cache due to timeout or write operation ).
- Generally speaking, read requests are faster , Writing requests is slower , The timing in the diagram is difficult to happen . PS: It's just that the probability is small , No, it won't happen . Thread scheduling /GC/ Reading is not optimized well, resulting in slow reading / Reading itself is a time-consuming operation It is possible to make the diagram sequence happen .
Sum up , Although this thing may happen , But the probability is very small . If the system allows a cache expiration period of error data , Then this may be the best caching scheme .
Caching process - No mistake is allowed
When mistakes are not allowed , We are usually very sensitive to dirty data , Dirty data with an expiration period is usually intolerable .
Serialization
The most complex problem we talked about above , They are all caused by concurrent resource operations . If you can serialize the operation of a single resource , Then things are simple .
There are usually two schemes for serialization , Locking and asynchronous update + Sequential consumption .
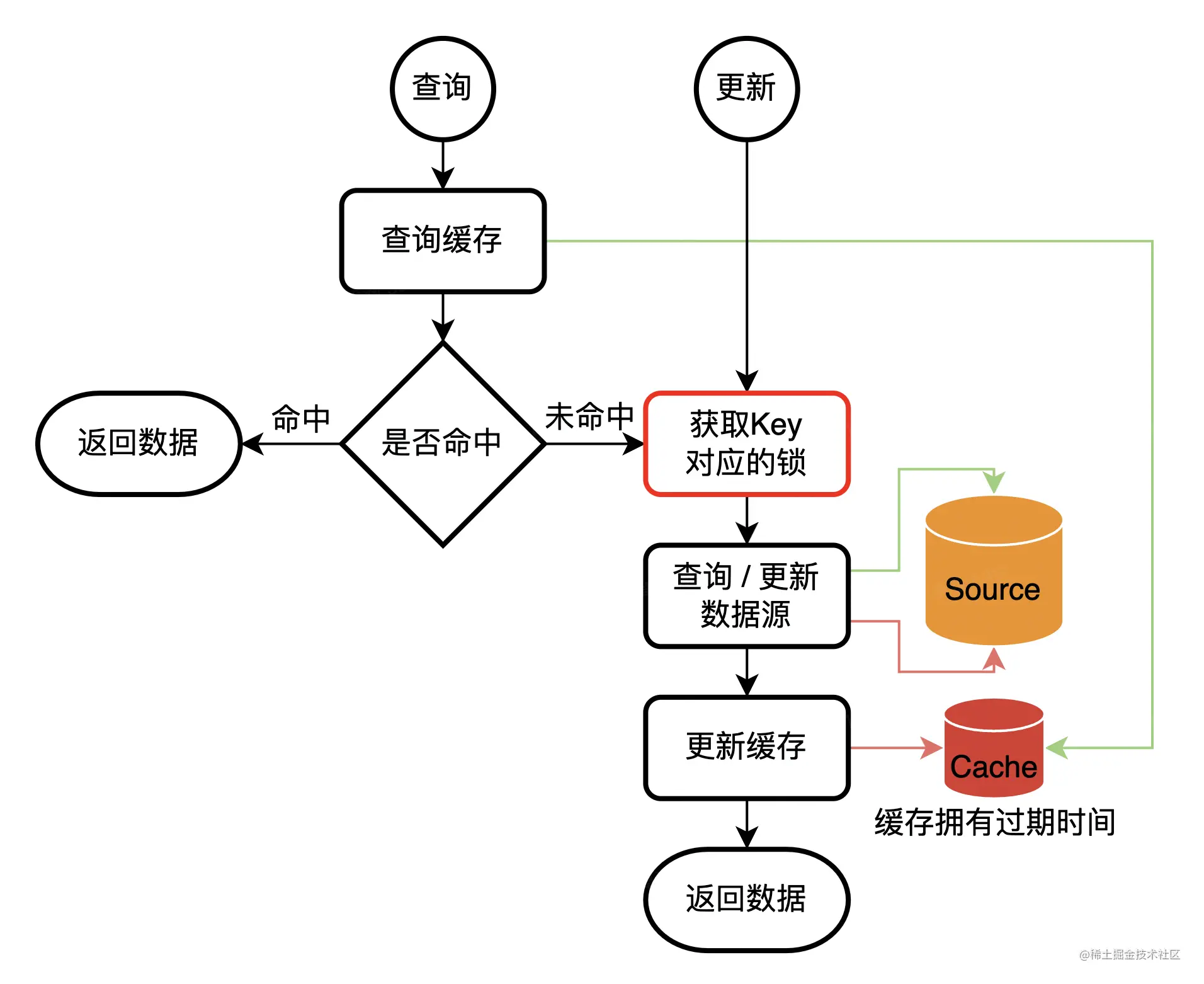
Lock
Let's assume an extremely simple business scenario : To the user id by key, User basic data is value, Cache . There are three interfaces in total : Add user 、 Query user data 、 Update user data .
- Increase the cache without user operation ;
- When querying user data , If the cache does not hit , Lock first , Check the database again , Then set the cache ;
- When updating user data , Lock first , Update the database , Update the cache again .
There are also many ways to lock , For example, use the lock of the database ; use redis Gets the lock ; Set up a lock release center ; Get a lease mechanism and so on . Various lock schemes have their own advantages and disadvantages , I won't discuss it here .
Asynchronous update Sequential consumption
If you are worried about locking, the request for change is slow , And don't care about the timeliness of updates , Update can be an asynchronous task , Post to message queue , Then consumers consume in sequence , Update the data source and cache .
However, there are many pitfalls and restrictions on sequential consumption , This plan will not be further developed . If you really want to implement , Need more extra work and some tolerance .
Add and update
hypothesis Web Application settings each request must be in 10s Finish in , Otherwise, forcibly terminate the request ; Or we can assume 99.9999% All the requests will be in 3s Finish in . Then we can add one 3s After execution Delete / Asynchronous task of updating cache . So this Delete / to update The cached operation must be executed after the request ends , Make the cache up to date .
Cache pits
An avalanche
A large number of hot spots key Simultaneous failure , Request all calls to the database .
reason
Usually because the cache expires automatically , Or updating the data will invalidate the cache .
Maybe it's because Cold start , Cause these hot spots key non-existent . The solution to this problem is “ Cold start ” In a chapter .
countermeasures
There is a relatively simple scheme , This problem can be avoided : The expiration time is set to a fixed value + random number , Like fixing 5 Minutes expired , Random 1 Expires around minutes . In this way, even if all data is cached at the same time , Will also be in 4-6 Slowly expire within minutes , It will not expire at the same time .
If this simple solution cannot be solved , Then we need some complicated schemes ~
- If it is a static resource ( Or relatively static , Few changes ) And the amount of data is small , Directly cache the full amount of data , Maintain the database and cache synchronously by locking ( See above “ Caching process - No mistake is allowed ”).
- If the amount of data is small , Design new and old caches , New cache 5 One minute expires , Old cache 1 Day one expires . Every cache refresh , Both refresh at the same time Old and new Two figures . In this way, even if the new cache fails , There will not be a large number of requests to hit the database .
- Identify hotspot data , For hot spot data , Background refresh cache and expiration time .
- Design level II expiration time . For example, the first level expiration time 5 minute , Second level expiration time 1h. Let the request read the cache at the same time , Update the first level expiration time of the cache . Original 5 Minutes of cache , Sure 1h Never expire within , however 1h It must expire once , Prevent data inconsistency .
breakdown
It is very similar to avalanche , Avalanches are a lot of hot spots key At the same time , Breakdown is an ultra-high hot spot key Be overdue . The strategy is similar .
through
Do a lot of queries with nonexistent data , Or do a lot of queries with queries that cannot be cached .
countermeasures
In general, someone is messing with you , In general, you can go through nginx Wait for the current limit to limit , Or check at the code level , such as id It must be in a certain interval , Or in a set , Or conform to a certain format . If the above two current limits are still uncertain , You can add some special caches : Yes “ Yes ” and “ No, ” Cache in both cases .
For example, for instance ID, First do regular matching , To make sure the format is correct ; And then ID Read out the time in , See if it belongs to the past ID; One more pass NotExisted Boolean filter , If it exists in Boolean filter , Then return to null directly , Otherwise, check the database ; If the database does not exist , Then you can put this ID Add to NotExisted Boolean filter .
Cache retirement strategy
If we cache too much data , Then we have to consider whether the cache system can store so much data , If it can't be stored , How to eliminate data ? If the elimination strategy is not selected well , Then all our previous carefully designed caching strategies may be defeated .
For all elimination algorithms , We should also consider its implementation The goal is And realized methods , These two points combine to form effect . such as LRU, Its The goal is Is to eliminate the last used data , Its best implementation methods yes HashMap+ Double linked list .
In different circumstances ,LRU、LFU、FIFO May become the best algorithm , And its different implementations or variants may have their own scenarios , If you can expand and talk about a lot of content . Skip here .
Cold start
There are two cold starts , One is that the cache component hangs , Restarting causes the cache to be empty . The other is the whole Web The server ( Include Web application , database , cache ) from 0 Began to run . In the case of the former , You can do cache persistence , Or make decisions and follow , To avoid cache loss . In the latter case , It can be random / According to a certain strategy ( Even the configuration of operation ) Stuff some data into the cache .
Unexpected hot spot data
This situation is relatively rare in daily development , Most of them appear on Weibo . Generally speaking, a single machine redis The concurrency of the server can fully meet the general website development , If not, then go to the cluster . If a Key The number of visits is particularly large , More than a single redis The ability to bear , Then it may break one redis.
From the perspective of operation and maintenance , Let's introduce a “ Group ” The concept of . Each group is responsible for one redis section . Each group has multiple redis example . Operation and maintenance dynamic monitoring redis The state of , And dynamically expand redis example .
From a development point of view , because Web Applications can be expanded infinitely horizontally ( Because it's pure logic 、 Pure process ). We can design a hotspot discovery system , Push hot data to each Web Cache the local memory of the application .
actual combat
B Like function of the station
- about B Every video of the station , Each user can like , Or cancel like . The above two operations can be repeated countless times .
- Each video should show the number of likes
- Each user should be able to check whether he likes each video
Raw data table
create table Zan (
id bigint primary key,
user_id varcher(255),
video_id varcher(255),
cancel bool, # Cancel like
);
create index scan_index on Zan (user_id, video_id);
Copy code Two caches :
- Cache of video likes
- Whether the user likes the cache
For the cache of video likes : A background program , every other 5 minute , Find out the videos played in an hour , Then update the likes in the cache , And update the expiration time of the cache . The likes cache of such hot videos will never expire .
Whether the user likes the cache : user id+ video id Be the only one key, Save one bool value . For reading and updating this value , You can use a lock or Twitter Strategy to achieve .
Best practices
One More Things
Cache Four paradigms / classification
There are generally four design patterns for caching Cache aside, Read through, Write through, Write behind caching.
It's today Web Cache The share of , namely ache Aside Pattern.
Cache Aside Pattern
Cache aside pattern It's the most common way , The basic concepts are as follows :
- The data is divided into source and cache.cache and source Usually different storage media 、 data structure 、 Software , such as cache Usually redis、mencache、ES、 even to the extent that mongoDB.source Usually MySQL、PostgreSQL、mongoDB wait .
- cache The data in basically exists in the form of key value pairs ,key Corresponding to a cache Data in , It also corresponds to one source Query for .
- cache Data in usually has expiration time ,cache There are usually capacity constraints .
Read/Write Through Pattern
We can see , Above Cache Aside In routine , Our application code needs to maintain two data stores , One is caching (Cache), One is the database (Repository). therefore , Application is verbose . and Read/Write Through The routine is to update the database (Repository) Operation of is represented by cache itself , therefore , For the application layer , It's a lot easier . It can be understood as , Application thinks the back end is a single storage , And store your own Cache.
such as MySQL5.6 in , Will put some hot data in memory ;CPU Cache on , Some memory pages will also be cached , The general idea is similar .
Read Through
Read Through The routine is to update the cache in the query operation , in other words , When the cache fails ( Expired or LRU Swap out ),Cache Aside The caller is responsible for loading the data into the cache , and Read Through The cache service itself will be used to load , So it is transparent to the application side .
Write Through
Write Through Routine and Read Through similar , Occurs when data is updated . When there is data update , If the cache is not hit , Update database directly , Then return . If the cache is hit , Update cache , And then by Cache Update the database yourself ( This is a synchronous operation )
I'm going to give you a Wikipedia Of Cache entry , I won't repeat anything else .
Write Behind Cache Pattern
This mode directly updates the cached data when the data is updated , Then set up asynchronous tasks to update the database . In this asynchronous way, the request response will be fast , The throughput of the system will be significantly improved .
such as MySQL Of WAL, Disk system , All have similar designs . This design takes advantage of the speed advantage of disk sequential storage to optimize . But in general Web After the server , We generally don't need to consider this way .
Go Of LocalCache How to achieve ZERO GC?
How to improve performance under concurrency ?
Realization Raft when Thinking about locking and avoiding deadlock (1-5 to update )
How to improve the correctness of concurrency ?
How to efficiently obtain the time difference ?
go Use monotonic clock to obtain accurate time interval
Reference material
Reading notes :Scaling Memcache at Facebook
Back end application caching best practices www.jianshu.com/p/c596e1050…)
边栏推荐
- [unity introduction plan] interface Introduction (2) -games view & hierarchy & Project & Inspector
- nanodet训练时出现问题:ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘nanodet‘的解决方法
- oracle 触发器创建
- 如何仅用递归函数和栈操作逆序一个栈
- Completely replace the redis+ database architecture, and JD 618 is stable!
- [programmer 2 Civil Servant] III. resource collection
- 9 best engineering construction project management systems
- While (~scanf ("%d", & n)) is equivalent to while (scanf ("%d", & n)! =eof)
- [programmer 2 Civil Servant] I. Basic Knowledge
- cesium简介
猜你喜欢
钉钉最新版,怎么清除登录手机号历史记录数据

How should enterprise users choose aiops or APM?
![[wechat applet] global style, local style, global configuration](/img/8e/c6241ab0f28e3f468dbfa923b91d20.png)
[wechat applet] global style, local style, global configuration
![[unity introduction program] basic concept - preform prefab](/img/c6/aac7bffdf99073978f9b2f8ff15fbb.png)
[unity introduction program] basic concept - preform prefab

A fast method of data set enhancement for deep learning

【Unity入门计划】基本概念-GameObject&Components
![[unity introduction program] basic concepts GameObject & components](/img/fc/7e0a6f057394a6fd4409a7bf518ba5.png)
[unity introduction program] basic concepts GameObject & components
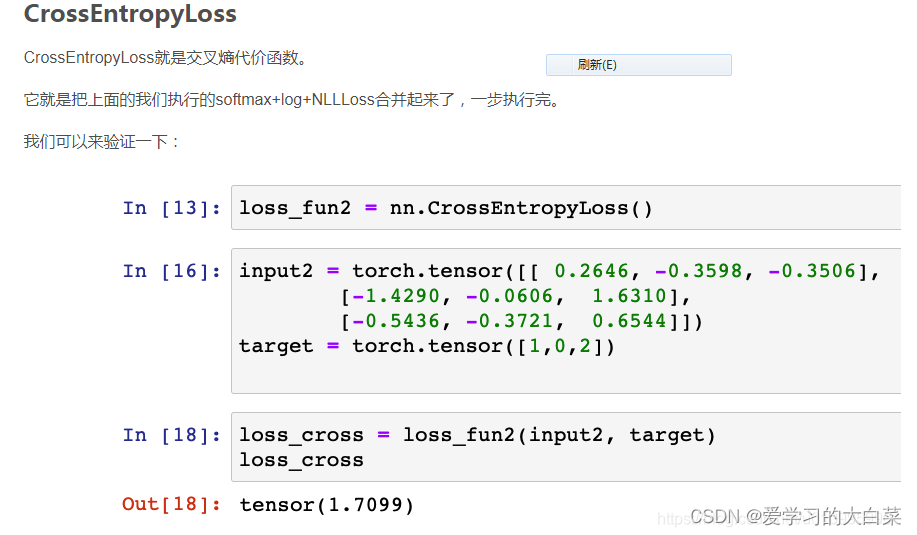
交叉熵计算公式

Leetcode (Sword finger offer) - 04. search in two-dimensional array
![[unity entry program] basic concept trigger](/img/16/cd0f8ae579627fc095935195136729.png)
[unity entry program] basic concept trigger
随机推荐
设计一个有getMin功能的栈
Bingbing's learning notes: classes and objects (Part 1)
Huawei wireless device sta black and white list configuration command
[paper notes] effective CNN architecture design guided by visualization
Tips - prevent system problems and file loss
纳米数据足球数据,足球赛事比分,体育数据api,卡塔尔世界杯
Completely replace the redis+ database architecture, and JD 618 is stable!
Polling, interrupt, DMA and channel
[unity introduction plan] interface Introduction (2) -games view & hierarchy & Project & Inspector
J1 common DOS commands (P25)
Growth path - InfoQ video experience notes [easy to understand]
The application of for loop and if judgment statement
Robot framework mobile terminal Automation Test ----- 01 environment installation
A fast method of data set enhancement for deep learning
MATLAB自编程系列(1)---角分布函数
If Debian infringes the rust trademark, will it be exempted by compromising and renaming?
用一个栈实现另一个栈的排序
Oracle19采用自动内存管理,AWR报告显示SGA、PGA设置的过小了?
P1047 [noip2005 popularization group t2] tree outside the school gate
Delete in elasticserach_ by_ What is the mechanism of query?