当前位置:网站首页>【模糊神经网络】基于matlab的模糊神经网络仿真
【模糊神经网络】基于matlab的模糊神经网络仿真
2022-06-28 00:51:00 【fpga和matlab】
1.软件版本
matlab2013b
2.系统概述
·第一个模型:
 ;
;![]()
·第二个模型
 ;
;![]() ,U=13.012
,U=13.012
第一:隶属函数的设计

隶属函数的设计,可以通过模糊编辑器,也可以通过如上的代码进行设计。
第二:模糊规则的设计
通过输入模糊规则量化表进行设计,所得到的模糊规则如下所示:
1. If (e is NB) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
2. If (e is NB) and (ec is NM) then (u is PB) (1)
3. If (e is NB) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
4. If (e is NB) and (ec is Z) then (u is PM) (1)
5. If (e is NB) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
6. If (e is NB) and (ec is PM) then (u is PS) (1)
7. If (e is NB) and (ec is PB) then (u is Z) (1)
8. If (e is NM) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
9. If (e is NM) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
10. If (e is NM) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
11. If (e is NM) and (ec is Z) then (u is PS) (1)
12. If (e is NM) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
13. If (e is NM) and (ec is PM) then (u is Z) (1)
14. If (e is NM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
15. If (e is NS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PM) (1)
16. If (e is NS) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
17. If (e is NS) and (ec is NS) then (u is PS) (1)
18. If (e is NS) and (ec is Z) then (u is PS) (1)
19. If (e is NS) and (ec is PS) then (u is Z) (1)
20. If (e is NS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
21. If (e is NS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
22. If (e is Z) and (ec is NB) then (u is PM) (1)
23. If (e is Z) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
24. If (e is Z) and (ec is NS) then (u is PS) (1)
25. If (e is Z) and (ec is Z) then (u is Z) (1)
26. If (e is Z) and (ec is PS) then (u is NS) (1)
27. If (e is Z) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
28. If (e is Z) and (ec is PB) then (u is NM) (1)
29. If (e is PS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
30. If (e is PS) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
31. If (e is PS) and (ec is NS) then (u is Z) (1)
32. If (e is PS) and (ec is Z) then (u is NS) (1)
33. If (e is PS) and (ec is PS) then (u is NS) (1)
34. If (e is PS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
35. If (e is PS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NM) (1)
36. If (e is PM) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
37. If (e is PM) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
38. If (e is PM) and (ec is NS) then (u is Z) (1)
39. If (e is PM) and (ec is Z) then (u is NS) (1)
40. If (e is PM) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
41. If (e is PM) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
42. If (e is PM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
43. If (e is PB) and (ec is NB) then (u is Z) (1)
44. If (e is PB) and (ec is NM) then (u is NS) (1)
45. If (e is PB) and (ec is NS) then (u is NS) (1)
46. If (e is PB) and (ec is Z) then (u is NM) (1)
47. If (e is PB) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
48. If (e is PB) and (ec is PM) then (u is NB) (1)
49. If (e is PB) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
第三:控制闭环的设计
通常,一个传统的模糊控制器的闭环结构如下所示:

模糊控制器的基本结构:

3.部分源码
addpath 'func\'
title_function
%初始化
fnn_parameter;
%被控对象
a1 = 1.2;
b1 = 1;
b2 = 0.8;
b3 = 0;
ta = 40;
sys = tf(a1,[b1,b2,b3]);
dsys = c2d(sys,0.1,'z');
[num,den] = tfdata(dsys,'v');
ts = 0.1;%采样时间T=0.1
%闭环控制器
for k=1:SIM_times
k
time(k) = k*ts;
%定义输入信号
yd(k) = 2;
%定义输出信号
if k < ta
yn = 0;
else
yn = -den(2)*y1 - den(3)*y2 + num(2)*u1 + num(3)*u2;
end
y2 = y1;
y1 = yn;
y(k) = yn;
u2 = u1;
e2 = e1;
e1 = yd(k)-yn;
e(k) = e1;
ec =(e1-e2);
x1 =(1-exp(-10*e1))/(1+exp(-10*e1));
x2 =(1-exp(-ec))/(1+exp(-ec));
%第1层输出
for i=1:7
o11(i) = x1;
o12(i) = x2;
end
o1=[o11;o12];
%第2层输出
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
z1(i,j) =-((o1(i,j)-a(i,j))^2)/(b(i,j));
o2(i,j) = exp(z1(i,j));
end
end
%第3层输出
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
o3((j-1)*7+l)=o2(1,j)*o2(2,l);
end
end
%第4层输出
I=0;
for i=1:49
I = I + o3(i)*Weight(i)/4;
end
o4 = I/(sum(o3));
u(k) = o4;
u1 = o4;
%梯度下降法调整权值
for i=1:49
dwp = e1*du*o3(i)/(sum(o3));
%迭代
Weight(i) = Weight(i) + eta*dwp;
end
%中心值更新
da11=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
da11(j) = da11(j)+(o2(2,l)*((Weight((j-1)*7+l)*sum(o3))-I));
end
da12(1,j) = -e1*du*(2*(o1(1,j)-a(1,j))*(o2(1,j)))/((b(1,j)^2)*(sum(o3))^2);
da1(j) = (da12(1,j))*(da11(j));
end
da21 = zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
da21(j) = da21(j)+(o2(1,l)*((Weight((l-1)*7+j)*sum(o3))-I));
end
da22(2,j) = -e1*du*(2*(o1(2,j)-a(2,j))*(o2(2,j))/((b(2,j)^2)*(sum(o3))^2));
da2(j) = (da22(2,j))*(da21(j));
end
da=[da1;da2];
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
a(i,j)=a(i,j)-eta*da(i,j);
end
end
a_s(:,:,k) = a;
if k == 1
a_(:,:,k) = a_s(:,:,1);
else
for i = 1:2
for j = 1:7
dist_tmp(i,j) = (a_s(i,j,k) - a_(i,j))^2;
end
end
dist = sqrt(sum(sum(dist_tmp)));
if dist < 0.1
tmps(:,:,1) = a_(:,:,k-1);
tmps(:,:,2) = a_s(:,:,k);
a_(:,:,k) = mean(tmps(:,:,1:2),3);
else
a_(:,:,k) = a_(:,:,k-1);
end
end
a = a_(:,:,k);
%宽度更新
db11=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
db11(j)=db11(j)+(o2(2,l)*((Weight((j-1)*7+l)*sum(o3))-I));
end
db12(1,j)=-e1*du*(2*(o1(1,j)-a(1,j))^2)*(o2(1,j))/((b(1,j)^3)*(sum(o3))^2);
db1(j)=(db12(1,j))*(db11(j));
end
db21=zeros(1,7);
for j=1:7
for l=1:7
db21(j)=db21(j)+(o2(1,l)*((Weight((l-1)*7+j)*sum(o3))-I));
end
db22(2,j)=-e1*du*(2*(o1(2,j)-a(2,j))^2)*(o2(2,j))/((b(2,j)^3)*(sum(o3))^2);
db2(j)=(db22(2,j))*(db21(j));
end
db=[db1;db2];
for i=1:2
for j=1:7
b(i,j)=b(i,j)-eta*db(i,j);
end
end
b_s(:,:,k) = b;
if k == 1
b_(:,:,k) = b_s(:,:,1);
else
for i = 1:2
for j = 1:7
dist_tmp(i,j) = (b_s(i,j,k) - b_(i,j))^2;
end
end
dist = sqrt(sum(sum(dist_tmp)));
if dist < 0.1
tmps(:,:,1) = b_(:,:,k-1);
tmps(:,:,2) = b_s(:,:,k);
b_(:,:,k) = mean(tmps(:,:,1:2),3);
else
b_(:,:,k) = b_(:,:,k-1);
end
end
b = b_(:,:,k);
%算法
s11 = y1;
s12 = y2;
s13 = u1;
s14 = u2;
s1 =[s11;s12;s13;s14];
for i=1:5
net2(i) = w2(i,:)*s1 + theta2(i);
s2(i) = (1-exp(-net2(i)))/(1+exp(-net2(i)));
end
net3 = w3*s2+theta3;
yg = am*(1-exp(-net3))/(1+exp(-net3));
for i=1:5
delta2(i)=0.5*(1-s2(i))*(1+s2(i));
end
delta3=0.5*am*(1-yg/am)*(1+yg/am);
for i=1:5
theta22(i) = theta2(i)-theta21(i);
theta21(i) = theta2(i);
theta2(i) = theta2(i)+eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*w3(i)*delta2(i)+beta1*theta22(i);
end
theta32 = theta3-theta31;
theta31 = theta3;
theta3 = theta3+eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3+beta1*theta32;
for i=1:5
for j=1:4
w22(i,j) = w2(i,j)-w21(i,j);
w21(i,j) = w2(i,j);
w2(i,j) = w2(i,j)-eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*w3(i)*delta2(i)*s1(j)+beta1*w22(i,j);
end
w32(i) = w3(i)-w31(i);
w31(i) = w3(i);
w3(i) = w3(i)-eta1*(yn-yg)*delta3*s2(i)+beta1*w32(i);
end
a2 = am-a1;
a1 = am;
am = am+eta1*(yn-yg)*yg/am+beta1*a2;
sum1 = 0;
for i=1:5
sum1 = sum1 + w3(i)*delta2(i)*w2(i,3);
end
du = delta3*sum1;
end
figure;
plot(time,y,'r', time,yd,'b');
grid on
figure;
subplot(121);
plot(a_s(1,:,SIM_times),a_s(2,:,SIM_times),'o');
grid on
axis square
subplot(122);
plot(b_s(1,:,SIM_times),b_s(2,:,SIM_times),'o');
grid on
axis square
save Simu_Results\fnn_result.mat time y
save Simu_Results\nfis.mat a b
这里重点介绍一下模糊神经网络控制器的设计,
第一:四层化神经网络层的结构设计:
第1层:

![]()
第2层:

![]()
第3层:

![]()
第4层:


第二:利用梯度下降法进行权值更新


4.仿真结果
模糊控制效果图(模型一):
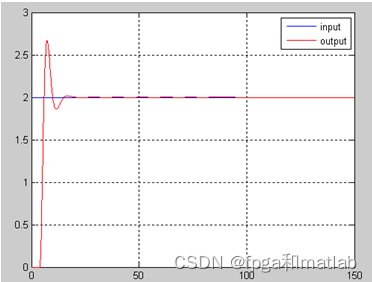
模糊控制效果图(模型二):
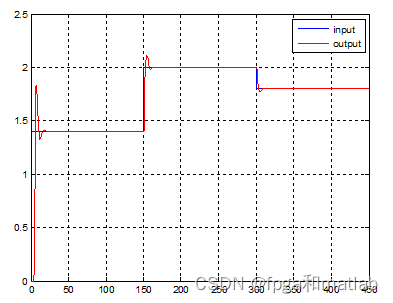
隶属函数如下所示:







A05-06
边栏推荐
- 【历史上的今天】6 月 18 日:京东诞生;网店平台 Etsy 成立;Facebook 发布 Libra 白皮书
- 【历史上的今天】6 月 25 日:笔记本之父诞生;Windows 98 发布;通用产品代码首次商用
- JS实现滑动拼图验证
- 系统管理员设置了系统策略,禁止进行此安装。解决方案
- 4G-learn from great partners
- Cvpr22 collected papers | hierarchical residual multi granularity classification network based on label relation tree
- 批阅2022春季学期课程小论文提交情况
- TD Hero online conference on July 2
- 【二维码图像矫正增强】基于MATLAB的二维码图像矫正增强处理仿真
- Redis~Geospatial(地理空间)、Hyperloglog(基数统计)
猜你喜欢

Jenkins - Pipeline syntax

ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor源码解读(二)

Use code binding DataGridView control to display tables in program interface

CVPR22收录论文|基于标签关系树的层级残差多粒度分类网络

Jenkins - access the Jenkins user-defined parameter variable, and handle the variable value containing spaces

【历史上的今天】6 月 5 日:洛夫莱斯和巴贝奇相遇;公钥密码学先驱诞生;函数语言设计先驱出生

Data governance and data standards

数据治理与数据标准

Protocole de transfert de fichiers - - FTP

Cvpr22 collected papers | hierarchical residual multi granularity classification network based on label relation tree
随机推荐
JS implementation of Slide Puzzle verification
OS module and os Learning of path module
SQL 注入绕过(五)
LeetCode - Easy - 197
关于st-link usb communication error的解决方法
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
stm32f1中断介绍
Adding text labels to cesium polygons the problem of polygon center point offset is solved
Cesium Click to draw polygons (dynamically draw polygons)
文件传输协议--FTP
Truth table of common anode digital tube
王心凌、谭维维 - 山海(副歌加长版) 在线试听无损FLAC下载
4G-learn from great partners
Jenkins - built in variable access
JS implementation clock
Low code solution - a low code solution for digital after-sales service covering the whole process of work order, maintenance and Finance
Jenkins - groovy postbuild plug-in enriches build history information
flask基础:模板继承+静态文件配置
SQL 注入繞過(二)
How to use data-driven "customer lifecycle management" to improve lead conversion rate and customer satisfaction?