In this paper, the source code :GitHub· Click here || GitEE· Click here
One 、 Layering strategy
MVC Pattern and code layering strategy ,MVC The full name is ModelViewController The model - View - controller , As a software design paradigm , Using a business logic 、 data 、 The interface displays the separated method organization code , Gather business logic into a component , While improving and personalizing the interface and user interaction , No need to rewrite business logic , It's a development model , But it's not the layered pattern of code in actual development , Usually SSM The framework's back-end code layers are as follows :
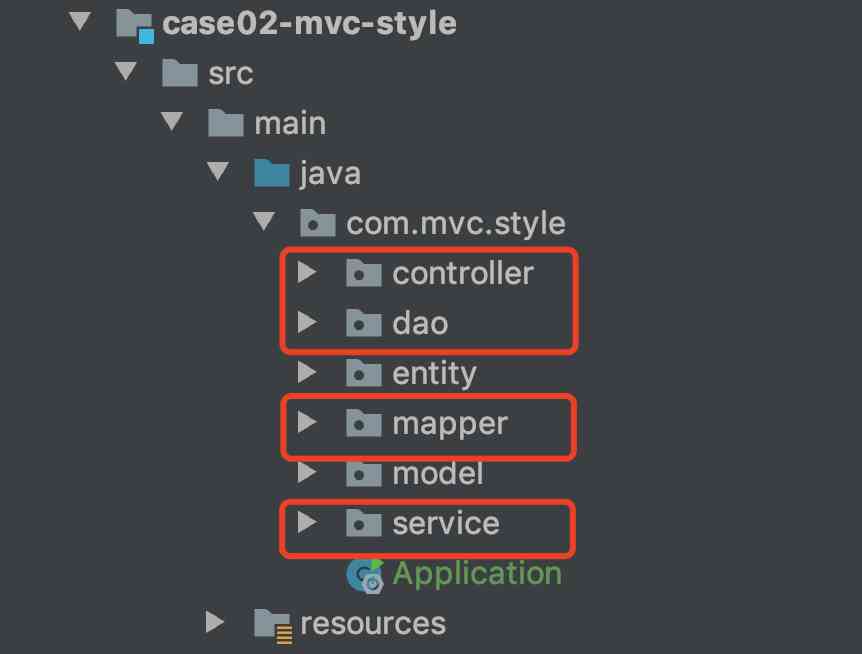
- controller Control layer : Define the server interface , In and out , And some input parameters ;
- service Business services layer : Assemble business logic , Business verification , The parameter model needed to build the control layer ;
- dao Data interaction layer : Provide the data query method needed by the service layer , Dealing with logic related to data interaction conditions ;
- mapper Persistence layer : be based on mybatis The framework needs native support , The most commonly used persistence layer component at present ;
Two 、 Control layer
1、Rest The interface style
Based on the logic of resource access and processing , Use different styles of annotations . For example, new resources , to update , Inquire about , Delete .
/**
* newly added
*/
@PostMapping("/insert")
public Integer insert (@RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo){
return baseInfoService.insert(baseInfo);
}
/**
* to update
*/
@PutMapping("/update/{id}")
public String update(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id,
@RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo) {
if (id<1){
return "error";
}
baseInfo.setId(id);
return "update="+baseInfoService.update(baseInfo);
}
/**
* Primary key query
*/
@GetMapping("/detail/{id}")
public InfoModel detail(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
return baseInfoService.detail(id) ;
}
/**
* Delete primary key
*/
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
baseInfoService.delete(id) ;
return "SUS" ;
}
2、 Interface reuse
High reuse of interfaces is not recommended , For example, add, delete, modify and check all the interfaces , The basic principle of , Different client side operations , For independent interfaces .
/**
* List loading
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
public List<BaseInfo> list() {
return baseInfoService.list(new BaseInfoExample()) ;
}
/**
* List search
*/
@PostMapping("/search")
public List<BaseInfo> search (@RequestParam("userName") String userName,
@RequestParam("phone") String phone) {
return baseInfoService.search(userName,phone) ;
}
For example, common list Interface ,list Usually, there will be conditional loading search Mechanism , And the search criteria are complex , It is suggested that there are two interfaces , From a practical point of view , Most of the scenarios are only used list Interface , Rarely used search Search for .
3、 In and out
Verification client must be conditional , For example, a certain condition is required , If there are questions , Quickly block the request link , The program entrance control layer intercepts and returns .
@PutMapping("/update/{id}")
public String update(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id,
@RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo) {
if (id<1){
return "error";
}
baseInfo.setId(id);
return "update="+baseInfoService.update(baseInfo);
}
The parameters are less than three , It can be displayed directly into the reference , If there are three or more parameters, entity classes can be used to encapsulate them .
@PostMapping("/search")
public List<BaseInfo> search (@RequestParam("userName") String userName,
@RequestParam("phone") String phone) {
return baseInfoService.search(userName,phone) ;
}
4、 Processing parameters
The basic principle of the processing degree of the output parameter format , Servers as public resources , Avoid unnecessary operations , For example, the client can judge whether the return value is empty ,null etc. , Or some common format processing , Use the client to share the server pressure properly .
3、 ... and 、 Business services layer
1、 Business verification
For example, pass in the order number , Through the database layer query , No order data , This is called a business nature exception , There's no problem with the code itself , But business logic doesn't work properly .
public InfoModel detail(Integer id){
BaseInfo baseInfo = baseInfoDao.selectByPrimaryKey(id) ;
if (baseInfo != null){
DetailInfoEntity detailInfoEntity = detailInfoDao.getById(id);
if (detailInfoEntity == null){
LOG.info("id="+id+" Missing data DetailInfo");
}
return buildModel(baseInfo,detailInfoEntity) ;
}
LOG.info("id="+id+" The data is completely missing ");
return null ;
}
2、 Assemble business logic
Usually, the service layer is a complex piece of logic , Used to splice business core steps , It can be determined by business logic that , Step by step, step by step , Avoid doing a lot of object creation and requirement data query at the program entrance .
public int insert (BaseInfo record){
record.setCreateTime(new Date());
int insertFlag = baseInfoDao.insert(record);
if (insertFlag > 0){
DetailInfoEntity detailInfoEntity = new DetailInfoEntity();
detailInfoEntity.setUserId(record.getId());
detailInfoEntity.setCreateTime(record.getCreateTime());
if(detailInfoDao.save(detailInfoEntity)){
return insertFlag ;
}
}
return insertFlag;
}
3、 Data model construction
Usually, the business layer is more complex , If you want to quickly understand the business layer , Can be used for complex business methods , In this paper, we provide a method to return the parameters to build , It is used to process the parameters returned by the service layer to the control layer , This will make the heavy service layer approach clearer .
private InfoModel buildModel (BaseInfo baseInfo,DetailInfoEntity detailInfo){
InfoModel infoModel = new InfoModel() ;
infoModel.setBaseInfo(baseInfo);
infoModel.setDetailInfoEntity(detailInfo);
return infoModel ;
}
Four 、 Data interaction layer
1、 Reverse engineering
Here to use mybatis Frame or mybatis-plus Frame as a reference . If it is mybatis frame , It is suggested that the template code of reverse engineering should not be modified by user , If you need a custom method , stay mapper and xml Level to customize an extension file , Used to store custom methods and SQL Logic , This avoids the strong discomfort caused by large changes in the table structure .
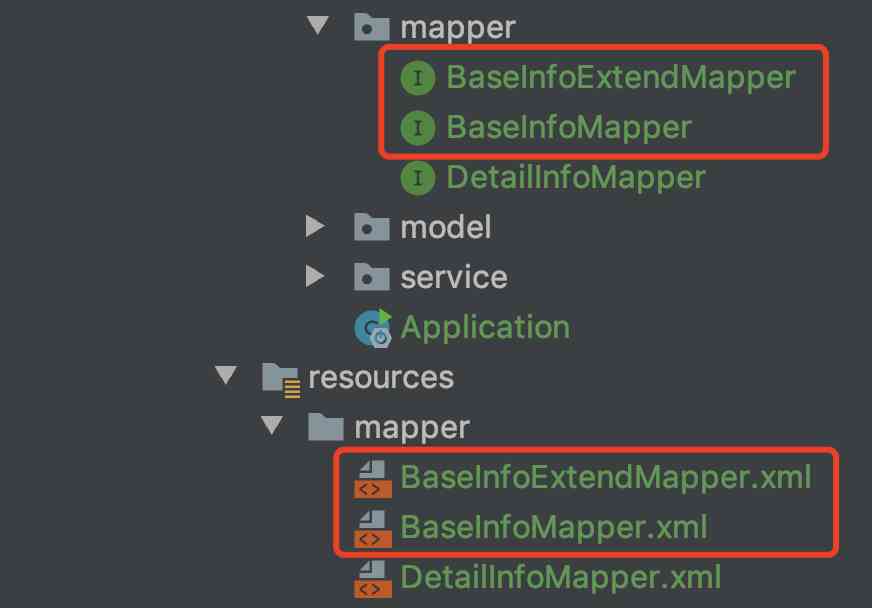
Now, of course, most of them will mybatis-plus As a persistence layer component , These problems can be avoided .
2、 Data interaction
For the needs of the business layer , Provide the corresponding data query method , Only deal with the logic of interacting with the database , Avoid business logic , Especially in the distributed architecture , Data query and assembly of different services , It shouldn't be on this layer .
public interface BaseInfoDao {
int insert(BaseInfo record);
List<BaseInfo> selectByExample(BaseInfoExample example);
int updateByPrimaryKey(BaseInfo record);
BaseInfo selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
BaseInfo getById (Integer id) ;
}
5、 ... and 、 Source code address
GitHub· Address
https://github.com/cicadasmile/data-manage-parent
GitEE· Address
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/data-manage-parent
Recommended reading : Programming system arrangement
| Serial number | Project name | GitHub Address | GitEE Address | Recommend index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Java Describe design patterns , Algorithm , data structure | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | ***** |
| 02 | Java Basics 、 Concurrent 、 object-oriented 、Web Development | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | **** |
| 03 | SpringCloud Details of micro service basic component case | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | *** |
| 04 | SpringCloud A comprehensive case of microservice architecture | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | ***** |
| 05 | SpringBoot Basic application of framework to advanced | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | **** |
| 06 | SpringBoot Framework integration development commonly used middleware | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | ***** |
| 07 | Data management 、 Distributed 、 Basic case of Architecture Design | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | ***** |
| 08 | Big data series 、 Storage 、 Components 、 Computing and other frameworks | GitHub· Click here | GitEE· Click here | ***** |