Yesterday's review
- Built in method of list
1. Type conversion
2. Operation of index value
3. Count the number of data in the list
(len) keyword
4. Increase the data value
(append) Add data value to the tail
(sinert) Index inserts data values
(extend) Extended list Underlying principle for+append
(+) You can also use + Number
5. Modify data values
Modify the data you want to modify through the index list[] = New value
6. Delete data value
(del) Index delete
(pop) Delete the tail by default You can also delete by index
(remove) Explicitly delete data values
7. Sort
(sort)
8. Flip
remevse
9. Comparison operations
- Variable type and immutable type
1. Variable types
To call a method is to modify itself
2. Immutable type
This is called by generating a new value You need to rebind the data value of the variable name
- Built in methods of tuples
1. Type conversion Support for Loop can be converted into tuples , Tuples convert tuples when empty parentheses
It should be noted that when a tuple has only one data value, the type is the type So add a comma after the data value
2. Index value
3. Count the number of data in the tuple len
4. Check and correct
Tuples support query Modification not supported
- Built in method of Dictionary
1. In the dictionary K V Key value pairs are unordered Index values are not supported
2. Value operation get
3. Count the number of key value pairs in the dictionary len
4. lookup Through the index K Search for or get Method
4. Modify and add
Through the index K To modify the
In the absence of K The time is to add
5. Delete
del、pop、popitem
6. Quick dictionary generation
formkeys
7. Get... Quickly K V Key value pair (key、vluses、items)
- Built in methods for collections
1. Type conversion
Support for Type of loop And must be data type immutable
2. Define empty sets set()
3. Bring your own weight removal function
4. Relationship between operation
& | ^ > <
Summary of today's content
- Garbage collection mechanism
- Introduction to character encoding
- The history of character coding
- Character coding practice
- Introduction to file operation
Today's content is detailed
Garbage collection mechanism
1. What is a garbage collection mechanism
stay python Editing in will produce a lot of data values When there is no data value bound to a variable, it will be garbage collected
'''python Will automatically apply for memory and free space '''
2. Reference count
When the data value does not count 0 It is still useful Will not be recycled
When the data value is 0 when Will be treated as garbage collection by the garbage mechanism
eg:
name = 'jason' # jason The reference count on the body is 1
name1 = name # here jason The reference count on the body is 2
del name # jason The quote count on the body is reduced 1
When a data value has a reference count, it will not be recycled by the garbage mechanism
3. Mark clear
Designed to solve the problem of circular references Check all the data generated by the program in memory Whether there is a cycle of one-time removal after marking
eg:
l1 = ['jason']
l2 = ['lisa']
l1.append(l2) # Reference count 2
l2.append(l1) # Reference count 2
del l1 # Disassociate variable names from l1 The bound list reference count of the list minus one
del l2 # Disassociate variable names from l2 The bound list reference count of the list minus one
When we put l1 and l2 The data of l1 and l2 The data of is still calling each other Counting the presence is one , So it can not be recycled by the garbage mechanism
4. Zonal recovery
Every once in a while, all the data should be checked Excessive consumption of resources
In order to reduce the resource consumption of garbage mechanism So we developed three generations of management The lower you go, the lower the frequency of detection 
Introduction to character encoding
1. Only text files have the concept of character encoding
2. The nature of data accessed inside a computer ( Binary system )
Computers only know 0 and 1
3. Why can we type out the words of different countries when we use computers
Because computers don't know our human language , So we humans define a transformation relationship of numbers
4. The transformation relationship cannot be changed casually There should be a unified standard
Character encoding table It records the correspondence between human characters and numbers
The history of character coding
1. A big family
The computer was invented by the Americans Americans need computers to recognize English characters
ps: All English characters add up to no more than 127 individual (2 The seventh power of ) However, Americans consider that new characters may appear in the future, so they add them as a precaution (2 The octave of )
ASCII: The internal value records the correspondence between English characters and data 1bytes To store characters 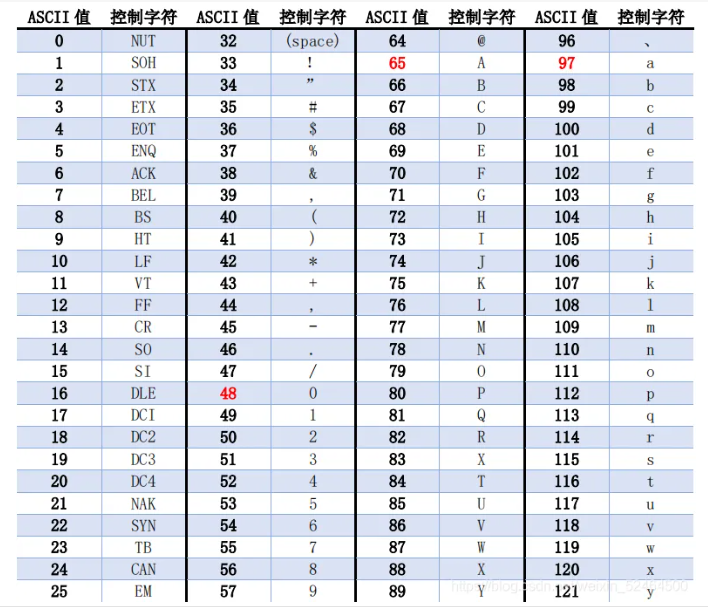
2. All the heroes are divided
because ASCII The table can only express English but not Chinese
Later, we in China developed a set of coding tables that can recognize Chinese
GBK clock : Chinese characters are recorded internally 、 The correspondence between English characters and numbers
2bybes Start storing Chinese ( You need to use more bytes when encountering rare words )
1bybes Store English
Korean corresponding coding table EUS_kr code
Korean characters and English characters are recorded 、 The correspondence of numbers
Coding table corresponding to Japan shift_JIS clock
Japanese and English characters are recorded 、 The correspondence of numbers
Be careful : At this time, the text of computer files in various countries cannot be directly interacted There will be garbled code
3. The world is unified
unicode (unicde): Compatible with universal characters
All characters can be used 2bytes Starting storage
utf family ( in the light of unicde Optimized version ):utf8
English is still used 1bytes
Others are uniformly adopted 3bybes
notes : Memory usage unicode The hard disk to use utf8
Character encoding practice
1. Only strings can participate in encoding and decoding Other data types need to be converted to strings first
2. How to solve the disorder
What code was used to store the data was used to solve the problem
3. Encoding and decoding
Convert human characters into numbers recognized by the computer according to the specified code
code : Human characters >>> Computer characters
Use encode It can convert human characters into computer characters
a = 'lisa: It is said that heaven is worthy of those who have a heart '
res = a.encode('utf8')
print(res) # b'lisa\xef\xbc\x9a\xe8\xaf\xb4\xe7\x9a\x87\xe5\xa4\xa9\xe4\xb8\x8d\xe8\xb4\x9f\xe6\x9c\x89\xe5\xbf\x83\xe4\xba\xba'
''' stay python in bytes Data of type can be regarded as binary numbers '''
decode : Computer characters >>> Human characters
b = a.decode(gbk)
print(a)
3. Interpreter level
python2 The default encoding is ASCII code
3.1 The file header # coding:utf8
3.2 Define string ( You need to prefix the string with u)
Why do you do this Because there's no way Only remedial measures can be taken
python3 The default encoding is utf8
Introduction to file operation
1. File operations ?
Automatically read and write files by writing code
2. What is a document ?
Double click the file icon to load data from hardware into memory
Saving after writing a file is actually brushing the data in the memory to the hard disk
The file is actually one of the shortcuts that the operating system exposes to the user to operate the computer hard disk
3. How to manipulate files with code
open(' File path ', Read write mode , Character encoding ')
Method 1:
f = open()
f.close()
Method 2:
with open() as Variable name
The subroutine automatically calls after it runs close() Method
4. For the file path, there may be a combination of letters and crowbars with special meanings
Prefix the string with a letter r Cancel special meaning 








