当前位置:网站首页>Large factory interview machine learning algorithm (0): Feature Engineering | data preprocessing
Large factory interview machine learning algorithm (0): Feature Engineering | data preprocessing
2022-07-23 11:14:00 【I'm a girl, I don't program yuan】
List of articles
The data is divided into buckets ( Separate boxes )
Concept
Data bucket division is a data preprocessing technology , By discretizing continuous variables , Improve model performance .
significance
- Discrete features are more important for outliers Robustness , Especially avoid Extreme outliers Interference of ;
- Model after feature discretization A more stable , Not because of the characteristic value Slight change And change the result ;
- Sparse vector inner product multiplication is fast , Algorithm Speed faster , It's also convenient Storage .
Barrel separation method
- Supervised :best-ks Split barrel and chi square split barrel
- Unsupervised : Equidistant barrel 、 Equal frequency bucket 、 Clustering bucket
Chi square is divided into barrels
The basic idea
Bottom up discretization method based on merging , Initially, each value is used as a sub box , Calculate the chi square value of adjacent intervals , Merge the interval with the lowest chi square value , Until the termination condition .
principle : Chi square test 
The application of chi square test in sub box
The core idea : The smaller the chi square value, the more similar the distribution .
With “ Age ” Is the variable to be divided ,“ Default or not ” Take the predictive variable as an example .
- To merge ages , First, age Sort , Then calculate the chi square value of each possible box combination .
With 20+25 Take the combination as an example , Suppose the age is 20 still 25 It has no significant impact on whether it defaults , therefore In default p yes 15/33, Non defaulting p yes 18/33, from E=np Expect , Then use the formula to calculate 20+25 Combined chi square value .
Extension : E = R T ∗ C T n E=\frac{RT*CT}{n} E=nRT∗CT
- Combine the combination with the smallest chi square value , And continue to calculate , Until the termination condition .
- Termination conditions :
Limit on the number of boxes ( Generally, it can be set to 5);
Threshold of chi square stop : You can choose a confidence of 0.9、0.95、0.99, freedom df=(R-1)(C-1), It's better than that 2.
Equidistant barrel
Global uniform statistics bucket (split_value_stat)
Map values to Equal size The range of . Ensure that features fall on each bucket The probability is the same . Such as :
import numpy as np
# Generate 20 individual 0-99 Random integer between
small_counts = np.random.randint(0, 100, 20)
# Carry out box splitting operation , By dividing the data by 10 be assigned to 0-9 in total 9 In a box ,
# The returned result is the number of the box to which the corresponding data should be divided
np.floor_divide(small_counts, 10)
# return : array([7,1,6,6,0,6,0,6,7,1,4,6,3,2,2,7,3,7,1])
shortcoming : It may lead to a large number of values in some intervals , Some are very few .
As an example, divide barrels evenly (split_value_stat_pos)
Different from the overall situation , Select the positive example data and divide the barrels evenly .
Example log Statistical bucket (split_value_stat_pos_log)
What is different from the normal example is , The given probability distribution is log Distribution . It is applicable to the situation that numbers span multiple orders of magnitude , Take the count of log value , Such as :
# Construct an example of an array with a larger interval , You can take logarithm log10 To separate boxes
large_counts = [296, 8286, 64011, 80, 3, 725, 867, 2215, 7689, 11495, 91897, 44, 28, 7971, 926, 122, 22222]
np.floor(np.log10(large_counts))
# return :array([2.,3.,4.,1.,0.,2.,2.,3.,3.,4.,4.,1.,1.,3.,2.,2.,4.])
Equal frequency bucket
It is also called sorting barrels by Quantile , Map values to intervals , Make the number of values contained in each interval roughly the same . have access to Pandas Library get quantile , Such as :
large_counts = [296, 8286, 64011, 80, 3, 725, 867, 2215, 7689, 11495, 91897, 44, 28, 7971, 926, 122, 22222]
# Map the data to the quantile of the required number
pd.qcut(large_counts, 4, labels=False)
# Calculate the data of the specified quantile point
large_counts_series = pd.Series(large_counts)
large_counts_series.quantile([0.25, 0.5, 0.75]
''' return : 0.25 122.0 0.50 926.0 0.75 8286.0 dtype:float64 '''
Clustering bucket
according to xgb Of get_split_value_histogram Function to obtain histogram, Take the split node value of the feature as split_value.
notes :
- Not every feature will have an appropriate split node value ;
- A feature may be used multiple times in the same tree , Split many times ;
- Finally, take the split value of the same feature on all trees as the bucket .
Dimensionless
Data normalization
min-max normalization
z-score
Data regularization
Simply speaking , Standardization deals with data according to the columns of characteristic matrix , The eigenvalues of samples are converted to the same dimension .
Regularization is to process data according to the rows of the characteristic matrix , Its purpose is to facilitate the point multiplication of sample vectors or the calculation of other kernel functions , In other words, they are transformed into “ Unit vector ”.
The process of regularization is to scale each sample to the unit norm ( The norm of each sample is 1), If we want to calculate the similarity between two samples later, such as dot product or other kernel methods ( Like cosine similarity ), This method will be very useful .
p Fan Count : ∣ ∣ X ∣ ∣ p = ( ∣ x 1 ∣ p + ∣ x 2 ∣ p + . . . + ∣ x n ∣ p ) 1 / p p norm :||X||^p=(|x1|^p+|x2|^p+...+|xn|^p)^{1/p} p Fan Count :∣∣X∣∣p=(∣x1∣p+∣x2∣p+...+∣xn∣p)1/p
more than string phase like degree : s i m ( x 1 , x 2 ) = x 1 ⋅ x 2 ∣ ∣ x 1 ∣ ∣ ⋅ ∣ ∣ x 2 ∣ ∣ Cosine similarity :sim(x_1,x_2)=\frac{x_1·x_2}{||x_1||·||x_2||} more than string phase like degree :sim(x1,x2)=∣∣x1∣∣⋅∣∣x2∣∣x1⋅x2
Data cleaning
Missing data

Noise data
- Identify the noise and remove it , Such as outlier identification ;
- Use other non noise data to smooth it , Such as data distribution .
Data inconsistency
Feature selection and feature extraction
feature selection
Feature selection mainly includes Two purposes :
- Reduce the number of features 、 Dimension reduction , Make model generalization more powerful , Reduce overfitting ;
- Enhance understanding between features and eigenvalues .
Feature selection can be divided into filter、wrapper、embedded There are three types of methods :
- Filter: Filtration method , according to Divergence perhaps The correlation Analyze each feature score , Set the threshold or the number of thresholds to be selected , Select features .
- Wrapper: Packaging method , according to Objective function ( It's usually a prediction score ), Select several features at a time , Or exclude some features .
- Embedded: Embedding method , First use Some machine learning algorithms Train with the model , Get the weight coefficient of each feature , Select features from large to small coefficients . Be similar to Filter Method , But it's training that determines the quality of a feature .
Correlation coefficient method
Calculate the correlation coefficient between independent variable and dependent variable , When the correlation coefficient is less than the threshold, the variable is discarded .
Chi square test
This method is used when the independent variable and dependent variable are classified variables , It is used to test whether there is significant correlation between independent variables and dependent variables . The specific method of chi square test is shown in “ Box splitting method - Chi square test ”.
Relief Algorithm
Relief The algorithm is a feature weight algorithm (Feature weighting algorithms), According to the characteristics and categories The correlation Give different weights to features , Features with weights less than a certain threshold will be removed .
Relief The correlation between features and categories in the algorithm is based on Distinguishing ability of features to close samples .
The main steps are as follows :
- Initialize all feature weights w i = 0 w_i=0 wi=0, Numerical attribute normalization ;
- From the training set D Select a sample at random R, Then from and R similar Find the nearest neighbor sample in the sample of H, be called Near Hit, From and R Different types Find the nearest neighbor sample in the sample of M, be called NearMiss;
- Update the weight of each feature : If R and Near Hit In a certain feature A The distance on the is less than R and Near Miss Distance on the road , It shows that this feature is beneficial to distinguish the nearest neighbors of the same kind and different kinds , Then increase the weight of the feature ; conversely , Then reduce the weight of the feature ;
w i = w i − d ( R . A , H . A ) + d ( R . A , M . A ) w_i = w_i-d(R.A,H.A)+d(R.A,M.A) wi=wi−d(R.A,H.A)+d(R.A,M.A)
- Repeat the above process m Time , Finally, the weight of each feature is obtained , Output features larger than the threshold .
example :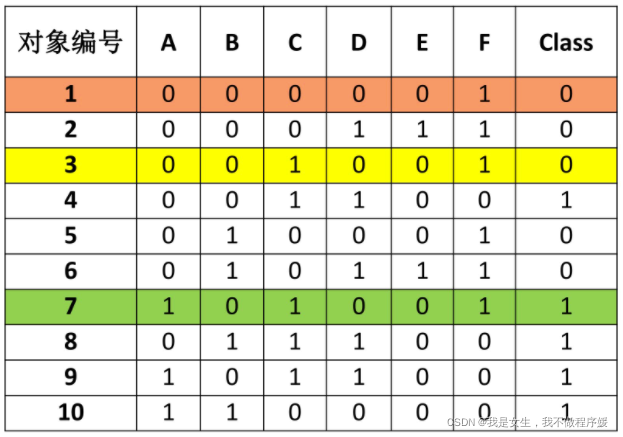
Relief The running time of the algorithm varies with the number of samples m And the number of original features N The increase of increases linearly , Therefore, the operation efficiency is very high .
feature extraction
PCA Algorithm
By modifying the original variables linear transformation , Extract new variables that reflect the essence of things , Remove redundancy at the same time 、 Reduce noise , achieve Dimension reduction Purpose .
- Given data set , contain n Objects ,m Attributes ;
- Centralization Data sets : Subtract the attribute mean from each attribute value , The average value of the centralized data is 0, use x n × m x_{n×m} xn×m Express ;
- Calculate the covariance matrix C, Elements c i j c_{ij} cij Attribute A i A_i Ai and A j A_j Aj The covariance between : c i j = ∑ k = 1 n ( x k i − A i ) ‾ ( x k j − A j ‾ ) c_{ij}=\sum_{k=1}^n(x_{ki}-\overline{A_i)}(x_{kj}-\overline{A_j}) cij=∑k=1n(xki−Ai)(xkj−Aj);
- Calculate the characteristic root and characteristic equation of covariance matrix , The characteristic roots are arranged in descending order as λ 1 ≥ λ 2 ≥ . . . ≥ λ m ≥ 0 \lambda_1≥\lambda_2≥...≥\lambda_m≥0 λ1≥λ2≥...≥λm≥0, be λ 1 \lambda_1 λ1 The corresponding eigenvector is the first principal component , λ 2 \lambda_2 λ2 The corresponding eigenvector is the second principal component , The first i The contribution rate of the principal components is : λ i ∑ k = 1 m λ k \frac{\lambda_i}{\sum_{k=1}^m\lambda_k} ∑k=1mλkλi;
- Leave the q The largest eigenvalues and their corresponding eigenvectors , Construct the principal component matrix P, Its first i Column vector p i p_i pi It's No i A principal component ( That is, the eigenvector );
- Calculate the reduced dimension matrix Y n × q = X n × m P m × q , q < n Y_{n×q}=X_{n×m}P_{m×q}, q<n Yn×q=Xn×mPm×q,q<n.
The new feature is a linear combination of the original feature .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Scattered notes of machine learning: some concepts and notes

7. Texture mapping
![[Doris]配置和基本使用contens系统(有时间继续补充内容)](/img/74/21c5c0866ed6b1bb6f9a1e3755b61e.png)
[Doris]配置和基本使用contens系统(有时间继续补充内容)

JDBC数据库连接池

Error when PLSQL creates Oracle Database: when using database control to configure the database, it is required to configure the listener in the current Oracle home directory. You must run netca to co

Data Lake: introduction to Apache iceberg

Data Lake: introduction to delta Lake

Flask blueprint

Activiti工作流使用之Activiti-app的安装及流程创建

cuda10.0配置pytorch1.7.0+monai0.9.0
随机推荐
Federated primary keys and indexes
面试必备之数据库专题
MySql语句查询某一级节点的所有子节点
Dictionary creation and copying
Leetcode daily question (1946. largest number after varying substring)
Fundamentals of software testing - design method of test cases
初识Flask
USCD行人异常数据集使用指南 | 快速下载
The super simple face recognition API can realize face recognition in just a few lines of code
同步发送短信验证码
知识点回顾
3. Threads in flask
Flask源码剖析(一)请求入口
2. Analysis of the return value of the startup function
人脸识别神经网络实现
After the formula in word in WPS is copied, there is a picture
IO should know and should know
mysql invalid conn排查
[pytho-flask筆記5]藍圖簡單使用
Copy a project /project in idea