gRPC The motive of
In practical projects, there are often more than one way to implement back-end services , And due to technical or business constraints , There are usually many languages Written Services . In order to communicate with each other, services must use a unified API A contract makes an agreement . The agreement shall stipulate that Set such as : Communication channel , Authentication mechanism 、 Load format 、 Data model and how to handle exceptions .
Of course, we hope that communication can be efficient ( Fast and light ), Because the amount of service information exchange between microservices is usually huge , So communication should be as fast as possible . At the same time, in the case of mobile applications or other situations where the network speed and bandwidth are limited , It is very important to have a lightweight communication protocol to interact with back-end services .
Last , We also want communication to be as simple as possible , For example, we now have a system with thousands of services , We don't want to spend a lot of time writing code that lets services communicate with each other . What we want is some kind of framework , Let the framework help us complete all communication related content , Let developers focus on implementing the core business logic of services .
gRPC What is it? ?
gRPC By the first google The development of , therefore gRPC Medium g Often considered to represent google It means , In fact gRPC 1.0 That's what happened when , However, the subsequent versions of g Equivalent to a version code ( for example 1.1 Of g representative good), Can be in gRPC Version code To view the . and gRPC Now belongs to Cloud native Foundation (CNCF) Part of ( Like k8s). that RPC What does it represent Why not? ?Remote Procedure Calls It is a form of call , Popular said , It is automatically processed by the underlying framework , Permit Allow a program on one computer to call a program on another computer . This kind of call is seen by the server , We call... Directly on the client A method of server code ( Or functions ).
gRPC How it works ?
client To have a stub ( pile ) It provides with Server Same method ,stub from gRpc Automatic generation . Stub Call... In the background gRPC The framework communicates with... Through the network server Exchange information . because stub The existence of ,client and server Now we only need to care about the implementation of the business Core logic of .

gRPC Code generation
gRPC How to help us generate stub Of ?
To give server and client Generate stub We have to start with Protocol Buffer In the file API contract ( The rules ), package enclosed Description of service And it's Message payload (payload).
Here's a simple protoBuf Format Protocol Buffer

In the example file on , Defined Hello Method ( function ), It uses HelloRequest As input , And return a HelloResponse , among HelloRequest Contains only one string name, HelloResponse There is also a string greet . From an original file like this , By the protocol buffer compiler according to the programming language , Generate server and client Of stub Code .
that gRPC Why did you use protocol buffer As API Statute ?
1. It is very easy to read and understand
2. Let different programming languages , Have a unified description
3. Use binary format , Same as JSON/XML And other text-based formats ,
smaller 、 Easier to transmit
and
Better sequence / Deserialization performance
4. Provides client and server Between the Strong type (Strongly typed) API contract
5. Have a lot of API Evolution rule , To ensure the API Moving forward / backward compatible
in fact gRPC Not with Protocol Buffer Strong binding , We can use Google Flatbuffers or Microsoft Bond Instead of Protocol Buffer . however Protocol Buffer It's a great rule , Because it is supported by many programming languages .
Native implementation :GO、Java、NodeJS
Packaging implementation :C/C++、C#、Objective-C、Python、Ruby、Dart、PHP
Unofficially supported third-party libraries :swift rust typescript ....
gRPC Why efficient
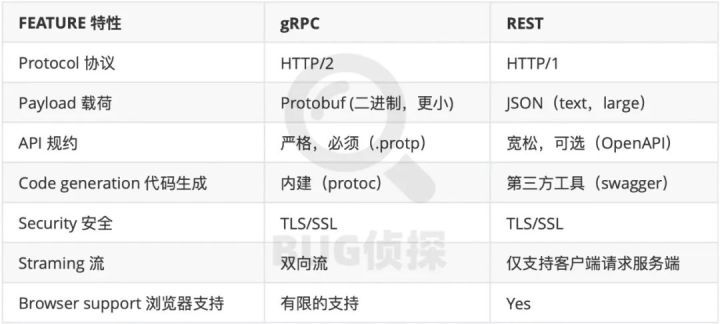
gRPC Use HTTP/2 As its transport protocol , therefore , It inherited HTTP/2 Some of the great features offered . for example Binary system Format , Compared with other protocols using text-based , Higher performance 、 More robust 、 The transmission is lighter 、 Decoding is more secure , And protocol buffer The combination of ; meanwhile Http/2 Also used HPACK Compress HEAD, Reduce overhead and improve performance ;Http/2 Not bad Multiplexing , This means that the client and the server can pass through a single TPC The connection sends multiple requests and receives multiple responses in parallel , This can effectively reduce the delay and improve the utilization efficiency of the network ;Http/2 It also allows the server to push , When a single request is made on the client Condition , The server can return multiple responses , In most cases , This is good for reducing client and Server side Round trip delay between is very valuable .

Http/2 How the bottom layer works
HTTP/2 One TCP The connection can withstand multiple two-way flows , Each flow has a unique identifier and carries multiple two-way messages , Every message ( request / Respond to ) Can be decomposed into multiple binary frames , A frame is the smallest unit that carries different data types , Such as :HEADERS( head )、SETTINGS( Set up )、PRIORITY( priority )、DATA( Data etc. ) etc. .

Frames on different streams are interleaved on the connection , And will be reassembled when reaching the other end .

HTTP/2 vs HTTP/1.1
Let's take another look at HTTP/2 Familiar with HTTP/1.1 Comparison of

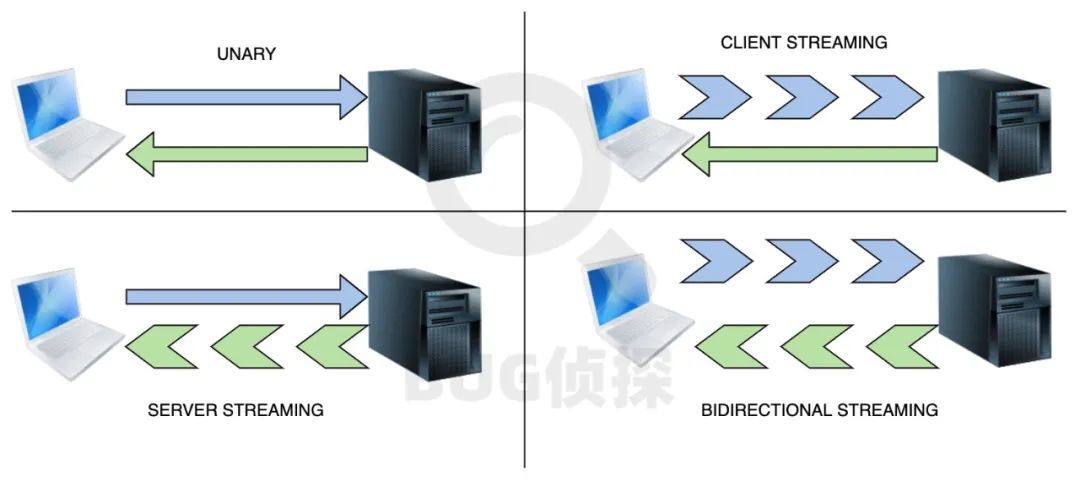
gRPC Four types of
One yuan unary:client Send a request ,server Reply to a response
Client stream client streaming: The client sends multiple message flow requests , expect server Reply to only one response
Server stream server streaming: The client sends only one request , The server replies to multiple message flow responses
Two-way flow bidirectional streaming: The client and server will send multiple requests and responses in parallel , It is very flexible and Non blocking , It means , Neither party needs to wait for a response before sending the next message .
gRPC vs REST
gRPC The applicable scenarios of
The service is gRPC Where it really works , Because it can achieve low latency and high throughput communication . Because many programming languages provide Out of the box code generation , So it can also be used in many languages . Point to point communication also uses gRPC Because it's good for both Provides good support for streams . Last , Because of its lightweight message format , It is also a good choice for the environment with limited network .



原网站版权声明
本文为[InfoQ]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/174/202206231533014129.html