当前位置:网站首页>JS position operation
JS position operation
2022-06-24 18:36:00 【Brother Mengfan】
Catalog
1.1.1、 The element itself has fixed location ,offsetParent yes null
1.1.2、 The element itself has no position or is relative or absolute ,offsetParent yes body
1.1.4、body Elemental offsetParent yes null
1.3、offsetWidth and offsetHeight
1.4、offset and style The difference between
1.5、offsetParent and parentNode difference
1.6.1、 Get the mouse coordinates in the box
3.3、 Rolling method scrollTo(x,y)
One 、offset
offset That's the offset , Use offset The position of the element can be obtained dynamically by series related attributes ( The offset )、 Size, etc .
(1) Get element distance With positioning The position of the parent element ;
(2) Get the size of the element itself ( Width and height ).
Be careful : None of the returned values have units .
offset Common properties :


(1)offsetWidth The calculation formula of is :border+ width + padding;
(2)offsetHeight Calculation formula :border+ height + padding;
1.1、offsetParent
1.1.1、 The element itself has fixed location ,offsetParent yes null
<div id="box" style="position: fixed;"></div>
<script>
var box = document.querySelector('#box');
console.log(box.offsetParent);
</script>1.1.2、 The element itself has no position or is relative or absolute ,offsetParent yes body
<div id="box">aaa</div>
<script>
var box = document.querySelector('#box');
console.log(box.offsetParent);
</script>1.1.3、 The element itself is not positioned , But the parent element has a location ,offsetParent Is the nearest parent positioning element
<div id="father" style="position: relative;">
<div>
<div id="box"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var box = document.querySelector('#box');
console.log(box.offsetParent);
</script>1.1.4、body Elemental offsetParent yes null
console.log(document.body.offsetParent);1.2、offsetTop and offsetLeft
No positioning :
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.grandfather {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: skyblue;
margin: 100px;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin-left: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="grandfather">
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var gf = document.querySelector('.grandfather');
console.log(gf.offsetTop); //100
console.log(gf.offsetLeft); //100
var f = document.querySelector('.father');
console.log(f.offsetTop); //100
console.log(f.offsetLeft); //200
var s = document.querySelector('.son');
console.log(s.offsetTop); //100
console.log(s.offsetLeft); //250
</script>to grandfather After positioning :
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.grandfather {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: skyblue;
margin: 100px;
position: relative;
}
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-left: 100px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin-left: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="grandfather">
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var gf = document.querySelector('.grandfather');
console.log(gf.offsetTop); //100
console.log(gf.offsetLeft); //100
var f = document.querySelector('.father');
console.log(f.offsetTop); //0
console.log(f.offsetLeft); //100
var s = document.querySelector('.son');
console.log(s.offsetTop); //0
console.log(s.offsetLeft); //150
</script>summary :
(1)offsetTop and offsetLeft You can get the offset position of the element , Returns a numeric value without units ;
(2)offsetTop and offsetLeft It is based on the nearest father with a location , If you have a father , But there is no positioning , with body For father .
1.3、offsetWidth and offsetHeight
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 50px;
padding: 50px;
border: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="son"></div>
<script>
var s = document.querySelector('.son');
console.log(s.offsetWidth);//200
console.log(s.offsetHeight);//200
</script>summary :offsetWidth and offsetHeight The size of is only related to border、height perhaps width、padding of , And magin irrelevant .
1.4、offset and style The difference between

<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
<div class="box" style="width: 100px;"></div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div')
console.log(div.offsetWidth); // 220 = 10 * 2 + 200
// div.offsetWidth = 300; // Invalid assignment
console.log(div.style.width); // 200px
// div.style.width = '300px'; // Assignment valid
</script>summary : want Get the element size use offset More appropriate , To give Element change value use style.
1.5、offsetParent and parentNode difference
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: pink;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin-left: 50px;
padding: 50px;
border: 50px;
}
</style>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
<script>
var s = document.querySelector('.son');
console.log(s.offsetParent);//body
console.log(s.parentNode);//father
</script>difference :
(1)offsetParent Positioning is required , If there is a father , But there is no positioning , Then return to body;
(2)parentNode No need to locate , Return to the nearest father .
1.6、 Case study
1.6.1、 Get the mouse coordinates in the box
As shown in the figure :

The code is as follows :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> Get the mouse coordinates in the box </title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
margin: 100px auto;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<script>
// 1. Get the box
var box = document.querySelector('.box')
box.onclick = function(e) {
// e.pageX Its value is the distance from the mouse position to the left of the page
// offsetLeft Its value is the distance from the current object to the left of the page
// When you want to calculate the mouse in div In the position of , Need to use e.pageX - offsetLeft Value
// console.log(e.pageX , this.offsetLeft)
var cursorPlaceX = e.pageX - this.offsetLeft;
//console.log(cursorPlaceX);
var cursorPlaceY = e.pageY - this.offsetTop;
this.innerHTML = 'X Coordinates are ' + cursorPlaceX + ',' + "Y Coordinates are " + cursorPlaceY;
// console.log(' The current position of the mouse :' + cursorPlaceX + ', ' + cursorPlaceY);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>1.6.2、 Drag the modal box
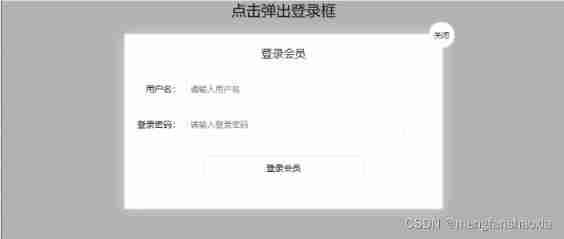
The code is as follows :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> Drag the modal box </title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.login-header {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
height: 30px;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 30px;
}
.login {
display: none;
width: 512px;
height: 280px;
position: fixed;
border: 1px solid #ebebeb;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
background: #ffffff;
box-shadow: 0 0 20px #ddd;
z-index: 9999;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
.login-title {
width: 100%;
margin-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
height: 40px;
font-size: 18px;
position: relative;
cursor: move;
}
.login-input-content {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.login-button {
width: 50%;
margin: 30px auto 0 auto;
line-height: 40px;
font-size: 14px;
border: 1px solid #ebebeb;
text-align: center;
}
.login-bg {
display: none;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .3);
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #000000;
}
.login-button a {
display: block;
}
.login-input input.list-input {
float: left;
line-height: 35px;
height: 35px;
width: 350px;
border: 1px solid #ebebeb;
text-indent: 5px;
}
.login-input {
overflow: hidden;
margin: 0 0 20px 0;
}
.login-input label {
float: left;
width: 90px;
padding-right: 10px;
text-align: right;
line-height: 35px;
height: 35px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.login-title span {
position: absolute;
font-size: 12px;
right: -20px;
top: -30px;
background: #ffffff;
border: 1px solid #ebebeb;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="login-header">
<a id="link" href="javascript:;"> Click to pop up the login box </a>
</div>
<div id="login" class="login">
<div id="title" class="login-title"> Login member
<span><a id="closeBtn" href="javascript:void(0);" class="close-login"> close </a></span>
</div>
<div class="login-input-content">
<div class="login-input">
<label> user name :</label>
<input type="text" placeholder=" Please enter a user name " name="info[username]" id="username" class="list-input">
</div>
<div class="login-input">
<label> The login password :</label>
<input type="password" placeholder=" Please enter the login password " name="info[password]" id="password" class="list-input">
</div>
</div>
<div id="loginBtn" class="login-button"><a href="javascript:void(0);" id="login-button-submit"> Login member </a></div>
</div>
<!-- Covering layer -->
<div id="bg" class="login-bg"></div>
<script>
// 1. Get elements
var link = document.querySelector('#link')
var login = document.querySelector('#login')
var title = document.querySelector('#title')
var closeBtn = document.querySelector('#closeBtn')
var mask = document.querySelector('#bg')
// 2. Click the box
link.onclick = function() {
login.style.display = 'block';
mask.style.display = 'block';
};
// 3. Click Close
closeBtn.onclick = function() {
login.style.display = 'none';
mask.style.display = 'none';
};
// 4. Drag the bullet box
title.onmousedown = function(e) {
e = e || window.event;
//var x = e.pageX - this.parentNode.offsetLeft;
// Get the mouse in login Window x Coordinates and y Position of coordinates
var x = e.pageX - login.offsetLeft;
var y = e.pageY - login.offsetTop;
// Add a move event to the document object
document.onmousemove = function(e) {
// modify login The location of the object
// e.pageX - x It's calculation login The distance from the left of the box to the left of the page
// e.pageY - y It's calculation login The distance between the top edge of the box and the top edge of the page
login.style.left = e.pageX - x + 'px';
login.style.top = e.pageY - y + 'px';
};
// Release the mouse
document.onmouseup = function(e) {
// Unbind event
document.onmousemove = null;
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Two 、client


Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>client attribute </title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 10px solid red;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
/**
* client Represents a client , It has four properties :
* 1. clientTop: Returns the top border of the element
* 2. clientLeft: Returns the left border of the element
* 3. clientWidth: Returns the inner margin of an element + The value of the content width
* 4. clientHeight: Returns the inner margin of an element + Value of content height
*/
var div = document.querySelector('div');
console.log(div.clientLeft); // 10
console.log(div.clientTop); // 10
console.log(div.clientWidth); // 220 = 10 + 200 + 20
console.log(div.clientHeight); // 220 = 10 + 200 + 20
// have access to clientWidth and clientHeight To get the size of the page
window.onresize = function () {
var doc = document.documentElement;
console.log(doc.clientWidth, doc.clientHeight);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>3、 ... and 、scroll
3.1、scroll Use

Example :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> Rolling height </title>
<style>
#test {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
border: 510x solid red;
padding: 50px;
margin: 100px auto;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<div id="test"> I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content, I am content </div>
<body>
<script>
var test = document.querySelector('#test')
console.log(test.clientHeight); //height+padding 200
console.log(test.scrollHeight); // Actual content height 495
test.addEventListener('scroll', function() {
console.log(test.scrollTop);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>3.2、 Page scrolling case
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> Page scrolling </title>
<style>
body {
height: 2000px;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
overflow: scroll;
}
#btn {
position: fixed;
bottom: 30px;
right: 30px;
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
</div>
<button id="btn"> Back to the top </button>
<script>
window.onscroll = function () {
var btn = document.querySelector('#btn')
// The height of the roll
var scrollVal = document.documentElement.scrollTop;
// The height of the visualization area
var showHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;
// Determine whether the scroll height exceeds the height of the visualization area ( Whether the distance of one screen is reached )
if (scrollVal <= showHeight) {
btn.style.display = 'none';
} else {
btn.style.display = 'block';
}
btn.onclick = function () {
document.documentElement.scrollTop = 0;
btn.style.display = 'none';
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>3.3、 Rolling method scrollTo(x,y)
scrollTo(x,y) Method to scroll through the current window The document shown in , Let the coordinates in the document be x,y The point of is in the upper left corner .
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title> Page scrolling </title>
<style>
body {
height: 2000px;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
overflow: scroll;
}
#btn {
position: fixed;
bottom: 30px;
right: 30px;
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
<p> Content </p>
</div>
<button id="btn"> Back to the top </button>
<script>
window.onscroll = function () {
var btn = document.querySelector('#btn')
// The height of the roll
var scrollVal = document.documentElement.scrollTop;
// The height of the visualization area
var showHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;
// Determine whether the scroll height exceeds the height of the visualization area ( Whether the distance of one screen is reached )
if (scrollVal <= showHeight) {
btn.style.display = 'none';
} else {
btn.style.display = 'block';
}
btn.onclick = function () {
// document.documentElement.scrollTop = 0;
scrollTo(0, 0)
btn.style.display = 'none';
};
};
</script>
</body>
</html>边栏推荐
- Nacos cluster starts throwing set of SQL_ SELECT_ LIMIT is not support
- Exception: Gradle task assembleDebug failed with exit code 1
- Monotone stack template
- High quality defect analysis: let yourself write fewer bugs
- 25.sql statement differentiation
- SDL: cannot play audio after upgrading openaudio to openaudiodevice
- Why are more and more people studying for doctors? Isn't it more and more difficult to graduate a doctor?
- Skills of writing test cases efficiently
- Data driven decision making: Decision intelligence and design thinking
- 如何在 R 中执行稳健回归
猜你喜欢
Online sequence flow chart making tool

360 digital released information security trends in January: 120000 fraud risks were captured and users were reminded 2.68 million times

High quality defect analysis: let yourself write fewer bugs
[golang] leetcode intermediate - jumping game & different paths

Regression testing strategy for comprehensive quality assurance system
R language Quantitative Ecology redundancy analysis RDA analysis plant diversity species data visualization
[quick news] the jeecgboot low code platform was successfully selected into the 2021 scientific innovation China · open source innovation list

Five skills of selecting embedded programming language
Ultimate Guide: comprehensive analysis of log analysis architecture of Enterprise Cloud native PAAS platform

Considerations for it project demand analysis
随机推荐
Eight recommended microservice testing tools
Uniapp wechat applet calls mobile map to navigate to the target point
微服务系统设计——子服务项目构建
How to select the best test cases for automation?
25.sql statement differentiation
电子元器件行业B2B电商市场模式、交易能力数字化趋势分析
Huitongda officially landed at the Hong Kong Stock Exchange: the gross profit margin continued to decline, and the book value of several shareholders still suffered losses
Implementation of pure three-layer container network based on BGP
Number of occurrences of numbers in the array (medium difficulty)
On software requirement analysis
如何在 R 中使用 Fisher 的最小显着性差异 (LSD)
Flex box flex attribute
Considerations for it project demand analysis
[North Asia data recovery]_ mdb_ catalog. Mongodb database data recovery case in case of WT file corruption
Keep two decimal places
Palindrome string (two methods)
如何在 R 中创建线性模型预测区间 并可视化
Tencent cloud TCS: an application-oriented one-stop PAAS platform
SAP license: ERP for supply chain management and Implementation
Can the money invested in financial products be withdrawn at any time?



![[quick news] the jeecgboot low code platform was successfully selected into the 2021 scientific innovation China · open source innovation list](/img/1a/c148d02eb7d58a15c92a91b6cdefc4)
