当前位置:网站首页>@The underlying principle of Autowired annotation
@The underlying principle of Autowired annotation
2022-07-25 23:56:00 【Chongling】
Spring The convenience of the framework makes it easy for us to use @Autowired Annotations implement dependency injection , This article will delve into Spring The source code parsing @Autowired How annotations work .
One 、@Autowired The role of annotations
1. @Autowired It's a comment , It can be to Members of the class Variable 、 Method and constructor for annotation , Give Way spring complete bean The work of automatic assembly .
2. @Autowired The default is to match by class , coordination @Qualifier Specify to assemble by name bean.
Two 、@Autowired Use of annotations
Mark on the method :@Bean+ Method parameter , Parameters get from container , Do not write by default @Autowired The effect is the same , Can be assembled automatically
Mark on the constructor : If there is only one parameterized construct on the component , This parameter structure @Autowired It can be omitted , The component at the parameter location can still be automatically retrieved from the container
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
boolean required() default true;
}
3、 ... and 、@Autowired Automatic assembly of annotations
@Autowired Automatic injection :
1. The default priority is to find the corresponding component in the container according to the type :applicationContext.getBean()
2. If multiple components of the same type are found , Then the name of the property is used as the component's ID Go to the container to find
Four 、@Autowired Annotation source code analysis
@Autowired The function of annotation is by AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor Realized , Looking at the source code of this class, you will find that it implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor Interface , Then, the... In the interface is realized postProcessMergedBeanDefinition Method , The core processing code is as follows :
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new LinkedList<>();
// Target class to be processed
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new LinkedList<>();
// Get all the fields of this class through reflection , And traverse each field , And by means of findAutowiredAnnotation The annotation used to traverse each field , And if you use autowired Modify the , Then return to auotowired Related properties
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
// There are many. @Autowired Embellished notes , All added currElements In this container , Deal with it together
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}
@Autowired Annotation is through postProcessMergedBeanDefinition This method implements the pre parsing of the injection type , Encapsulate the attribute information that needs dependency injection into InjectionMetadata Class , Finally, what this method returns is to include all with autowire An annotation decorated InjectionMetadata aggregate . This class consists of two parts :
public InjectionMetadata(Class<?> targetClass, Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.injectedElements = elements;
}
One is the target class we deal with , The second is obtained by the above method, so elements aggregate .
With the target class , After a collection of all the elements that need to be injected , We can do it autowired Dependency injection logic , The implementation method is as follows :
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) {
if (!this.validatedBeanNames.contains(beanName)) {
if (!this.shouldSkip(this.beanFactory, beanName)) {
List<String> invalidProperties = new ArrayList();
PropertyDescriptor[] var6 = pds;
int var7 = pds.length;
for(int var8 = 0; var8 < var7; ++var8) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = var6[var8];
if (this.isRequiredProperty(pd) && !pvs.contains(pd.getName())) {
invalidProperties.add(pd.getName());
}
}
if (!invalidProperties.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanInitializationException(this.buildExceptionMessage(invalidProperties, beanName));
}
}
this.validatedBeanNames.add(beanName);
}
return pvs;
}
The method it calls is InjectionMetadata As defined in inject Method , as follows :
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elementsToIterate = checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements;
if (!((Collection)elementsToIterate).isEmpty()) {
Iterator var6 = ((Collection)elementsToIterate).iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement element = (InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement)var6.next();
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
The logic is to traverse , And then call inject Method ,inject The implementation logic of the method is as follows :
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field)this.member;
// Instantiate and assign values to objects through reflection
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(target, this.getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
} else {
if (this.checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method)this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, this.getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
} catch (InvocationTargetException var5) {
throw var5.getTargetException();
}
}
}
Reflection technology is used here , It is divided into fields and methods . Called makeAccessible Such a method can be called brute force cracking , Instantiate and assign values to objects through reflection technology .getResourceToInject The parameters of the method are the parameters to be injected bean Name , This method is based on this bean Your name to get it .
边栏推荐
- MySQL的DDL、DML和DQL的基本语法
- 1223. Dice simulation range DP
- redis-基本数据类型(String/list/Set/Hash/Zset)
- Leetcode 0135. distribute candy
- 下一代终端安全管理的关键特征与应用趋势
- Practical experience of pair programming
- BOM 浏览器对象模型
- Article 75: writing skills of academic papers
- Nacos 下线服务时报错 errCode: 500
- Fixed and alternate sequential execution of modes
猜你喜欢
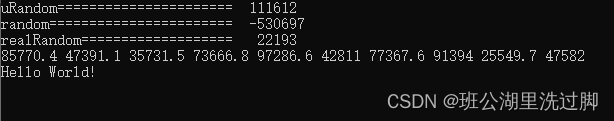
Generating random number random learning uniform_ int_ distribution,uniform_ real_ distribution
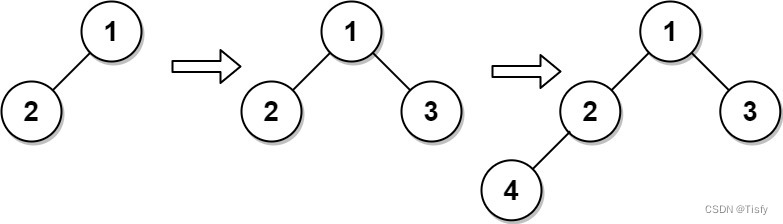
Leetcode 0919. complete binary tree inserter: array representation of complete binary tree
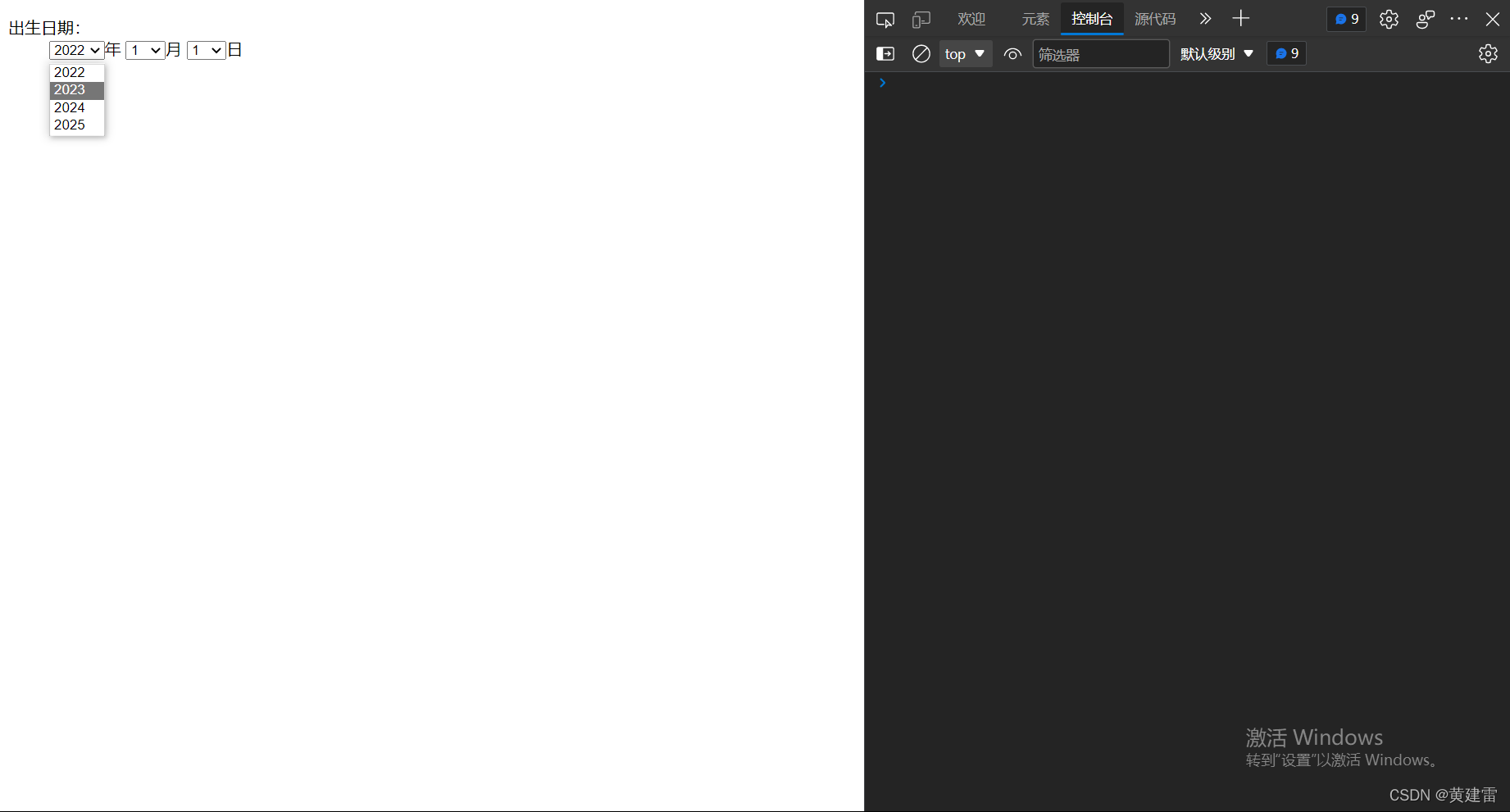
Write a select drop-down list

调用钉钉api报错:机器人发送签名过期;solution:签名生成时间和发送时间请保持在 timestampms 以内
![[learning notes] solid works operation record](/img/f7/0535b473755643ce32996f00fa5554.png)
[learning notes] solid works operation record

安全文档归档软件

String functions and memory operation functions

如何用yolov5 做个闯红灯监控的智能交通系统(1)

智牛股--09

Dead letter queue and message TTL expiration code
随机推荐
typescript ts 基础知识之类
R language installation tutorial | graphic introduction is super detailed
利用用户脚本优化 Yandere/Konachan 站点浏览体验
老旧笔记本电脑变服务器(笔记本电脑+内网穿透)
Getting started with Servlet
Topsis与熵权法
意向不到的Dubug妙招
Leetcode 0135. distribute candy
Imitating the magnifying glass effect of JD products -- JS Foundation
ArcGIS cuts TIF images (grid data) according to the vector range, merges shp files in batches, cuts vectors in the region according to the vector range, outputs the geographic coordinate system, conve
What is the difference between hot deployment and hot loading?
Seventy second: pedestrian detection
Firewall command simple operation
[Muduo] thread package
How does JS judge whether the current date is within a certain range
Macro task, micro task and event cycle mechanism
【英雄哥七月集训】第 24天: 线性树
What is inode? It will help you understand inode and what help inode provides when creating and deleting files.
Key features and application trends of next generation terminal security management
你还在用浏览器自带书签?这款书签插件超赞