当前位置:网站首页>One question to explain the past and present life of dynamic planning
One question to explain the past and present life of dynamic planning
2022-06-10 19:51:00 【Starlight technician】
The past and present life of dynamic planning
subject : Give an array Arr=[2,3,5,7,5],aim=10; Get the composition of the array aim What is the minimum number of elements in the ;
Here are three ways to solve the problem in turn , Step by step from recursive solution to dynamic programming
1. Recurrence of violence
- Ideas
set up f(index,aim) From index In the beginning coin , form aim The minimum number of coins ; So our goal is f(0,10);
f(index,aim) = min(f(index+1,aim),1+f(index+1,aim-Arr[index]))
The first item means that the index A coin ; The second item indicates the use of index A coin
/******************** Recurrence of violence ****************/
//index From index Coins to choose
//rest How much money is left to add up
// return index After the beginning of the coin also need to use rest individual
int process1(vector<int>& Arr, int index, int rest)
{
if (rest < 0)
return -1;
if (rest == 0)
return 0;
//rest>0 But the coin is gone
if (index == Arr.size())
return -1;
//rest>0 And there are coins
int p1 = process1(Arr, index + 1, rest);
int p2Next = process1(Arr, index + 1, rest - Arr[index]);
if (p1 == -1 && p2Next == -1)
return -1;
else if (p1 == -1)
return p2Next + 1;
else if (p2Next == -1)
return p1;
return min(p1, 1 + p2Next);
}
// Get the minimum number of coins
int get_mincoin1(vector<int>& Arr, int aim)
{
return process1(Arr, 0, aim);
}

2. Memory search solution
The first solution , There will be double counting , Like f(3,5) It will be calculated on both branches , This leads to a waste of computing resources ; So compared with the first violent recursive solution, the memory search solution adds a storage mechanism , Save the calculated f(index,rest) Value ; When we meet again , Use it directly , No double counting
- code
/************* Memory search *************/
int process2(vector<int>& Arr, int index, int rest,vector<vector<int>>& dp)
{
if (rest < 0)
return -1;
if (dp[index][rest] != -2)
return dp[index][rest];
if (rest == 0)
dp[index][rest] = 0;
//rest>0
else if (index == Arr.size())
dp[index][rest] = -1;
else
{
//rest>0 And coins
int p1 = process2(Arr, index + 1, rest,dp);
int p2Next = process2(Arr, index + 1, rest - Arr[index],dp);
if (p1 == -1 && p2Next == -1)
dp[index][rest] = -1;
else if (p1 == -1)
dp[index][rest] = p2Next + 1;
else if (p2Next == -1)
dp[index][rest] = p1;
else
dp[index][rest] = min(p1, 1 + p2Next);
}
return dp[index][rest];
}
int get_mincoin2(vector<int>& Arr, int aim)
{
vector<vector<int>> dp(Arr.size() + 1, vector<int>(aim + 1, -2));
return process2(Arr, 0, aim, dp);
}
3. Strict table structure
Strict table structure is what we call dynamic programming , State transition matrix ; In the transformation from memory search solution to strict table structure , There are a few steps that need to be taken
1) Find out the number and range of variable parameters , Used for definition dp Array ;
2) Need to search the algorithm according to memory if Conditions , determine dp Positions in the array that do not need to be evaluated ;
3) Look for the rules of position dependence of other positions in the table
The approximate form of the state transition matrix ( It also needs to be divided according to the details )
dp(index,aim) = dp(f(index+1,aim),1+dp(index+1,aim-Arr[index]))
- code
/************* Strict table structure *************/
int get_mincoin3(vector<int>& Arr, int aim)
{
vector<vector<int>> dp(Arr.size() + 1, vector<int>(aim + 1,0));
for (int index = 0; index < Arr.size(); index++)
dp[index][0] = 0;
for (int rest = 1; rest <= aim; rest++)
dp[Arr.size()][rest] = -1;
for (int index = Arr.size() - 1; index >= 0; index--)
{
for (int rest = 1; rest <= aim; rest++)
{
int p1 = dp[index + 1][rest];
int p2Next = -1;
if(rest - Arr[index] >= 0)
p2Next = dp[index + 1][rest - Arr[index]];
if (p1 == -1 && p2Next == -1)
dp[index][rest] = -1;
else if (p1 == -1)
dp[index][rest] = p2Next + 1;
else if (p2Next == -1)
dp[index][rest] = p1;
else
dp[index][rest] = min(p1, 1 + p2Next);
}
}
return dp[0][aim];;
}
4. summary
actually , The essence of the final state transition matrix of the dynamic programming problem is transformed from the first solution by violence recursion ; The most important thing is to determine the idea of recursion , And the premise for the determination of recursive thinking , Is to find the parameters of the transformation index and rest; So the most important thing is to find these two changing parameters and the idea of recursion , Then the state transition matrix can be easily solved ;
In dynamic programming , Also important are the order of traversal and the range of transformation parameters
边栏推荐
- [01] every high-quality author deserves to be seen. Let's take a look at this week's high-quality content!
- 100003 words, take you to decrypt the system architecture under the double 11 and 618 e-commerce promotion scenarios
- It is forbidden to throw away rotten software. A guide for software test engineers to advance from elementary level to advanced level will help you promote all the way
- Code solution of simplex method (including super detailed code notes and the whole flow chart)
- Apicloud visual development - one click generation of professional source code
- SPSS introductory notes
- Zabbix Server Trapper远程代码执行漏洞(CVE-2017-2824)
- Mongodb 唯一索引
- 【C语言进阶】数据的存储【上篇】【万字总结】
- 今年高考期间各考点秩序井然,未发生影响安全的敏感案事件
猜你喜欢
![[6.4-6.10] wonderful review of Blog](/img/66/0cfc97bf4bc0c2b6e66c0419690ce5.png)
[6.4-6.10] wonderful review of Blog

MySQL数据库设计概念(多表查询&事务操作)

MATLAB 根据任意角度、取样点数(分辨率)、位置、大小画椭圆代码

SAR image focusing quality evaluation plug-in

Esp8266 system environment setup

一文详解EventMesh落地华为云的探索及实践
叮咚抢菜-派送时段监听及推送工具
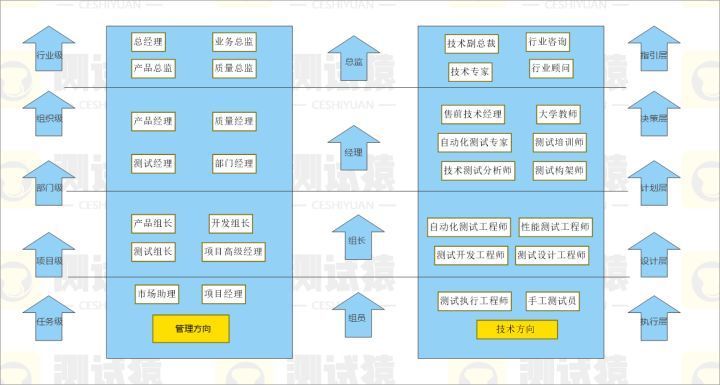
2022最强版应届生软件测试面试攻略,助你直通大厂

Computer: successfully teach you how to use one trick to retrieve the previous password (the password once saved but currently displayed as ******)
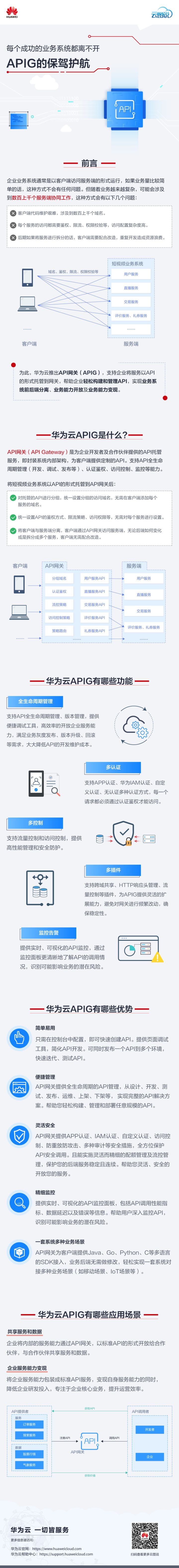
云图说|每个成功的业务系统都离不开APIG的保驾护航
随机推荐
[web] personal homepage web homework "timetable", "photo album" and "message board"
2022.05.27 (lc_647_palindrome substring)
Logback exclude specified package / class / method log output
Only three steps are needed to learn how to use low code thingjs to connect with Sen data Dix data
Morris traversal of binary tree
如何在VR全景作品中添加独立热点?
2022.05.23 (lc_300_longest increment subsequence)
In the all digital era, how can enterprise it complete transformation?
Nature Biotechnol | 李家洋/余泓团队利用平铺删除策略打破性状连锁,突破水稻产量瓶颈
DDD落地实践复盘 - 记理论培训&事件风暴
金融行业的密钥及加密机制
[advanced C language] data storage [Part 2] [ten thousand words summary]
Congratulations | Najie research group of Medical College revealed the function of junB in the process of differentiation of artificial blood progenitor cells in vitro through multi group analysis
SAR图像聚焦质量评价插件
2022.05.25 (lc_718_longest repeating subarray)
Micronet practice: image classification using micronet
The annual salary of testers in large factories ranges from 300000 to 8K a month. Roast complained that the salary was too low, but he was ridiculed by netizens?
Logback排除指定包/类/方法日志输出
腾讯Libco协程开源库 源码分析 全系列总结博客
Rmarkdown easily input mathematical formula
