当前位置:网站首页>Study note 7 -- traffic environment behavior prediction
Study note 7 -- traffic environment behavior prediction
2022-07-23 16:41:00 【FUXI_ Willard】
This blog series includes 6 A column , Respectively :《 Overview of autopilot Technology 》、《 Technical foundation of autopilot vehicle platform 》、《 Autopilot positioning technology 》、《 Self driving vehicle environment perception 》、《 Decision and control of autonomous driving vehicle 》、《 Design and application of automatic driving system 》.
This column is about 《 Decision and control of autonomous driving vehicle 》 Book notes .
2. Traffic environment behavior prediction

- The behavior decision module belongs to the decision planning layer of auto drive system ;
- When making decisions and planning for smart cars , First, get the road topology information from the environment awareness module 、 Real time traffic information 、 obstacle ( Traffic participants ) Information and the status information of the main vehicle , Then according to this information, other dynamic obstacles ( Traffic participants ) Predict the future trajectory ;
- Motion prediction is divided into : Long term forecast and short-term forecast , Involving intention identification 、 Behavior prediction and trajectory prediction ;
2.1 Traffic participant behavior prediction
- For a moving car , According to the driving scene 、 Road topology and driving direction , The driving intention and predicted trajectory can be roughly analyzed ; For other participants in the traffic environment , The uncertainty of its movement is higher ; After predicting the trajectory of all moving obstacles , It is necessary to analyze the collision relationship between driverless cars and them , Provide decision-making basis for the obstacle avoidance process of driverless vehicles ;
- Behavior prediction is generally divided into : Short term forecast and long-term forecast . The short-term forecast usually lasts for 1s within , The prediction time of long-term prediction is a few seconds or even tens of seconds ;
- Short term forecast : The intention of target behavior remains unchanged , Or the intention of the target may change, but the dynamic behavior of the target is not changed in time , here , Short range behavior can be derived from kinematics or dynamics ;
- Long term forecast : The behavior intention of the target may change and the dynamic behavior can change accordingly , here , Target behavior is greatly influenced by target intention and surrounding environmental information ;
- Atev S Collect a series of driving tracks for each intention of the target vehicle , Then match the similarity between the actual driving track and the collected tracks online to get the target intention , Then predict the subsequent driving trajectory of the car ;
- Based on multi-layer perceptron 、 Logical regression 、 Support vector machine 、 Hidden Markov identifies the target intention , And then through RRT、 The method of generating prediction path by Gauss algorithm is in the leading research position ;
2.1.1 Car behavior prediction
- The driving track of a car is the result of the joint action of two factors : First, the behavior of car drivers , Such as : The process of changing lanes that reflects intention ; Secondly, external environmental factors , Such as : Traffic information that affects the vehicle trajectory during driving ;
- Different trajectory prediction ideas : Trajectory prediction based on physical model 、 Trajectory prediction based on behavior model 、 Trajectory prediction based on Neural Network 、 Interaction based trajectory prediction 、 Trajectory prediction based on bionics and trajectory prediction combined with various ways ;
Different trajectory prediction ideas :
Trajectory prediction based on physical model
Trajectory prediction based on physical model is to express the car as a dynamic entity governed by physical laws based on physical motion model ; Use dynamic and kinematic models to predict future motion , Input some control ( Such as : to turn to 、 The acceleration ), Car properties ( Such as : weight ) And external conditions ( Such as : Friction coefficient of pavement ) And the evolution of the car state ( Such as : Location ) Connect ;
The kinetic model
The vehicle dynamics model is based on Lagrange equation , Consider the effects of different forces that affect the motion of the car , Such as : Longitudinal and transverse tyre forces or road inclination ; Cars are subject to complex physics ( Driver to engine 、 The transmission 、 The effect of the action of the wheel ) The control of , Therefore, the dynamic model may be very complex , And it involves many internal parameters of the car ;
In trajectory prediction , Always use " Bicycle " The model replaces the complex vehicle dynamics model , Simplify a four-wheel car into a two wheel car , And move on the two-dimensional plane ;
Kinematic model
The kinematic model is based on motion parameters ( Such as : Location 、 Speed 、 The acceleration ) To describe the movement of cars , Regardless of the forces that affect motion ; In the kinematic model , Friction is ignored , And assume that the speed of each wheel is the same as the direction of the wheel ;
The simplest kinematic model is constant velocity (CV) And constant acceleration (CA) Model , All assume that the car moves in a straight line ; Constant rotation and speed (CTRV) And constant rotational acceleration (CTRA) In the model, the yaw angle and yaw rate variables are introduced into the vehicle state vector to consider the detour z z z Change of axis ;
Trajectory prediction based on behavior model
- The behavior based model solves the problem that the model based on physical mechanism does not consider the behavior of cars , In this model, each traffic vehicle is regarded as a certain traffic behavior ( Such as : Turn left 、 Lane change ) Objective moving target , Based on the prior information of behavior, it can help infer the movement characteristics that conform to a certain behavior in the future , Therefore, long-term motion prediction can be realized more accurately ;
- The trajectory prediction method based on behavior model usually has two ways: directly predicting the prototype trajectory and identifying the driving intention first ;
- In a structured road environment , Vehicle trajectories can usually be classified into finite trajectory clusters according to road topology , These trajectory clusters correspond to typical automobile behavior ;
- Method based on prototype trajectory : Match the perceived trajectory of other vehicles with a priori motion model , Then the motion prediction is carried out according to the matching results and the trajectory of the prototype ; Usually through learning , Classify and learn sample tracks , So as to obtain the prototype trajectory ; The collected trajectories can be classified by spectral clustering , It can also be classified by simply solving the mean and standard deviation of samples ;
- In the process of track classification , Gaussian mixture model (Gaussian Mixture Model,GMM) Have a good performance , The basic idea is : Project trajectory in high dimensional space , And then use GMM Method , Classify the track length ; If the collected trajectory is regarded as a multi-dimensional Gaussian distribution in discrete time , First use K The average method classifies the lateral acceleration of the vehicle , Then based on GMM Classify sample trajectories , Prototype trajectory can be solved ;
- In the trajectory prediction method based on prototype , The matching method between the perceived historical trajectory of the target and the calculated motion pattern is the key to the accuracy of prediction ; In the process , It is necessary to define a measure to represent the degree of fit between a track and the prototype track , Some methods express this measure by Euclidean distance between locus points in two trajectories , Some methods calculate the similarity between two trajectory sequences through the longest common sequence ;
- The main problem of using the prototype trajectory method for trajectory prediction is : Heavy dependence on pavement topology information ; The collection of sample tracks and the training of motion patterns depend on the known road topology ; The trained model can only be applied to scenes with similar road structures , The scalability of the method is poor ; The accuracy of such methods largely depends on the choice of matching metrics , In the scene with large speed changes ( Such as : Car parking at intersections 、 Start and other phenomena ) It is often difficult to formulate accurate measurements ;
- Some trajectory prediction methods based on behavior model : First, estimate the driving intention of other cars on the road , Motion prediction based on the driving intention of these cars ; This kind of method is based on machine learning to identify the driving intention of the car , Does not depend on the prototype trajectory , Therefore, it can be used for any road structure ; When using this kind of method to estimate the driving intention , You need to define a finite set of behaviors first ( Include : Lane keep 、 Lane change 、 overtaking 、 Turn at the intersection, etc ), Then classify the future behavior of cars according to the perceived characteristics of road car movement ; These features include : Traffic vehicle state variables that can be observed by sensors ( The speed of the car 、 The acceleration 、 Location 、 Drive towards 、 Turn signal, etc ), Road structure ( Such as : crossroads 、 ramp 、 Expressway ), Traffic information ( Traffic light 、 Identification cards 、 Traffic rules, etc );
- Different machine learning methods have been applied to the classification of vehicle driving intention :
- Schlechtriemen Based on generative classifier (Generative Classifier) The lane changing behavior of other vehicles in the expressway scene is recognized ;
- Kumar Based on support vector machine (Support Vector Machines,SVM) Combined with Bayesian filtering (Bayesian Filtering) Method to realize recognition ;
- Dogan Compared with recurrent neural networks (Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)、 Feedforward neural networks (Feedforward Neural Network,FNN) And the performance of support vector machine method in predicting the lane changing behavior of other vehicles on the road ;
- Bayesian network and its special form hidden Markov model (Hidden Markov Models,HMM) It is also widely used in behavior prediction , The principle of this kind of method : Generally, the hidden variables such as vehicle behavior intention are solved based on the observable other vehicle state information and environmental information as evidence variables ;
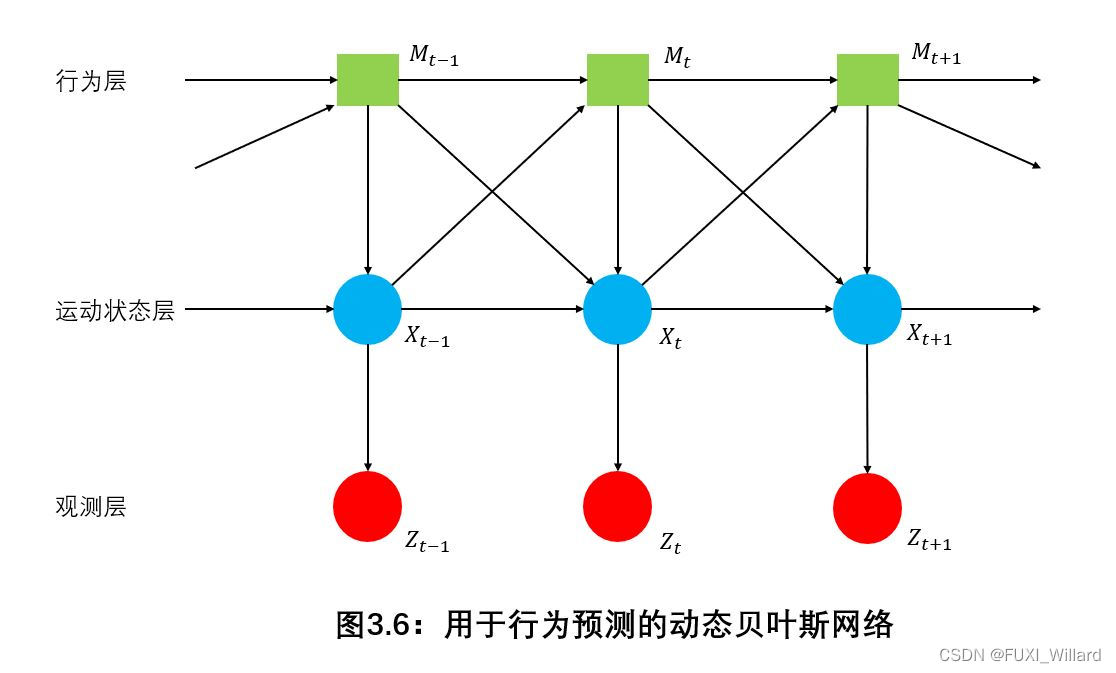
- The top layer is the behavior layer , M t M_t Mt Is a discrete implicit random variable , Represents different behaviors of cars ;
- The middle layer is the motion state layer , X t X_t Xt Represents the motion state of the car , Cannot be observed directly ;
- The lowest layer is the observation layer , vector Z t Z_t Zt Is vector X t X_t Xt Measured value with noise ;
- From the sensor Z t Z_t Zt After that, the motion state variables of other vehicles in the road can be obtained by observing the model X t X_t Xt Estimation , Then infer the possible behavior of the car from the motion state of the car M t M_t Mt;
Trajectory prediction based on Neural Network
- Compared with analyzing road structure through vehicle physical model 、 traffic rules 、 The influence of a series of factors such as driver intention on trajectory prediction , Deep neural network model learning is carried out on the vehicle motion trajectory data that covers all the above complex factors in the way of big data learning , It will be more expressive , Will get better results ;
- It is usually necessary to preprocess the collected trajectory data before trajectory prediction , Eliminate abnormal noise trace points , So as to improve the accuracy ; The preprocessing step can be based on the trajectory Gaussian mixture model clustering algorithm ;
- Based on long-term and short-term memory (Long Short Term Memory,LSTM) The neural network can learn the short-term driving behavior of surrounding vehicles and predict the trajectory , The network receives the sensor measurement data arranged for the surrounding cars in the coordinate system , After training, the occupied grid map is generated , The map contains the possible location and probability of the surrounding cars in the future , Here's the picture :

- LSTM yes RNN A form of , Each node of the network is replaced by a memory unit , The problem of gradient dispersion is solved ; adopt " door "(Gate) To control discarding or adding information , So as to realize the function of forgetting or memory ;" door " It is a structure that allows information to pass selectively , By a Sigmoid() Function and a dot multiplication operation ;Sigmoid() The output value of the function is in [0,1] Section ,0 Means to discard completely ,1 On behalf of full adoption ; One LSTM The unit has three such doors , The forgotten door (Forget Gate)、 Input gate (Input Gate)、 Output gate (Ouput Gate), As shown in the figure below :
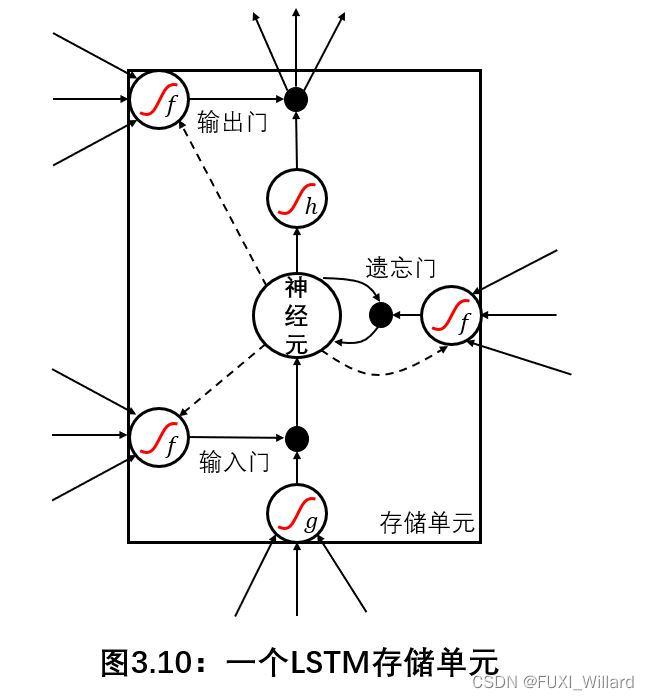
- Memory unit : Decide and accumulate what the unit wants to remember ;
- Enter the threshold : Decide whether input information is allowed to enter the module ;
- Output threshold : Decide whether the output should be sent out by the module ;
Interaction based trajectory prediction
- Interaction based trajectory prediction is used to predict the motion of other vehicles , Think of your car and other cars around you as interacting , Consider the behavioral dependencies between them ;
- When considering the interaction between traffic participants , One way is to assume that all drivers try to avoid collisions , And choose the driving behavior with the least risk ; This method first calculates the prior probability distribution of each vehicle's driving intention , Then risk assessment is carried out by modeling the interaction between cars , Then the prior distribution is modified ;
- Another method is to use dynamic Bayesian Networks . This method will be between cars (Agent(i)、Agent(j)) Consider the interaction of ,Agent(j) The state of motion x t − 1 ( j ) x_{t-1}(j) xt−1(j) Will be right Agent(i) Scene state c t ( i ) ct(i) ct(i) An impact ; When implemented mathematically, the interaction between cars is decomposed into logarithmic linear combinations of pairwise dependencies ; At the same time, when modeling the behavior of cars , Take the traffic rules into consideration , Then statistical reasoning is used to calculate the posterior probability distribution of the motion state ;
- In terms of car motion prediction , Game theory is generally applied to the modeling and prediction of automobile behavior ; Non cooperative games can be used to analyze the motion of cars , When calculating the income of the car, we should first consider the cost of the trajectory itself generated under different behaviors , Then use collision detection to calculate the final benefit ;
- One of the advantages of game theory is that it can model the lane changing behavior of vehicles with and without the function of the Internet of vehicles , These two situations can be regarded as complete information game and incomplete information game ; Game theory can also establish a traffic model that reflects the interaction between multiple drivers ;
Trajectory prediction based on bionics
Trajectory prediction combined with multiple approaches
- Trajectory prediction is realized by combining trajectory prediction based on physical model and behavioral model , Trajectory prediction based on physical model can ensure the accuracy of short-term prediction under the consideration of vehicle dynamics parameters , Trajectory prediction based on behavior model can realize long-term prediction ;
- In the trajectory prediction based on physical model, the unscented Kalman filter is fused to predict the uncertain information ; Trajectory prediction based on behavior model introduces uncertain random elements into dynamic Bayesian Network , To infer the trajectory corresponding to each behavior process ;
2.1.2 Pedestrian trajectory prediction
Pedestrian trajectory prediction : It refers to the track of pedestrians in the past period , Predict its future trajectory ; The difficulty of pedestrian behavior prediction :
- How to make the predicted pedestrian trajectory comply with physical constraints , And conform to social norms . Conform to physical constraints : It means that the predicted trajectory should meet the physical requirements , Such as : One person can't wait through another person ; Social norms : It refers to some sociological behaviors of pedestrians , Such as : Go in groups , Mutual comity, etc ;
- How to model the interaction between different pedestrians , In places with dense pedestrians , Each pedestrian needs to consider the behavior of other pedestrians when making decisions , Include : avoid 、 Catch up with 、 Follow 、 More than equal interactive behavior ;
- How to predict multiple reasonable trajectories . In the real world , Often not only one trajectory meets the conditions , There are usually multiple trajectories that are reasonable ;
Current pedestrian trajectory prediction methods :
- Based on the social force model ;
- Based on Markov model ;
- The method based on recurrent neural network ;
- Method of generating countermeasure network ;
2.2 Security evaluation algorithm
- The biggest challenge of decision algorithm : How to achieve the high safety and reliability required by automatic driving ;
- Right of way (Right Of Weight,ROW): It refers to the road user according to the law , The power to use a certain road space at a certain time ; Intelligent driving , The right of way is used to describe the road space needed to meet the current safe driving of vehicles ;
- The row of a moving smart car is a flowing sector , And the size of this car 、 Speed 、 Traffic flow around 、 The space ahead is closely related , Is a nonlinear function of the speed of the car , It can be expressed by distance and angle ;
- The right of way is divided into : Expected row and actual row , When the two are inconsistent , Adjustments are needed to resolve conflicts ;
- Mobileye Developed a set of responsibility sensitive security (Responsibility Sensitive Safety,RSS) Model system , I hope that by establishing mathematical formulas , Make the autonomous vehicle have the ability to judge its own safety state , So as to avoid accidents as much as possible ;
- RSS The model hopes to adopt a rigorous formula Algorithm , To guide the autonomous driving decision algorithm to make reasonable and safe judgments in specific scenarios ;
- In defining RSS When modeling ,Mobileye I think there are two principles that must be observed :
- Autonomous vehicle must not cause collisions or accidents for their own reasons ;
- When other cars cause potential risks and may cause traffic accidents , Autonomous vehicle should take appropriate countermeasures , To avoid possible traffic accidents ;
- In actual modeling ,RSS The model adopts four formal rules , To ensure that the car can ensure safety and avoid becoming a party to the car accident when it is self driving :
- Keep a safe distance from the car in front ;
- Leave enough reaction time and space for people or cars on the side ;
- Be more cautious in traffic jams ;
- Use the right of way reasonably ( Priority should be given to safety in the use of row );
- Automatic driving is divided into : perception 、 Decision making 、 Perform three steps ; Perception mainly depends on environmental sensors including vehicle 、 High precision map and other parts ; At the decision-making level , Rely more on a set of processes AI The trained algorithm is used to judge how the car should react under the current situation ; Finally, including the control of steering 、 brake 、 The electronic components of the car body with various actions such as acceleration realize corresponding operations ;Mobileye Of RSS The model is positioned after the decision 、 Before execution ;
- RSS After the car itself makes a judgment through the decision algorithm , Enter this command into RSS Verify the corresponding results in the model ; If the decision algorithm makes braking judgment in a certain state , Then this judgment is input into RSS In the model , Get whether the braking operation can ensure the safety of the car under the current situation ; If the result shows safety , Then this command will be executed directly ; If the result shows that there will be danger , be RSS The model returns this instruction to the decision algorithm for secondary decision , Until you get the safest result ;

边栏推荐
- PgSQL mistakenly deletes PG_ Wal file, service startup failed
- EmguCV录制视频
- 动态规划背包问题之多重背包详解
- The new business form of smart civil aviation has emerged, and Tupo digital twin has entered the civil aviation flight network of the Bureau
- 百度编辑器上传图片设置自定义目录
- pytest接口自动化测试框架 | 汇总
- FreeRTOS个人笔记-创建/删除动态任务,启动调度器
- 15001. System design scheme
- Stm32f103+rfid-rc522 module realizes simple card reading and writing demo "recommended collection"
- Fastadmin, non super administrator, has been granted batch update permission, but it still shows no permission
猜你喜欢

动态规划背包问题之完全背包详解

【Error】TypeError: expected str, bytes or os.PathLike object, not int

Oralce中实现将指定列的指定内容替换为想要的内容

【2022新生学习】第二周要点

CNCF基金会总经理Priyanka Sharma:一文读懂CNCF运作机制

Navicat15下载安装

Esp8266 nodemcu flash file system (spiffs)

UiPath Studio Enterprise 22.4 Crack

将.calss文件转为.jar-idea篇
卷积神经网络模型之——GoogLeNet网络结构与代码实现
随机推荐
CNCF基金会总经理Priyanka Sharma:一文读懂CNCF运作机制
【笔记】线性回归
聊一聊JVM的内存布局
Circuit structure and output mode of GPIO port of 32-bit single chip microcomputer
pytest接口自动化测试框架 | pytest常用运行参数
STM32F103+RFID-RC522模块 实现简单读卡写卡demo「建议收藏」
TS encapsulates the localstorage class to store information
Why is apple x charging slowly_ IPhone 12 supports 15W MagSafe wireless charging. What will happen to iPhone charging in the future_ Charger
Differences between LRU and LFU elimination strategies in redis
Complete knapsack explanation of dynamic programming knapsack problem
Frequently asked questions about MySQL
The new business form of smart civil aviation has emerged, and Tupo digital twin has entered the civil aviation flight network of the Bureau
牛客-TOP101-BM35
go run,go build,go install有什么不同
20220722 beaten record
Squid 代理服务之透明代理服务器架构搭建
SQL156 各个视频的平均完播率
C#中单例模式的实现
UiPath Studio Enterprise 22.4 Crack
【Taro】小程序picker动态获取数据