当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to alluxio
Introduction to alluxio
2022-06-26 05:17:00 【Air transport Alliance】
Alluxio brief introduction
1. Introduce
Alluxio It is the world's first open source for cloud based data analysis and artificial intelligence Data arrangement technology . It builds a bridge between data-driven applications and storage systems , Move data from the storage tier closer to data-driven applications to make it easier to access . This also enables the application to pass through a Public interface Connect to many storage systems . Alluxio The memory first hierarchical architecture makes the data access speed several orders of magnitude faster than the existing schemes .
Big data in the ecosystem ,Alluxio Located in a data-driven framework or application ( Such as Apache Spark、Presto、Tensorflow、Apache HBase、Apache Hive or Apache Flink) And various persistent storage systems ( Such as Amazon S3、Google Cloud Storage、OpenStack Swift、HDFS、GlusterFS、IBM Cleversafe、EMC ECS、Ceph、NFS 、Minio and Alibaba OSS) Between . Alluxio Unify the data stored in these different storage systems , Provide a unified client for its upper layer data-driven applications API And global namespace .
2. advantage
By simplifying the way applications access their data ( No matter what format or location the data is ),Alluxio It can help overcome the difficulties of extracting information from data .Alluxio Advantages include :
Memory speed I/O:Alluxio Can be used as a distributed share Caching services , In this way Alluxio Communication computing applications can transparently cache frequently accessed data ( Especially from remote locations ), To provide memory level I/O Throughput rate . Besides ,Alluxio The hierarchical storage mechanism can make full use of memory 、 Solid state drives or disks , Reduce the cost of data-driven applications with elastic expansion characteristics .
Simplify cloud storage and object storage access : Compared to traditional file systems , Cloud storage systems and object storage systems use different semantics , The impact of these semantics on performance is also different from traditional file systems . Common file system operations on cloud storage and object storage systems ( Such as listing directories and renaming ) It usually leads to significant performance overhead . When accessing data in cloud storage , The application does not have node level data locality or cross application caching . take Alluxio Deploying with cloud storage or object storage can alleviate these problems , Because it will from Alluxio Retrieve and read data from , Instead of retrieving and reading from underlying cloud storage or object storage .
Simplify data management :Alluxio Provides a single point of access to multiple data sources . In addition to connecting different types of data sources ,Alluxio It also allows users to connect different versions of the same storage system at the same time , Such as multiple versions of HDFS, And there is no need for complex system configuration and management .
Application deployment is easy :Alluxio Manage communication between applications and file or object storage , Convert the data access request of the application into the request of the underlying storage interface .Alluxio And Hadoop Ecosystem compatibility , Existing data analysis applications , Such as Spark and MapReduce Program , Without changing any code, you can Alluxio Up operation .
Technological innovation
Alluxio Combine innovation in three key areas , Provides a unique set of functions .
Global namespace :Alluxio Ability to provide a single point of access to multiple independent storage systems , Regardless of the physical location of these storage systems . this It provides a unified view of all data sources and standard interfaces for applications . For more information , see also Unified namespace document .
Intelligent multi-level cache :Alluxio The cluster can act as a read-write cache of data in the underlying storage system . can Configure auto optimized data placement policies , To achieve cross memory and disk (SSD/HDD) Performance and reliability . Caching is transparent to users , Use buffering to maintain consistency with persistent storage . For more information , see also Cache function document .
Server side API Translation conversion :Alluxio Support for industrial scenarios API Interface , for example HDFS API, S3 API, FUSE API, REST API. It can transparently switch from standard client interface to any storage interface .Alluxio Responsible for managing communication between applications and file or object stores , This eliminates the need to configure and manage complex systems . File data can look like object data , vice versa .
Alluxio The classic single master many worker framework . When deploying in cluster independent mode , In order to solve master A single point of question ,Alluxio Use more master Realization , adopt Zookeeper To ensure global uniqueness . similar Hadoop Of HA function . How it works is shown in the figure below

Master: Mainly responsible for processing and storing system metadata , Metadata is managed through a tree structure , Each leaf node of the tree structure represents a file or an empty directory . foreign ( Client or other programs ) Provide access and modification of metadata information . internal ( be-all Worker) Be responsible for collecting statistics of each Worker The data block information sent by the periodic heartbeat is related to each Worker Operating state .Master Will not actively communicate with other components , Only communicate with other components in the form of request response .
Worker: Responsible for managing local resources , Such as local memory 、SSD、 Disks, etc . Provide Client Read / write data request service , The data sent by the client or other programs will be displayed in block The way to manage ( Multiple of a file block Will be distributed and stored in multiple Worker Node ). Every Worker Cache data using Ramfs, It is Linux The next one is based on RAM File system for storage , The upper layer can operate it like an ordinary hard disk . It also provides the same speed as accessing memory .
Client: Programs that use data , It can be Spark executor It can also be MapReduce Of task Or other procedures . Alluxio allow Client Through and with Master Communication to perform metadata operations , And Worker Communication to read and write data . At the same time, the client can bypass Alluxio Access to the underlying storage system .
Zookeeper: Achieve fault tolerance and Leader The election , To ensure the provision of external services leader(master) Uniqueness .
Under File System: Real storage systems , It can be S3、 HDFS、 GlusterFS And so on .
http://blog.iwantfind.com/archives/76
Alluxio: Architecture and data flow - Simple books (jianshu.com)
Alluxio Cache policy _ Dongfang xiaoshuo -CSDN Blog
3. Memory 、 External storage
Alluxio Hierarchical storage of makes full use of each Tachyon Worker Local storage resources on , take Alluxio The data blocks in are stored in different storage layers according to different heat levels . at present Alluxio The local storage resources used include MEM(Memory, Memory )、SSD(Solid State Drives, Solid state disk ) and HDD(Hard Disk Drives, disk ). stay Tachyon Worker in , Each type of storage resource is treated as a layer (Storage Tier), Each layer can consist of multiple directories (Storage Directory) form , And users can set the capacity of each storage directory .
Tiered storage category :
- 1、MEM ( Memory )
- 2、SSD ( Solid state disk )
- 3、HDD ( Hard drive )
Computer memory can be divided into Main memory and Secondary storage , Main memory is also called internal memory ( Main memory or memory for short ), Auxiliary memory is also called external memory ( Referred to as external storage ).
External storage Usually magnetic media or optical disks , Like a hard disk , floppy disk , Magnetic tape ,CD etc. , It can keep information for a long time , And do not rely on electricity to store information , But driven by mechanical parts , Speed vs CPU It is much slower than that .
PC The common external memory of the computer is Floppy disk memory 、 Hard disk memory 、 CD-ROM .
The types of hard disks can be divided into :
- Solid state disk (SSD), Use flash memory particles to store ; The advantage is fast , Daily reading and writing is dozens of times faster than mechanical hard disk , In addition, it also has low power consumption 、 Good shock resistance and fall resistance 、 Advantages of low fever . The disadvantage is the high unit cost , Not suitable for mass storage .
- Mechanical drive (HDD), Use magnetic discs to store ; The advantage is that the unit cost is low , Suitable for mass storage , But it's not as fast as SSD.
- Hybrid drive (HHD), It's a kind of hard disk that integrates magnetic hard disk and flash memory .
** Memory ( Main memory )** It refers to the storage unit on the motherboard , yes CPU Communicate directly with , And using it to store data , Store data and programs currently in use , Its physical essence is one or more groups of integrated circuits with data input and output and data storage functions , Memory is only used for temporary storage of programs and data , In case of power off or power failure , The program and data will be lost .
There are many types of memory .** Random access memory ( RAM)** It is used as a cache during calculation . Data can be RAM Storage in 、 Read and replace with new data . When the computer is running RAM Is available . It contains information placed at the problem the computer is dealing with at the moment . majority RAM yes “ Unstable ”, This means that information will be lost when the computer is turned off . read-only memory (ROM) It is stable. . It is used to store the instruction set that the computer needs when necessary . Stored in ROM The information in the is hardwired ”( namely , It is a physical component of electronic components ), And can't be changed by the computer ( So called “ read-only ”). Variable ROM, be called Programmable read only memory (PROM), It can be exposed to an external electrical device or optical device ( Like a laser ) To change .
Ram
Random access memory is a kind of random access memory ∕ A memory for writing data , Also known as reading ∕ Write memory .RAM There are two characteristics : First, you can read , Can also be written . The original stored contents are not damaged during reading , The original stored content is modified only when writing . Two is RAM It can only be used for temporary storage of information , Once the power is , The stored content disappears immediately , That is, it is volatile .RAM Usually by MOS Type semiconductor memory , According to the mechanism of saving data, it can be divided into dynamic (DynamicRAM) And static (StaticRAM) Two categories: .DRAM It is characterized by high integration , Mainly used for large capacity memory ;SRAM Is characterized by fast access speed , Mainly used for cache memory .
read-only memory
ROM Read only memory , seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , Its characteristic is that it can only read the original content , No new content can be written by the user . The original stored content was written by the manufacturer at one time using mask technology , And forever . It is generally used to store special fixed programs and data . Read only memory is a kind of nonvolatile memory , Once the message is written , No additional power is required to save the information , Not lost due to power failure .
The difference between memory and external memory :
- Fast memory processing 、 Small storage capacity 、 Loss of information after power failure ;
- External memory processing speed is slow 、 Large storage capacity 、 Information is permanently stored .
CPU、 cache 、 The relationship between memory and local disk :
CPU
CPU Is the abbreviation of central processing unit , It can read instructions from memory and cache , Place in instruction register , And can issue control instructions to complete the execution of an instruction . however CPU It is not possible to read programs or data directly from the hard disk .
Memory
Memory as with CPU Components for direct communication , All programs run in memory . Its function is to temporarily store CPU Operation data of , And the data exchanged with the hard disk . It's also equivalent to CPU Bridge with hard disk . As long as the computer is running ,CPU The data to be calculated will be transferred to memory for operation , When the operation is finished CPU And then pass on the results .
cache
The cache is CPU Part of , Exist in CPU in . because CPU Your access speed is very fast , And the speed of memory is very slow , In order not to let CPU Operate in memory that runs relatively slowly every time , Cache appears as a middleman . Some commonly used data or addresses , Directly stored in the cache , such , The next time you call, you don't need to look in memory . therefore ,CPU Every time I go back, I first go to my cache to find what I want ( commonly 80% Everything can be found ), When you can't find it, go to the memory to get . The initial cache production cost was high , Expensive , So in order to store more data , And don't want the cost to be too high , The concept of L2 cache appears , They don't use L1 caching SRAM( static state RAM), Instead, the performance ratio is adopted SRAM A little less , But faster than memory DRAM( dynamic RAM)
Hard disk
We all know that memory is the part where data disappears after power failure , therefore , Long term data storage relies more on hard disk, a local disk, as a storage tool .
A simple summary :
CPU The runtime will first look in its own cache , If you don't find it in memory .
The data in the hard disk will be written into memory before it can be used CPU Use .
The cache will record some commonly used data and other information , So as not to go into memory every time , Save time , Improved efficiency .
Memory + cache -> Memory space
Hard disk -> External storage space
4. common problem
If you add a new node to the cluster , To balance memory space utilization between nodes ,Alluxio Whether there will be rebalancing ( Move cached blocks to new nodes )?
no , Currently, the rebalancing of data blocks has not been realized .
Alluxio master Whether the node has fault tolerance ?
Yes . Please refer to Run in cluster mode Alluxio file .
What is the underlying storage system ?Alluxio How many underlying storage systems are supported ?
Alluxio Use the underlying storage system as its persistent storage system , The current support Amazon S3, Swift, GCS, HDFS And many other storage systems .
What if the dataset is not suitable for storage in memory ?
It depends on the system settings .Alluxio Can use local SSD and HDD For storage , Thermal data ( Frequently accessed data ) Be kept in Alluxio Medium and cold data ( Infrequently accessed data ) Stored in the underlying storage system . Can be in Cache function document Read about Alluxio Store more information about settings .
Alluxio Must be in HDFS Run it on ?
No, it isn't ,Alluxio Can run on different underlying storage systems , Such as HDFS,Amazon S3,Swift and GlusterFS etc. .
Alluxio Can it work with other frameworks ?
Yes , Alluxio You can talk to Spark, Flink, Hadoop, HBase, Hive And so on .
5. Core functions
One 、 cache
- Alluxio Storage overview
- To configure Alluxio Storage
- Single layer storage
- Multi tier storage
- Block annotation strategy
- Tiered storage management
- Alluxio Data lifecycle management in
- stay Alluxio Manage data replication in
- Check Alluxio Cache capacity and usage
Alluxio Storage overview
The purpose of this document is to introduce the user Alluxio Storage and stay Alluxio The concept behind the actions that can be performed in the storage space . Metadata related operations For example, synchronization and namespaces , see also [ Pages about Namespace Management ] (…/…/en/core-services/Unified-Namespace.html)
Alluxio While helping to unify user data across various platforms, it also helps to improve the overall performance of users I / O throughput . Alluxio This is achieved by dividing storage into two different categories .
- UFS( The underlying file store , Also known as underlying storage ) - This storage space represents a storage space that is not affected by Alluxio Managed space . UFS The storage may come from an external file system , Include HDFS or S3. Alluxio May be connected to one or more UFS And uniformly present such underlying storage in a namespace . - Usually ,UFS Storage is designed for quite a long time Persistent storage Large amount of data .
- Alluxio Storage
- Alluxio As a distributed cache to manage Alluxio workers The local store , Including memory . This fast data layer between user applications and various underlying storage brings about significant improvement I / O performance .
- Alluxio Storage is mainly used for Storing thermal data , Transient data , Instead of long-term persistent data storage .
- Every Alluxio The amount and type of storage to be managed by the node is determined by the user configuration .
- Even if the data is not currently Alluxio In storage , adopt Alluxio Connected UFS The files in are still Yes Alluxio Customers can see . When a client attempts to read from only UFS The data will be copied to Alluxio In storage .

Alluxio Storage improves performance by storing data in the memory of the compute node . Alluxio Data in storage can be copied to form “ heat ” data , Easier I/O Parallel operation and use .
Alluxio Copies of data in are independent of UFS May already exist in . Alluxio The number of data copies in the storage is dynamically determined by the cluster activity . because Alluxio Rely on the underlying file store to store most of the data , Alluxio No need to save unused copies of data .
Alluxio It also supports tiered storage that is perceived by the system storage software , Make similar to L1/L2 CPU Cache like data storage optimization becomes possible .
To configure Alluxio Storage
Single layer storage
To configure Alluxio The easiest way to store is to use the default single tier mode .
Please note that , This part is about The local store , Such as
mountTerms like mount on a local storage file system , Don't go with Alluxio External underlying storagemountConceptual confusion .Make a distinction between Alluxio Own storage And Multiple storage mounted at the bottom
1) Single storage media
When it starts ,Alluxio Will be in each worker Issue one on the node ramdisk And occupy Use a certain proportion of the total memory of the system . this ramdisk Assign as to each Alluxio worker Of Unique storage media .
RamDisk In fact, it is to set aside a part of the memory for use as a partition , let me put it another way , Is to use a part of the memory as a hard disk , You can save files inside .
RamDisk Not a real file system , It's a mechanism to load the actual file system into memory , And as the root file system . In fact, the file system it uses is ext2.
So why use RamDisk Well ?a) Suppose there are several files to be used frequently , If you add them to memory , The speed of the program will be improved , Because the read and write speed of memory is much higher than that of hard disk . Besides, memory is cheap , a PC Yes 4G or 8G It's nothing new . Setting aside part of the memory improves the overall performance as much as replacing it with a new one CPU.b) ramdisk It's a memory based file system , It has the feature of not saving after power failure , Suppose you do something to the file system that causes the system to crash , It can be recovered as long as it is powered on again .
adopt Alluxio The configuration of the alluxio-site.properties To configure the Alluxio Storage . For details, see configuration settings.
A common change to the default value is to explicitly set ramdisk Size . for example , Set each worker Of ramdisk The size is 16GB:
alluxio.worker.ramdisk.size=16GB
2) Multiple storage media
Another common change is Specify multiple storage media , for example ramdisk and SSD. need to update alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.path To specify each storage medium you want to use For a corresponding storage directory . for example , To use ramdisk( Mounted on /mnt/ramdisk On ) And two SSD( Mounted on /mnt/ssd1 and /mnt/ssd2):
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.path=/mnt/ramdisk,/mnt/ssd1,/mnt/ssd2
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.mediumtype=MEM,SSD,SSD
Please note that , The order of media types must match the order of paths .MEM and SSD yes Alluxio Two preconfigured storage types in . alluxio.master.tieredstore.global.mediumtype Is a configuration parameter that contains all available media types , The default setting is MEM,SSD,HDD. If you have additional storage media types, you can modify this configuration to add .
The path provided should point to the path in the local file system where the appropriate storage media is mounted . In order to realize short circuit operation , For these paths , Client users should be allowed to read on these paths , Write and execute . for example , For and startup Alluxio The user group of the service should be given 770 jurisdiction .
After updating the storage media , It is necessary to indicate how much storage space is allocated for each storage directory . for example , If you want to in ramdisk Upper use 16 GB, At every SSD Upper use 100 GB:
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.quota=16GB,100GB,100GB
Be careful The order of storage space configuration must be consistent with that of storage directory .
Alluxio Through Mount or SudoMount When the option starts , Configure and mount ramdisk.( Appoint Alluxio Storage media for storage , Mount memory ) This ramdisk The size is determined by alluxio.worker.ramdisk.size affirmatory . By default ,tier 0 Set to MEM And manage the whole ramdisk. here alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.quota The value of is the same as alluxio.worker.ramdisk.size equally . If tier0 To use except the default ramdisk Other than that , You should explicitly set alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.quota Options .
Multi tier storage
It is generally recommended that heterogeneous storage media also use a single storage tier . In a particular environment , The workload will benefit from being based on I/O Speed storage media is clearly sorted . Alluxio Assume According to the press I/O Sort multi tier storage from high to low performance . for example , Users often specify the following layers :
- MEM( Memory )
- SSD( Solid state storage )
- HDD( Hard disk storage )
Writing data
When a user writes a new data block , By default, it is written to the top-level storage . If there is not enough free space on the top floor , Will try the next layer of storage . If no storage space is found on all tiers , because Alluxio The design of Volatile storage ,Alluxio Will free up space to store newly written data block . according to Block annotation strategy , The space release operation will start from work Release data block in . Block annotation policy . If the space release operation cannot release new space , Writing data will fail .
** Be careful :** The new free space model is a synchronous mode and will perform the free space operation on behalf of the client that requests to free new blank storage space for the data block to be written . With the help of the block annotation strategy , Synchronous mode frees up space without causing performance degradation , Because there is always a sorted block list available . However , Can be alluxio.worker.tieredstore.free.ahead.bytes( The default value is :0) It is configured to release more bytes than the number of bytes required by the free space request each time to ensure that there is excess free space to meet the write data requirements .
Users can also use the configuration settings To specify the write data layer .
Reading data
If the data already exists in Alluxio in , Then the client will simply read data from the stored data block . If you will Alluxio The configuration is multi-layer , It is not necessary to read the data block from the top , Because the data may have been transparently moved to a lower tier of storage .
use ReadType.CACHE_PROMOTE The read data will be from worker Try to move the data block to before reading the data Top level storage . It can also be used as a data management strategy Explicitly move hot data to higher-level storage for reading .
Configure tiered storage
You can use the following methods in Alluxio Enable tiered storage in Configuration parameters . by Alluxio Specify additional storage tiers , Use the following configuration parameters :
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.levels
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level{x}.alias
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level{x}.dirs.quota
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level{x}.dirs.path
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level{x}.dirs.mediumtype
for example , If the plan will Alluxio Configured with two tiers of storage , Memory and hard disk storage , You can use a configuration similar to the following :
# configure 2 tiers in Alluxio
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.levels=2
# the first (top) tier to be a memory tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.alias=MEM
# defined `/mnt/ramdisk` to be the file path to the first tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.path=/mnt/ramdisk
# defined MEM to be the medium type of the ramdisk directory
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.mediumtype=MEM
# set the quota for the ramdisk to be `100GB`
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level0.dirs.quota=100GB
# configure the second tier to be a hard disk tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level1.alias=HDD
# configured 3 separate file paths for the second tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level1.dirs.path=/mnt/hdd1,/mnt/hdd2,/mnt/hdd3
# defined HDD to be the medium type of the second tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level1.dirs.mediumtype=HDD,HDD,HDD
# define the quota for each of the 3 file paths of the second tier
alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level1.dirs.quota=2TB,5TB,500GB
There is no limit to the number of configurable layers However, each layer must be identified by a unique alias . A typical configuration will have three layers , Memory ,SSD and HDD. To be in HDD Multiple hard disk storage in the tier , Need to be configured alluxio.worker.tieredstore.level{x}.dirs.path Specify multiple paths when .
Block annotation strategy
Alluxio from v2.3 Start using the block annotation policy to maintain the strict order of data blocks in storage . The annotation policy defines the order of cross layer blocks , And in the following operation process for reference : - Release space - Dynamic block placement .
A free space operation that occurs synchronously with a write operation will attempt to force the sequential deletion of blocks according to the block annotation policy and free their space for the write operation . The last block of the annotation sequence is the first free space candidate , No matter which layer it is on .
Out of the box annotation strategy implementation includes :
- LRUAnnotator: Annotate and release blocks in the least recently used order . This is a Alluxio Default annotation policy for .
- LRFUAnnotator: The blocks are annotated according to the least recently used and least frequently used order of the configuration weights .
- If the weight is completely biased to the least recently used , Then the behavior will And LRUAnnotator identical .
- The applicable configuration attributes are
alluxio.worker.block.annotator.lrfu.step.factoralluxio.worker.block.annotator.lrfu.attenuation.factor.
workers The annotation strategy selected for use is determined by Alluxio attribute alluxio.worker.block.annotator.class decision . This attribute should specify the policy name for full authentication in the configuration . Currently available options are :
alluxio.worker.block.annotator.LRUAnnotatoralluxio.worker.block.annotator.LRFUAnnotator
Free space simulation
The old free space strategy and Alluxio The implementation provided has now been removed , And replace with the appropriate annotation strategy . Configure old Alluxio The free space policy will result in worker Boot failure , And report an error java.lang.ClassNotFoundException. Again , The old watermark based configuration has expired . therefore , The following configuration options are invalid :
-alluxio.worker.tieredstore.levelX.watermark.low.ratio -alluxio.worker.tieredstore.levelX.watermark.high.ratio
However ,Alluxio Support the simulation mode of implementing algorithm data block annotation based on user-defined free space . This simulation mode assumes that the configured free space policy creates a plan to free space based on a certain order , And support block annotation activities by periodically extracting this custom order .
The old free space configuration should be changed as follows . ( Because the old free space implementation has been deleted , Failure to change the following configuration based on the old implementation will result in class Load error .)
-LRUEvictor-> LRUAnnotator -GreedyEvictor-> LRUAnnotator -PartialLRUEvictor-> LRUAnnotator -LRFUEvictor-> LRFUAnnotator
Tiered storage management
Because block allocation / Release no longer forces new writes to be written to a specific storage tier , New data blocks may eventually be written to any configured storage tier . This allows writing more than Alluxio Storage capacity data . however , This requires Alluxio Dynamically manage block placement . To ensure that the layer is configured from fastest to slowest ,Alluxio Data blocks are moved between tiers of storage based on a block annotation policy .
Each individual tier management task follows the following configuration :
alluxio.worker.management.task.thread.count: Number of threads used to manage tasks . ( The default value is :CPU Check the number )alluxio.worker.management.block.transfer.concurrency.limit: How many block transfers can be performed simultaneously . ( Default :CPU Check the number/2)
Block alignment ( Dynamic block placement )
Alluxio Data blocks will be moved dynamically across tiers , To make the block composition consistent with the configured block annotation policy .
Align auxiliary blocks ,Alluxio Will monitor I/O Patterns and reorganize data blocks across tiers , In order to ensure that The lowest block of the higher layer has a higher order than the highest block of the lower layer .
This is through “ alignment ” This management task . This administrative task is between detected layers When the order is out of order , It can effectively align each layer with the configured annotation strategy by exchanging block positions between layers to eliminate disorder . About how to control these new background tasks for users I/O Influence , See Management tasks are postponed part .
Used to control layer alignment :
alluxio.worker.management.tier.align.enabled: Whether to enable the layer alignment task . ( Default :true)alluxio.worker.management.tier.align.range: How many blocks are aligned in a single task run . ( The default value is :100)alluxio.worker.management.tier.align.reserved.bytes: When configuring multiple layers , The amount of space reserved on all directories by default . ( Default :1GB) For internal block movement .alluxio.worker.management.tier.swap.restore.enabled: Control a special task , This task is used when the internal reserved space is exhausted unblock Layer alignment . ( Default :true) because Alluxio Supports variable block sizes , Therefore, the reserved space may be exhausted , therefore , When the block sizes do not match, block swapping between layers during block alignment will result in a reduction in directory reserve .
Block upgrade
When there is free space on the higher floor , Lower level blocks will move up , To better utilize faster disk media , Because it is assumed that the higher tier is configured with faster disk media .
Used to control dynamic layer upgrade :
alluxio.worker.management.tier.promote.enabled: Whether to enable the layer upgrade task . ( Default :true)alluxio.worker.management.tier.promote.range: The number of upgrade blocks in a single task run . ( The default value is :100)alluxio.worker.management.tier.promote.quota.percent: Each layer can be used to upgrade the maximum percentage . Once its used space exceeds this value , Upgrading to this tier will stop . (0 Never upgrade ,100 Always upgrade .)
Management tasks are postponed
Layer management tasks ( alignment / upgrade ) Users will be considered I/O And in worker/disk Push back operation under heavy load . This is to ensure that internal management tasks do not affect users I/O Performance has a negative impact .
Can be in alluxio.worker.management.backoff.strategy Property to set two available push types , Namely Any and DIRECTORY.
-ANY; When there are any users I/O when ,worker Administrative tasks will be pushed back . This mode will ensure low overhead of administrative tasks , In order to improve instant users I/O performance . however , To make progress in management tasks, we need to make progress in worker Spend more time on .
-DIRECTORY; Administrative tasks will start with persistent users I/O In the table of contents . It is easier to make progress in this mode . however , Due to the increase of management task activities , May reduce instant users I/O throughput .
Another attribute that affects these two postponement strategies is alluxio.worker.management.load.detection.cool.down.time, Control how long users I/O Count as in the goal directory/worker A load on .
Alluxio Data lifecycle management in
Users need to understand the following concepts , To make the right use of available resources :
- free: Releasing data means from Alluxio Delete data from cache , Not from the bottom UFS Delete data from . After the release operation , Data is still available to users , But yes Alluxio Attempt to access the file after releasing it The performance of the client may be degraded .
- load: Loading data means removing it from UFS Copied to the Alluxio In cache . If Alluxio Use Memory based storage , After loading, the user may see I/O Performance improvement .
- persist: Persistent data means that Alluxio Data that may or may not have been modified in storage is written back to UFS. By writing data back to UFS, Can guarantee that if Alluxio When a node fails, the data is recoverable .
- TTL(Time to Live):TTL Property to set the lifetime of files and directories , With Remove data from when it exceeds its lifetime Alluxio Delete from space . It can also be configured TTL To delete data stored in UFS The corresponding data in .
from Alluxio Release data from storage free
In order to be in Alluxio Manually release data in , have access to ./bin/alluxio File system commands Line interface .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs free ${PATH_TO_UNUSED_DATA}
This will come from Alluxio Delete the data in the given path from the storage . If the data is stored persistently to UFS , you can still access the data . For more information , Reference resources Command line interface documentation
Be careful , Users usually do not need to manually start from Alluxio Release data , because Configured Annotation strategy Will be responsible for deleting unused or old data .
Load data into Alluxio In storage load
If the data is already in UFS in , Use alluxio fs load
$ ./bin/alluxio fs load ${PATH_TO_FILE}
To load data from the local file system , Use command alluxio fs copyFromLocal. This will only load the file into Alluxio In storage , Instead of persisting data to UFS in . Set the write type to MUST_CACHE Write type will not persist data to UFS, And set to CACHE and CACHE_THROUGH Will persist . Manual loading of data... Is not recommended , because , When using a file for the first time Alluxio The data will be automatically loaded into Alluxio In cache .
stay Alluxio Persistent retention of data in persist
command alluxio fs persist Allows users to transfer data from Alluxio Cache push to UFS.
$ ./bin/alluxio fs persist ${PATH_TO_FILE}
If you load into Alluxio The data for is not from the configured UFS, Then the above command is very useful . in the majority of cases , Users don't have to worry about manually persisting retained data .
Set the lifetime (TTL)
Alluxio Support for each file and directory in the namespace ” Time to live (TTL)” Set up . this Functions can be used to effectively manage Alluxio cache , Especially in strict In an environment that guarantees data access patterns . for example , If we analyze the data extracted in the previous week , be TTL The function can be used to explicitly refresh old data , This frees up cache space for new files .
Alluxio There are... Associated with each file or directory TTL attribute . These properties will be saved as Part of the log , Therefore, the cluster can be maintained for a long time after it is restarted . active master Node responsible When Alluxio Store metadata in memory when providing services . In the internal ,master Run a background Threads , The thread periodically checks whether the file has reached its TTL Due time .
Be careful , Background threads run at configured intervals , The default setting is one hour . Reach its... Immediately after inspection TTL Term data will not be deleted immediately , Instead, the next inspection interval will not be deleted until an hour later .
Such as the Interval setting by 10 minute , stay alluxio-site.properties Add the following configuration :
alluxio.master.ttl.checker.interval=10m
Please refer to Configuration page CN To get the settings Alluxio More details of configuration .
API
There are two ways to set the path TTL Method of attribute .
- adopt Alluxio shell Command line
- Each metadata load or file creates a passive setting
TTL API as follows :
SetTTL(path,duration,action)
`path` Alluxio Path in namespace
`duration` TTL The number of milliseconds before the action takes effect , This overrides any previous settings
`action` To be executed after the lifetime has passed `action`. `FREE` Will result in file
from Alluxio Delete release from storage , Whatever its current state . `DELETE` Will lead to
File from the Alluxio Namespace and underlying storage .
Be careful :`DELETE` Is the default setting for some commands , It will cause the file to be
Permanently delete .
Command line usage
Learn how to use setTtl Command in Alluxio shell Revision in China TTL Properties see the detailed Command line documentation .
Alluxio Passive on file in TTL Set up
Alluxio The client can be configured as long as Alluxio Namespace when you add a new file TTL attribute . When the intended user is using the file temporarily , passive TTL It is useful to , But it is inflexible , Because all requests from the same client will inherit same TTL attribute .
passive TTL Configure... With the following options :
alluxio.user.file.create.ttl- stay Alluxio Set on the file in TTL The duration of the . By default , Not set TTL The duration of the .alluxio.user.file.create.ttl.action- For file settings TTL Actions after expiration stay Alluxio in . Be careful : By default , This action “DELETE”, It will cause the file to be permanently deleted .
TTL It is not used by default , Enable only if the customer has strict data access mode .
for example , want 3 Minutes later delete by runTests Created files :
$ ./bin/alluxio runTests -Dalluxio.user.file.create.ttl=3m \
-Dalluxio.user.file.create.ttl.action=DELETE
For this example , Make sure alluxio.master.ttl.checker.interval Is set to short interval , For example, one minute , In order to master Can quickly identify expired documents .
stay Alluxio Manage data replication in
Passive replication
Like many distributed file systems ,Alluxio Each file in contains one or more storage blocks distributed across the cluster . By default ,Alluxio The replication level of different blocks can be automatically adjusted according to workload and storage capacity . for example , When more customers take the type CACHE or CACHE_PROMOTE Request to read this block Alluxio More copies of this particular block may be created . When existing copies are used less ,Alluxio Some existing copies that are not commonly used may be deleted To reclaim space for frequently accessed data ( Block annotation strategy ). Different blocks in the same file may have different number of copies depending on the frequency of access .
By default , This copy or recall decision and the corresponding data transmission Access to is stored in Alluxio Users and applications of data in are completely transparent .
Active replication
In addition to dynamic replication tuning ,Alluxio Also provide API And the command line The interface allows users to clearly set the target range of file replication level . In especial , Users can go to Alluxio Configure the following two properties for the file in :
alluxio.user.file.replication.minIs the minimum number of copies of this file . The default value is 0, That is, by default ,Alluxio May start from... After the file gets cold Alluxio Manage space to completely delete the file . By setting this property to a positive integer ,Alluxio The replication level of all blocks in this file will be checked periodically . When certain blocks When the number of copies of is insufficient ,Alluxio None of these blocks will be deleted , Instead, they actively create more Replica to restore its replication level .alluxio.user.file.replication.maxIs the maximum number of copies . Once the file has this attribute Set to a positive integer ,Alluxio The replication level will be checked and the extra copy . Set this property to -1 No upper limit ( By default ), Set to 0 To prevent stay Alluxio Any data stored in this file . Be careful ,alluxio.user.file.replication.maxValue Must be no less thanalluxio.user.file.replication.min.
for example , Users can initially use at least two copies of the local file /path/to/file Copied to the Alluxio:
$ ./bin/alluxio fs -Dalluxio.user.file.replication.min=2 \
copyFromLocal /path/to/file /file
Next , Set up /file The replication level range of is 3 To 5. It should be noted that , After setting the new replication level range in the background process, this command will return to , Achieving replication goals is done asynchronously .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs setReplication --min 3 --max 5 /file
Set up alluxio.user.file.replication.max There is no upper limit .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs setReplication --max -1 /file
Repeat recursively copying directories /dir All file replication levels under ( Including its subdirectories ) Use -R:
$ ./bin/alluxio fs setReplication --min 3 --max -5 -R /dir
The target copy level of the file to be checked , function
$ ./bin/alluxio fs stat /foo
And find... In the output replicationMin and replicationMax Field .
Check Alluxio Cache capacity and usage
Alluxio shell command fsadmin report Provide a brief summary of available space And other useful information . The output example is as follows :
$ ./bin/alluxio fsadmin report
Alluxio cluster summary:
Master Address: localhost/127.0.0.1:19998
Web Port: 19999
Rpc Port: 19998
Started: 09-28-2018 12:52:09:486
Uptime: 0 day(s), 0 hour(s), 0 minute(s), and 26 second(s)
Version: 2.0.0
Safe Mode: true
Zookeeper Enabled: false
Live Workers: 1
Lost Workers: 0
Total Capacity: 10.67GB
Tier: MEM Size: 10.67GB
Used Capacity: 0B
Tier: MEM Size: 0B
Free Capacity: 10.67GB
Alluxio shell It also allows the user to check Alluxio How much space is available and in use in the cache .
get Alluxio The cache always runs in bytes :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs getUsedBytes
get Alluxio Total cache capacity in bytes
$ ./bin/alluxio fs getCapacityBytes
Alluxio master web The interface provides users with a visual overview of the cluster, including how much storage space has been used . Can be in http:/{MASTER_IP}:${alluxio.master.web.port}/ Find . of Alluxio Web More details of the interface can be found in The related documents Find .
Two 、 Unified namespace
This page summarizes how to Alluxio Manage different underlying storage systems in the file system namespace .
- Introduce
- Transparent naming mechanism
- Mount the underlying storage system
- Alluxio and UFS The relationship between namespaces
- UFS Metadata synchronization
- Used to manage UFS How to synchronize
- Example
- Transparent naming
- HDFS Metadata active synchronization
- Unified namespace
- resources
Introduce
Alluxio By using a transparent naming mechanism and mounting API To achieve effective data management across different underlying storage systems .
Unified namespace
Alluxio One of the main benefits provided is to provide a unified namespace for applications . Through the abstraction of unified namespace , Applications can access multiple independent storage systems through unified namespaces and interfaces . Communicate with each individual storage system , Applications can only connect to Alluxio And entrust Alluxio To communicate with different underlying storage .

master Configuration properties alluxio.master.mount.table.root.ufs Specified directory Mount to Alluxio Namespace root , This directory represents Alluxio Of ”primary storage”. On this basis , Users can mount API Add and remove data sources .
void mount(AlluxioURI alluxioPath, AlluxioURI ufsPath);
void mount(AlluxioURI alluxioPath, AlluxioURI ufsPath, MountOptions options);
void unmount(AlluxioURI path);
void unmount(AlluxioURI path, UnmountOptions options);
for example , You can create a new S3 The bucket is mounted to Data Directory
mount(new AlluxioURI("alluxio://host:port/Data"), new AlluxioURI("s3://bucket/directory"));
UFS Namespace
except Alluxio Out of the uniform namespace provided , Each mounted base file system stay Alluxio Namespace has its own namespace ; be called UFS Namespace . If you fail to pass Alluxio Changed UFS Files in the namespace , UFS Namespace and Alluxio Possible unsynchronized namespaces . When this happens , You need to perform UFS Metadata synchronization Action to resynchronize the two namespaces .
Transparent naming mechanism
The transparent naming mechanism ensures Alluxio Consistent with the namespace identity of the underlying storage system .

When the user Alluxio Namespace when creating objects , Sure Select whether these objects are to be in the underlying storage system Persistence . For objects that need persistence , Alluxio The path where the underlying storage system stores these objects is saved . for example , A user created a in the root directory Users Contents and Alice and Bob Two subdirectories , The underlying storage system will also store the same directory structure and naming . Similarly , When the user Alluxio When renaming or deleting a persistent object in the namespace , The same rename or delete operation will be performed on the underlying storage system .
Alluxio Be able to transparently discover that the underlying storage system is not through Alluxio Created content . for example , The underlying storage system contains a Data Folder , It includes Reports and Sales file , Not through Alluxio Created , When they are first accessed , If the user requests to open the document Pieces of ,Alluxio These objects will be loaded automatically Metadata . However, in the process Alluxio File content data will not be loaded , To load its contents into Alluxio, It can be used FileInStream To read the data , Or by Alluxio Shell Medium load command .
Mount the underlying storage system
Definition Alluxio Namespace and UFS Namespaces are associated by mounting the underlying storage system to Alluxio The mechanism of file system namespace . stay Alluxio To mount the underlying storage in the Linux Mounting a volume in a file system is similar to . mount The order will UFS Mount to Alluxio File system tree in namespace .
Root mount point
Alluxio The root mount point of the namespace is in masters On ’conf/alluxio-site.properties’ Configured in . The next line is a sample configuration , One HDFS The path is mounted to Alluxio Namespace root .
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.ufs=hdfs://HDFS_HOSTNAME:8020
Use the configuration prefix to configure the mount options for the root mount point :
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.<some alluxio property>
for example , The following configuration adds... For the root mount point AWS voucher .
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.aws.accessKeyId=<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.aws.secretKey=<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
The following configuration shows how to set additional parameters for the root mount point .
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.alluxio.security.underfs.hdfs.kerberos.client.principal=client
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.alluxio.security.underfs.hdfs.kerberos.client.keytab.file=keytab
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.alluxio.security.underfs.hdfs.impersonation.enabled=true
alluxio.master.mount.table.root.option.alluxio.underfs.version=2.7
Nested mount points
In addition to the root mount point , Other underlying file systems can also be mounted to Alluxio In the namespace . These additional mount points can be accessed through mount Commands are added to at run time Alluxio. --option Option allows the user to pass additional parameters to the mount operation , Such as voucher .
# the following command mounts an hdfs path to the Alluxio path `/mnt/hdfs`
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount /mnt/hdfs hdfs://host1:9000/data/
# the following command mounts an s3 path to the Alluxio path `/mnt/s3` with additional options specifying the credentials
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount \
--option aws.accessKeyId=<accessKeyId> --option aws.secretKey=<secretKey> \
/mnt/s3 s3://data-bucket/
Be careful , Mount points can also be nested . for example , If you will UFS Mount to alluxio:///path1, Can be in alluxio:///path1/path2 Mount another UFS.
Mount using a specific version UFS
Alluxio Supports mounting specific different versions HDFS. therefore , Users can convert different versions of HDFS Mount to the same Alluxio In the namespace . For more details , Please refer to HDFS Underlying storage .
Alluxio and UFS The relationship between namespaces
Alluxio Provides a unified namespace , Acts as a data cache layer for one or more underlying file storage systems . This section discusses Alluxio How to interact with the underlying file system to discover and pass Alluxio Render these files .
adopt Alluxio visit UFS And direct passage of documents UFS Access the same file . If UFS The root directory is s3://bucket/data, Then list alluxio:/// The following should be the same as listing s3://bucket/data identical . stay alluxio:///file Up operation cat The result should be the same as in s3://bucket/data/file Up operation cat Same result for .
Alluxio On demand from UFS Load metadata . In the example above ,Alluxio There is nothing about... At startup s3://bucket/data/file Information about . Until the user tries to list alluxio:/// Or try to use cat alluxio:///file when , To find the file . This has the advantage of preventing the installation of new UFS Unnecessary document discovery work .
By default ,* Alluxio expect All changes to the underlying file system are adopt Alluxio To carry out *. such Alluxio Just scan each UFS Catalog once , Thus in UFS Significantly improve performance when metadata operations are slow . When Appear in the Alluxio Outside right UFS In the case of changes , You need to use the metadata synchronization function to synchronize the two namespaces .
UFS Metadata synchronization
UFS The metadata synchronization function is added from version
1.7.0.
When Alluxio scanning UFS Directory and load its subdirectories Metadata when , It will create a copy of the metadata , So that in the future there is no need to start from UFS load . A cached copy of the metadata will be based on alluxio.user.file.metadata.sync.interval Configured by client properties Interval refresh . This attribute applies to client operations . for example , If the customer executes a command based on the configuration with the interval set to one minute , If the last refresh was a minute ago , The relevant metadata will be based on UFS Refresh . Set value to 0 Indicates that real-time metadata synchronization will be performed for each operation , And the default value -1 Indicates that metadata will not be resynchronized after initial loading .
Low interval value send Alluxio The client can quickly discover the right UFS External modification of , However, due to the result that UFS The number of times increased , So Reduce performance At a cost .
Metadata synchronization preserves each UFS Fingerprint records of documents , In order to Alluxio You can update the file when it changes . Fingerprint records include information such as file size and last modification time . If in UFS The file was modified in ,Alluxio The change will be detected by fingerprint , Release existing files Metadata , Then reload the metadata of the update file . If in UFS Added or deleted files in ,Alluxio The update will also refresh the metadata in its namespace accordingly .
Used to manage UFS How to synchronize
Regular metadata synchronization
If UFS Update at scheduled intervals , It can be triggered manually after the update sync command . Run the following command to set the synchronization interval to 0:
$ ./bin/alluxio fs ls -R -Dalluxio.user.file.metadata.sync.interval=0 /path/to/sync
Centralized configuration
For the use of... From frequent updates UFS Cluster job of data , It is inconvenient to specify a synchronization interval for each client . If in master The synchronization interval is set in the configuration , All requests will be processed at the default synchronization interval .
stay master Point on alluxio-site.properties Set in :
alluxio.user.file.metadata.sync.interval=1m
Be careful , need
1) Synchronize configuration to all nodes alluxio copyDir conf/
2) Restart master Node to enable New configuration .
### Others load new UFS Method of file
It is recommended to use the UFS Synchronization method to synchronize UFS Changes in . Here are some other ways to load files :
*alluxio.user.file.metadata.load.type: This client property can be set to ALWAYS,ONCE or NEVER. This property is similar to alluxio.user.file.metadata.sync.interval, But there are precautions : 1. It will only find new files , Modified or deleted files will not be reloaded . 1. It only applies to exists,list and getStatus RPC.
`ALWAYS` Configuration means that people always check UFS Is there a new file in ,`ONCE` The default value... Will be used Scan each directory only once , and `NEVER` Under configuration Alluxio Not at all Scan new files .
*alluxio fs ls -f /path:ls Of -f Option is equivalent to setting alluxio.user.file.metadata.load.type by ALWAYS. It will find new files , but Do not detect modified or deleted UFS file . To detect modified or deleted UFS The only way to file is by passing -Dalluxio.user.file.metadata.sync.interval=0 Options to ls.
Example
The following example assumes Alluxio The source code in ${ALLUXIO_HOME} Under the folder , And there is a local running Alluxio process .
Transparent naming
First, create a temporary directory in the local file system that will be mounted as the underlying storage :
$ cd /tmp
$ mkdir alluxio-demo
$ touch alluxio-demo/hello
The directory that will be created mount To Alluxio In the namespace , And confirm that the mounted directory is in Alluxio in :
$ cd ${ALLUXIO_HOME}
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount /demo file:///tmp/alluxio-demo
Mounted file:///tmp/alluxio-demo at /demo
$ ./bin/alluxio fs ls -R /
... # note that the output should show /demo but not /demo/hello
Verify that it does not pass Alluxio Created content , When first visited , Its metadata is loaded into Alluxio in :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs ls /demo/hello
... # should contain /demo/hello
Create a file in the mount Directory , And confirm that the file is also created with the same name in the underlying file system :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs touch /demo/hello2
/demo/hello2 has been created
$ ls /tmp/alluxio-demo
hello hello2
stay Alluxio Rename a file in , And verify that the file has also been renamed in the underlying file system :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mv /demo/hello2 /demo/world
Renamed /demo/hello2 to /demo/world
$ ls /tmp/alluxio-demo
hello world
stay Alluxio Delete a file in , Then confirm whether the file has been deleted in the underlying file system :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs rm /demo/world
/demo/world has been removed
$ ls /tmp/alluxio-demo
hello
Uninstall the mount Directory , And confirm that the directory is already in Alluxio Namespace deleted , But the directory is still stored in the underlying file system .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs unmount /demo
Unmounted /demo
$ ./bin/alluxio fs ls -R /
... # should not contain /demo
$ ls /tmp/alluxio-demo
hello
HDFS Metadata active synchronization
stay 2.0 Version of the , A new feature has been introduced , Used in UFS by HDFS Keep Alluxio Space and UFS Synchronization between . This function is called active synchronization , Can be monitored HDFS Events and with master The upper and background tasks are scheduled in the UFS and Alluxio Synchronize metadata between namespaces . Since the active synchronization function depends on HDFS event , So only if UFS HDFS Version higher than 2.6.1 when , This feature is only available . You may need to change in the configuration file alluxio.underfs.version Value . About supported Hdfs List of versions , Please refer to HDFS Underlying storage .
To enable active synchronization on a directory , Run the following Alluxio command .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs startSync /syncdir
You can change it alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.interval Option to control the active synchronization interval , The default value is 30 second .
To stop using active synchronization on a directory , Run the following Alluxio command .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs stopSync /syncdir
Be careful : Release
startSyncwhen , A full scan of the synchronization point is scheduled . If the Alluxio Run as superuser ,stopSyncAll incomplete scans will be interrupted . If running as another user ,stopSyncWill wait for the full scan to complete before executing .
You can use the following command to check which directories are currently actively synchronized .
$ ./bin/alluxio fs getSyncPathList
The silent period of active synchronization
Active synchronization attempts to avoid synchronizing when the target directory is frequently used . It will try to UFS Active period look for a quiet period , To start UFS and Alluxio Synchronization between spaces , To avoid UFS Overload it when busy . There are two configuration options to control this feature .
alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.max.activities yes UFS Maximum number of activities in the directory . The calculation of the number of activities is a heuristic method based on the exponential moving average of the number of events in the directory . for example , If the directory has... In the last three time intervals 100、10、1 Events . Its activities are 100/10 * 10 + 10/10 + 1 = 3alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.max.age Is synchronizing UFS and Alluxio The maximum number of intervals that will wait before the space .
The system guarantees that if the directory “ silent ” Or not synchronized for a long time ( The maximum period has been exceeded ), We will start synchronizing the directory .
for example , The following settings
alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.interval=30sec
alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.max.activities=100
alluxio.master.ufs.active.sync.max.age=5
Indicates that the system every 30 The number of events in this directory will be counted once per second , And calculate their activities . If the number of activities is less than 100, It is regarded as a silent period , And start synchronizing This directory . If the number of activities is greater than 100, And recently 5 Not synchronized in time intervals , perhaps 5 * 30 = 150 second , It will start synchronizing directories . If the number of activities is greater than 100 And at least recently 5 Synchronized once in intervals , Active synchronization will not be performed .
Unified namespace
This example will install several different types of underlying storage , To show the abstract role of the unified file system namespace . This example will use a different AWS Account and a HDSF Two aspects of service S3 bucket .
Use corresponding vouchers <accessKeyId1> and <secretKey1> The first one. S3 The bucket is mounted to Alluxio in :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mkdir /mnt
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount \
--option aws.accessKeyId=<accessKeyId1> \
--option aws.secretKey=<secretKey1> \
/mnt/s3bucket1 s3://data-bucket1/
Use corresponding vouchers ’’ and ’ ’ Put the second S3 The bucket is mounted to Alluxio:
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount \
--option aws.accessKeyId=<accessKeyId2> \
--option aws.secretKey=<secretKey2> \
/mnt/s3bucket2 s3://data-bucket2/
take HDFS The storage is mounted to Alluxio:
$ ./bin/alluxio fs mount /mnt/hdfs hdfs://<NAMENODE>:<PORT>/
All three directories are contained in Alluxio In a namespace of :
$ ./bin/alluxio fs ls -R /
... # should contain /mnt/s3bucket1, /mnt/s3bucket2, /mnt/hdfs
resources
- A blog post , Explained Unified namespace
- About [ Optimize to speed up metadata operations ] Blog post (https://www.alluxio.io/blog/how-to-speed-up-alluxio-metadata-operations-up-to-100x/)
3、 ... and 、Catalog
summary
Alluxio 2.1.0 Introduced a Alluxio New for directory services Alluxio service . Alluxio The directory is used to manage Structured data access Service for , The services provided are similar to Apache Hive Metastore
SQL Presto,SparkSQL and Hive Wait for the engine to use these A service similar to metadata storage determines what data to read and how much data to read when executing a query .Catalog Store information about different database directories in , surface , Storage format , Data location and more . Alluxio The directory service is designed to make Presto Query engine provides structured table metadata retrieval and service, which becomes simpler and more direct , for example PrestoSQL,PrestoDB and Starburst Presto.
System architecture
Alluxio The design of directory service is similar to that of common Alluxio File systems are very similar . The service itself is not responsible for keeping all data , But as one from another location ( Such as MySQL,Hive) Of Metadata caching service . These are called UDB(Under DataBase). UDB Responsible for metadata management and storage . At present ,Hive It's the only one that supports UDB. Alluxio The directory service passes Alluxio File system namespace to cache and make metadata globally available .
Query Engine Metadata service Under meta service
+--------+ +--------------------------+ +----------------+
| Presto | <---> | Alluxio Catalog Service | <---> | Hive Metastore |
+--------+ +--------------------------+ +----------------+
When user tables span multiple storage services ( namely AWS S3,HDFS,GCS) when , In order to make query and read requests , Usually users need to configure their SQL The engine is connected to each storage service one by one , Used Alluxio After directory service , Users only need to configure one Alluxio client , adopt Alluxio You can read and query any supported underlying storage system and data .
Use Alluxio A directory service
Here are Alluxio The basic configuration parameters of the directory service and the Alluxio How directory services interact . More details Can be in [ Command line interface documentation ] Find (…/…/en/operation/User-CLI.html#table-operations).
Alluxio Server configuration
By default , The directory service is enabled . Explicitly stop the directory service , Add the following configuration lines to alluxio-site.properties
alluxio.table.enabled=false
By default , The mounted databases and tables will be displayed in Alluxio/catalog Under the table of contents . It can be configured as Directory service configuration Non default root directory ,
alluxio.table.catalog.path=</desired/alluxio/path>
Additional database
In order to make Alluxio It can provide information services about structured table data , Must inform Alluxio About the location of the database . Use Table CLI To perform any and from Alluxio additional , Browse or detach database related operations .
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio tableUsage: alluxio table [generic options] [attachdb [-o|--option <key=value>] [--db <alluxio db name>] [--ignore-sync-errors] <udb type> <udb connection uri> <udb db name>] [detachdb <db name>] [ls [<db name> [<table name>]]] [sync <db name>] [transform <db name> <table name>] [transformStatus [<job ID>]]
To attach a database , Use attachdb command . at present ,hive and glue Is to support the <udb type>. For more details, see attachdb Command document . The following commands are available from Thrift://metastore_host:9083 The metadata store for will hive database default Mapping to Alluxio Middle name is alluxio_db The database of
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table attachdb --db alluxio_db hive \ thrift://metastore_host:9083 default
** Be careful :** After attaching the database , All tables are from the configured UDB Synced . If the database or table is updated out of band , And users want the query results to reflect these to update , The database must be synchronized . For more information, see Synchronize database .
Explore additional databases
Once the database is attached , adopt alluxio table ls Check the mounted database
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table lsalluxio_db
adopt alluxio tables ls <db_name> List all tables under the database . The corresponding hive All tables that exist in the database will be listed by this command
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table ls alluxio_dbtest
In the above case ,alluxio_db There is a table test. To get more information about tables in the database , function
$ alluxio table ls <db_name> <table_name>
This command will output the information of the table through the console . The output example is as follows :
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table ls alluxio_db testdb_name: "alluxio_db"table_name: "test"owner: "alluxio"schema { cols { name: "c1" type: "int" comment: "" }}layout { layoutType: "hive" layoutSpec { spec: "test" } layoutData: "\022\004test\032\004test\"\004test*\345\001\n\232\001\n2org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe\022(org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat\032:org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat\0227alluxio://localhost:19998/catalog/test/tables/test/hive\032\v\020\377\377\377\377\377\377\377\377\377\001 \0002\v\022\002c1\032\003int*\000"}parameters { key: "totalSize" value: "6"}parameters { key: "numRows" value: "3"}parameters { key: "rawDataSize" value: "3"}parameters { key: "COLUMN_STATS_ACCURATE" value: "{\"BASIC_STATS\":\"true\"}"}parameters { key: "numFiles" value: "3"}parameters { key: "transient_lastDdlTime" value: "1571191595"}
Detach database
If you need to detach the database , It can be downloaded from Alluxio Namespace with the following command
$ alluxio table detach <database name>
For the previous example , The detached database can run :
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table detachdb alluxio_db
Run the above command before running alluxio table ls The detached database will no longer be displayed .
Synchronize database
When the original underlying database and tables are updated , Users can call sync command To refresh the storage in Alluxio The corresponding information in the catalog metadata . For more details, see sync Command document .
$ alluxio table sync <database name>
For the previous example , You can run the following command to sync data
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table sync alluxio_db
Above sync The command will be based on UDB Table update , Delete , And add, etc Alluxio Corresponding catalog metadata .
adopt Presto Use Alluxio Structured data
PrestoSQL edition 332 Or later and PrestoDB edition 0.232 Or higher in its hive-hadoop2 A pair of... Is built into the connector Alluxio Directory service support . About using PrestoSQL or PrestoDB Corresponding version settings Alluxio Description of the directory service , see also PrestoSQL file documentation or PrestoDB file documentation.
If you are using PrestoSQL or PrestoDB Early versions , You can use alluxio Included in the distribution hive-alluxio The connector . Abreast of the times Alluxio The distribution includes a presto The connector jar file , By putting it in $ {PRESTO_HOME}/plugins Directory activation via Presto Connection to directory service .
stay Presto Enable Alluxio A directory service
Assume that the are already on the local computer ‘ ` ‘{ALLUXIO_HOME} and ${PRESTO_HOME}` Installed on Alluxio and Presto , To enable the Alluxio Directory services need to be in all Presto The node will Alluxio The connector file is copied to as a new plug-in Presto Installing .
about PrestoSQL install , Run the following command .
$ cp -R ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/client/presto/plugins/presto-hive-alluxio-319/ ${PRESTO_HOME}/plugin/hive-alluxio/
about PrestoDB install , Run the following command .
$ cp -R ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/client/presto/plugins/prestodb-hive-alluxio-227/ ${PRESTO_HOME}/plugin/hive-alluxio/
in addition , You also need to create a new directory to use Alluxio Connectors and Alluxio A directory service
/etc/catalog/catalog_alluxio.propertiesconnector.name=hive-alluxiohive.metastore=alluxiohive.metastore.alluxio.master.address=HOSTNAME:PORT
establish catalog_alluxio.properties file , It means a named catalog_alluxio New directory Add to Presto. Set up connector.name=hive-alluxio Will set the connector type to Presto new Alluxio Connector name , namely hive-alluxio. If you are using PrestoSQL edition 332 Or later and PrestoDB edition 0.232 Or later ,hive-hadoop2 A pair of... Is built into the connector Alluxio Catalog Service Support for , Therefore, it should be set connector.name=hive-hadoop2. hive.metastore=alluxio Express Hive The metadata store connection will use alluxio The type and Alluxio Directory services communicate . Set up hive.metastore.alluxio.master.address=HOSTNAME:PORT Defined Alluxio The host and port of the directory service , And Alluxio master The host and port are the same . Once configured on each node , Restart all presto coordinators and workers.
### stay Presto Use in Alluxio A directory service
In order to use Alluxio Presto plug-in unit , Start with the following command presto CLI( hypothesis /etc/catalog/catalog_alluxio.properties File created )
$ presto --catalog catalog_alluxio
By default ,presto Any query executed will pass Alluxio To get database and table information .
Confirm that the configuration is correct by running some of the following queries :
- List additional databases :
SHOW SCHEMAS;
- List tables in a database schema :
SHOW TABLES FROM <schema name>;
- Run a simple query , The query will read the data from the metadata store and load the data from the table :
DESCRIBE <schema name>.<table name>;SELECT count(*) FROM <schema name>.<table name>;
Four 、 Data conversion
Data conversion
Through job service and directory service ,Alluxio You can convert a table to a new table . If the table is not partitioned , The transformation is run at the table level . If the table is partitioned , The conversion will run at the partition level . The data of the original table will not be modified , The data of the new table will be in Alluxio Managed new storage locations are permanently preserved . Once the conversion is complete ,Presto Users can query new data transparently .
There are currently two supported conversion types :
1. Merge files , So that each file is at least a certain size , And no more than a certain number of documents . 2. take CSV The file is converted to Parquet file
stay Alluxio edition 2.3.0 in , The converted data will always be written as Parquet Format .
Before running the conversion , First of all attach A database . The following command will Hive Medium “ Default ” database attach To Alluxio.
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table attachdb hive thrift://localhost:9083 default
The conversion is invoked through the command line interface . The following command will list test The files under each partition of are merged to a maximum of 100 File . Can be found in command line interface documentation Find out about transform Other details of the command .
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table transform default test
After running the above command , You will see the following output
Started transformation job with job ID 1572296710137, you can monitor the status of the job with './bin/alluxio table transformStatus 1572296710137'.
Now? , Monitor the status of data transformation according to the instructions in the output
$ ${ALLUXIO_HOME}/bin/alluxio table transformStatus 1572296710137
The above command will display the status of the conversion job
database: defaulttable: testtransformation: write(hive).option(hive.file.count.max, 100).option(hive.file.size.min, 2147483648)job ID: 1572296710137job status: COMPLETED
Because the conversion completed successfully , Now you can run transparently directly on the converted table Presto Inquire about .
You can use the following Presto Query to find the location of the converted data :
presto:default> select "$path" from test;
You should see output similar to the following :
alluxio://localhost:19998/catalog/default/tables/test/_internal_/part=0/20191024-213102-905-R29w
边栏推荐
- Fedora alicloud source
- cartographer_ fast_ correlative_ scan_ matcher_ 2D branch and bound rough matching
- Pycharm package import error without warning
- 6.1 - 6.2 introduction to public key cryptography
- SSH connected to win10 and reported an error: permission denied (publickey, keyboard interactive)
- How does P2P technology reduce the bandwidth of live video by 75%?
- C# 40. byte[]与16进制string互转
- uni-app吸顶固定样式
- Official image acceleration
- -Discrete Mathematics - Analysis of final exercises
猜你喜欢

Happy New Year!

2. < tag dynamic programming and conventional problems > lt.343 integer partition

PHP 2D / multidimensional arrays are sorted in ascending and descending order according to the specified key values
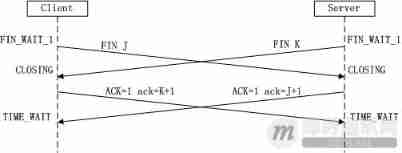
Classic theory: detailed explanation of three handshakes and four waves of TCP protocol
Technical problems to be faced in mobile terminal im development
![C# 39. string类型和byte[]类型相互转换(实测)](/img/33/046aef4e0c1d7c0c0d60c28e707546.png)
C# 39. string类型和byte[]类型相互转换(实测)
cartographer_ optimization_ problem_ 2d

瀚高数据库自定义操作符‘!~~‘

关于支付接口回调地址参数字段是“notify_url”,签名过后的特殊字符url编码以后再解码后出现错误(¬ , ¢, ¤, £)
Wechat team sharing: technical decryption behind wechat's 100 million daily real-time audio and video chats
随机推荐
Why does the mobile IM based on TCP still need to keep the heartbeat alive?
递归遍历目录结构和树状展现
Learn from small samples and run to the sea of stars
The best Chinese open source class of vision transformer, ten hours of on-site coding to play with the popular model of Vit!
【上采样方式-OpenCV插值】
How to rewrite a pseudo static URL created by zenpart
SSH connected to win10 and reported an error: permission denied (publickey, keyboard interactive)
Baidu API map is not displayed in the middle, but in the upper left corner. What's the matter? Resolved!
cartographer_ backend_ constraint
Secondary bootloader about boot28 Precautions for ASM application, 28035
skimage. morphology. medial_ axis
cartographer_ pose_ graph_ 2d
Douban top250
Chapter 9 setting up structured logging (I)
Status of processes and communication between processes
[greedy college] Figure neural network advanced training camp
2021年OWASP-TOP10
Fedora alicloud source
cartographer_fast_correlative_scan_matcher_2d分支定界粗匹配
【红队】要想加入红队,需要做好哪些准备?
