当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of C language pointer function and function pointer
Analysis of C language pointer function and function pointer
2022-07-27 10:56:00 【BSP primary school monk】
Blog home page :https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46094737?type=blog
Feel free to leave a comment Please correct any mistakes !
This article was originally written by primary school student Lian , First appeared in CSDN
The future is long , It's worth our effort to go to a better life !
Pointer function
Definition :
Pointer function , In a nutshell , It's a function that returns a pointer , Its essence is a function , The return value of this function is a pointer .
The declaration format is :* Type identifier Function name ( Parameters )
It doesn't seem hard to understand , Let's go further .
Take a look at the following function declaration :
int fun(int x,int y);
This statement should be familiar , It's a simple one int Type of fun function , namely The return value is one int Type value .
int *fun(int x,int y);
The difference between this declaration and the above is that there is an additional pointer identifier *.
And this function is a pointer function . Its The return value is one int Pointer to type , It's an address .
This description should be easy to understand , So called pointer function is nothing special , Compared with ordinary functions, it's just Returned a pointer ( That is, the address value ) nothing more .
Pointer function writing
int *fun(int x,int y);
int * fun(int x,int y);
int* fun(int x,int y);
The above three ways of writing are all ok , This way of writing depends on personal habits , In fact, if * Close to the return value type, it's probably easier to understand its definition . That is, the first way of writing is very clear , At first glance, it is a pointer function .
Example
#include <stdio.h>
int * fun();
int main()
{
int *p;
int i;
p=(*fun)();
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
printf("arr[%d]=%d ",i,*(p+i));
return 0;
}
int *fun()// Pointer function It's a function that returns a pointer , Its essence is a function , The return value of this function is a pointer
{
static arr[2]={10010,911};
int *p=arr;
return arr;
}From the above code, you can clearly see the use of pointer functions , Define a arr Array , Store it in the static area , Then use the pointer *p Point to the first address of the array , Return the first address of the array , Call this pointer function in the main function , Print the array value returned at one time .
Running results :arr[0]=10010 arr[1]=911
A function pointer
Definition :
A function pointer , Its essence is a pointer variable , This pointer points to this function . In conclusion , A function pointer is a pointer to a function .
Declaration format : Type specifier (* Function name ) ( Parameters )
as follows :
int (*fun)(int x,int y);
Function pointer is to assign the address of a function to it , There are two ways of writing :
fun = &Function;
fun = Function;
Add or not add address characters & Fine . Because a function identifier represents its address , If it's a function call , It must also contain a parameter list enclosed in parentheses .
There are also two ways to call function pointers :
x = (*fun)();
x = fun();
Either way , The second one looks no different from ordinary function calls , If you can , The first one is recommended , Because it can be clearly indicated that the function is called by pointer .
Example
#include <stdio.h>
/* Pointer function , In a nutshell , It's a function that returns a pointer , Its essence is a function , The return value of this function is a pointer */
// Define a solution int Pointer function of type number square value , Return the address with the square value
int *sqare(int a)
{
a = a *a ;
int *p = &a ;
return p;// Return pointer , Square value address
}
/* A function pointer , Its essence is a pointer variable , This pointer points to this function . In conclusion , A function pointer is a pointer to a function .*/
// Define function first
int add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
// Define a function pointer , Two functions int Type parameter , Function return value type is int
int (*fun)(int,int);
int main ()
{
/* Pointer function */
printf(" Example output of pointer function :\n");
int *m = sqare(10) ;//sqare(10) The value of is address , To assign a pointer variable
printf("10 The square of is %d\n",*m) ;// Print out 10 The square value of
printf("12 The square of is %d\n\n",*sqare(12)) ;// Print 12 The square value of
/* A function pointer */
printf(" Example output of pointer function :\n");
// Print add Address of function , It can be seen from the following print results add Add before or not & The printing results of symbols are the same
printf(" No addition & The symbol add The function address is %d, Add & Symbol add The address of the function is %d.\n",add,&add);
printf(" As can be seen from the above print results add Add before or not & The printing results of symbols are the same \n");
// A function pointer fun Point to add function
fun = add;
printf("10 add 5 be equal to %d.\n",fun(10,5));
// Function pointer to sub function
fun = ⊂
printf("10 subtract 5 be equal to %d.\n\n",sub(10,5));
// There are also two ways to call function pointers , Suggest the first , Because it can be clearly indicated that the function is called by pointer .
int p = fun (8,6);// Call mode one
int q = (*fun)(8,6);// Call mode 2
printf(" Call mode one 8 subtract 6 As the result of the %d,\n Call mode 2 8 subtract 6 As the result of the %d\n",p,q);
return 0;
}
Running results :
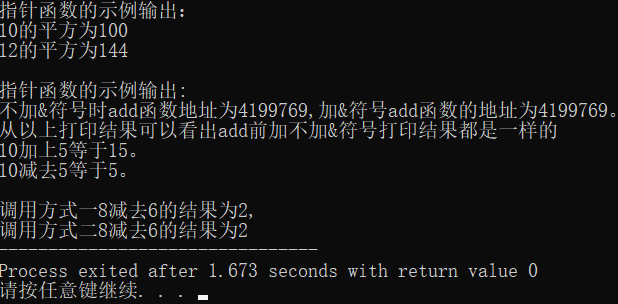
Difference between the two
Through the above introduction , We should be able to clearly understand the definition of both . So simply sum up the difference between the two :
Different definitions
A pointer function is essentially a function , Its return value is a pointer .
A function pointer is essentially a pointer , It points to a function .
The writing is different
Pointer function :int *fun(int x,int y);
A function pointer :int (*fun)(int x,int y);
It can be simply understood as , Pointer function * It's data type , The asterisk of the function pointer belongs to the function name .
More simply , You can distinguish the two in this way : The function name with parentheses is the function pointer , Otherwise, it's a pointer function .
Homework 1
#include <stdio.h>
/*
Write a program , Make a statement 3*5 And initialize , Specific values are optional , Program print out
The number , Then double the value , Then print out the new value again , To write - A function to display the contents of the array ,
Writing another function to perform the doubling function , The array name and the number of array rows are passed to the function by the program as parameters
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int fuzhi(int arr[3][5],int x,int y);
int doublt(int arr[3][5],int x,int y);
int main()
{
int arr[3][5]={0};
fuzhi(arr,3,5);
printf("\n");
doublt(arr,3,5);
return 0;
}
int fuzhi(int arr[3][5],int x,int y)
{
int i,j;
srand(time(0));
for(i=0;i<x;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<y;j++)
arr[i][j]=rand()%20+1;
}
for(i=0;i<x;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<y;j++)
printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int doublt(int arr[3][5],int x,int y)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<x;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<y;j++)
arr[i][j] *= 2;
}
for(i=0;i<x;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<y;j++)
printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}Running results :

Homework 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int fuzhi(int arr[],int n);
//fun(int *arr,int n,int *odd,int *even);
//int *sum_oushu(int arr[],int n);
//int *sum_jishu(int arr[],int n);
int fun(int *arr,int n,int *odd,int *even);
int main()
{
int i;
int sum01=0, sum02=0;
int arr[10]={0};
int *odd,*even;
fuzhi(arr,10);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
odd = &sum01;
even = &sum02;
fun(arr,10,odd,even);
printf(" The sum of even numbers is :%d\n",*odd);
printf(" The sum of odd numbers is :%d",*even);
return 0;
}
int fuzhi(int arr[],int n)
{
int i;
srand(time(0));
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
arr[i]=rand()%10+1;
}
}
//int *sum_oushu(int arr[],int n)
//{
// int i,sum=0;
// for(i=0;i<n;i++)
// {
// if(arr[i]%2==0)
// sum += arr[i];
// }
// int *even=∑
// printf("%d",*even);
// return even;
//}
//
//int *sum_jishu(int arr[],int n)
//{
// int i,sum=0;
// for(i=0;i<n;i++)
// {
// if(arr[i]%2!=0)
// sum += arr[i];
// }
// int *odd=∑
// return odd;
//}
int fun(int *arr,int n,int *odd,int *even)
{
int i;
int j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr[i]%2==0)
*odd += arr[i];
}
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(arr[j]%2!=0)
*even += arr[j];
}
}Running results :

Homework 3
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
int cheng(int x,int y)
{
return x*y;
}
int chu(int x,int y)
{
return x/y;
}
int (*fun[4])(int,int)={add,sub,cheng,chu};// A function pointer , Encapsulate function modules , By an array of function pointers (*fun[]) Unified management
int main ()
{
int x,y;
char ch;
printf(" Please enter operator :\n");
ch=getchar();
switch(ch)
{
case '+':
printf(" Please enter two integers :\n");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
printf("%d+%d=%d",x,y,fun[0](x,y));
break;
case '-':
printf(" Please enter two integers :\n");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
printf("%d-%d=%d",x,y,fun[1](x,y));
break;
case '*':
printf(" Please enter two integers :\n");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
printf("%d*%d=%d",x,y,fun[2](x,y));
break;
case '/':
printf(" Please enter two integers :\n");
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
printf("%d/%d=%d",x,y,fun[3](x,y));
break;
default:
break;
}
// fun = &add;
// printf("10 add 5 be equal to %d\n",fun(10,5));
// fun = ⊂
// printf("10 subtract 5 be equal to %d\n",fun(10,5));
// fun = &cheng;
// printf("10 multiply 5 be equal to %d\n",fun(10,5));
// fun = &chu;
// printf("10 except 5 be equal to %d",fun(10,5));
return 0;
}Running results :

边栏推荐
- TDengine 商业生态合作伙伴招募开启
- The core concept and fast practice of shardingsphere
- How to build a data index system is the most effective. It will take you a quick start from 0 to 1
- 厉害了!VMware ESXi安装记录,附下载
- The largest square of leetcode (violence solving and dynamic programming solving)
- 全校软硬件基础设施一站式监控 ,苏州大学以时序数据库替换 PostgreSQL
- tf.AUTO_ Function of reuse
- Customized modification based on jira7.9.2
- Codeforces Round #807 (Div 2.) AB
- No Identifier specified for entity的解决办法
猜你喜欢

JVM -- Analysis of bytecode

jvm--字节码浅析

Solved syntaxerror: (Unicode error) 'Unicode scape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated

深度解析:什么是Diffusion Model?

让人深思:句法真的重要吗?邱锡鹏组提出一种基于Aspect的情感分析的强大基线...
最短移动距离和形态复合体的熵

phpstudy中Apache无法启动

发动机悬置系统冲击仿真-瞬时模态动态分析与响应谱分析
[intensive reading of thesis]bert

Free DIY trip
随机推荐
MySQL 索引、事务与存储引擎
Alibaba mailbox web login turn processing
Views, triggers and stored procedures in MySQL
TDengine 商业生态合作伙伴招募开启
Want to speed up the vit model with one click? Try this open source tool!
[shutter] SharedPreferences
Application scenarios, key technologies and network architecture of communication perception integration
Time and power allocation method to ensure fairness in sensor fusion system
Beijing publicized the spot check of 8 batches of children's shoes, and qierte was listed as unqualified
phpstudy中Apache无法启动
推导重叠积分的详细展开式 STO overlap integrals
树形数据转换
全校软硬件基础设施一站式监控 ,苏州大学以时序数据库替换 PostgreSQL
如何组装一个注册中心
MySQL log management, backup and recovery
Eslint's error message module error (from./node_modules/ [email protected] @Eslint loader / index. JS)
Loop traversal of foreach and some of ES6
计算重叠积分的第二种方法
MySQL日志管理、备份与恢复
[brother hero July training] day 16: queue
![[intensive reading of thesis]bert](/img/7f/7202f79ab22ddff5f477299d2cd3d5)