当前位置:网站首页>BigDecimal basic use
BigDecimal basic use
2022-06-22 01:16:00 【llp1110】
BigDecimal Basic use
One 、BigDecimal summary
Java stay java.math Provided in the package API class BigDecimal, Used for more than 16 The number of significant bits of a bit is calculated precisely . Double precision floating point variables double Can handle 16 Bit significant number , But in practice , It may be necessary to calculate and process larger or smaller numbers .
In general , For those numbers that do not need accurate calculation accuracy , We can use it directly Float and Double Handle , however Double.valueOf(String) and Float.valueOf(String) Will lose precision . So in development , If we need accurate results , Must be used BigDecimal Class .
BigDecimal What is created is an object , So we can't use the traditional +、-、*、/ And so on arithmetic operator directly carries on the mathematics operation to its object , You have to call its corresponding method . The parameter in the method must also be BigDecimal The object of . A constructor is a special method of a class , Specifically for creating objects , Especially objects with parameters .
Two 、BigDecimal Common constructors
2.1、 Common constructors
BigDecimal(int)
Create an object with the integer value specified by the parameter
BigDecimal(double)
Create an object with the double value specified by the parameter
BigDecimal(long)
Create an object with the long integer value specified by the parameter
BigDecimal(String)
Create an object with a string value specified by the parameter
2.2、 Use problem analysis
Examples of use :
BigDecimal a =new BigDecimal(0.1);
System.out.println("a values is:"+a);
System.out.println("=====================");
BigDecimal b =new BigDecimal("0.1");
System.out.println("b values is:"+b);
Result example :
a values is:0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625
=====================
b values is:0.1
Cause analysis :
- Parameter type is double The result of the construction method of is unpredictable . Some people may think that in Java writes newBigDecimal(0.1) Created BigDecimal It's exactly the same as 0.1( Non scale value 1, Its scale is 1), But it's actually equal to 0.1000000000000000055511151231257827021181583404541015625. This is because 0.1 It can't be expressed exactly as double( Or in this case , Can't be expressed as any finite length binary decimal ). such , The value passed into the constructor will not exactly equal 0.1( Although on the surface it's equal to the value ).
- String The construction method is completely predictable : write in newBigDecimal(“0.1”) Will create a BigDecimal, It's exactly what's expected 0.1. therefore , comparison , It is usually recommended to give priority to String Construction method .
- When double Must be used as BigDecimal Source time of , Please note that , This construction method provides an accurate transformation ; It does not provide the same results as the following operations : First use Double.toString(double) Method , And then use BigDecimal(String) Construction method , take double Convert to String. To get the result , Please use static valueOf(double) Method .
3、 ... and 、BigDecimal Detailed explanation of common methods
3.1、 Common methods
add(BigDecimal)
BigDecimal Add the values in the object , return BigDecimal object
subtract(BigDecimal)
BigDecimal The values in the object are subtracted , return BigDecimal object
multiply(BigDecimal)
BigDecimal Multiply the values in the object , return BigDecimal object
divide(BigDecimal)
BigDecimal Divide the values in the object by , return BigDecimal object
toString()
take BigDecimal The value in the object is converted to a string
doubleValue()
take BigDecimal The value in the object is converted to a double
floatValue()
take BigDecimal The value in the object is converted to a single precision number
longValue()
take BigDecimal The value in the object is converted to a growing integer
intValue()
take BigDecimal The value in the object is converted to an integer
3.2、BigDecimal Size comparison
java Chinese vs BigDecimal Compare the size of the general use is bigdemical Of compareTo Method
int a = bigdemical.compareTo(bigdemical2)
Return result analysis :
a = -1, Express bigdemical Less than bigdemical2;
a = 0, Express bigdemical be equal to bigdemical2;
a = 1, Express bigdemical Greater than bigdemical2;
give an example :a Greater than or equal to b
new bigdemica(a).compareTo(new bigdemical(b)) >= 0
Four 、BigDecimal format
because NumberFormat Class format() Methods can be used BigDecimal Object as its parameter , You can use BigDecimal To exceed 16 The currency value of a significant number , Percentage value , As well as general numerical value for formatting control .
To take advantage of BigDecimal Format currency and percentage as an example . First , establish BigDecimal object , Conduct BigDecimal After the arithmetic operation of , Create references to currency and percentage formatting, respectively , The use of BigDecimal Object as format() Method parameters , Output its formatted currency value and percentage .
NumberFormat currency = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(); // Create currency formatting references
NumberFormat percent = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance(); // Create percentage formatting references
percent.setMaximumFractionDigits(3); // Percentages have the most decimal points 3 position
BigDecimal loanAmount = new BigDecimal("15000.48"); // Loan amount
BigDecimal interestRate = new BigDecimal("0.008"); // The interest rate
BigDecimal interest = loanAmount.multiply(interestRate); // Multiply
System.out.println(" Loan amount :\t" + currency.format(loanAmount));
System.out.println(" The interest rate :\t" + percent.format(interestRate));
System.out.println(" interest :\t" + currency.format(interest));
result :
Loan amount : ¥15,000.48 The interest rate : 0.8% interest : ¥120.00
BigDecimal Format hold 2 Is a decimal , Make up for the deficiency 0:
public class NumberFormat {
public static void main(String[] s){
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal("3.435")));
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal(0)));
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal("0.00")));
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal("0.001")));
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal("0.006")));
System.out.println(formatToNumber(new BigDecimal("0.206")));
}
/** * @desc 1.0~1 Between BigDecimal decimal , Lose the front... After formatting 0, Add... Directly to the front 0. * 2. The parameter passed in is equal to 0, Return the string directly "0.00" * 3. Greater than 1 Decimals of , Format the return string directly * @param obj The decimal number passed in * @return */
public static String formatToNumber(BigDecimal obj) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");
if(obj.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO)==0) {
return "0.00";
}else if(obj.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO)>0&&obj.compareTo(new BigDecimal(1))<0){
return "0"+df.format(obj).toString();
}else {
return df.format(obj).toString();
}
}
}
The result is :
3.44
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.01
0.21
5、 ... and 、BigDecimal Common abnormal
5.1、 Exception in Division
java.lang.ArithmeticException: Non-terminating decimal expansion; no exact representable decimal result
Cause analysis :
adopt BigDecimal Of divide Method to divide without dividing , When infinite recurring decimals occur , I'm going to throw an exception :java.lang.ArithmeticException: Non-terminating decimal expansion; no exact representable decimal result.
resolvent :
divide Method to set the exact decimal point , Such as :divide(xxxxx,2)
6、 ... and 、BigDecimal summary
6.1、 summary
Use when accurate decimal calculation is needed BigDecimal,BigDecimal Performance ratio of double and float Bad , Dealing with the big , It's especially obvious when it comes to complex operations . Therefore, it is unnecessary to use the general accuracy calculation BigDecimal. Try to use parameter type String Constructor for .
BigDecimal It's all immutable (immutable) Of , In every four operations , A new object is created , So when doing addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, remember to save the value after operation .
6.2、 Recommended tools
package com.vivo.ars.util;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/** * Used for high precision processing of commonly used mathematical operations */
public class ArithmeticUtils {
// Default division precision
private static final int DEF_DIV_SCALE = 10;
/** * Provide precise addition operations * * @param v1 Augend * @param v2 Addition number * @return The sum of two parameters */
public static double add(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.add(b2).doubleValue();
}
/** * Provide precise addition operations * * @param v1 Augend * @param v2 Addition number * @return The sum of two parameters */
public static BigDecimal add(String v1, String v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.add(b2);
}
/** * Provide precise addition operations * * @param v1 Augend * @param v2 Addition number * @param scale Retain scale Decimal place * @return The sum of two parameters */
public static String add(String v1, String v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.add(b2).setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Provides accurate subtraction operations * * @param v1 minuend * @param v2 Subtract * @return The difference between the two parameters */
public static double sub(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.subtract(b2).doubleValue();
}
/** * Provides accurate subtraction operations . * * @param v1 minuend * @param v2 Subtract * @return The difference between the two parameters */
public static BigDecimal sub(String v1, String v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.subtract(b2);
}
/** * Provides accurate subtraction operations * * @param v1 minuend * @param v2 Subtract * @param scale Retain scale Decimal place * @return The difference between the two parameters */
public static String sub(String v1, String v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.subtract(b2).setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Provide accurate multiplication * * @param v1 Multiplier * @param v2 The multiplier * @return The product of two parameters */
public static double mul(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.multiply(b2).doubleValue();
}
/** * Provide accurate multiplication * * @param v1 Multiplier * @param v2 The multiplier * @return The product of two parameters */
public static BigDecimal mul(String v1, String v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.multiply(b2);
}
/** * Provide accurate multiplication * * @param v1 Multiplier * @param v2 The multiplier * @param scale Retain scale Decimal place * @return The product of two parameters */
public static double mul(double v1, double v2, int scale) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return round(b1.multiply(b2).doubleValue(), scale);
}
/** * Provide accurate multiplication * * @param v1 Multiplier * @param v2 The multiplier * @param scale Retain scale Decimal place * @return The product of two parameters */
public static String mul(String v1, String v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.multiply(b2).setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Provide ( relative ) A precise division operation , When there is an inexhaustible situation , Accurate to * After the decimal point 10 position , The next figures are rounded off to * * @param v1 Divisor * @param v2 Divisor * @return The quotient of two parameters */
public static double div(double v1, double v2) {
return div(v1, v2, DEF_DIV_SCALE);
}
/** * Provide ( relative ) A precise division operation . When there is an inexhaustible situation , from scale Parameter refers to * Set the accuracy , The next figures are rounded off to * * @param v1 Divisor * @param v2 Divisor * @param scale The representation needs to be accurate to several decimal places . * @return The quotient of two parameters */
public static double div(double v1, double v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.divide(b2, scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
}
/** * Provide ( relative ) A precise division operation . When there is an inexhaustible situation , from scale Parameter refers to * Set the accuracy , The next figures are rounded off to * * @param v1 Divisor * @param v2 Divisor * @param scale It needs to be accurate to several decimal places * @return The quotient of two parameters */
public static String div(String v1, String v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v1);
return b1.divide(b2, scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Provide accurate decimal rounding * * @param v A number that needs to be rounded * @param scale How many decimal places to keep * @return The result of rounding */
public static double round(double v, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v));
return b.setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
}
/** * Provide accurate decimal rounding * * @param v A number that needs to be rounded * @param scale How many decimal places to keep * @return The result of rounding */
public static String round(String v, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal(v);
return b.setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Take the remainder * * @param v1 Divisor * @param v2 Divisor * @param scale How many decimal places to keep * @return remainder */
public static String remainder(String v1, String v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
return b1.remainder(b2).setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).toString();
}
/** * Take the remainder BigDecimal * * @param v1 Divisor * @param v2 Divisor * @param scale How many decimal places to keep * @return remainder */
public static BigDecimal remainder(BigDecimal v1, BigDecimal v2, int scale) {
if (scale < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"The scale must be a positive integer or zero");
}
return v1.remainder(v2).setScale(scale, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
}
/** * Compare the size * * @param v1 The number being compared * @param v2 Comparison number * @return If v1 Greater than v2 be return true otherwise false */
public static boolean compare(String v1, String v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(v1);
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(v2);
int bj = b1.compareTo(b2);
boolean res;
if (bj > 0)
res = true;
else
res = false;
return res;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Error 4 opening dom ASM/Self in 0x8283c00
- IDEA 提示 Duplicated code fragment (15 lines long)
- English语法_副词 - loud /aloud / loudly
- Graphical understanding of the article "text classification of Sina News Based on tensorflow+rnn"
- [dailyfresh] course record 3 -- product search related
- Install tensorflow and transformer on Orange Pie orangepi4b
- [其他] 浅析ELF中的GOT与PLT
- Conversion between three file handles
- Leetcode content
- pytorch学习01:梯度下降实现简单线性回归
猜你喜欢

Today's content
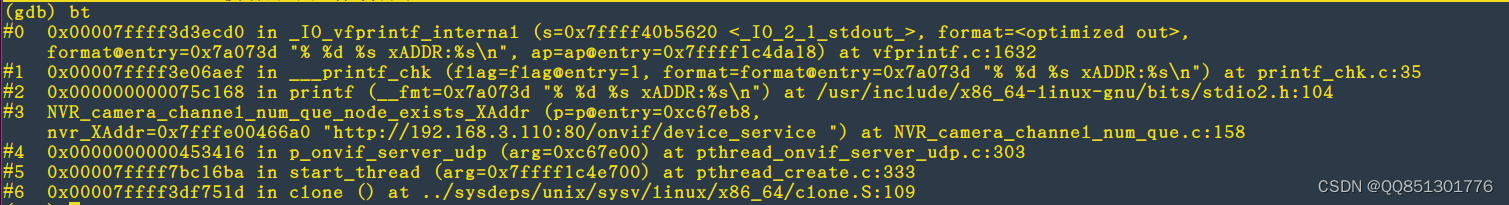
0x00007ffff3d3ecd0 in _IO_vfprintf_internal (s=0x7ffff40b5620 <_IO_2_1_stdout_>

单点登录SSO与OAuth2 方案

pytorch学习02:手写数字识别
【DailyFresh】课程记录3--商品搜索相关

Broadening - simple strategy test

pytorch学习07:Broadcast广播——自动扩展

编译原理-递归下降子程序法

企业可通过4个方法提高数据库安全

0x00007ffff3d3ecd0 in _ IO_ vfprintf_ internal (s=0x7ffff40b5620 <_IO_2_1_stdout_>
随机推荐
Pytorch learning 09: basic matrix operations
mysql整理
编译原理-递归下降子程序法
0x00007ffff3d3ecd0 in Io Vfprintf Interne (S = 0x7ffff40b5620 < io 2 1 stdout >
Pytorch learning 06: tensor dimension transformation
【环境踩坑】用opencv打开图片时报错
3分钟,带你玩转聊天机器人自动化【顶级模板】
pytorch学习06:Tensor维度变换
Small protocol with great power, why can't digital transformation without nvme full flash memory?
[environment stepping on the pit] open the picture with OpenCV and report an error
Compilation principle - recursive descent subroutine method
[environmental footprint] set up fastdfs on your own computer
3371. comfortable cow
isnull() ifnull() nullif()
[redis] install redis in Ubuntu and the basic usage and configuration of redis
Pre add post add exploration and function call exploration
SparkRDD 案例:计算总成绩
对知识图谱与深度学习的关系理解
Today's content
Error 4 opening dom ASM/Self in 0x8283c00