当前位置:网站首页>Fast power code
Fast power code
2022-06-13 05:17:00 【Python's path to becoming a God】
Basic questions : Ask for numbers
a
a
a Of
n
n
n Power .
The basic idea , It's a one-time multiplication , The time complexity is
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n).
The code is as follows :
using ll = long long;
ll pow(ll a, ll n)
{
ll ret = 1;
for (ll i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ret *= a;
}
return ret;
}
A little thought will reveal , To calculate a number
n
n
n Power does not need to be multiplied
n
n
n Time . If we knew
a
a
a Of
n
/
2
n/2
n/2 Power , You can use two
a
n
/
2
a^{n/2}
an/2 Multiply , get
a
n
a^n
an. Follow this thought , Think about it
n
n
n Split into binary form , In this way, the answer can be obtained by multiplying the powers obtained from the corresponding binary digits . give an example : When
n
n
n by 7 when , We want to
6
7
6^7
67.
7
7
7 According to binary, it can be divided into
00000111
00000111
00000111. Then we just need to know
6
1
6^1
61,
6
2
6^2
62 and
6
4
6^4
64, Then multiply them .
The code is as follows :
ll qpow(ll a, ll n)
{
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else if (n % 2 == 1) {
return qpow(a, n - 1) * a;
} else {
ll ret = qpow(a, n / 2);
return ret * ret;
}
}
ll qpow2(ll a, ll n)
{
ll ret = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1) {
ret *= a;
}
a *= a;
n >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
One is recursion , The second is the way of iteration . Consider call stack switching , Mode 2 will be faster . This method of splitting powers into binary numbers , Is called a fast power .
The complete code is as follows :
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
ll pow(ll a, ll n)
{
ll ret = 1;
for (ll i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ret *= a;
}
return ret;
}
ll qpow(ll a, ll n)
{
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else if (n % 2 == 1) {
return qpow(a, n - 1) * a;
} else {
ll ret = qpow(a, n / 2);
return ret * ret;
}
}
ll qpow2(ll a, ll n)
{
ll ret = 1;
while (n) {
if (n & 1) {
ret *= a;
}
a *= a;
n >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
ll a = 7, n = 16;
clock_t startTime, endTime;
startTime = clock(); // cpu clock time
cout << pow(a, n) << endl;
endTime = clock();
cout << (endTime - startTime) << endl;
startTime = clock(); // cpu clock time
cout << qpow(a, n) << endl;
endTime = clock();
cout << (endTime - startTime) << endl;
startTime = clock(); // cpu clock time
cout << qpow2(a, n) << endl;
endTime = clock();
cout << (endTime - startTime) << endl;
}
You can see the latter two cpu The period is generally lower than the previous one .
边栏推荐
- float类型取值范围
- Create a harbor image library from the command line
- External sort
- Jeffery0207 blog navigation
- Detailed explanation of R language sparse matrix
- QT signal is automatically associated with the slot
- Reductive elimination
- C language learning log 1.24
- MySQL table data modification
- Interpretation of QT keypressevent
猜你喜欢

Bm1z002fj-evk-001 startup evaluation

Solutions to conflicts between xampp and VMware port 443

RTSP streaming using easydarwin+ffmpeg

Qmessagebox in pyqt5
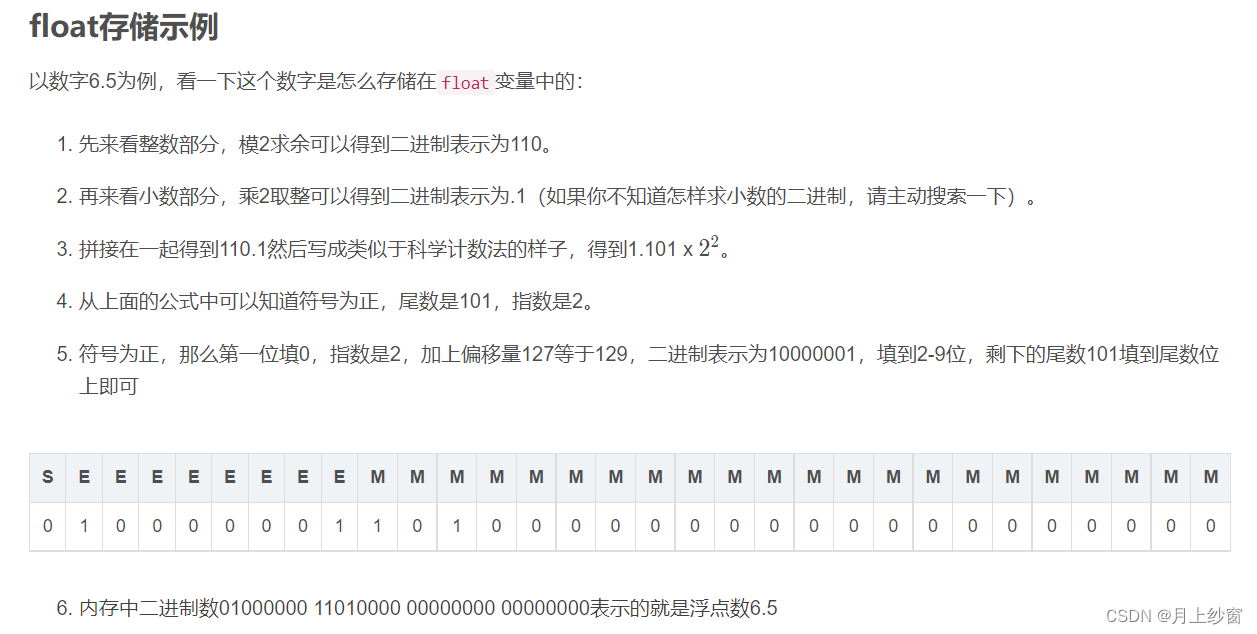
float类型取值范围

Pychart error resolution: process finished with exit code -1073741819 (0xc0000005)

Time display of the 12th Blue Bridge Cup

C language learning log 12.14

QT interface rendering style

External sort
随机推荐
Use of mongodb
Simple-SR:Best-Buddy GANs for Highly Detailed Image Super-Resolution论文浅析
Elliptic curve encryption
动态规划-最长公共子串
Sub paragraph of Chapter 16
Binary search and binary answer
关于匿名内部类
Chapter 18 pagination: Introduction
Case - simulated landlords (upgraded version)
C language learning log 1.22
mongo
Windbos run command set
Interpretation of QT keypressevent
QT using layout manager is invalid or abnormal
What is the saturate operation in opencv
About anonymous inner classes
Luogu p1036 number selection
metaRTC4.0稳定版发布
Std:: Map empty example
QT brushes and brushes