当前位置:网站首页>C程序设计-方法与实践(清华大学出版社)习题解析
C程序设计-方法与实践(清华大学出版社)习题解析
2022-07-31 21:33:00 【程序员 DELTA】
1. 前言
本习题解析只是作为一种参考,代码不唯一!
2. C语言概述
1)习题 2.3
编写程序,由键盘输入任意3个数,找出其中最小的数
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x, y, z,min;
printf("请输入第1个数:");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("请输入第2个数:");
scanf("%d", &y);
printf("请输入第3个数:");
scanf("%d", &z);
if (x < y){
if (x < z){
min = x;
}
else{
min = z;
}
}
else{
if (y > z){
min = z;
}
else {
min = y;
}
}
printf("3个数的最小值是:%d", min);
return 0;
}
总结:
本质是打擂台!
2)习题 2.4
编写程序,从键盘输入两个整数分别给变量x、y,如果x>y,则输出x及x-y的值;否则,输出y及y-x的值。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int x, y;
printf("请输入x:");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("请输入y:");
scanf("%d", &y);
if (x > y) {
printf("x的值为:%d\nx-y的值为:%d", x,x-y);
}
else
{
printf("y的值为:%d\ny-x的值为:%d", y, y-x);
}
return 0;
}
3)习题 2.5
编写程序,求1+3+5+……+99。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i=i+2)
{
sum += i;
}
printf("1+3+5+…+99的和为:%d", sum);
return 0;
}
4)习题 2.6
编写程序,统计1000以内的自然数中3的倍数之和。
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int sum = 0,j = 1;
for (int i = 3; i < 1000; i = 3 * j)
{
//printf("i为:%d\n", i);
sum += i;
j++;
}
printf("1000以内的自然数中3的倍数之和为:%d", sum);
return 0;
}
5)习题 2.7
编写程序,输出0°~360°中所有度数为5°倍数的角度的正弦值和余弦值,即输出0°、5°、10°、15°、……、360°的正弦值和余弦值。
备注:
使用正余弦函数需要添加头文件math.h
正余弦函数(参数只能接受弧度制)
- double sin(double x);
- double cos(double x);
反余弦函数(参数值为-1-1)
- double acos(double x); 返回以弧度制表示的x的反余弦
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main() {
/* int n; double pi = acos(-1);//以弧度表示的 x 的反余弦 printf("弧度:%f", pi);//3.1415…… scanf("%d", &n);//度数 printf("%f %f\n", sin(n / 180.0 * pi), cos(n / 180.0 * pi));//sin和cos内必须使用弧度制; */
int degree = 0;
double Pi = acos(-1);
for (int i = 0; degree<= 360; i++)
{
degree = 5 * i;
double y = sin(Pi / 180.0 * degree);
double x = cos(Pi / 180.0 * degree);
printf("%d度的正弦值为:%f,余弦值为:%f\n",degree,y,x);
}
return 0;
}
6)习题 2.8
编写程序,由键盘输入20个整数,统计其中的正整数、负整数、0分别有多少个?并分别计算其中的正整数、负整数之和以及各自的平均值(结果为浮点型,输出时保留2位小数)。
补充:
1.保留2位小数,使用点‘’.”+数字 例如:%.2f(保留2位小数)
2.默认右对齐
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int posNum = 0, negNum = 0 , zero = 0;
double posSum = 0, negSum = 0;
//double posAver, negAver = 0;
int num;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("请输入整数:");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num > 0)
{
posNum++;
posSum += num;
}
else if (num < 0)
{
negNum++;
negSum += num;
}
else
{
zero++;
}
}
printf("正整数有:%d个,负整数有:%d个,0有:%d个\n",posNum,negNum,zero);
printf("正整数之和为:%.2f,负整数之和为:%.2f\n", posSum, negSum);
printf("正整数的平均值为:%.2f,负整数的平均值为:%.2f", posSum / posNum, negSum / negNum);
return 0;
}
7)习题 2.9
编写程序,由键盘输入20个整数,分别找出其中的最大正整数、最小正整数、最大负整数、最小负整数
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int data[20];
int num;
int posAppear = 0, negAppear = 0;
int posMax, posMin, negMax, negMin;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d个数:", i + 1);
scanf("%d", &num);
data[i] = num;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++)
{
if (data[j] > 0) {
posAppear++;
if (posAppear == 1)
{
posMax = posMin = data[j];
}
else
{
posMax = posMax > data[j] ? posMax : data[j];
posMin = posMin < data[j] ? posMin : data[j];
}
}
else if (data[j] < 0)
{
negAppear++;
if (negAppear == 1)
{
negMax = negMin = data[j];
}
else
{
negMax = negMax > data[j] ? negMax : data[j];
negMin = negMin < data[j] ? negMin : data[j];
}
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
if (posAppear != 0 && negAppear != 0) //存在整数也存在负数
{
printf("最大正整数为:%d,最小正整数为:%d\n", posMax, posMin);
printf("最大负整数为:%d,最小负整数为:%d\n", negMax, negMin);
}
else
{
if (posAppear == 0 && negAppear == 0)
{
printf("输入全为0,不存在最大最小正负整数!");
}
else if (negAppear == 0)
{
printf("最大正整数为:%d,最小正整数为:%d\n", posMax, posMin);
printf("不存在最大、最小负整数!");
}
else
{
printf("不存在最大、最小正整数!");
printf("最大负整数为:%d,最小负整数为:%d\n", negMin, negMin);
}
}
return 0;
}
总结:
使用数组完成打擂台,数组是个好工具
数组的创建:int 数组名[长度];
数组不初始化,默认的值是不确定的
全初始化:例 int data[10] = {0},默认值都为0
3. 数据类型与输入输出
1)习题 3.3 程序阅读
(1)若x为int型变量,则执行以下语句后的输出结果是什么?
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x = 0xDEF;
printf("%4d,%4o,%4x", x, x, x);
return 0;
}
结果:
注意:
1.DEF输出后是小写的
2.%o代表8进制,%x代表16进制
3.记忆:o是October,x是sixteen,d是decimal
(2)若x、y为int型变量,则执行以下语句后的输出结果是什么?
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x, y;
x = 015,y = 0x15;
printf("%4o%4x\n",x,y);
printf("%4x%4d\n",x,y);
printf("%4d%4o\n",x,y);
return 0;
}
结果:
补充:
1.0开头代表八进制,0x开头代表16进制
2.程序默认右对齐
3.左对齐可以使用“-”,例如:%-4f
以上两题主要考察进制的转化,要熟悉了解进制的转化规则:
1.二进制转十进制,主要是乘2的几次幂再相加
2.十进制转二进制:除2取余法
3.二进制转八进制:取三合一法(反之亦然)
4.二进制转十六进制:取四合一法(反之亦然)
(3)执行以下语句后的输出结果是什么
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char c1 = 'a', c2 = 'b', c3 = 'c', c4 = '\101', c5 = '\116';
printf("abc\tde\bh\rA\tg\n");
printf("a%cb%c\tc%c\tabc\n",c1,c2,c3);
printf("\t\b%c%c", c4, c5);
return 0;
}
结果:
总结:
特别注意\t和\r
区别:
- \t是制表符(不一定是8个或者4个),就是空几个格,这里有个公式:spaceNum = |n - 8| % 8(n代表\t前的字符个数,包括%等)
- \r是回车符(注意几种情况),如果回车后的字符多于前面的原始字符,则进行替换。如果不足则将原始数据进行补充
- \t注意光标的位置,和\t一起使用时,可能会出现局部替换的情况
- 字符串结束时会添加一个\0的结束符
- \XXX代表以8进制表示的数
(4)设a、b为int型变量,x、y为float型变量,c1、c2为char型变量,且设a=5,b=10,x=3.5,y=10.8,c1=‘A’,c2=‘B’。为了得到以下的输出格式和结果,请写出对应的printf语句。
x-y=-7.3 a-b=-5
c1=A or 65(ASCII)
c2=B or 66(ASCII)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 5, b = 10;
float x = 3.5, y = 10.8;
char c1 = 'A', c2 = 'B';
printf("x-y=%.1f a-b=%d\n", x - y, a - b);
printf("c1=%c or %d(ASCII)\n", c1, c1);
printf("c2=%c or %d(ASCII)\n",c2,c2);
return 0;
}
(5)若已有说明:
int a = 123;
float b = 456.78;
double c = -123.45678;
试写出以下各printf语句相应的输出结果
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 123;
float b = 456.78;
double c = -123.45678;
printf("%.3f %.3e %f\n",b,b,c);
printf("%8.3f %8.3e %g\n", b, b, c);
printf("%u %-10.3f %-10.3e\n",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
结果:
(6)对于如下语句
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x=0; float y=0.0; char z=‘0’;
scanf(“%3d%f%3c”, &x, &y, &z);
printf(“x的值为:%d,y的值为:%f,z的值为:%c”, x,y,z);
return 0;
}
输入以下数据
12345abc
则x、y和z的值分别是什么?
结果:
2)习题 3.4 (排序算法)
写一个程序,首先向数组中输入10个得分,然后去掉一个最高分,去掉一个最低分,计算剩下的平均分,并输出。
使用冒泡排序算法
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float score[10] = {
0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d位同学的得分:", i+1);
scanf("%f", &score[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10 - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (score[j] > score[j+1])
{
float temp = score[j];
score[j] = score[j + 1];
score[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
//计算剩下的平均分
double sum = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < 9; k++)
{
sum += score[k];
}
printf("去掉一个最高分:%.0f,去掉一个最低分:%.0f\n", score[9], score[0]);
printf("平均分为:%.1f", sum/8);
return 0;
}
使用选择排序算法
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float score[10] = {
0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("请输入第%d位同学的得分:", i+1);
scanf("%f", &score[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < 10; j++)
{
if (score[i] > score[j])
{
float temp = score[i];
score[i] = score[j];
score[j] = temp;
}
}
}
//计算剩下的平均分
double sum = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < 9; k++)
{
sum += score[k];
}
printf("去掉一个最高分:%.1f,去掉一个最低分:%.1f\n", score[9], score[0]);
printf("平均分为:%.1f", sum/8);
return 0;
}
总结:
冒泡排序是相邻比,选择排序是和每一个比
3)习题 3.6
编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,输出其中ASCII码最大的字符。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char s[10] = {
'\0' };
printf("请输入一个字符串(长度小于10):");
gets_s(s, 9);
int max = s[0];
for (int i = 1; i < 9; i++)
{
max = max > s[i] ? max : s[i];
}
printf("ASCII码最大的字符是:%c", max);
return 0;
}
总结:
- 字符串的输入有3种方式:gets(不安全,已经被替代)、fgets、gets_s
- 推荐使用fgets、gets_s,可以设定输入长度(边界),安全性更高
- fget(数组名,数组长度,文件指针)
- gets_s(数组名,长度)
- fegts会在数组后添加换行符
- 循环输入使用组合键ctrl+Z结束输入
4)习题 3.7
编写一个程序,输入一个字符串,分别统计并输出其中大写字母(A~Z)和小写字母(a ~z)出现的次数。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char s[40];
int upperNum = 0, lowerNum = 0;
printf("请输入一个字符串:");
gets_s(s, 39);
for (int i = 0; s[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z')
{
lowerNum++;
}
else if (s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'Z')
{
upperNum++;
}
}
printf("大写字母出现的次数:%d,小写字母出现的次数:%d", upperNum, lowerNum);
return 0;
}
总结:
1.空格不等于‘\0’,空格是空串,\0是输入语句的结束符
2.判断输入是否完成可以使用 xxx != ‘\0’
5)习题 3.8
想一想,怎么判断一个字符串是否为空串?编写程序,输入一个字符串,如果不是空串,则照原样输出;如果是空串,则输出“空串”。例如,如果输入“hello”(不含引号),则输出“你输入的是:hello”;如果什么都没有输入,则输出“你输入的是空串!”
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char s[40];
printf("请输入一个字符串:");
gets_s(s, 39);
if (s[0] == '\0')
{
printf("你输入的是空串!");
}
else {
printf("你输入的是:%s", s);
}
return 0;
}
总结:
输出字符串可以使用%s
4. 运算符与表达式
1)习题 4.5
若x、y为int型变量,则执行以下语句后结果是什么?
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x, y;
for ( x = 1; x < 5; x+=2)
{
for (y = 1; y < 5; y++)
printf("%3d", x * y);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
2)习题 4.6
程序填空题。零存整取问题:每月同一天存入银行50元钱,单利计息,月利率为5%,求一年以后的本利和。
#include <stdio.h>
#define M 50
#define R 0.005
int main() {
int i;
float sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for ( i = 1; i <= 12;/*填空1*/ i++)
{
sum1 = sum1 + M;
sum2 = sum2 + sum1 * R/*填空2*/;
}
printf("sum1=%.2f sum2=%.2f sum1+sum2=%.2f\n", sum1, sum2, sum1 + sum2);
return 0;
}
结果:
边栏推荐
- 高效并发:Synchornized的锁优化详解
- Introduction to Audio Types and Encoding Formats in Unity
- A solution to the server encountered an internal error that prevented it from fulfilling this request [easy to understand]
- How to change npm to Taobao mirror [easy to understand]
- 给定一个ip地址,子网掩码怎么算网络号(如何获取ip地址和子网掩码)
- 【愚公系列】2022年07月 Go教学课程 025-递归函数
- Efficient Concurrency: A Detailed Explanation of Synchornized's Lock Optimization
- multithreaded lock
- 【公开课预告】:超分辨率技术在视频画质增强领域的研究与应用
- How to identify fake reptiles?
猜你喜欢

财务盈利、偿债能力指标
![[Code Hoof Set Novice Village 600 Questions] Leading to the combination of formulas and programs](/img/91/63d4f7869e0a55d19701c5ca5c9ed8.png)
[Code Hoof Set Novice Village 600 Questions] Leading to the combination of formulas and programs

Basic configuration of OSPFv3
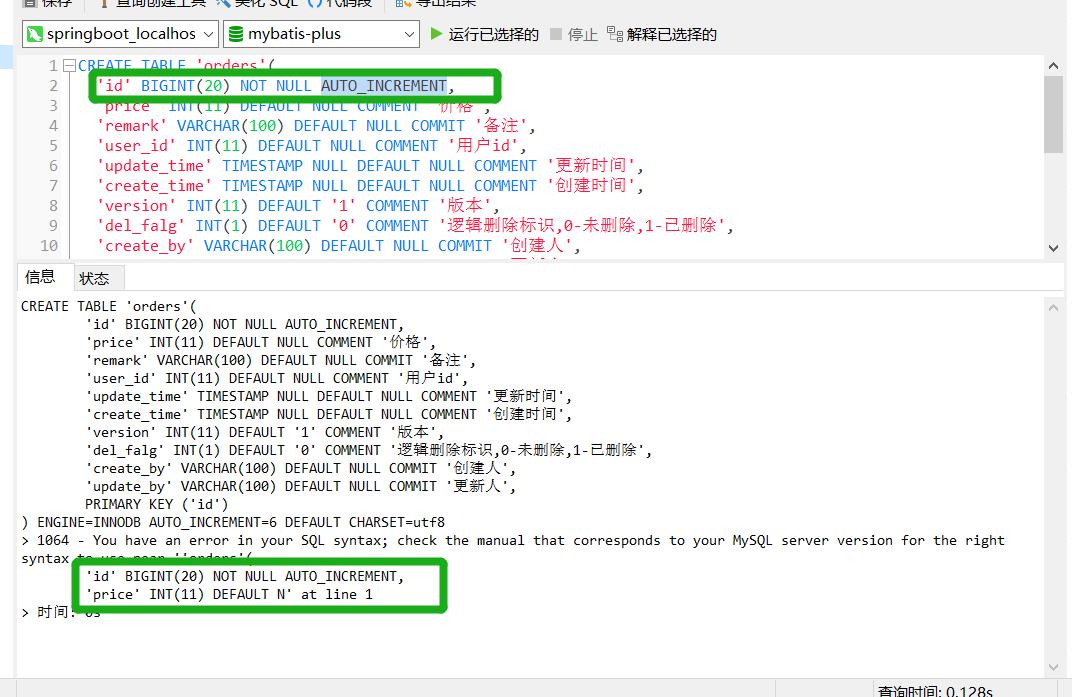
What's wrong with the sql syntax in my sql

Financial profitability and solvency indicators
![leetcode: 6135. The longest ring in the graph [inward base ring tree + longest ring board + timestamp]](/img/91/284de3dcbb8d143d85775b314dd41c.png)
leetcode: 6135. The longest ring in the graph [inward base ring tree + longest ring board + timestamp]
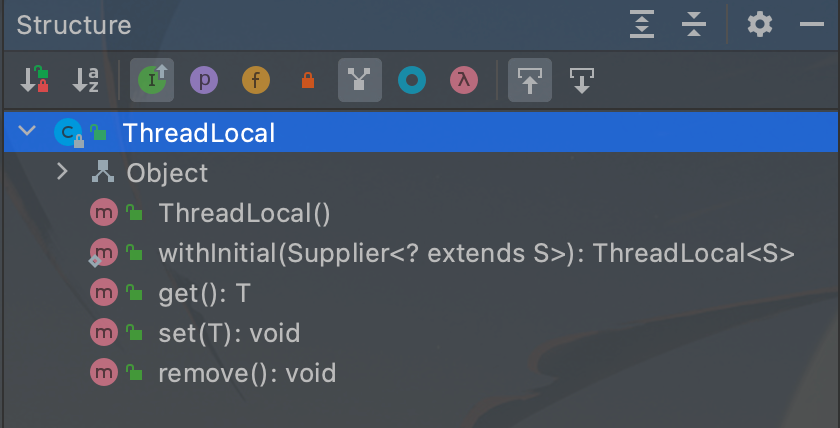
ThreadLocal

Apache EventMesh distributed event-driven multi-runtime

Count characters in UTF-8 string function
![[Intensive reading of the paper] iNeRF](/img/a7/910667911e1ce8996b9d22de63ea04.png)
[Intensive reading of the paper] iNeRF
随机推荐
PCB stackup design
[Intensive reading of the paper] iNeRF
Three. Introduction to js
1161. 最大层内元素和 : 层序遍历运用题
[NLP] What is the memory of the model!
架构实战营模块八作业
返回一个零长度的数组或者空的集合,不要返回null
BOW/DOM (top)
Short-circuit characteristics and protection of SiC MOSFETs
cas and spin locks (is lightweight locks spin locks)
uni-app中的renderjs使用
Cache and Database Consistency Solutions
Student management system on the first day: complete login PyQt5 + MySQL5.8 exit the operation logic
matplotlib ax bar color Set the color, transparency, label legend of the ax bar
One thing to say, is outsourcing company worth it?
Talking about the algorithm security of network security
Financial profitability and solvency indicators
rj45对接头千兆(百兆以太网接口定义)
广汽本田安全体验营:“危险”是最好的老师
Memblaze发布首款基于长存颗粒的企业级SSD,背后有何新价值?