当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode-- array
Leetcode-- array
2022-06-11 17:03:00 【Rain curtain】
Catalog
1. Two points search
Dichotomous Conditions : Ordered array 、 There are no repeating elements
Dichotomy a key :
① Pay attention to the interval
Left closed right closed interval :[left,right] You can get it. left == right So the loop is written as while(left<=right) right = length - 1
Left closed right open interval :[left,right) You can't get left == right So the loop is written as while(left<right) right = length
② Be careful middle Value : To prevent spillage middle = left + (right - left) / 2, because left + right It might spill over
704 Two points search
The first way to write it
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1; //target It's defined in [left,right] Within the interval
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[middle] > target )
{
right = middle -1;
}else if(nums[middle] < target){
left = middle + 1;
}else{
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
Time complexity :O(log n), among n Is the length of the array .The second way
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size(); // Definition target In the interval between left closed and right open , namely :[left, right)
while (left < right) { // because left == right When , stay [left, right) It's invalid space , So use <
int middle = left + ((right - left) / 2);
if (nums[middle] > target) {
right = middle; // target In the left range , stay [left, middle) in
} else if (nums[middle] < target) {
left = middle + 1; // target In the right range , stay [middle + 1, right) in
} else { // nums[middle] == target
return middle; // Target value found in array , Return the subscript directly
}
}
// Target value not found
return -1;
}35 Search insert location
int searchInsert(vector<int> &nums, int target){
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[middle] > target){
right = middle - 1;
}else if(nums[middle] < target){
left = middle + 1;
}else{
return middle;
}
}
return right + 1;
}34 Find the first and last positions of the elements in the sort array
target There are three situations :
1.target On the leftmost or rightmost side of the array return [-1,-1]
2.target Within the range of the array , But the array does not exist target return [-1,-1]
3.target Within the range of the array , And the array contains target Return the corresponding subscript
// Find the left border about [3,3] If the array is less than or equal to 3 Number of numbers return -1; Find more than 3 Number of numbers return -2
int getLeftBorder(vector<int> nums, int target){
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
int leftborder = -2;
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[middle] >= target){
right = middle - 1;
leftborder = right;
}else{
left = middle + 1;
}
}
return leftborder;
}
// Find the right border about [3,3] If the array is larger than 3 Number of numbers ( Include 3) return 2; Find less than 3 Number of numbers return -2
int getRightBorder(vector<int> nums, int target){
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
int rightborder = -2;
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[middle] > target){
right = middle - 1;
}else{
left = middle + 1;
rightborder = left;
}
}
return rightborder;
}
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int leftborder = getLeftBorder(nums,target);
int rightborder = getRightBorder(nums,target);
// Situation 1 target On the left and right borders As long as one is -2 It means at the boundary
if(leftborder == -2 || rightborder == -2) return {-1,-1};
// Situation three
if(rightborder - leftborder > 1) return {leftborder + 1, rightborder - 1};
// Situation two
return {-1,-1};
}69 x The square root of
Ideas : You can also use bisection to find the square root ,left = 0 right = x, Just judge mid Sum of squares x Can be found x The square root of , This question requires that the integer part be returned , The decimal part is rounded off
int mySqrt(int x) {
int left = 0,right = x;
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left)/2;
if( (long)middle * middle <= x){
left = middle + 1;
}else{
right = middle - 1;
}
}
return right;
}
// Time complexity O(log x)
// Spatial complexity O(1)367 Effective complete square number
Ideas : Similar to the above question , Use binary search , stay if The judgment is different , There are three situations :mid Square is just equal to num return true; Less than left = mid + 1; Greater than right = mid -1
bool isPerfectSquare(int num) {
int left = 0, right = num;
while(left <= right){
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if((long)middle * middle == num){
return true;
}else if((long)middle * middle < num){
left = middle + 1;
}else{
right = middle - 1;
}
}
return false;
}2. Double pointer
27 Remove elements
Remove an array equal to val The value of the elements , The empty position is filled by the next element .
This... Cannot be deleted directly val Why : The memory address of the array is continuous , Only the value of the element can be overwritten .
Ideas : Double finger needling ,left and right The pointer starts at the beginning of the array , If so right The value pointed to by the pointer is not the element to be deleted , use left The pointer records the value , then left++; If right Points to the element to be deleted ,left The pointer does nothing ,right Point to the next value , Last left The index value of is the length of the array of removed elements (left++)
//27 Remove elements
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int left = 0;
for(int right = 0; right < nums.size(); right++){
if(nums[right] != val){
nums[left] = nums[right];
left++;
// The above two lines of code are simplified to nums[left++] = nums[right];
}
}
return left;
}
Time O(n)
Space O(1)26 Move duplicates in the sort array
Ideas : First, determine the size of the array , If 0, Go straight back to 0; If the array length is greater than 0, Index values from an array 1 Start using the double pointer at the position of , The judgment method is the same as the previous code
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 0){
return 0;
}
int left = 1,right = 1;
for(;right < n;right++){
if(nums[right] != nums[right - 1]){
nums[left] = nums[right];
left++;
}
}
return left;
}
O(n)
O(1)283 Move zero
void swap(vector<int>& nums,int left,int right){
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
for(;right < nums.size(); right++){
if(nums[right] != 0){
swap(nums,left,right); //left and right The same exchange operation is equivalent to not doing , If not, it means that the current left The element that points to is 0
left++;
}
}
}844 Compare strings with backspace
Ideas : Use a double fingered needle , Traverse the string from back to front , Definition snums Is string s in ‘#’ The number of , It is also the number of characters to be deleted . Start traversing string :
- When traversal to ‘#’, snums++;
- When traversing to normal characters , Determine the number of characters to delete , When snums Greater than 0, The current character should be deleted , then snums-1, If snums be equal to 0, Indicates that the current character does not need to be deleted , There are no characters to delete at this time , Exit loop .( Note the index value of the exit loop )
for instance : about ”abc#“, Execute to b Position when the loop has exited , The index value at this time is 1; about ”a#b#“ The loop executes until the index value is -1 until ; about 'a#bc', Exit search directly # The cycle of quantity , The index value is 3
I can't understand the code of this problem. I can give you a few examples debug, have a look i and j How it changed
bool backspaceCompare(string s, string t) {
int snums = 0, tnums = 0;
int i = s.length() -1;
int j = t.length() -1;
while(1){
for(; i >= 0; i--){
if(s[i] == '#') snums++;
else{
if(snums > 0) snums--; // Greater than 0 Indicates that the current character is to be deleted ,
else break; // Indicates that the current character should not be deleted , Exit loop
}
}
for(;j >= 0; j--){
if(t[j] == '#') tnums++;
else{
if(tnums > 0) tnums--; // Greater than 0 Indicates that the current character is to be deleted ,
else break; // Indicates that the current character should not be deleted , This cycle
}
}
// For strings ‘a#b#’ i=-1 character string ‘abc#’ j=1
// Compare after both characters are judged s[i] and t[i]
if(i < 0 || j < 0) break; // When a string has finished all traversal , Exit loop
if(s[i] != t[j]) return false;
i--;j--;
}
if(i == -1 && j == -1) return true;
return false;
}
Time complexity O(n+m)
Spatial complexity O(1)In addition to double pointers, stack can be used to solve this problem
Ideas : Define a string a As a stack , Traverse s character string , When a character is encountered, put it in a in , encounter '#' From a Delete an element
bool backspaceCompare1(string s, string t) {
string a;// Use as a stack
string b;// Use as a stack
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(s[i] != '#')
a = a + s[i];
else if(!s.empty())
a.pop_back();
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
if(t[i] != '#')
b = b + t[i];
else if(!t.empty())
b.pop_back();
}
if( a == b)
return true;
else
return false;
}
Time complexity O(n+m)
Spatial complexity O(n+m)977 The square of an ordered array
Ideas : Put the square of each number in the array , Sort the array , The time complexity is O(n+nlongn) = O(nlogn), You can also use two finger needling , Because there may be negative numbers in the array , The maximum square is the leftmost or rightmost number of the array , therefore left Point to the starting position ,right Point to the end position , Put the largest square value at the end of the new array , The new array is the same length as the original array .
vector<int> sortedSquares(vector<int>& nums) {
int k = nums.size() - 1;
vector<int> newnums(nums.size(),0); // Each element is 0
int left = 0, right = nums.size()- 1;
while(left <= right){
if(nums[left] * nums[left] <= nums[right] * nums[right]){
newnums[k] = nums[right] * nums[right];
k--;
right--;
}else { //[left]^2 > [right]^2
newnums[k] = nums[left] * nums[left];
k--;
left++;
}
}
return newnums;
}
Time complexity O(n)
Spatial complexity O(1)3. The sliding window
209 Subarray with the smallest length
Ideas : The first uses two for Loop traversal , Find a sub array that meets the requirements .
int minSubArrayLen(vector<int> nums,int s){
// The minimum length of the initializer is infinite INT_MAX
int length = INT_MAX;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
int sum = 0;
for(int j = i; j < nums.size(); j++){
sum += nums[j];
if(sum >= s){
length = min(length, j - i + 1);
break;
}
}
}
return length == INT_MAX ? 0 : length;
}Ideas : The complexity of violence law is O(n^2), You can also use the sliding window method , Continuously adjust the starting and ending positions of subsequences .i and j It all points to 0,j move backward , As long as The value of the current window is greater than s, The window needs to move backwards , That is to say i++, At this point, the sum of the elements in the window is sum - nums[i].
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums) {
int length = INT_MAX; // Returns the length of the subarray
int sum = 0;
int i = 0,j = 0;
while(j < nums.size()){
sum += nums[j];
while(sum >= target){ // The current window meets s
length = min(length, j - i + 1);
sum = sum - nums[i];
i++;
}
j++;
}
return length == INT_MAX ? 0 : length;
}904 Fruit baskets
Ideas : This question is understood as The largest continuous subsequence of two elements
right To the right , If fruits[right] It points to one of the two fruits , Calculate the current length , then right Move right ; If fruits[right] Not one of the two fruits will left Move to right The previous position , here left You need to look forward to see if there are the same numbers , On the condition that left Greater than or equal to one ( If left be equal to 0 There is no need to look forward ) meanwhile left-1 and left Point to the same number , Meet the conditions left-1 Keep looking , Find the top one left Then calculate the length at this time
int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
int length = 0;
int a = fruits[left], b = fruits[right];
while(right < fruits.size()){
if(fruits[right] == a || fruits[right] == b){ //right Point to the satisfaction of one of the two fruits
length = max(length , right - left + 1);
right++;
}else{ // dissatisfaction ,left = right - 1 meanwhile left Also need to look forward to whether there is the same
left = right - 1;
a = fruits[left];
while(left >= 1 && fruits[left-1] == a){ //left Look forward to , If at this time left It's already 0 There is no need to move forward , therefore left Greater than 1 At the same time judge left-1 Whether and left Point to the same number
left--; // Meet the conditions and continue to look forward again
}
//left The front has been found
b = fruits[right];
length = max(length , right - left + 1);
}
}
return length;
}summary :209 Subarray with the smallest length and 904 Fruit baskets They are to find the minimum subarray and the maximum subarray that meet the conditions .
For the smallest array :L and R Point to the starting position ,R To the right , If the elements in the window meet the conditions ,L Narrow the window to the right , Calculate the optimal result ; If the elements in the window do not meet the conditions ,R Continue to expand to the right .
while ( R < s.size()) { The right end of the window is extended , add s[R], Update conditions while( Meet the conditions ) { Compare the minimum length The left end of the window is removed s[L], Update conditions ,L++ } R++; }For the maximum array template :L and R Point to the starting position ,R To the right , If the elements in the window meet the conditions ,R Move the enlarged window to the right , Update results ; If the elements in the window do not meet the conditions ,L Narrow the window to the right .
while ( R < s.size()) { The right end of the window is extended , add s[R], Update conditions while( Not meeting the conditions ) { The left end of the window is removed s[L], Update conditions , then L++ } Compare the maximum length R++; }
about String problem You can also use the sliding window problem , Some big men have summarized the substring problem Templates
/* Sliding window algorithm framework */
void slidingWindow(string s, string t) {
//need The record is t Number of characters ,window Record the number of occurrences of characters in the current window
unordered_map<char, int> need, window;
for (char c : t) need[c]++;
int left = 0, right = 0;
//valid Indicates that the window is satisfied need The number of characters of the condition , If valid = need.size It indicates that the current window completely covers t character string
int valid = 0;
while (right < s.size()) {
// c Is the character that will be moved into the window
char c = s[right];
// Move the window right
right++;
// Make a series of updates to the data in the window
...
// Determine whether the left window should shrink
while (window needs shrink) {
// If it is to find the smallest string , Update the final results here
// d Is the character that will be moved out of the window
char d = s[left];
// Move the window to the left
left++;
// Make a series of updates to the data in the window
...
}
// If it is to find the largest substring , Update the final results here
}
return
}Two places ... Is where the window data is updated , There are four issues that should be paid attention to when using templates :
1. Move right What data needs to be updated when expanding the window ?
2. When to start narrowing the window ( Move left)?
3. Move left What data needs to be updated when ?
4. The desired results are updated when the window is enlarged or narrowed ? For the problem of finding the minimum class , Update the final result in a smaller window
76 Minimum cover substring It is equivalent to finding the minimum substring satisfying the condition
Ideas :① When a character enters a window , increase window Counter ;② When valid = need.size Zoom out the window when ;③ The character removal window is reduced window Counter ;④ Update the final result when you zoom out
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
unordered_map<char,int>need, window; //need yes t Number of characters
for(char a : t)
need[a]++;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int valid = 0; //valid Indicates that the window is satisfied need The number of characters of the condition , If valid = need.size It indicates that the current window completely covers t character string , Then narrow the exposure
// Record the starting index and length of the smallest string
int start = 0, len = INT_MAX;
while(right < s.length()){
char a = s[right]; //a Is the character that enters the window
right++;
// Update data in the window
if(need.count(a)){ //count In container key return 1, Otherwise return to 0
window[a]++;
if(window[a] == need[a]) // Two containers record the same number of times for the same character
valid++;
}
// Windows shrink
while(valid == need.size()){
// Update final results
if(right - left < len){
start = left;
len = right - left;
}
// Determine if any characters need to be removed
char b = s[left];
left++;
// Update window data
if(need.count(b)){
if(window[b] == need[b]) // A character occurs the same number of times
valid--; // Exit the zoom out window
window[b]--;
}
}
}
return len == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(start,len);
}3 The longest repeatless substring It is equivalent to finding the largest substring satisfying the condition
int lengthOfLongestSubstring2(string s) {
unordered_map<char,int>window;
int left = 0, right = 0;
int length = 0;
while(right < s.length()){
char ref = s[right];
right++;
// Update window data
window[ref]++;
// shrink windows
while(window[ref] > 1){
char cur = s[left];
left++;
// Update window
window[cur]--;
}
// Update final results
length = max(length,right - left);
}
return length;
}4. Spiral matrix
54 Spiral matrix
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size();
int n =matrix[0].size();
vector<int>ans;
int up = 0, down = m - 1, left = 0, right = n - 1;
while(1){
// The upper boundary begins Traverse left to right , After traversing the upper boundary, move down , If the upper boundary moves larger than the lower boundary , Exit loop
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++) ans.push_back(matrix[up][i]);
if(++up > down) break;
// Right border , Traverse from top to bottom , After traversing the right boundary, move left
for(int i = up; i <= down; i++) ans.push_back(matrix[i][right]);
if(--right < left) break;
// Lower boundary , Traverse from right to left , After traversing the lower boundary, move up
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--) ans.push_back(matrix[down][i]);
if(--down < up) break;
// Left boundary , From the bottom up , After traversing the left boundary, move right
for(int i = down; i >= up; i--) ans.push_back(matrix[i][left]);
if(++left > right) break;
}
return ans;
}59 Spiral matrix Ⅱ
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
int up = 0, down = n - 1, left = 0, right = n - 1;
int num = 1;
vector<vector<int>> ans(n,vector<int>(n));
while(1){
// The upper boundary begins Traverse left to right , After traversing the upper boundary, move down , If the upper boundary moves larger than the lower boundary , Exit loop
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++) ans[up][i] = num++;
if(++up > down) break;
// Right border , Traverse from top to bottom , After traversing the right boundary, move left
for(int i = up; i <= down; i++) ans[i][right] = num++;
if(--right < left) break;
// Lower boundary , Traverse from right to left , After traversing the lower boundary, move up
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--) ans[down][i] = num++;
if(--down < up) break;
// Left boundary , From the bottom up , After traversing the left boundary, move right
for(int i = down; i >= up; i--) ans[i][left] = num++;
if(++left > right ) break;
}
return ans;
}边栏推荐
- 启牛商学院给的证券账户是安全的吗?开户收费吗
- 2022 simulated examination question bank and simulated examination for crane driver (limited to bridge crane)
- Wechat applet timestamp conversion time format + time subtraction
- ^32 execution context stack interview questions
- Global and Chinese molten carbonate fuel cell industry outlook and market panoramic Research Report 2022-2028
- Oracle database merge row records, wmsys WM_ Use of the concat function and group in MySQL_ Use and comparison of concat (ID).
- CS0006 C# 未能找到元数据文件“C:\Users\...问题
- LeetCode——24. Exchange the nodes in the linked list in pairs (three pointers)
- GemBox.Bundle 43.0 Crack
- Classic reading of multi task learning: MMOE model
猜你喜欢

消息队列-推/拉模式学习 & ActiveMQ及JMS学习

Kernel density estimation (2D, 3D)
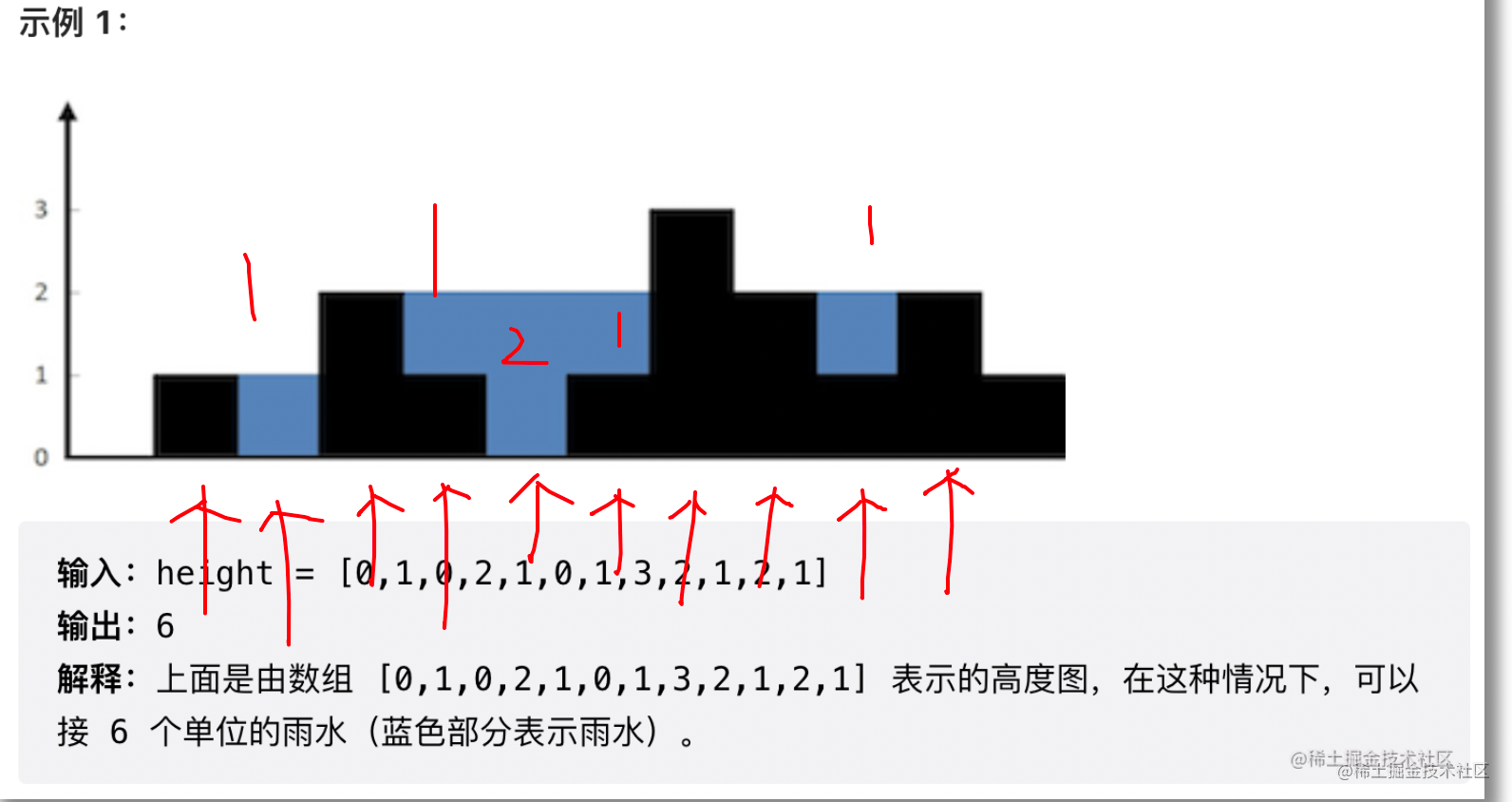
LeetCode——42. Connected to rainwater (double pointer)

485 days, 21 experiences of my remote office sharing | community essay solicitation

【pytest学习】pytest 用例执行失败后其他不再执行

Solr (I) installation and permission control of Solr

Regression prediction | realization of RBF RBF neural network with multiple inputs and single output by MATLAB

API management artifact that allows you to call wow directly

TypeScript学习笔记(二)

【opencvsharp】opencvsharp_samples.core示例代码笔记
随机推荐
Is the stock account recommended by qiniu safe? Is it reliable
solr(一)solr的安装及权限控制
数据库备份(Mysql)
cocoapod只更新指定库(不更新索引)
Environment configuration and pymysql installation
The micro service failed to connect to the cloud sentinel console and the link blank problem occurred after the connection was successful (resolved)
A journey of database full SQL analysis and audit system performance optimization
RSP:遥感预训练的实证研究
2022 high voltage electrician special operation certificate examination question bank and online simulation examination
[pytest learning] after the pytest case fails to execute, the others will not be executed
Composition of JVM
启牛推荐开通的股票账户安全吗?靠谱吗
JSP page initial loading method
Solr (II) Solr adds core and dependent package path
Leetcode 450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
Message queue push / pull mode Learning & ActiveMQ and JMS learning
Analysis report on sales status and supply and demand prospects of phosphoric acid fuel cell industry in the world and China 2022-2028 Edition
R1 Quick Open Pressure Vessel Operation test Library and Simulation Test in 2022
LeetCode-859. 亲密字符串
unittest 如何知道每个测试用例的执行时间