当前位置:网站首页>How to implement a distributed lock with redis
How to implement a distributed lock with redis
2022-06-23 11:14:00 【InfoQ】
Scene simulation

@RestController
public class SkillController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// Seckill interface
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
// Lock
synchronized (this) {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock").toString());
if (stock > 0) {
// stock -1
int realStock = stock - 1;
// Deducting the inventory
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + "");
System.out.println(" Deduction succeeded , Surplus stock :" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println(" Deduction failed , Insufficient inventory ");
}
}
return "8080";
}
}
@RestController
public class SkillController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// Seckill interface
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
// Lock
synchronized (this) {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock").toString());
if (stock > 0) {
// stock -1
int realStock = stock - 1;
// Deducting the inventory
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + "");
System.out.println(" Deduction succeeded , Surplus stock :" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println(" Deduction failed , Insufficient inventory ");
}
}
return "8090";
}
}


JVM lock



Redis SETNX
@RestController
public class SkillController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock")
public String deductStock() {
// goods ID, In the specific application, the request should be passed in
String lockKey = "lock:product_01";
// SETNX Lock
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "product");
// If false It means that the lock exists , Go straight back to
if (!result) {
// Simulate the return service
return " The system is busy ";
}
int stock = Integer.parseInt(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock").toString());
if (stock > 0) {
// stock -1
int realStock = stock - 1;
// Deducting the inventory Simulate more business operations
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + "");
System.out.println(" Deduction succeeded , Surplus stock :" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println(" Deduction failed , Insufficient inventory ");
}
// The lock needs to be released after locking
redisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
return "8080";
}
}try catchtry finally
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "product");
redisTemplate.expire(lockKey, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockKey, "product", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);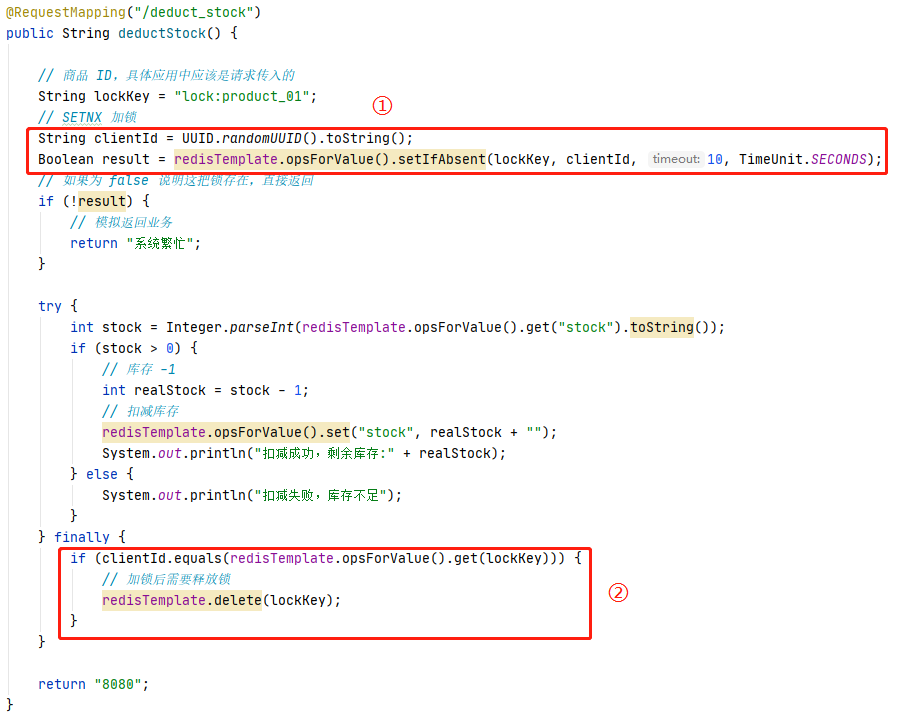
Redisson
@RestController
public class RedissonController {
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/deduct_stock1")
public String deductStock() {
// goods ID, In the specific application, the request should be passed in
String lockKey = "lock:product_01";
// Get the lock
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
// Lock
lock.lock();
try {
int stock = Integer.parseInt(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock").toString());
if (stock > 0) {
// stock -1
int realStock = stock - 1;
// Deducting the inventory
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", realStock + "");
System.out.println(" Deduction succeeded , Surplus stock :" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println(" Deduction failed , Insufficient inventory ");
}
} finally {
// Release the lock
lock.unlock();
}
return "8080";
}
}

lualuaRedissonLock.lock()--->lockInterruptibly()--->tryAcquire()--->tryLockInnerAsync()tryLockInnerAsync()<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
// If the lock doesn't exist , Through hset Set its value , And set expiration time
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// If the lock already exists , It is the current thread , Through hincrby Incrementing the value 1, That is, the re-entry of the lock
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
// If the lock already exists , Not the current thread , The expiration time is returned ttl
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}RedissonLock.lock()--->lockInterruptibly()--->tryAcquire()--->scheduleExpirationRenewal()scheduleExpirationRenewal()lua// getName() Is the name of the current lock
RFuture<Boolean> future = commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
// Judge this lock getName() Whether in redis in , If there is one, go ahead pexpire delay Default 30s
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
getName()pexpirelockWatchdogTimeout=30slockWatchdogTimeout/3=10s边栏推荐
- R and rstudio download and install detailed steps
- 圖片存儲--引用
- Stockage d'images - référence
- 运行时应用自我保护(RASP):应用安全的自我修养
- The simplest DIY pca9685 steering gear control program based on the integration of upper and lower computers of C # and 51 single chip microcomputer
- 每日一题day7-1652. 拆炸弹
- Esp32-cam high cost performance temperature and humidity monitoring system
- Stm32f1 and stm32subeide programming example - infrared tracking sensor driver
- Picture storage -- Reference
- Vone新闻 | 旺链科技赋能众享链网自组织管理,打造企业级联盟DAO
猜你喜欢
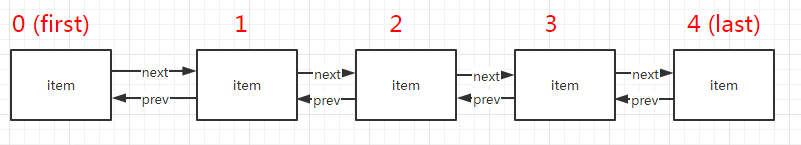
六张图详解LinkedList 源码解析

Simplest DIY steel patriot machine gun controller based on Bluetooth, 51 MCU and steering gear

ESP32-CAM、ESP8266、WIFI、蓝牙、单片机、热点创建嵌入式DNS服务器
Deveco device tool helps openharmony device development

A child process is created in the program, and then the parent and child processes run independently. The parent process reads lowercase letters on the standard input device and writes them to the pip

Experience of using thread pool in project

Maui uses Masa blazor component library

从0到1,IDE如何提升端侧研发效率?| DX研发模式

技术创造价值,手把手教你薅羊毛篇

【ML】QuantileRegressor
随机推荐
Noi OJ 1.3 15: apple and bug C language
Noi OJ 1.3 16: calculating segment length C language
强化责任意识和底线思维 全力筑牢抗洪抢险“安全堤”
NFS挂载时一直没有同步文件
程序中创建一个子进程,然后父子进程各自独自运行,父进程在标准输入设备上读入小写字母,写入管道。子进程从管道读取字符并转化为大写字母。读到x结束
Noi OJ 1.4 05: integer size comparison C language
The simplest DIY actuator controller based on 51 single chip microcomputer
Deep dive kotlin synergy (XIV): problems of shared state
Which securities company has the lowest Commission for opening a mobile account? Is it safe to open an account online now?
Design and implementation of esp32-cam wireless monitoring intelligent gateway
当 Pandas 遇见 SQL,一个强大的工具库诞生了
Noi OJ 1.3 11: C language for calculating the remainder of the division of floating-point numbers
Noi OJ 1.3 17: calculating triangle area C language
1154. 一年中的第几天
Why does the pointer not change the corresponding value as a formal parameter
How to write a literature review? What should I do if I don't have a clue?
Flutter series: wrap in flutter
Noi OJ 1.2 conversion between integer and Boolean C language
torch权重转mindspore
运行时应用自我保护(RASP):应用安全的自我修养