当前位置:网站首页>Time processing of basic library in go
Time processing of basic library in go
2022-07-24 11:51:00 【Ch3n】
time package
time The package provides functions for displaying and measuring time . The calendar is calculated in the Gregorian calendar .
Time type
time.Time Type represents time . We can go through time.Now() Function to get the current time object , Then obtain the date, month, hour, minute, second and other information of the time object . The sample code is as follows :
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// Get the current time 2022-07-19 10:03:42.70981 +0800 CST m=+0.000080935
now := time.Now()
fmt.Println(now)
fmt.Println(now.Year())
fmt.Println(now.Month())
fmt.Println(now.Day())
fmt.Println(now.Hour())
fmt.Println(now.Minute())
fmt.Println(now.Second())
}
Time stamp
The time stamp is from 1970 year 1 month 1 Japan (08:00:00GMT) The total number of milliseconds to the current time . It's also called Unix Time stamp (UnixTimestamp).
The sample code for obtaining time stamp based on time object is as follows :
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// Get the current time 2022-07-19 10:03:42.70981 +0800 CST m=+0.000080935
now := time.Now()
fmt.Println(now)
// Time stamp second
fmt.Println(now.Unix())
// Time stamp millisecond
fmt.Println(now.UnixMilli())
// Time stamp nanosecond
fmt.Println(now.UnixNano())
}
Use time.Unix() Function to convert a timestamp to a time format .
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// Get the current time 2022-07-19 10:03:42.70981 +0800 CST m=+0.000080935
now := time.Now()
fmt.Println(now)
// Timestamp to time type
unix := time.Unix(now.Unix(), 0)
fmt.Println(unix)
}
The time interval
time.Duration yes time A type of package definition , It represents the time between two time points , In nanoseconds .time.Duration A time interval , The longest period that can be expressed is about 290 year .
time The constants of the interval type defined in the package are as follows :
for example :time.Duration Express 1 nanosecond ,time.Second Express 1 second .
const (
Nanosecond Duration = 1
Microsecond = 1000 * Nanosecond
Millisecond = 1000 * Microsecond
Second = 1000 * Millisecond
Minute = 60 * Second
Hour = 60 * Minute
)
meanwhile ,time.Duration It provides a method to obtain the value of each time granularity
func (d Duration) Nanoseconds() int64 {
} // nanosecond
func (d Duration) Microseconds() int64 {
} // Microsecond
func (d Duration) Milliseconds() int64 {
} // millisecond
func (d Duration) Seconds() float64 {
} // second
func (d Duration) Minutes() float64 {
} // minute
func (d Duration) Hours() float64 {
} // Hours
Time operation
AddThe function is used to add / Reduce ( d A positive value of indicates an increase 、 Negative values indicate a decrease ) time.Time Duration of . For an instantaneous time , Increase or decrease the time above the specified nanosecond .func (t Time) Add(d Duration) Time {}SubFunction can get the duration between two time instants .func (t Time) Sub(u Time) Duration {}AddDateThe function is based on the year 、 The dimensions of month and day increase / Reduce time.Time Value .func (t Time) AddDate(years int, months int, days int) Time {}
Of course , Based on the current time instant time.Now() Computing is the most common requirement . therefore ,time The package also provides the following convenient time calculation functions .
SinceThe function istime.Now().Sub(t)A shortcut to .func Since(t Time) Duration {}UntilThe function ist.Sub(time.Now())A shortcut to .func Until(t Time) Duration {}
Examples of use
t := time.Now()
fmt.Println(t) // 2022-07-17 22:41:06.001567 +0800 CST m=+0.000057466
// Time increases 1 Hours
fmt.Println(t.Add(time.Hour * 1)) // 2022-07-17 23:41:06.001567 +0800 CST m=+3600.000057466
// Time increases 15 minute
fmt.Println(t.Add(time.Minute * 15))// 2022-07-17 22:56:06.001567 +0800 CST m=+900.000057466
// Time increases 10 Second
fmt.Println(t.Add(time.Second * 10))// 2022-07-17 22:41:16.001567 +0800 CST m=+10.000057466
// Time reduction 1 Hours
fmt.Println(t.Add(-time.Hour * 1)) // 2022-07-17 21:41:06.001567 +0800 CST m=-3599.999942534
// Time reduction 15 minute
fmt.Println(t.Add(-time.Minute * 15))// 2022-07-17 22:26:06.001567 +0800 CST m=-899.999942534
// Time reduction 10 Second
fmt.Println(t.Add(-time.Second * 10))// 2022-07-17 22:40:56.001567 +0800 CST m=-9.999942534
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5)
t2 := time.Now()
// Calculation t To t2 Duration of
fmt.Println(t2.Sub(t)) // 5.004318874s
// 1 Years later
t3 := t2.AddDate(1, 0, 0)
// Calculate from t To the current duration
fmt.Println(time.Since(t)) // 5.004442316s
// Calculate the duration from now to next year
fmt.Println(time.Until(t3)) // 8759h59m59.999864s
Time format
There's a way for time types Format format , In other languages , Generally, a general time template is used to format the time . for example Python, It USES %Y Represents the year 、%m Representative month 、%d Representative day, etc . It should be noted that Go Formatting time templates in languages is not common Y-m-d H:M:S But use Go The birth time of 2006 year 1 month 2 Number 15 spot 04 branch ( The formula of memory is 2006 1 2 3 4). Maybe this is the romance of technicians .
Add : If you want to format it as 12 Hour mode , Need to specify PM.
Formate The function is used to time.Time Object is converted into a time string according to the given layout .
now := time.Now()
// The formatted template is Go The birth time of 2006 year 1 month 2 Number 15 spot 04 branch Mon Jan
// 24 hourly
fmt.Println(now.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05.000 Mon Jan"))
// 12 hourly
fmt.Println(now.Format("2006-01-02 03:04:05.000 PM Mon Jan"))
fmt.Println(now.Format("2006/01/02 15:04"))
fmt.Println(now.Format("15:04 2006/01/02"))
fmt.Println(now.Format("2006/01/02"))
Parse The function is used to convert a time string into time.Time object .
now := time.Now()
fmt.Println(now)
// Load time zone
loc, err := time.LoadLocation("Asia/Shanghai")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Parse string time in the specified time zone and format
timeObj, err := time.ParseInLocation("2006/01/02 15:04:05", "2019/08/04 14:15:20", loc)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(timeObj)
fmt.Println(timeObj.Sub(now))
边栏推荐
- LogBack & MDC & a simple use
- JMeter while controller
- 1184. 公交站间的距离 : 简单模拟题
- Is there any charge for PDF processing? impossible!
- Use prometheus+grafana to monitor server performance in real time
- C#入门系列(二十九) -- 预处理命令
- Hash - 15. Sum of three numbers
- Video playback | how to become an excellent reviewer of international journals in the field of Geoscience and ecology?
- 三、MFC消息映射机制实现原理
- Easy to use example
猜你喜欢

MySQL advanced (XVII) cannot connect to database server problem analysis
JMeter while controller
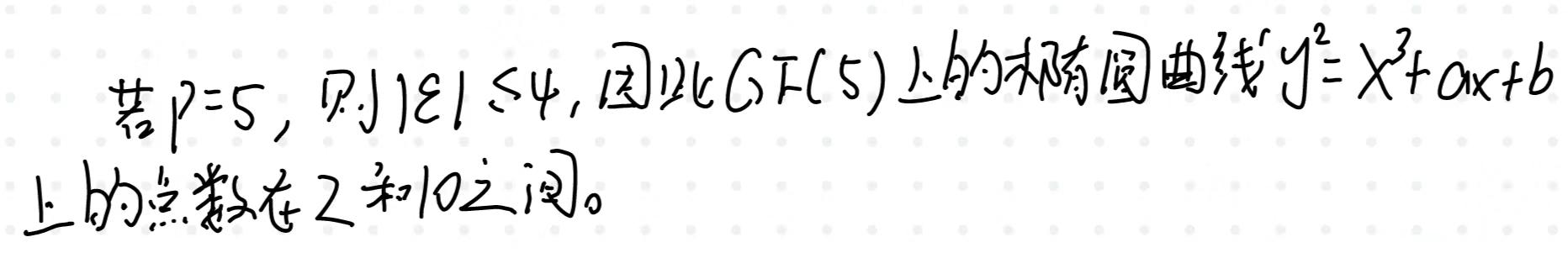
【网络空间安全数学基础第9章】有限域

字符串——344.反转字符串

Cgo+gsoap+onvif learning summary: 9. Go and C conduct socket communication and onvif protocol processing

Video playback | how to become an excellent reviewer of international journals in the field of Geoscience and ecology?
![[deserialization vulnerability-01] Introduction to serialization and deserialization](/img/e4/6b9ee6ee74f3cdc3c886ed3af9ef73.png)
[deserialization vulnerability-01] Introduction to serialization and deserialization

The third day of hcip mGRE experiment

L1-059 ring stupid bell

IT圈中的Bug的类型与历史
随机推荐
Common formulas and application scenarios of discrete distribution
离散分布常用公式及应用场景
字符串——剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
哈希——242.有效的字母异位词
使用Prometheus+Grafana实时监控服务器性能
L1-043 阅览室
Easy to use example
MySql的DDL和DML和DQL的基本语法
What is cloud native? Why is cloud native technology so popular?
Jackson parsing JSON detailed tutorial
Microservice - eruka
安装jmeter
[markdown grammar advanced] make your blog more exciting (IV: set font style and color comparison table)
CCF 201803_ 1 jump jump
Hash - 202. Happy number
L2-011 玩转二叉树
Shell Scripting tips
Mysql database
Nacos permissions and databases
Convergence rules for 4 * 4 image weights