当前位置:网站首页>Target detection series -- detailed explanation of RCNN principle
Target detection series -- detailed explanation of RCNN principle
2022-06-22 07:35:00 【Bald little Su】
Author's brief introduction : Bald Sue , Committed to describing problems in the most popular language
Looking back :ubuntu Use guide Alibaba cloud object storage oss+picgo+typora Implementation steps and solution of unable to upload pictures
Near term goals : Have 10000 fans
Support Xiao Su : give the thumbs-up 、 Collection 、 Leaving a message.
List of articles
RCNN principle
Write it at the front
RCNN It is a pioneering work in the field of target detection , The author is Ross Girshick , We call it RGB A great god Can be in google Look at the articles written by Daniel in academic circles , Look at the number of citations , Can only exclaim !!!
Next, we will introduce... In detail RCNN Principle , Let's take a look at this classic picture in the paper . This picture shows RCNN Implementation process , There are four main steps , Each step is explained below .

Candidate area generation
Candidate regions are generated in RCNN It is used in selective search 【 abbreviation SS Algorithm 】, The principle of this algorithm is roughly through color 、 size 、 Some features such as shape cluster the image , The result of the algorithm is to generate a series of candidate boxes in a picture ,RCNN Make every image generate 2000 Candidate box . These candidate boxes have a lot of overlap , Therefore, we need to remove these overlapping candidate boxes later , Get a relatively accurate candidate box .【 notes : Here is wrong SS Explain the algorithm in detail , Those who are interested can consult and understand by themselves 】 The following figure shows SS The approximate result of the algorithm , It can be seen that multiple candidate boxes will be generated for a target .【 notes :RCNN in SS The number of candidate frames generated by each image is 2000】

Feature extraction by neural network
In the last step, we started from SS The algorithm gets... From a picture 2000 Candidate box , Next, we need to extract the features of these candidate boxes , That is, separate 2000 Candidate box areas are fed ALexNet Network training , The extracted features .【 notes : of ALexNet I introduced the network structure of , Unclear click * Learn more 】 For the convenience of reading , I put ALexNet The network structure of is also posted for your reference , As shown in the figure below :

It should be noted that , stay RCNN in , We don't need the last softmax layer , You only need to go through the last two full connection layers , Using the extracted features can . In addition, due to the existence of full connection layer , You need to limit the size of the output picture , That is, the resolution of the picture is 227*227. The method used in this paper is regardless of the size or aspect ratio of the candidate region , First expand around it 16 Adjacent pixels , Then force all pixels to zoom to 227*227 Size .【 notes : It can be seen that this scheme will distort the original image , For example, people become shorter and fatter 】 The relevant scaling scheme is shown in the following figure :

SVM Classifier classification
We have passed the previous step ALexNet The network extracts features , Each candidate box area will generate 4096 The eigenvectors of the dimensions , As shown in the figure below :

The above figure shows the feature extracted from a candidate box , We use SS The algorithm generates... From an image 2000 Candidate box , Enter all candidate boxes into the network , Will get 2000*4096 The characteristic matrix of dimension . take 2000*4096 The characteristic matrix of dimension and 20 individual SVM The weight matrix 4096*20 Multiply , You'll get 2000*20 The probability matrix of dimension , Each row represents the probability that a candidate box belongs to each target category .【 Be careful : If you use VOC Data sets , So the category should have 21 class , Include a background class 】

To make it easier for everyone to understand , For the above structure ① Explain in more detail , As shown in the figure below :
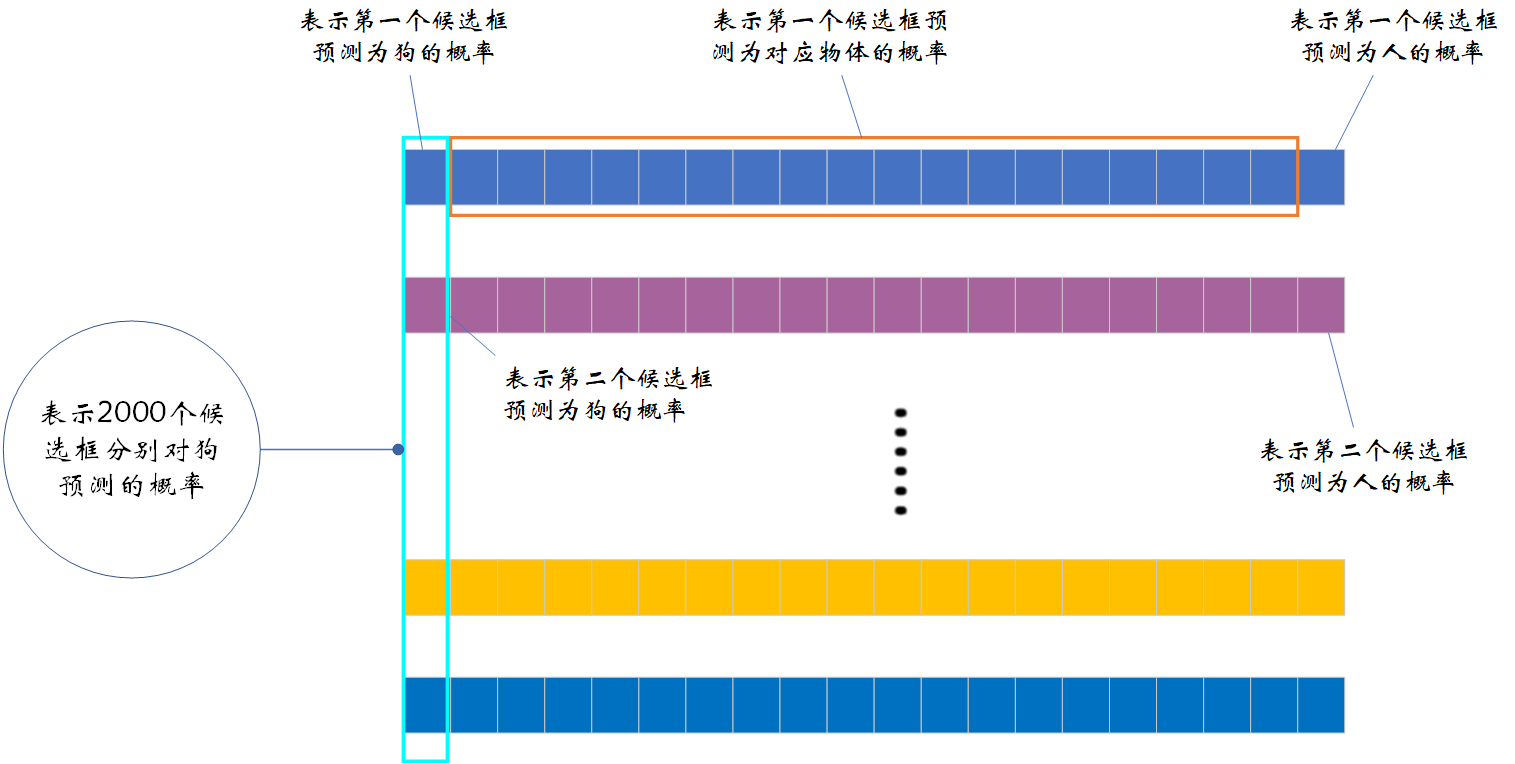
As can be seen from the above figure ,2000*20 Each column of a dimensional matrix represents 2000 The prediction probability of each candidate box for a certain class , For example, the first column indicates 2000 The prediction probability of each candidate box to the dog . We perform non maximum suppression for each column or class (NMS) Used to eliminate overlapping candidate boxes , Get the suggestion box with the highest score in the column . Specifically NMS The process is as follows :

This part may be a bit confusing at first , Why delete IOU Big goals ? I have had this question before , In fact, we are not very clear about this process . First, we will find the goal with the highest score in a certain column , Then it will calculate other goals and the goal with the highest score IOU【 Note that it is not calculation and Ground Truth Of IOU】, This IOU What does big mean ? The larger the value, the more the two candidate boxes overlap , It means that the two candidate boxes are likely to represent the same object , Then it is easy to understand to delete the candidate box with low score . The following figure shows the relevant process :

The regressor corrects the position of the candidate box
In the previous step, we eliminated many candidate boxes , Next, we need to further filter the remaining candidate boxes , That is to say, use respectively 20 A regressor for the above 20 The remaining candidate boxes in each category are regressed , Finally, get the highest score of each category after correction bounding box.
So how do we get the final prediction box from the candidate box ? We will still be ALexNet The output eigenvector is used to get the prediction result of the regressor , The result is ( d x ( P ) , d y ( P ) , d w ( P ) , d h ( P ) ) (d_x(P),d_y(P),d_w(P),d_h(P)) (dx(P),dy(P),dw(P),dh(P)) , It represents the center point coordinate offset and the scaling factor of the width and candidate box Height offset . The result of its prediction G i ∧ {\mathop {\rm{G_i}}\limits^ \wedge} Gi∧ The expression for is as follows :

We solve the inverse of the above equation ( d x ( P ) , d y ( P ) , d w ( P ) , d h ( P ) ) (d_x(P),d_y(P),d_w(P),d_h(P)) (dx(P),dy(P),dw(P),dh(P)) The expression of , Current use ( t x , t y , t w , t h ) (t_x,t_y,t_w,t_h) (tx,ty,tw,th) Express , Because the dimension box parameters and candidate box parameters are given , therefore ( t x , t y , t w , t h ) (t_x,t_y,t_w,t_h) (tx,ty,tw,th) It can also be calculated directly , For real value .

Next use ( d x ( P ) , d y ( P ) , d w ( P ) , d h ( P ) ) (d_x(P),d_y(P),d_w(P),d_h(P)) (dx(P),dy(P),dw(P),dh(P)) Value de fitting ( t x , t y , t w , t h ) (t_x,t_y,t_w,t_h) (tx,ty,tw,th) value , Minimize the loss function , The loss function is as follows :

Summary
RCNN That's all for the principle of , I hope it can help you . It will be updated continuously in the future fast_RCNN and Faster_RCNN And related code explanation , Come on !!!
Reference link
If the article is helpful to you , It would be
Whew, whew, whew ~~duang~~ A great bai
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Real MySQL interview question (18) -- practical operation analysis

MySQL面试真题(二十)——视频数据分析实战

Chromedriver所有版本下载

Rviz ROS wiki official website tutorial learning notes (1) - User Guide

Propeller framework v2.3 releases high reusable operator library Phi: Restructure development paradigm, reduce cost and increase efficiency

How to backup the treasures in the store and upload them to multiple stores
The solution of word document being locked and unable to edit

Canoe learning notes (1) illustration of new project and channel configuration steps

Chromedriver所有版本下載

How was the coffee supply chain leveled?
随机推荐
Solve syntaxerror: cannot use import statement outside a module
okcc呼叫中心的权限管理
Flutter input field maxlines dynamic change
Qualcomm platform msm8953 display subsystem learning
How was the coffee supply chain leveled?
How to import and upload a CSV generated by a third-party platform to a Taobao store
Application and problem solving of robotframework
[standard version 4.3] marketing activities (group bargaining second kill) error reporting under orders
6、 Scrollview component
Real MySQL interview questions (20) -- video data analysis practice
Tikz learning notes (III) marking and intersection of graphics
What are the ways for Taobao merchants to put their babies on the shelves in batches
Error e: unable to locate package sudo
How to upload Taobao tmall products with one click
Solution to the problem of "brand abuse such as brand inconsistency and stacking in the published product information" prompted by copying and uploading
Lean production | lean management
Examples of Algebra: understanding of normal subgroups and quotient groups
Kuangshi brain++ Tianyuan platform megstudio
MTK platform execution disable_ Interrupt signals masked during IRQ will be enabled when I execute enable_ Continue triggering after IRQ
5、 Image component
