当前位置:网站首页>AWS saves data on the cloud (3)
AWS saves data on the cloud (3)
2022-06-28 08:22:00 【Xinyouyou】
Related resource documents :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/index.html

1. Store the object S3 and Glacier
- 1.1 Object storage concept
- 1.2Amazon S3
- 1.3Amazon Glacier
- 1.4 Store objects programmatically
- 1.5 Use S3 To achieve static website hosting
- 1.6 The internal mechanism of object storage
2. Store data on the hard disk :EBS And instance storage
3. Use relational database services :RDB
4. Use NoSQL Database services :DynamoDB
1. Store the object S3 and Glacier
Object storage can help users store : picture , file , video , Executable file .
AWS Provide object storage services Amazon S3 and Storage services for backup and archiving Amazon Glacier.
Object storage concept
In the object store , Data is stored as objects .
Each object consists of three parts :
- A globally unique identifier
- Metadata
- ( Content ) The object itself consists of .
The globally unique identifier of the object becomes the key , With this globally unique identifier , To access each object using different devices and machines in the distributed file system .
The separation of metadata and data enables customers to directly manipulate metadata to manage and query data , Load the data itself only if necessary .
Amazon S3
file :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/s3/?id=docs_gateway
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) It's a kind of face Internet Storage services for . You can Amazon S3 At any time Web Data of any size stored and retrieved anywhere on the . You can use AWS The management console is simple and intuitive web Interface to complete these tasks .
S3 It's a typical Web service , Allow users to access HTTPS and API To store and access data .
S3 Provides unlimited storage space , Make user data highly available and highly persistent .
Users can save any type of data , Such as : picture , Documentation and binaries , As long as the capacity of a single object does not exceed 5TB.
The user needs to save in S3 Every GB Capacity payment , At the same time, a small amount of cost is spent on each data request and data transmission traffic .
You can use... Through the management console HTTPS Agreement to access S3, adopt CLI,SDK And third-party tools to upload and download objects .
S3 Organize objects using buckets .
A bucket is a container for objects .
Users can create up to 100 A bucket , Each bucket has a unique name in the world .
Typical use scenarios :
- Use S3 and AWS CLI To backup and restore files
- Archive objects to Amazon Glacier Archive to S3 More cost saving
- Use AWS SDK Integrate Amazon S3 To the application , To save and read files like pictures
- Hosting static web site content , Make it accessible to everyone
Use CLI Upload data and from S3 Download data :
aws CLI Command to use :aws <service> <action> [key Value...]aws help: Show all available servicesaws <service> help: Displays all available actions for the serviceaws <service> <action> help: Displays all options for a specific service or operation
1. First create a for the data S3 bucket , The name of the storage bucket must be unique in the worldaws s3 mb s3://<bucket-name>
2. Upload your own data : Select a directory we want to back up , Such as desktop directory .
Try to choose a suitable Directory , The file size is no more than 1GB, And the number of documents shall not be less than 1000 individual , This will not wait too long , It will not exceed the amount of free useaws s3 sync $LocalPath s3://<bucket-name>/< Directory name in bucket >
sync The command compares the local directory with s3 Directory in bucket , Then upload only new or modified files
3. Download the uploaded data :aws s3 cp --recursive s3://<bucket-name>/< Directory name in bucket > $LocalPath
4. Delete uploaded files
rb:remove bucket
force Option before deleting the bucket , Force to delete every object in the bucketaws s3 rb --force s3://<bucket-name>
5. Removing the storage bucket causes BucketNotEmpty Report errors
If the bucket version control function is activated , An error will be reported when deleting a bucket BucketNotEmpty error .
Not applicable in this case CLI To delete a bucket , But use Web GUI Interface to delete the storage bucket :
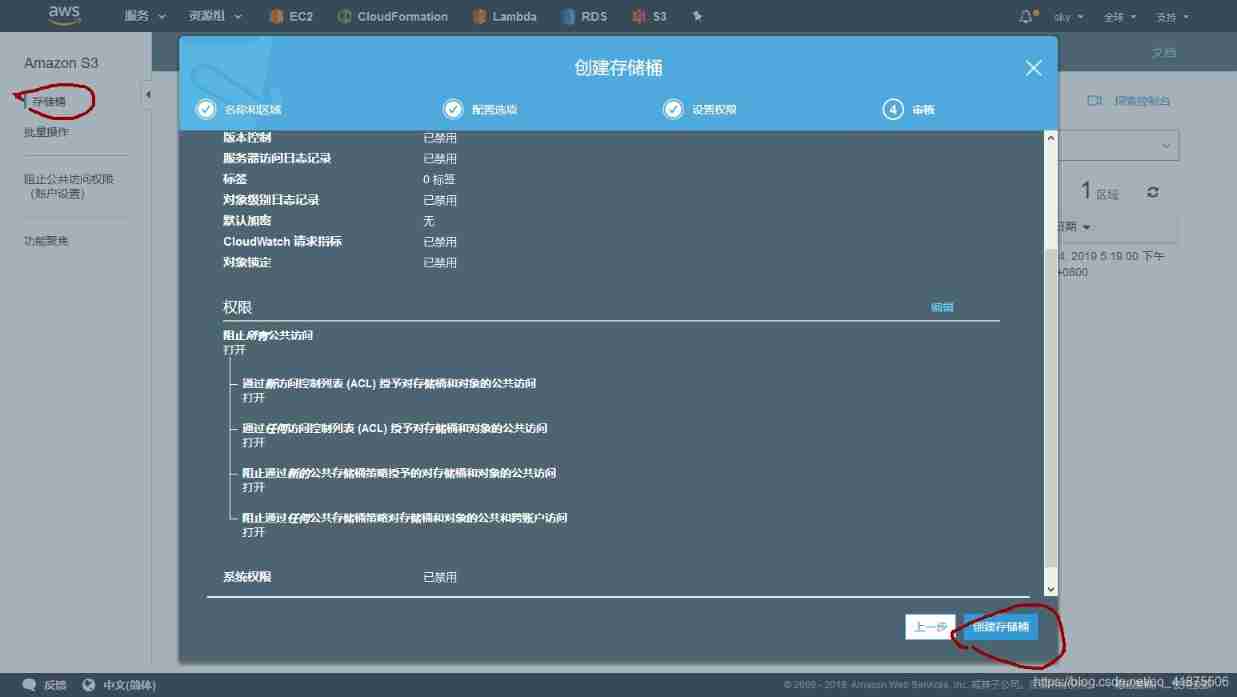
【 Administrative console 】—【s3 service 】----【 bucket 】----【 operation 】----【 Delete buckets 】
The version of the object
By default ,S3 Bucket has version disabled : That is, only one copy of data with the same primary key can exist .
Version control can be activated for buckets to protect data .aws s3api put-bucket-versioning --bucket <bucket-name> --versioning-configuration Status=Enable
Use the following command to get all the objects and versionsaws s3api list-object-versions --bucket <bucket-name>
Be careful : The capacity of the bucket that needs to be paid will increase with the increase of the new version
We don't need to worry about storing in s3 Loss of data on ,s3 Persistence by default .
Amazon Glacier
file :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/glacier/?id=docs_gateway
Amazon Glacier It is a kind of data that is not commonly used (“ Cold data ”) Optimized storage services . This service provides a durable and extremely low-cost storage solution and security features for data archiving and backup . Use Amazon Glacier, You can cost effectively store data for months 、 several years , Even for decades .Amazon Glacier Allows you to expand storage to AWS And remove the burden of operation and management , such , You don't have to worry about capacity planning 、 hardware configuration 、 Data replication 、 Hardware fault detection and recovery , Or time-consuming hardware migration .
If you want to reduce the cost of backup storage , Should consider using Glacier service .
stay Glacier The cost of storing data in is about S3 Medium 1/3.
Use S3 and Glacier The difference between storing data :
| S3 | Glacier | |
|---|---|---|
| Every time GB Capacity cost | 0.003 dollar | 0.001 dollar |
| Data access speed | Immediate access to | When submitting a request 3-5h after |
| persistence | The design is annual 99.999999999% Data persistence for | The design is annual 99.999999999% Data persistence for |
The user can go through HTTPS Use it directly Glacier service , Or integration S3 Use it together .
establish S3 The storage barrel fits Glacier Use it together : How to integrate S3 and Glacier To reduce the storage cost of data
1. First create a new S3 bucket : This use Web GUI instead of CLI establish
【 Administrative console 】----【s3 service 】----【 Create buckets 】---- Enter a unique bucket name , Select area ---- Click on 【 establish 】
Add a lifecycle rule to the bucket that has been created :
You can add one or more lifecycle rules to a bucket , To manage the life cycle of objects .
Lifecycle rules can be used to archive or delete objects after a given date , Can help put S3 Objects are archived to Glacier.
Add a lifecycle rule to move objects to Glacier:
1.【s3】— Select a bucket that has been created -----【 management 】----【 Life cycle 】-----【 Add lifecycle rule 】
2. Complete the wizard settings for the lifecycle rule :
First step : Select the goal of the lifecycle rule , Enter the rule name , Leave the text box of the filter blank , To apply lifecycle rules to the entire bucket , Click next
The second step : Configure lifecycle rules , choice 【 current version 】 For the configured conversion target , Click on 【 Add transformation 】, choice 【 The switch to Glacier Pass by before …】. In order to trigger the life cycle rule transformation as soon as possible to archive the object once it is created , Select Create in object 0 Convert after days
The third step : skip , Click directly to next
Step four : After checking the details of the rules , Click on 【 preservation 】
test Glacier And lifecycle rules
Test the lifecycle management rule you just created , It will automatically change the object from S3 The bucket is transferred to Glacier.
Be careful : Move object to Glacier It will probably cost 24h About time , from Glacier Recover data to S3 Probably need 3-5h.
Select a bucket , Click on 【 Upload 】 To upload files to the bucket .
By default , All files are saved in 【 standard 】 Storage class , This means that they are currently stored in S3 in .
Lifecycle rules will move objects to Glacier. But even if the time is set to 0 God , The move process will still require 24h about .
When the object is moved to Glacier after , The storage category will be switched to Glacier.
Users cannot download directly stored in Glacier Documents in , But it can trigger a 【 Restore storage 】 The process comes from Glacier Restore objects to S3.
Use the following steps to trigger the recovery operation in the management console :
【s3 bucket 】— Select what you want from Glacier Restore the object and click 【 more 】---- choice 【 Start restore 】— In the pop-up dialog box, select the object from Glacier After recovery, keep it in S3 Days of , Select the speed item to retrieve ( Standard search 3-5h)— Click on 【 Restore 】 To initiate a recovery ---- Recovering objects will probably require 3-5h, After the recovery , Can download objects
utilize Web GUI Clean up resources : Delete your own bucket
Store objects programmatically
S3 Can pass HTTPS and API visit , This means that users can integrate S3 Into the application , Call by program API To submit a request to S3.
Amazon S3 REST API Introduction :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/AmazonS3/latest/API/Welcome.html
Use S3 To achieve static website hosting
have access to S3 To serve a static website , And service static content , Such as :HTML,CSS, picture (PNG,JPG,JIF), Audio , Video etc. .
Can't be in S3 Execute server-side script ( Such as PHP or JSP), But it can be executed on the client side and stored in S3 Client script file on ( Such as Javascript).
adopt CDN(Content Delivery Network, Content distribution network ) To speed up the website :
Use CDN Help reduce the loading time of static website content .
CDN Distribute... Globally HTML,CSS And static content like pictures .
Once a user requests access to static content ,CDN Results can be returned to the user from the nearest location with minimal delay .
Amazon S3 Is not a CDN, But you can make S3 As AWS Of CDN The server :Amazon CloudFront Source server for .
Amazon CloudFront Accelerates distribution of static and dynamic Web Content ( for example ,.html、.css、.php、 Images and media files ) The process of . When a user requests content ,CloudFront Deliver content through a global network of edge sites that provide low latency and high performance .
file :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/cloudfront/?id=docs_gateway
S3 It also provides some functions of service static website :
- Specify custom index Documentation and error file
- Define redirection for all or specific page requests
- by S3 Bucket settings custom domain name
Use S3 Hosting static website content
Can be used later S3 As CloudFront Source server for , utilize CDN Accelerate the access speed of static websites .
1. Create a bucket and upload a static website
adopt CLI Create a new bucket :aws s3 mb s3://<bucket-name>
Now the bucket is empty , Next save a HTML Documents go in .
Use CLI( You can also use Web GUI, The management console )aws s3 cp $LocalPath/<htmlFileName> s3://<bucket-name>/<xxx.html>
2. Configure buckets to implement static website hosting
By default , Only the owner of the file can access S3 Bucket files .
Use S3 To provide static website services , You need to allow everyone to view or download the files in the bucket .
Bucket strategy It can be used to globally control the access rights of objects in the bucket .
The bucket strategy is similar to IAM Strategy .
IAM Strategy : Use JSON Define permissions , It contains one or more declarations , And a declaration allows or denies access to a resource by a specific operation .
Bucket strategy source code :https://s3.amazonaws.com/awsinaction/chapter7/bucketpolicy.json{ "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement":[ { "Sid":"AddPerm", "Effect":"Allow", // allow access to "Principal": "*", // anybody "Action":["s3:GetObject"], // To download objects "Resource":["arn:aws:s3:::$BucketName/*"] // From your bucket } ] }Use the following command to add a bucket policy to the bucket :
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket $BucketName --policy file://$PathToPolicy/bucketpolicy.json
Now all the objects in the bucket can be downloaded by anyone .
Next you need to activate and configure S3 Service static website :aws s3 website s3://$BucketName --index-document helloworld.html
The bucket is now configured as a static web site , Use helloworld As an index page .
3. visit S3 A static website hosted on
You can access the static website through the browser .
To select the correct endpoint now , Depending on the area where the bucket is located ,S3 The endpoints of static websites may also be different :$BucketName.s3-website-$Region.amzonaws.com
Now this bucket is created in the default areaus-east-1, So the input$BucketNameTo form the endpoint of the bucket , Replace$Regionbyus-east-1$BucketName.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com
Use a browser to open this URL You can see a Hello World Website .
4. Associate a custom domain name to s3 bucket
If the user does not want to use$BucketName.s3-website-$Region.amazonaws.comSuch a domain name is used as the domain name of a static website , Users can associate a custom domain name to S3 bucket .
Users only need to add one for their domain name CNAME Alias record , Let the record point to S3 The end point of the storage bucket .
CNAME Alias records only take effect when the following conditions are met :
- The bucket name must be the same as the alias record . for example : To create a CNAME to static.yourdomain.com, The bucket name must also be static.yourdomain.com.
- CNAME Alias records do not apply to the primary domain name . Resources that can create alias records for subdomains , Such as static or www A domain name with such a prefix . If you want to associate the primary domain name to s3 bucket , Need to use AWS Provided Route53 Of DNS service .
5. Resources to clean up
After completing the example, in order not to incur additional costs , Use the following code to clean up the resources used :aws s3 rb --force s3://$BucketName
The internal mechanism of object storage
S3 Storage is ultimately consistent .
Ensure data consistency
stay s3 To create a , Updating or deleting objects is an atomic operation : That is, if the user is creating , Read this object after updating or deleting , Never read invalid or half data . But it is possible that the read operation will only return the old data for a period of time .
s3 What's provided is ultimate consistency : If you upload a new version of an existing object , also s3 A success code is returned for the request , It means that the data has been safely stored in s3, however , Downloading the updated object immediately may still return to the old version . The updated version can only be obtained after a period of time .
After uploading new objects , Read requests submitted immediately will read consistent data , But the read request after update or deletion will return a final consistent result .
Select the appropriate key
For storage in S3 Select the appropriate key for the object on the : The name of the key determines which partition the key is saved in .
Using the same string at the beginning of the key for all objects will limit s3 The maximum size of the bucket I/O performance .
You should select a string with a different beginning for the object as the key , This will bring the greatest I/O performance .
namely : To improve I/O performance , Don't use the same string as the key
By adding... For each object's key Hash prefix Can make the beginning string of each key as different as possible , This helps to assign object keys to different partitions , So as to achieve the optimal I/O performance .
Use a slash in the key (/) The effect is like creating a directory for objects . If the key of the object created by the user is folder/object.png, When browsing buckets through a graphical interface such as the management console , The user will see the directory . But from the essence of Technology , The key of the object is still folder/object.png.
2. Store data on the hard disk :EBS And instance storage
Users are just like on personal computers , You can use a disk file system (FAT32,NTFS,ext3,ext4,XFS etc. ) And block level storage to store files .
Blocks are sequential bytes and the smallest addressing unit .
OS Between the application that needs to access the file and the underlying file system and block storage .
FS Responsible for managing where files are stored in the underlying block level ( Which block's address ).
Block level storage can only be used at run time OS Of EC2 Use .
OS By opening the , Write , read System calls are used to provide access to block level storage .
Simplified read request operation process :
- The application wants to read the file /path/to/file.txt, Then a read system call is submitted
- OS Forward a read request to FS
- FS hold /path/to/file.txt A block of data translated into a disk that stores data
database Such applications use system calls to read and write files , They must be able to access Block level storage to persist data . because MySQL You must use system calls to access files , So we can't put MySQL Of DB The file is stored in the object store ( Such as S3,Glacier).
AWS Provides two levels of block storage :
- Network Attached Storage ( High availability ): Attach to by network card EC2 example
- Instance store ( High performance ): Provide your EC2 The normal physical disk provided by the host system of the instance
Most of the time , Network attached storage is the best choice , Because it provides 99.999% The usability of , But instance storage provides better performance , Because the instance storage does not need a network , Use it directly EC2 The physical disk of the instance .
Network Attached Storage
EBS(Elastic Block Storage) Elastic block storage provides network attached , Block level storage , And to provide 99.999% The usability of .
How to be in EC2 Use EBS volume
EBS volume :
- EBS Volumes are independent resources , No EC2 Part of the example , But it can be attached to a EC2 Use , They are attached to by a network card EC2 example . If it ends EC2 example ,EBS The volume still exists .
- It can exist independently or be attached to a EC2 For instance
- It can be used like a normal disk
- Be similar to RAID1, Save data to multiple disks in the background
- You cannot mount one piece at the same time EBS Roll to multiple machines EC2 example
1. establish EBS Volume and mount to the server
EBS A volume is a separate resource , This means that it can be independent of EC2 Instance exists , But I need one EC2 The server can be used EBS volume .
The following is ruzai CloudFormation Create a with the help of EBS volume , And mount to a EC2 example ."Server": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance", "Properties": { [...] } }, "Volume": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Volume", //EBS Volume description "Properties": { "AvailabilityZone": {"Fn::GetAtt" ["Server", "AvailabilityZone"]}, "Size": "5", //5GB Capacity "VolumeType": "gp2" // be based on SSD } }, "VolumeAttachment": { // additional EBS Roll to EC2 example ( The server ) "Type": "AWS::EC2::VlomeAttachment", "Properties": { "Device": "/dev/xvdf", // Device name , Usually EBS The volume can be in /dev/xvdf To /dev/xvdp Find below . "instanceId": {"Ref": "Server"}, "VolumeId": {"Ref": "Volume"} } }2. Use elastic block storage
https://s3.amazonaws.com/awsinaction/chapter8/ebs.json Of CloudFormation Templates , Create a stack based on this template , Set up AttachVolume Parameter is yes, And then copy it Public-Name Output , And through SSH Connect .
UsefdiskThe command can see what has been attached EBS volume .
Usually EBS The volume can be in /dev/xvdf To /dev/xvdp Find below .
Root roll /dev/xvda It's an exception : Start up EC2 When an instance , It is based on the selected AMI establish , It also contains all the information used to boot the instance ( Operating system files ).sudo fdisk -l
Create a new EBS Volume time , You must create a file system on it .
You can also EBS Create different partitions on the volume , But the partition does not use EBS Best practices for volumes .
You should create a volume of the same capacity size as the demand , In the case of two separate partitions , It is more appropriate to create two volumes directly .
stay Linux in , have access tomkfsCommand to create a file system .
The following example creates a ext4 File system :sudo mkfs -t ex4 /dev/xvdf
After the file system is created , You can mount the file system to a directory :sudo mkdir /mnt/volume/sudo mount /dev/xvdf /mnt/volume/
Usedf -hThe command can view the mounted volumes
EBS One of the biggest advantages of volume : They don't belong EC2 example , Is an independent resource ( This feature enables stateless servers ).
We can save the file to EBS volume , Then remove the mount , And from EC2 Remove the volume from the , So you can see that it is independent of EC2 Characteristics of :sudo touch /mnt/volume/testfilesudo umount /mnt/volume/
Update now CloudFormation Stack , modify AttachVolume Parameter is no, This operation will start from EC2 Take it off EBS volume , After stack update ,EC2 Only the system root volume is left on the .sudo fdisk -l
/mnt/volume/ There are no test files in :ls /mnt/volume/
Now re mount EBS Roll to EC2 example : change CloudFormation Stack , And modify it AttachVolume Parameter is yes.
After the update is complete ,/dev/xvdf You can visit again :sudo mount /dev/xvdf /mnt/volume/ls /mnt/volume/testfile
CloudFormation
The design :
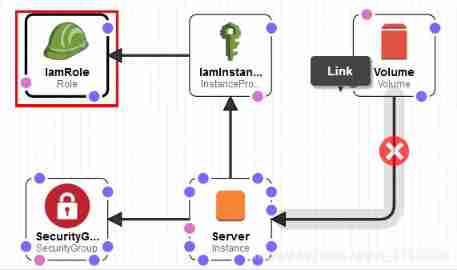
IamRole(AWS::IAM::Role)"IamRole": { "Type": "AWS::IAM::Role", "Properties": { "AssumeRolePolicyDocument": { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": [ "ec2.amazonaws.com" ] }, "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole" ] } ] }, "Path": "/", "Policies": [ { "PolicyName": "ec2", "PolicyDocument": { "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:DescribeVolumes", "ec2:CreateSnapshot", "ec2:DescribeSnapshots", "ec2:DeleteSnapshot" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } } ] }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "c4bf970b-5ecd-429f-96f9-af91bfe1f21d" } } },IamInstanceProfile(AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile)
"IamInstanceProfile": { "Type": "AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile", "Properties": { "Path": "/", "Roles": [ { "Ref": "IamRole" } ] }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "09d2b1eb-9208-4747-bc95-77f1dbf00e16" } } },SecurityGrop(AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup)
"SecurityGroup": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup", "Properties": { "GroupDescription": "My security group", "VpcId": { "Ref": "VPC" }, "SecurityGroupIngress": [ { "CidrIp": "0.0.0.0/0", "FromPort": 22, "IpProtocol": "tcp", "ToPort": 22 } ] }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "0e2bac9c-7411-4e1f-a69e-e0ac3d7f2b64" } } },Server(AWS::EC2::Instance)
"Server": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance", "Properties": { "IamInstanceProfile": { "Ref": "IamInstanceProfile" }, "ImageId": { "Fn::FindInMap": [ "EC2RegionMap", { "Ref": "AWS::Region" }, "AmazonLinuxAMIHVMEBSBacked64bit" ] }, "InstanceType": "t2.micro", "KeyName": { "Ref": "KeyName" }, "SecurityGroupIds": [ { "Ref": "SecurityGroup" } ], "SubnetId": { "Ref": "Subnet" } }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "1c8d95d3-6952-4c57-a08d-3ae4cbe0fd7b" } } },Volume(AWS::EC2::Volume)
"Volume": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Volume", "Properties": { "AvailabilityZone": { "Fn::GetAtt": [ "Server", "AvailabilityZone" ] }, "Size": "5", "VolumeType": "gp2" }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "a59cfe7b-622c-4a85-a281-c3aeae14d395" } } },3. performance
The test performance of hard disk is usually divided into read operation and write operation .
Users can use many different tools to test , A simple tool isdd, It can be done by specifying the data source if=/ To source path and The goal is of=/ To the target path To perform block level read / write tests .sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/volume/tempfile bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync,notruncEvery time 1M, Conduct 1024 Write test for the first timeecho 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_cachesCache empty to disksudo dd if=/mnt/volume/tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024Every time I read 1M, Conduct 1024 First reading test
EBS Volumes are more complex : Storage performance depends on EC2 Instance type and EBS Type of volume .
Depending on the workload , You need to choose one that can provide enough bandwidth EC2 Instance type , in addition EBS The volume must be able to make full use of EC2 Bandwidth provided .
No matter how much capacity is used ,EBS The volume is charged according to the volume capacity .
If you are using physical disks , For each time I/O Operation fee .
If preconfigured IOPS The performance of the EBS volume (SSD disk ), It also needs to be pre configured IOPS Performance payment .
It is recommended to use the general... By default SSD disk , If the workload requires more IOPS performance , Preconfigured... Is recommended IOPS The performance of the SSD disk .
Users can attach multiple EBS Roll into a EC2 Instance to increase capacity or overall performance , But one EBS Volumes can only be mounted to one at the same time EC2 example .
You can put more than one EBS Mount volumes to the same machine EC2 example , And use the software RAID0 To improve performance .RAID0 Technology enables data to be spread across multiple disks , But the same data is stored on only one disk , stay Linux Can be used inmdadmTo create software RAID
4. The backup data
EBS Volume provision 99.999% The usability of , But it still needs to back up data from time to time ( It is particularly important for the banking system )
EBS Volumes provide optimized, easy-to-use snapshot capabilities to back up EBS Volume data .
Snapshots are stored in S3 Block level data replication on .
EBS The charge for snapshots of a volume depends on the GB Capacity .
If the volume size is 5GB, And it holds 1GB The data of , The size of the first snapshot is 1GB about , After the first snapshot is created , Only the changed data will be saved in S3, To save backup capacity .
Snapshot creation :
Before creating a snapshot, you need to obtain EBS Roll up ID, Can be in CloudFormation Found in the output of VolumeId volume ID, Or by CLI Run the following command :aws --region us-east-1 ec2 describe-volumes --filters "Name=size,Values=5" --query "Volumes[].VolumeId" --output text
With a roll ID, Then you can create a snapshot :aws --region us-east-1 ec2 create-snapshot --volume-id $VolumeId
Depending on the size of the volume and the amount of data changed , The time to create the snapshot is also different , Use the following command to view the status of the snapshot :aws --region us-east-1 ec2 describe-snapshots --snapshot-ids $SnapshotId
It can be used in a that is already mounted and in use EBS Create a snapshot on the volume , But if there is still data in the memory cache that has not been written to the disk , This may cause some problems , If you have to EBS Create snapshots when the volume is in use , You can use the following steps to create a snapshot safely :
- Run on the server
fsfreeze -f /mnt/volumeCommand to freeze all writes- Create a snapshot
- Use
fsfreeze -u /mnt/volumeCommand to resume the write operation- Wait for the snapshot operation to complete
Users only need to freeze when they start requesting snapshot creation I/O.
From a AMI(AMI It's a snapshot ) establish EC2 When ,AWS Use EBS Snapshot to create a new EBS volume ( Root roll )
To recover the data in the snapshot , You must create a new one based on the snapshot EBS volume . When the user from AMI To create a EC2 When an instance ,AWS Create a new... Based on a snapshot EBS volume .
Deleting snapshots :aws --region us-east-1 ec2 delete-snapshot --snapshot-id $SnapshotId
At the end of this section, you also need to delete the entire stack to clean up all used resources , Otherwise, you will pay for the resources you use .
Instance store
Instance storage provides block level storage like physical disks .
The instance store is EC2 Part of ( Therefore, stateless servers cannot be implemented ), And only in EC2 Available only when the instance is running normally . If the instance is stopped or terminated , The above data will not be persisted , So you don't need to pay for instance storage separately , The price of instance storage is included in EC2 Example price .
And mount on the Internet EC2 Upper EBS Different volumes , The instance store is contained in the virtual server , There is no virtual server .
Do not use instance storage to store data that cannot be lost , Use it to store the cache , Temporary data and some applications that replicate data between multiple nodes, such as some DB. If you use NoSQL DB, Applications are likely to be responsible for replicating data , In this way, users can safely use instance storage to obtain the highest I/O performance .
Be careful : If the user stops or terminates his own EC2 example , The data on the instance store will be lost , This means that the user's data will be deleted and cannot be recovered .
AWS Provide SSD And physical disk instance storage .
adopt Web GUI(AWS console,AWS Console ) To create an instance store EC2 example :
- Open console , function EC2 Instance creation wizard
- complete 1-3 Step
- In the 4 Step is to configure the instance store : Click on 【 Add new volume 】, The rest can be set by default .
- complete 5-7 Step : Tag instances , Configure security groups , Check and start the instance
Now? EC2 Instances can be stored using instances .
Use CloudFormation To create an instance store
If the user starts EBS The volume is the root volume EC2 example ( Default ) User must define BlockDeviceMappings To map EBS Volumes and instances are stored to specific device names .
And the creation of EBS The template of the volume is different , Instance storage is not a standard independent resource , The instance store is EC2 Part of : Depending on the instance type , You can choose 【0-n】 Instances are stored as mappings ."Server": { "Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance", "Properties": { "InstanceType": "m3.medium", [...] "BlockDeviceMappings": [{ "DeviceName": "/dev/xvda", //EBS Root roll , Deposit OS file "Ebs": { "VolumeSize": "8", "VolumeType": "gp2" } },{ "DeviceName": "/dev/xvdb", // The instance store will be displayed as /dev/xvdb Device file "VirtualName": "ephemeral0" // The virtual name of the instance store is ephemeral0 or ephemeral1 }] } }1. Use instance storage
https://s3.amazonaws.com/awsinaction/chapter8/instance_store.json Use this CloudFormation Template creation stack , Copy PublicName Output , And use SSH Log in to EC2 example , have access to fdisk Command to view the mounted instance store . Usually, instance storage can be done in /dev/xvdb To /dev/xvde Found in device file .sudo fdisk -lView the mounted instancedf -hView mounted volumes
The instance store will be automatically mounted to /media/ephemeral0 Under the table of contents .
If EC2 Instances have multiple instance stores , Will be mounted to ephemeral1,ephemeral2 Wait for the directory .
2. Performance testing
Use the same performance tests to compare instance storage with EBS volumesudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/media/ephemeral0/temfile bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync,notruncEBS Triple read performancesudo dd if=/media/ephemeral0/tempfile of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024EBS Quadruple write performance
Instance storage is like an ordinary disk , The performance is similar to that of an ordinary disk .
3. The backup data
The instance storage volume has no built-in method to back up data , have access to liunx Scheduled tasks in cron Orders and AWS S3 Combine to back up data regularly .aws s3 sync /path/to/data s3://<bucketName>/<fileName>
If you need to back up the data stored by the instance , Probably persistent EBS Volume would be a more appropriate choice , Instance storage is more suitable for data that does not require high data persistence .
Compare block storage solutions :S3,EBS( Network Attached Storage ), Instance store
| S3 | EBS | Instance store | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common use scenarios | Integrated into the application to save the content uploaded by the user | For those that require block level storage DB Or traditional applications provide persistence | Provide temporary data storage or high-performance storage for applications with built-in replication technology to prevent data loss |
| Independent resources | yes | yes | no |
| How to access data | HTTPS API | EC2 example / system call | EC2 example / system call |
| Whether there is a file system FS | nothing | Yes | Yes |
| Prevent data loss | Very high | high | low |
| Every time GB Capacity cost | in | high | low |
| O & M costs | nothing | low | in |
Use instances to store and EBS Volume provides sharing FS
Use only AWS The block level storage solution provided cannot solve the following problems : At the same time in multiple EC2 Shared block storage between instances .
Users can use the network file system NFS(Network File System) Agreement to solve the problem .
Amazon Elastic File System
file :https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/efs/?id=docs_gateway
EFS Is a distributed file storage system , Based on the fourth edition of network file system (Network File System Version 4,NFSv4) agreement . Users can use EFS To solve the need to share data blocks among multiple servers .
3. Use relational database services :RDB
*====*
4. Use NoSQL Database services :DynamoDB
*====*
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Do you know TCP protocol (2)?

三角变换公式
![[learning notes] shortest path + spanning tree](/img/38/42b7e321389e3a47304fca5c37a2cf.png)
[learning notes] shortest path + spanning tree

安装nrm后,使用nrm命令报错internal/validators.js:124 throw new ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE(name, ‘string‘, value)

Little artist huangxinyang was invited to participate in the Wuhan station of children's unit of Paris Fashion Week

Usage record of Xintang nuc980: self made development board (based on nuc980dk61yc)
Unity 获取当前物体正前方,一定角度、距离的坐标点

城联优品向英德捐赠抗洪救灾爱心物资
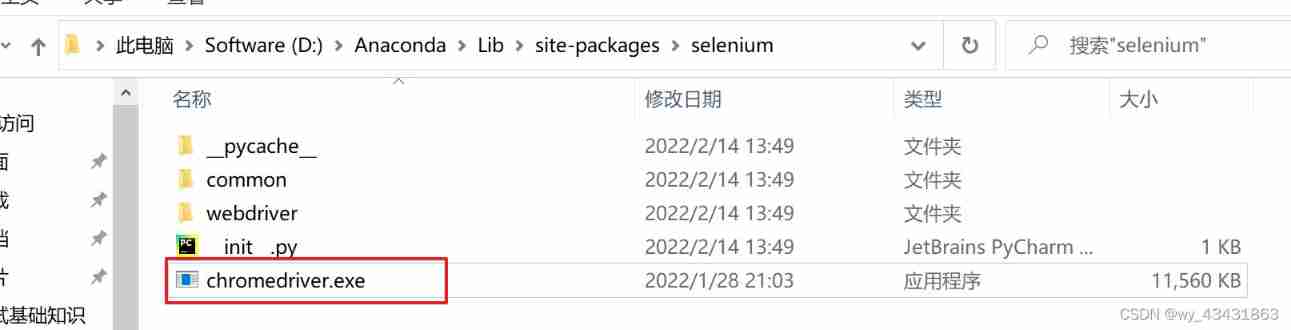
Solution: selenium common. exceptions. WebDriverException: Message: ‘chromedriver‘ execu

设置网页的标题部分的图标
随机推荐
找合适的PMP机构只需2步搞定,一查二问
Prometheus service discovery
duilib 入门基础十二 样式类
Discussion on the application of GIS 3D system in mining industry
Redis02 -- an operation command of five data types for ending redis (it can be learned, reviewed, interviewed and collected for backup)
The maximum number of Rac open file descriptors, and the processing of hard check failure
Estimation of SQL execution cost by MySQL query optimizer
Installing MySQL under Linux
npm清理缓存
B_QuRT_User_Guide(27)
On the solution of insufficient swap partition
Oracle RAC -- understanding of VIP
NLP sequence can completely simulate human brain intelligence
Vagrant installation
【学习笔记】拟阵
Jenkins' common build trigger and hook services (V)
ROS notes (08) - definition and use of service data
Little artist huangxinyang was invited to participate in the Wuhan station of children's unit of Paris Fashion Week
B_QuRT_User_Guide(28)
B_ QuRT_ User_ Guide(30)