当前位置:网站首页>Understanding of "dof: a demand oriented framework for imagedenoising"
Understanding of "dof: a demand oriented framework for imagedenoising"
2022-07-26 00:16:00 【RrS_ G】
translate :"DOF: Demand oriented image denoising framework "
-- IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics -- 2021
Catalog
One 、 introduction
Most image denoising algorithms focus on maximizing the quality of image denoising , There is still considerable room to reduce the number of parameters and computational complexity . When facing different tasks , For the number of parameters 、 The requirements of computational complexity and denoising quality are different . In order to overcome this problem , The author of this paper proposes a flexible demand-oriented framework (DOF), By selecting the appropriate super parameters in the training stage , Generate one that can be prioritized The number of arguments 、 Computational complexity and Denoising quality Controllable model of .
The structure of the method in this paper includes a Scale encoder , One Shunt module And a Scale decoder .
Two 、 Method
The author proposes a demand oriented framework , To achieve the following three goals :
(1)、 Demand orientation : According to the application scenario , be based on DOF Denoising can balance the above three performance indicators .
(2)、 universality : The framework can be applied to other systems based on CNN De-noising model , Through this framework , Reconstructing the model can reduce the number of parameters , Improve computational efficiency .
(3)、 Robustness : When the proposed framework is applied to other models to reduce the computational complexity and the number of parameters , The denoising model reconstructed based on the proposed framework should achieve similar performance to the original model in terms of denoising quality .
A、 Demand oriented framework
The image degradation model can be expressed as :

among x It's a clean image ,y Indicates noise observation ,v It's additive noise .
DOF The model estimates the noise map by the following formula :
![]()
Besides , In order to improve the calculation efficiency and reduce the number of parameters ,DOF With the help of the scale decoder , Transform the estimation of the whole noise map into the estimation of several smaller noise maps . therefore , Each sub noise map is estimated using a scale encoder and a shunt module .
(1)、 Scale encoder : First step , The step size of the scale encoder is 1 Convolution layer to extract features , Find useful and redundant information ; The second step , Use steps of 2 The convolution layer reduces the scale of the feature , Reduce spatial redundant information with the help of training process . such , This method achieves the effect of denoising with low computational complexity . As shown in Table 1 , The effect of this scheme is better .

In order to make the network more controllable , The author introduces a scale factor  To control the space size of shallow features ,j Represents the number of convolution layers in the scale encoder . Given a size of W x H, The scale factor is S Observed image of y, The scale encoder discards the spatial redundancy information , Extract shallow features :
To control the space size of shallow features ,j Represents the number of convolution layers in the scale encoder . Given a size of W x H, The scale factor is S Observed image of y, The scale encoder discards the spatial redundancy information , Extract shallow features :

(2)、 Shunt module : Structure is shown in figure 1 (b) Shown .

It consists of several simple network branches , Its number is determined by the super parameter G To configure . Each branch takes part of the extracted shallow features as input , Further extract deep features through several layers of convolution . Generally speaking , Network branches can adopt different structures , The structure of each branch can be a low complexity version of any existing denoising model . Given size is  Shallow features of f, The shunting module first divides it into a given group
Shallow features of f, The shunting module first divides it into a given group  . Then these shallow features are fed back to G A network branch . This process is expressed as :
. Then these shallow features are fed back to G A network branch . This process is expressed as :

In each network branch , Introduce a capacity ratio R To control the amount of data found . Let the information found by each branch flow across all branches . Pictured 2 Shown ,

Each network branch divides the discovered information into G Group . then , It keeps a set of original information , Let other information flow between each branch . Please note that , Information flow operation emphasizes information sharing . After information flow operation , The restructured information can be expressed as :

then , The next feature extractor of each branch network takes the reorganized information as input , Update depth feature I. Operate through information flow , The information of one network branch will be shared with other network branches . therefore , Each network branch can utilize all the information from different network branches , Although the input of a network branch only accounts for a small part of the whole information . Last , The shunting module uses the depth feature to estimate the subnoise map :
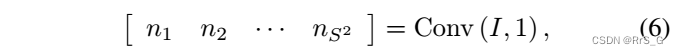
The left side of the equation is the output of the network , Represent subnoise graph .
Note that this information flow operation does not require additional learnable parameters and floating-point operations .
(3)、 Scale decoder : The goal of the scale decoder is to generate a final noise image with the same size as the input noise image , Use the subnoise graph with size to reconstruct the noise graph with size H × W The noise map of . Pictured 1(a) Shown , The scale decoder rearranges the pixels of the sub noise map to the spatial dimension of the noise map . Give stator noise diagram , Reconstruct the final noise map through the following formula  :
:

there E Indicates the decoder .
Note that the proposed scale decoder does not require any learnable parameters . The scale decoder propagates the error back to each subnoise map , Make the prediction of noise mapping learnable .
B、 be based on DOF Network of
DOF There are three important hyperparameters : The scaling factor S, Number of branches G, Capacity ratio R. The author formulates different networks according to the choice of these three parameters , There were :parameter-oriented DONet (DONet-P),computation-oriented DONet (DONet-C), quality-oriented DONet (DONet-Q), and balanced DONet (DONet-B). seeing the name of a thing one thinks of its function , The requirements of each network are different . Then the optimization objectives are as follows :

3、 ... and 、 experiment
Here are some experimental results :
边栏推荐
- “动物币”凶猛,陷阱还是机遇?2021-05-12
- Binary tree related knowledge
- Binary tree -- 222. Number of nodes of a complete binary tree
- Jd.com searches for product API instructions by keyword
- MySQL——数据库日志
- Get JD product details original data API
- appium 从启动到测试再到结束流程梳理
- Binary tree -- 111. Minimum depth of binary tree
- Binary tree -- 104. Maximum depth of binary tree
- 测试7年,面试华为最后面议要薪1万,HR说我不尊重华为,他们没有那么低薪资的岗位~
猜你喜欢

痞子衡嵌入式:MCUXpresso IDE下将源码制作成Lib库方法及其与IAR,MDK差异

对“DOF: A Demand-oriented Framework for ImageDenoising“的理解

MPLS实验
Binary tree - 617. Merge binary tree

Piziheng embedded: the method of making source code into lib Library under MCU Xpress IDE and its difference with IAR and MDK

软件测试同行评审到底是什么?

MySQL——数据库日志

Thymeleaf view integration

【论文笔记】—目标姿态估计—EPro-PnP—2022-CVPR

MySQL - database log
随机推荐
京东按关键字搜索商品 API 的使用说明
Binary tree 101. Symmetric binary tree
什么是 Web3 游戏?
Stack and queue - 239. Sliding window maximum
Js理解之路:Object.call与Object.create()实现继承的原理
appium 从启动到测试再到结束流程梳理
12.神经网络模型
C语言 预处理详解
计算物理期刊修改
Thymeleaf view integration
Stm32- analyze latency based on assembly
Js理解之路:Js常见的6中继承方式
C语言实战之猜拳游戏
LeetCode 刷题系列 -- 931. 下降路径最小和
Stack and queue - 150. Inverse Polish expression evaluation
Cherish time and improve efficiency
链表相关方法
通货膨胀之下,后市如何操作?2021-05-14
合肥提前批
J9 number theory: what is Dao mode? Obstacles to the development of Dao