当前位置:网站首页>A summary of PostgreSQL data types. All the people are here
A summary of PostgreSQL data types. All the people are here
2022-06-23 04:06:00 【It bond】
hello ! Hello everyone , I am a 【IT bond 】, Jianghu people jeames007,10 year DBA Work experience
A highly motivated 【 Bloggers in big data field 】!
China DBA union (ACDU) member , Currently engaged in DBA And program programming ,B Station and Tencent classroom lecturer , Live broadcast volume breaking 10W
Good at mainstream data Oracle、MySQL、PG Operations and development , Backup recovery , Installation migration , performance optimization 、 Fault emergency treatment, etc .
If there is a pair of 【 database 】 Interested in 【 Cutie 】, Welcome to your attention 【IT bond 】
️️️ Thank you, big and small !️️️
List of articles
- Preface
- ️ 1. value type
- ️ 2. Type of currency
- ️ 3. Character type
- ️ 4. date / Time type
- ️ 5. Boolean type
- ️ 6. Enumeration type
- ️ 7. Enumeration type
- ️ 8. Network address type
- ️ 9. Bit string type
- ️10. Text search type
- ️11.UUID type
- ️12.XML type
- ️13.JSON type
- ️14. An array type
- ️15. The compound type
- ️16. Range type
- ️17. Object identifier type
- ️18. Pseudo type
Preface
This paper deals with PostgreSQL The data types are summarized comprehensively , I hope that's helpful️ 1. value type
The following table lists them PostgreSQL Supported numeric types

postgres=# create table jem (id serial ,name varchar(20));
postgres=# insert into jem(name) values(‘IT bond ’);

️ 2. Type of currency
money Type stores monetary amounts with fixed decimal precision .
numeric、int and bigint The value of type can be converted to money,
Floating point numbers are not recommended to handle currency types , Because there is the possibility of rounding errors .
name storage capacity describe Range
money 8 byte The amount of money -92233720368547758.08 To +92233720368547758.07
️ 3. Character type
PostgreSQL Supported character types :
Serial number name & describe
1 varchar(n) Lengthening , Limited length
2 character(n), char(n) Fixed length , Fill in the blanks
3 text Lengthening , No length limit
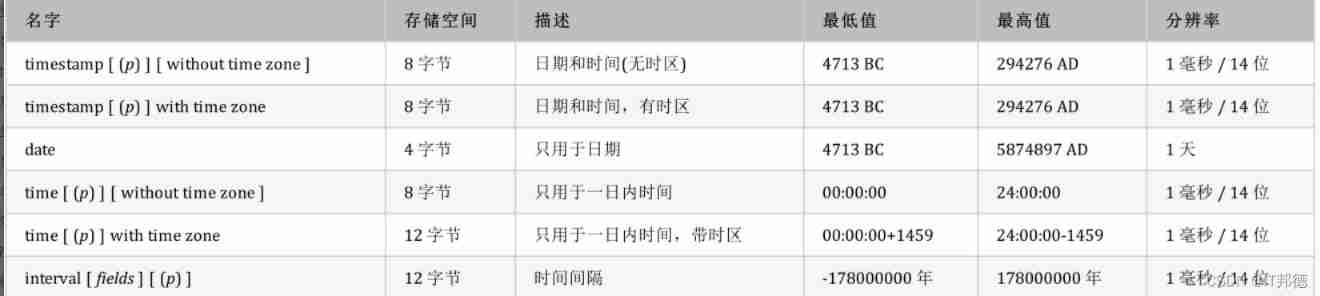
️ 4. date / Time type
The following table lists them PostgreSQL Supported date and time types
️ 5. Boolean type
PostgreSQL Supporting the standard boolean data type .
boolean Yes "true"( really ) or "false"( false ) Two states ,
The third kind of "unknown"( Unknown ) state , use NULL Express .

️ 6. Enumeration type
An enumeration type is a data type that contains an ordered collection of static and values .
PostgtesSQL The enumeration types in are similar to C In language enum type .
Unlike other types, enumeration types need to use CREATE TYPE Command to create
postgres=# CREATE TYPE mood AS ENUM ('sad', 'ok', 'happy');
Create a few days of the week , As shown below :
postgres=# CREATE TYPE
week AS ENUM ('Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun');
Just like other types , Once created , Enumeration types can be used for table and function definitions .
postgres=# CREATE TABLE person (
name text,
current_mood mood
);
postgres=# INSERT INTO person VALUES ('Moe', 'happy');
postgres=# SELECT * FROM person WHERE current_mood = 'happy';

️ 7. Enumeration type
Geometric data types represent two-dimensional planar objects .
The following table lists them PostgreSQL Supported geometry types .
Most basic types : spot . It is the basis of other types .

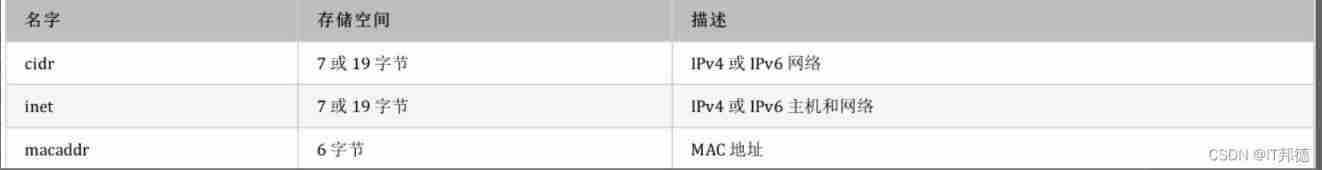
️ 8. Network address type
PostgreSQL Provide for storage IPv4 、IPv6 、MAC Data type of address .
Using these data types to store network addresses is better than using plain text types ,
Because these types provide input error checking and special operations and functions
️ 9. Bit string type
A bit string is a string 1 and 0 String . They can be used to store and visualize bitmasks .
We have two kinds of SQL A type of :bit(n) and bit varying(n), there n Is a positive integer .
bit Data of type must exactly match the length n, Trying to store shorter or longer data is wrong .
bit varying Type data is the longest n Variable length type of ; Longer strings will be rejected . Write a without length bit Equivalent to bit(1),
Having no length bit varying It means no length limit .
️10. Text search type
Full text retrieval is to find those searches that match a query through the collection of natural language documents .
PostgreSQL Two data types are provided to support full-text retrieval :

️11.UUID type
uuid Data types are used to store RFC 4122,ISO/IEF 9834-8:2005 And the universal unique identifier defined by relevant standards (UUID). ( Some systems consider this data type to be a globally unique identifier , or GUID.)
This identifier is generated by an algorithm 128 Bit identifier ,
Make it impossible for it to use the same algorithm in a module known to use the same identifier as that generated in other ways .
therefore , For distributed systems , This identifier can provide better uniqueness guarantee than sequence ,
Because sequences can only be guaranteed to be unique in a single database .
UUID Written as a sequence of lowercase hexadecimal digits , Divided into groups by characters ,
Especially a group 8 Digit number +3 Group 4 Digit number + A group of 12 Digit number , in total 32 A number stands for 128 position ,
One such standard UUID Examples are as follows :
a0eebc99-9c0b-4ef8-bb6d-6bb9bd380a11
️12.XML type
xml Data types can be used to store XML data .
take XML Data stored in text The advantage of type is that it can check the input value for well structured ,
And it also supports functions to check its type security .
To use this data type , Compile with configure --with-libxml.
xml Can be stored by XML The standard definition is well formed " file ",
And by XML Standard XMLDecl? content Defined " Content " fragment , In general ,
This means that content fragments can have multiple top-level elements or character nodes .
xmlvalue IS DOCUMENT Expressions can be used to determine a particular xml Is the value a complete file or a fragment of content .
Using functions xmlparse: To generate... From character data xml Type value :
XMLPARSE (DOCUMENT '<?xml version="1.0"?>
<book><title>Manual</title><chapter>...</chapter></book>')
XMLPARSE (CONTENT 'abc<foo>bar</foo><bar>foo</bar>')
️13.JSON type
json Data types can be used to store JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) data ,
Such data can also be stored as text,
however json The data type makes it easier to check that each stored value is available JSON value .
In addition, there are related functions to deal with json data :

️14. An array type
PostgreSQL Allows fields to be defined as multidimensional arrays of variable length .
The array type can be any basic type or user-defined type , Enumeration type or composite type .
14.1 Declaration array
When creating a table , We can declare arrays , The way is as follows :
#pay_by_quarter Is a one-dimensional integer array 、schedule An array of two-dimensional text types .
postgres=# CREATE TABLE sal_emp (
name text,
pay_by_quarter integer[],
schedule text[][]
);
## We can also use “ARRAY” keyword
postgres=# CREATE TABLE sal_emp (
name text,
pay_by_quarter integer ARRAY[4],
schedule text[][]
);
14.2 Insert value
# Insert values using curly braces {}, The elements are in {} Separated by commas :
postgres=# INSERT INTO sal_emp VALUES (‘Bill’,
‘{10000, 10000, 10000, 10000}’,
‘{ {“meeting”, “lunch”}, {“training”, “presentation”}}’);
postgres=# INSERT INTO sal_emp
VALUES (‘Carol’,’{20000, 25000, 25000, 25000}’,
‘{ {“breakfast”, “consulting”}, {“meeting”, “lunch”}}’);

14.3 Access array
Now we can run some queries on this table .
First , We show how to access an element of an array . This query retrieves the names of employees whose salaries changed in the second quarter :
postgres=# SELECT name FROM sal_emp WHERE pay_by_quarter[1] <> pay_by_quarter[2];

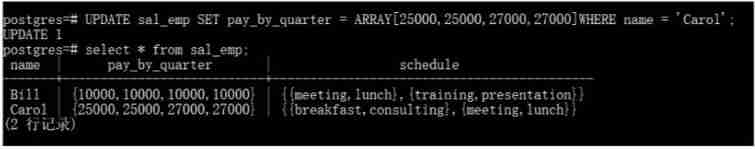
14.4 Modify array
## We can modify the value of the array :
postgres=# UPDATE sal_emp SET pay_by_quarter = ‘{25000,25000,27000,27000}’
WHERE name = ‘Carol’;
## Or use ARRAY Constructor Syntax
UPDATE sal_emp SET pay_by_quarter = ARRAY[25000,25000,27000,27000]
WHERE name = ‘Carol’;
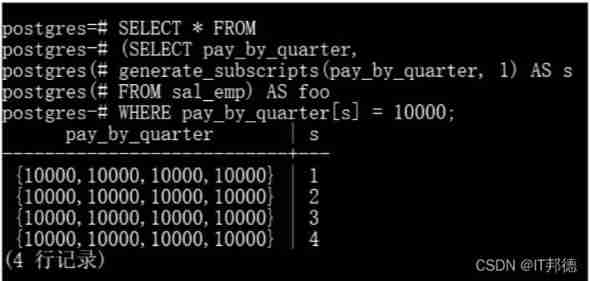
14.5 Retrieve... From the array
## To search for values in an array , You must check every value of the array
SELECT * FROM sal_emp WHERE pay_by_quarter[1] = 10000 OR
pay_by_quarter[2] = 10000 OR
pay_by_quarter[3] = 10000 OR
pay_by_quarter[4] = 10000;
## in addition , You can use the following statement to find out that the values of all elements in the array are equal to 10000 The line of :
SELECT * FROM sal_emp WHERE 10000 = ALL (pay_by_quarter);
️15. The compound type
A composite type represents the structure of a row or a record ;
It's actually just a list of field names and their data types .
PostgreSQL Allow composite types to be used like simple data types .
such as , A field of a table can be declared as a composite type .
️16. Range type
The range data type represents the value of an element type within a certain range .
for example ,timestamp The range may be used to represent the time range within which a conference room is scheduled .
PostgreSQL The built-in range types are :
int4range — integer The scope of the
int8range —bigint The scope of the
numrange —numeric The scope of the
tsrange —timestamp without time zone The scope of the
tstzrange —timestamp with time zone The scope of the
daterange —date The scope of the
Besides , You can define your own scope type :
CREATE TABLE reservation (room int, during tsrange);
INSERT INTO reservation VALUES
(1108, ‘[2010-01-01 14:30, 2010-01-01 15:30)’);
– contain
SELECT int4range(10, 20) @> 3;
– overlap
SELECT numrange(11.1, 22.2) && numrange(20.0, 30.0);
– Extract the upper boundary
SELECT upper(int8range(15, 25));
– Calculation crossover
SELECT int4range(10, 20) * int4range(15, 25);
– Whether the range is empty
SELECT isempty(numrange(1, 5));
️17. Object identifier type
PostgreSQL Use object identifiers internally (OID) As the primary key of various system tables .
meanwhile , The system will not add a to the table created by the user OID System fields ( Unless it is stated that WITH OIDS Or configure parameters default_with_oids Set to on ).oid Type represents an object identifier . in addition to oid There are several aliases :regproc, regprocedure, regoper, regoperator, regclass, regtype, regconfig, and regdictionary.

️18. Pseudo type
PostgreSQL The type system contains a series of special-purpose entries ,
They are called pseudo types by category . A pseudo type cannot be used as the data type of a field ,
But it can be used to declare the parameter or result type of a function .
Pseudo types in a function do not simply accept and return some kind of SQL Useful in the case of data types .
The following table lists all pseudo types :

Everybody likes it 、 Collection 、 Focus on 、 Comments WeChat official account
边栏推荐
- [OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 construction 4: Construction and link of third-party databases p2pmfc exe
- Full analysis of embedded software testing tool tpt18 update
- 仿360桌面悬浮球插件
- How to realize data transaction
- innodb_ruby 视角下 MySQL 记录增删改
- 如何保证应用程序的安全性
- The tax software exits when it detects that it is a virtual machine. How to solve this problem?
- Common events for elements
- Firewall and IP security policy configuration
- mysql能不能在linux中使用
猜你喜欢

mysql如何删除表的一行数据

AI 视频云 VS 窄带高清,谁是视频时代的宠儿

MySQL common instructions
One of the touchdesigner uses - Download and install
![[OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 construction 4: Construction and link of third-party databases p2pmfc exe](/img/cd/7f896a0f05523a07b5dd04a8737879.png)
[OWT] OWT client native P2P E2E test vs2017 construction 4: Construction and link of third-party databases p2pmfc exe
线上MySQL的自增id用尽怎么办?

AI video cloud vs narrowband HD, who is the favorite in the video Era

mysql常用指令

第一批00后下场求职:不要误读他们的“不一样”

浅析2022年物联网现状
随机推荐
Talk about memory model and memory order
怎么使用Shell脚本实现监测文件变化
How to solve the problem that the web page fails to log in after the easycvr service is started?
SVG+JS智能家居监控网格布局
电商如何借助小程序发力
Full analysis of embedded software testing tool tpt18 update
Google Earth Engine(GEE)——长时间序列逐月VCI数据提取分析和面积计算(墨西哥为例)
[JS reverse hundreds of cases] the login of a HN service network is reverse, and the verification code is null and void
[Zeng shuge's laser slam notes] gmapping filter based slam
Select sort method
1-1 introduction to VMWare
[machine learning] wuenda's machine learning assignment ex2 logistic regression matlab implementation
直接插入排序
What is the difference between the poll () method and the remove () method?
R tree of search tree
For patch rollback, please check the cbpersistent log
1-1VMware介绍
冒泡排序法
Why APP But Not WebPage
Which insurance company is the most cost-effective for purchasing serious illness insurance?