当前位置:网站首页>Machine learning (zhouzhihua) Chapter 2 model selection and evaluation notes learning experience
Machine learning (zhouzhihua) Chapter 2 model selection and evaluation notes learning experience
2022-07-24 05:51:00 【Ml -- xiaoxiaobai】
The first 2 Chapter Model selection and evaluation The learning
A few nouns
Error rate (error rate)
The proportion of misclassified samples in the total samples
precision (accuracy)
The ratio of the number of correctly classified samples to the total number of samples ;
be equal to 1 subtract Error rate
Confusion matrix (confusion matrix)
The first line represents a real positive example , The second line represents a real counterexample ; The first column represents the positive example of model prediction , The second column represents the counter example of the model prediction .
Real examples (true positive,TP)
True example , And it is judged as a positive example by the model . Confusion matrix (1,1) Elements .
False counter example (false negative,FN)
True example , But it was misjudged as a counterexample by the model . Confusion matrix (1,2) Elements .
False positive example (false positive,FP)
Real counterexample , But it was misjudged as a positive example by the model . Confusion matrix (2,1) Elements .
True counter example (true negative,TN)
Real counterexample , And is judged as a counterexample by the model . Confusion matrix (2,2) Elements .
Precision rate (precision,P)
Take information retrieval as an example , Namely “ How much of the retrieved information is of real interest to users ”, Or in the retrieved positive example , How many are real positive examples .
P = T P T P + F P P = \frac{TP}{TP + FP} P=TP+FPTP
Macro accuracy rate (macro-P)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , You can calculate their respective precision rates and then average , Get macro precision .
macro- P = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n P i \text { macro- } P=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} P_{i} macro- P=n1i=1∑nPi
Micro precision (micro-P)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , The average confusion matrix can be calculated , Then get the micro precision .
micro- P = T P ‾ T P ‾ + F P ‾ \text { micro- } P=\frac{\overline{T P}}{\overline{T P}+\overline{F P}} micro- P=TP+FPTP
Recall rate (recall,R)
Take information retrieval as an example , Namely “ How much of the information users are interested in has been retrieved ”, Or in the real positive example , What proportion is detected by the model .
R = T P T P + F N R = \frac{TP}{TP + FN} R=TP+FNTP
Macro recall (macro-R)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , You can calculate their recall rates and then average , Get macro recall .
macro- R = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n R i \text { macro- } R=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} R_{i} macro- R=n1i=1∑nRi
Micro recall (micro-R)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , The average confusion matrix can be calculated , Then get micro recall .
micro − R = T P ‾ T P ‾ + F N ‾ \operatorname{micro}-R=\frac{\overline{T P}}{\overline{T P}+\overline{F N}} micro−R=TP+FNTP
F β F_\beta Fβ
Performance evaluation based on comprehensive precision and recall (performance measure)
F β = ( 1 + β 2 ) × P × R ( β 2 × P ) + R F_{\beta}=\frac{\left(1+\beta^{2}\right) \times P \times R}{\left(\beta^{2} \times P\right)+R} Fβ=(β2×P)+R(1+β2)×P×R
among β > 0 \beta > 0 β>0, It shows the relative importance of recall ratio to precision ratio . When β < 1 \beta \lt 1 β<1 It means that the accuracy rate is more important , When β > 1 \beta \gt 1 β>1 Means recall is more important .
F 1 F_1 F1
When β = 1 \beta = 1 β=1, Precision is as important as recall , At this time F β F_\beta Fβ Turn into F 1 F_1 F1.
F 1 = 2 × P × R P + R = 2 × T P Total number of samples + T P − T N F 1=\frac{2 \times P \times R}{P+R}=\frac{2 \times T P}{\text { Total number of samples }+T P-T N} F1=P+R2×P×R= Total number of samples +TP−TN2×TP
In fact, it is the harmonic average of precision and recall :
1 F 1 = 1 2 ⋅ ( 1 P + 1 R ) \frac{1}{F 1}=\frac{1}{2} \cdot\left(\frac{1}{P}+\frac{1}{R}\right) F11=21⋅(P1+R1)
macro F 1 F_1 F1(macro- F 1 F_1 F1)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , You can calculate their precision and recall, and then , Then calculate the macro precision and macro recall , Finally get macro F 1 F_1 F1.
macro- F 1 = 2 × macro- P × macro − R macro- P + macro- R \text { macro- } F 1=\frac{2 \times \text { macro- } P \times \text { macro }-R}{\text { macro- } P+\text { macro- } R} macro- F1= macro- P+ macro- R2× macro- P× macro −R
tiny F 1 F_1 F1(micro- F 1 F_1 F1)
When there are multiple confusion matrices , We should integrate their results , The average confusion matrix can be calculated , Then calculate the micro precision and micro recall , Finally, we get micro F 1 F_1 F1.
micro- F 1 = 2 × micro − P × micro- R micro- P + micro − R \text { micro- } F 1=\frac{2 \times \operatorname{micro}-P \times \text { micro- } R}{\text { micro- } P+\operatorname{micro}-R} micro- F1= micro- P+micro−R2×micro−P× micro- R
ROC(Receiver Operating Ccharacteristic) curve
Measure model performance , Abscissa personal leave positive rate (False Positive Rate,FPR), That is, the proportion of cases wrongly judged as positive examples to real counter examples :
T P R = T P T P + F N \mathrm{TPR}=\frac{T P}{T P+F N} TPR=TP+FNTP
The ordinate is the real example rate (True Positive Rate), That is, the accuracy rate :
F P R = F P T N + F P \mathrm{FPR}=\frac{F P}{T N+F P} FPR=TN+FPFP
AUC(area under ROC curve)
ROC The area under the curve , The biggest is 1( Ideal situation ).
Training error (training error)/ Experience in error (empirical error)
Model / The error of the learner on the training set ;
So-called “ Experience ” It is the estimation of the real error .
Normalization error (generalization error)
Model / The error of the learner on the test set .
Over fitting (overfitting)
A small error can be obtained in the training set , That is, the empirical error is small , But the normalization error is large , The model learns many specific rules of the training set itself .
Just believe in “ P ≠ N P P\neq NP P=NP” Then there must be a fitting problem , Over fitting can only alleviate but not eliminate .
Under fitting (underfitting)
And Over fitting contrary , Did not learn the essential laws of the training set , Can't classify well .
Deviation and variance decomposition (bias-variance decomposition)
On the model / The generalization error rate of the learner is decomposed . In the end, you can get :
E ( f ; D ) = bias 2 ( x ) + var ( x ) + ε 2 E(f ; D)=\text { bias }^{2}(\boldsymbol{x})+\operatorname{var}(\boldsymbol{x})+\varepsilon^{2} E(f;D)= bias 2(x)+var(x)+ε2
The first item represents deviation bias 2 ( x ) = ( f ˉ ( x ) − y ) 2 \operatorname{bias}^{2}(\boldsymbol{x})=(\bar{f}(\boldsymbol{x})-y)^{2} bias2(x)=(fˉ(x)−y)2, The degree of deviation between the expected prediction and the true value of the model is measured , The fitting ability of the model itself is described ; The second term represents variance var ( x ) = E D [ ( f ( x ; D ) − f ˉ ( x ) ) 2 ] \operatorname{var}(\boldsymbol{x})=\mathbb{E}_{D}\left[(f(\boldsymbol{x} ; D)-\bar{f}(\boldsymbol{x}))^{2}\right] var(x)=ED[(f(x;D)−fˉ(x))2], Measured the same size , Changes in learning performance caused by changes in different data sets ( Instability ), The influence on data disturbance is described ; The third item represents noise ε 2 = E D [ ( y D − y ) 2 ] \varepsilon^{2}=\mathbb{E}_{D}\left[\left(y_{D}-y\right)^{2}\right] ε2=ED[(yD−y)2], Because the data itself is inevitably relative to the ideal distribution of noise , It is also the lower bound of the expected generalization error that any model can achieve , It depicts the difficulty of the learning problem itself .
Therefore, the generalization error is determined by the learning ability of the model 、 Sufficiency of data 、 The difficulty of the learning task itself determines .
deviation - Variance dilemma (bias-variance dilemma)
Generally speaking, deviation and variance “ shift ”, It is summarized as an intuitive picture :
Model selection (model selection)
The so-called model selection , Is to adopt what algorithm / Hypothesis function , What parameters are set / Hyperparameters .
Divide training / Method of test set
Set aside method (hold-out)
Directly divide the data set into training and testing sets , The two sets are mutually exclusive .
The single set aside method is often not reliable , May produce unexpected bias, So it can be random many times shuffle, Take the average , At the same time, the standard deviation of the evaluation results can also be obtained .
Usually about 2/3~4/5 As a training set .( see bias/variance tradeoff)
Stratified sampling (stratified sampling)
Samples that retain the category scale .
deviation / Variance tradeoff (bias/variance tradeoff)
If the test set is too small , test result / Variance of evaluation results (variance) more ;
If the training set is too small , The training model itself may lead to deviation (bias) more .
K Crossover verification
Divide the data set into k Equal parts , Take one of them as the test set in turn , The remaining k-1 As a training set , Will get the test results ( altogether k Time ) Average , That is the final evaluation result . Because there is still randomness when dividing the data set , So you can do it several times at random k Crossover verification , For many times k Fold cross validation average , for example ,10 Time 10 Crossover verification .
k The most commonly used is 10, In addition, it is also commonly used 5、20.
Leave a cross validation (Leave-One-Out,LOO)
When k In cross validation k When the total number of samples is equal to , Each divided set contains only one sample , It's called leave a cross validation .
Self help law (bootstrapping)
The key lies in the use of self-service sampling (bootstrap sampling), That is, a data set with the same sample size as the original data set is sampled back from the original data set . Suppose the original data set has m Samples , Then the probability that a sample will not be taken out is ( 1 − 1 m ) m \left(1-\frac{1}{m}\right)^{m} (1−m1)m, When the data set is large enough :
lim m ↦ ∞ ( 1 − 1 m ) m ↦ 1 e ≈ 0.368 \lim _{m \mapsto \infty}\left(1-\frac{1}{m}\right)^{m} \mapsto \frac{1}{e} \approx 0.368 m↦∞lim(1−m1)m↦e1≈0.368
So about 1/3 The sample of was not taken ( So it's also called “ Out of the bag estimate ”,out-of-bag estimate), Thus, the data set obtained by autonomous sampling method can be used as the training set , The original data set is used as the test set .
But the self-help method naturally introduces deviation in this process bias, Therefore, its shortcomings at this time .
Adjustable parameter (parameter tuning)
you 're right , It's called tuning parameter . Parameters are generally divided into two types , One is the parameters of the model itself , That is, the model needs to be constantly modified through learning , There are often many ; The other is called “ Hyperparameters ” In fact, I think the choice is about the model / Parameters of the algorithm , Usually not too much .
边栏推荐
- 多商户商城系统功能拆解04讲-平台端商家入驻
- Jupyter notebook选择conda环境
- 多商户商城系统功能拆解09讲-平台端商品品牌
- "Statistical learning methods (2nd Edition)" Li Hang Chapter 16 principal component analysis PCA mind map notes and after-school exercise answers (detailed steps) PCA matrix singular value Chapter 16
- Likeshop100% open source encryption free B2B2C multi merchant mall system
- 多商户商城系统功能拆解06讲-平台端商家入驻协议
- SqlServer 完全删除
- Problems in SSM project configuration, various dependencies, etc. (for personal use)
- ERP+RPA 打通企业信息孤岛,企业效益加倍提升
- Logical structure of Oracle Database
猜你喜欢

What do programmers often mean by API? What are the API types?

Multi merchant mall system function disassembly Lecture 14 - platform side member level

【深度学习】手把手教你写“手写数字识别神经网络“,不使用任何框架,纯Numpy
Introduction to PC mall module of e-commerce system

Help transform traditional games into gamefi, and web3games promote a new direction of game development

likeshop单商户SAAS商城系统无限多开

列表写入txt直接去除中间的逗号
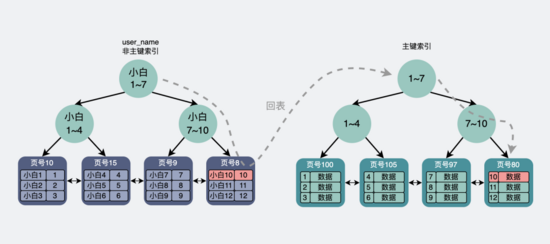
Are you still trying to limit MySQL paging?

西瓜书/南瓜书--第1,2章总结

多商户商城系统功能拆解03讲-平台端商家管理
随机推荐
likeshop单商户SAAS商城系统搭建,代码开源无加密。
CRC-16 Modbus代码
Logical structure of Oracle Database
找ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>>中出现次数最多的ArrayList<Double>
OSError: [WinError 127] 找不到指定的程序。Error loading “caffe2_detectron_ops.dll“ or one of its dependencies
On the concepts of "input channel" and "output channel" in convolutional neural networks
Highcharts use custom vector maps
Multi merchant mall system function disassembly lecture 06 - platform side merchant settlement agreement
likeshop单商户SAAS商城系统无限多开
LSTM神经网络
主成分分析计算步骤
[activiti] activiti introduction
《统计学习方法(第2版)》李航 第22章 无监督学习方法总结 思维导图笔记
世界坐标系、相机坐标系和图像坐标系的转换
多商户商城系统功能拆解04讲-平台端商家入驻
多商户商城系统功能拆解12讲-平台端商品评价
@Async does not execute asynchronously
多商户商城系统功能拆解11讲-平台端商品栏目
快速打开管理工具的命令
How to quickly recover data after MySQL misoperation