当前位置:网站首页>MySQL advanced - personal notes
MySQL advanced - personal notes
2022-06-21 10:46:00 【Code knower】
Learning video : Silicon Valley MySQL Database advanced ,mysql Optimize , Database optimization _ Bili, Bili _bilibili
The document is a copy of Shang Silicon Valley's review materials , Personally, just for the convenience of review .
Catalog
Mysql Introduction to logical architecture
The first 4 Chapter SQL preheating
The first 5 Chapter Index optimization analysis
1.2 Advantages and disadvantages
2.3 Clustered index and non clustered index
2.4 Time complexity ( Expand )
4.1 Suitable for index creation
4.2 Not suitable for index creation
The first 6 Chapter Explain Performance analysis
12.7 select tables optimized away
The first 7 Chapter Batch data script
1.6 Batch delete all indexes on a table
The first 8 Chapter Common index failures in single table indexes
1. Full value matching my favorite
1.1 There are the following SQL sentence
3. Don't do any calculations on the index column
3.1 The function... Is used on the query column
3.2 A transformation is made on the query column
4. Cannot have range query on index column
6. Use is not equal to (!= perhaps <>) When
7. Field is not null and is null
8. like Fuzzy matching before and after
The first 9 Chapter Association query optimization
2.3 Analysis of four related query cases
The first 10 Chapter Sub query optimization
The first 11 Chapter Sorting and grouping optimization
2. Wrong order , No sorting is required
3. In the opposite direction , No sorting is required
Mysql Introduction to logical architecture
1. Overall architecture
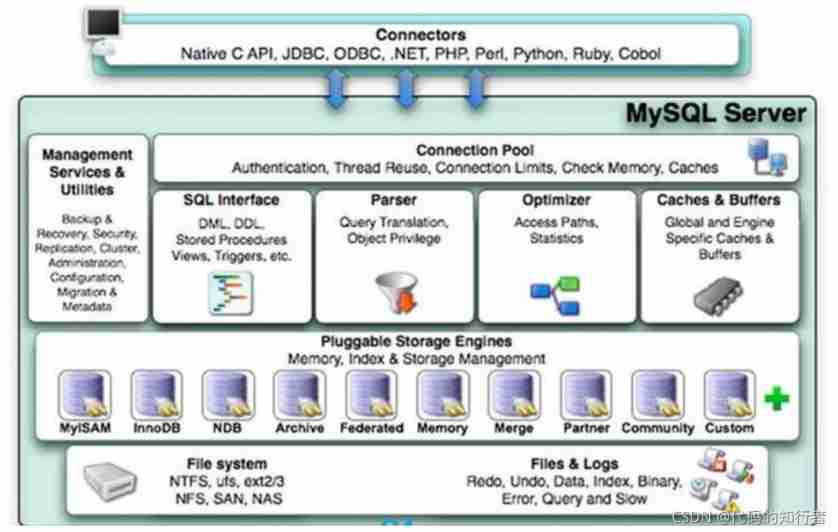
1.1 adjoining course
1.2 Service layer
Management Serveices & Utilities | System management and control tools |
|---|---|
SQL Interface: | SQL Interface . Accept user's SQL command , And returns the result of the query that the user needs . such as select from It's called SQL Interface |
Parser | Parser . SQL Commands are validated and parsed by the parser when they are passed to the parser |
Optimizer | Query optimizer . SQL The statement optimizes the query using the query optimizer before the query , Such as the where When the conditions , The optimizer decides whether to project or filter first . |
Cache and Buffer | The query cache . If the query cache has a hit query result , The query statement can be directly retrieved from the query cache data . The caching mechanism consists of a series of small caches . For example, table caching , Record the cache ,key cache , Authority cache, etc |
1.3. Engine layer
1.4. Storage layer
2. show profile
2.1 Turn on profile

2.2 Use profile

according to Query_ID, It can be further implemented show profile cpu,block io for query Query_id Check it out. sql Specific implementation steps of .
![]()

2.3 General query process
2.4 SQL Execution order of


![]()

2.5 MyISAM and InnoDB
Contrast item | MyISAM | InnoDB |
Foreign keys | I won't support it | Support |
Business | I won't support it | Support |
Row table lock | Table locks , Even operating on one record locks the entire table , Not suitable for highly concurrent operations | Row lock , Lock only one line during operation , It doesn't affect anything else , Suitable for high concurrency The operation of |
cache | Cache index only , Don't cache real data | Not only index but also real data , High memory requirements , And inside Memory size has a decisive impact on performance |
concerns | Read performance | Write concurrently 、 Business 、 resources |
Default installation | Y | Y |
By default | N | Y |
since belt system system surface Use | Y | N |
show engines: View all database engines


The first 4 Chapter SQL preheating
1. common Join Query graph

2. Join Example
2.1 Create table statement
CREATE TABLE `t_dept` (`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`deptName` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,`address` VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `t_emp` (`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,`age` INT(3) DEFAULT NULL,`deptId` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,empno int not null,PRIMARY KEY (`id`),KEY `idx_dept_id` (`deptId`)#CONSTRAINT `fk_dept_id` FOREIGN KEY (`deptId`) REFERENCES `t_dept` (`id`)) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' Huashan Mountain ',' Huashan Mountain ');INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' Beggars' sect ',' luoyang ');INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' emei ',' Mount Emei ');INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' Wudang ',' Wudang Mountain ');INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' Mingjiao ',' Bright Summit ');INSERT INTO t_dept(deptName,address) VALUES(' Shaolin ',' The shaolin temple ');INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' The breeze pure Yang ',90,1,100001);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' yue buqun ',50,1,100002);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' linghu chong ',24,1,100003);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' master hongqi ',70,2,100004);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' Xiao feng ',35,2,100005);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' Extinction teacher ',70,3,100006);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' Zhou Zhiruo ',20,3,100007);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' Zhang Sanfeng ',100,4,100008);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' zhang wuji ',25,5,100009);INSERT INTO t_emp(NAME,age,deptId,empno) VALUES(' Trinket ',18,null,100010);
2.2 Case study
select * from t_emp a inner join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id

2. List all personnel and their department information
select * from t_emp a left join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id

3. List the personnel information of all departments
select * from t_emp a right join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id

4. List the personnel information without department
select * from t_emp a left join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id where b.id is null

5. List the Department information without personnel
select * from t_emp a right join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id where a.id is null

6. Correspondence of all personnel and departments
select * from t_emp a left join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id
union
select * from t_emp a right join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id

7. All those who are not in the Department and those who are not in the Department
select * from t_emp a left join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id where b.id is null
union
select * from t_emp a right join t_dept b on a.deptId = b.id where a.id is null

The first 5 Chapter Index optimization analysis
1. The concept of index
1.1 What is it?

1.2 Advantages and disadvantages
- Improve the data retrieval The efficiency of , Reduce the IO cost .
- Sort data through index columns , Reduce the cost of sorting data , To reduce the CPU Consumption of .
- Although the index greatly improves the query speed , At the same time, it will reduce the speed of updating the table , Such as on the table INSERT、UPDATE and DELETE. Because when updating tables ,MySQL Not only to save data , Also save the fields in the index file that have index columns added every time it is updated , Will adjust because The index information after the key value changes caused by the update .
- The index is actually a table , The table holds the primary key and index fields , And points to the record of the entity table , So index columns also need to Occupancy space Of
2. Mysql The index of
2.1 Btree Indexes
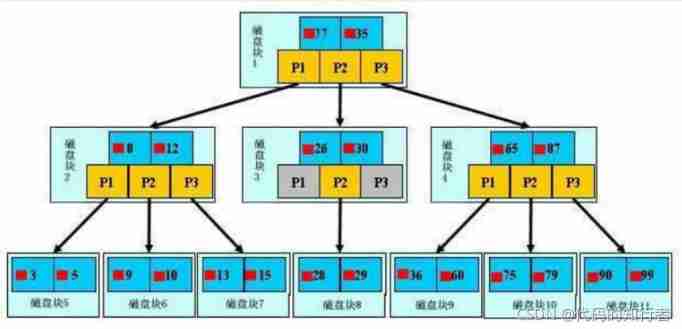
2.2 B+tree Indexes
2.3 Clustered index and non clustered index

2.4 Time complexity ( Expand )
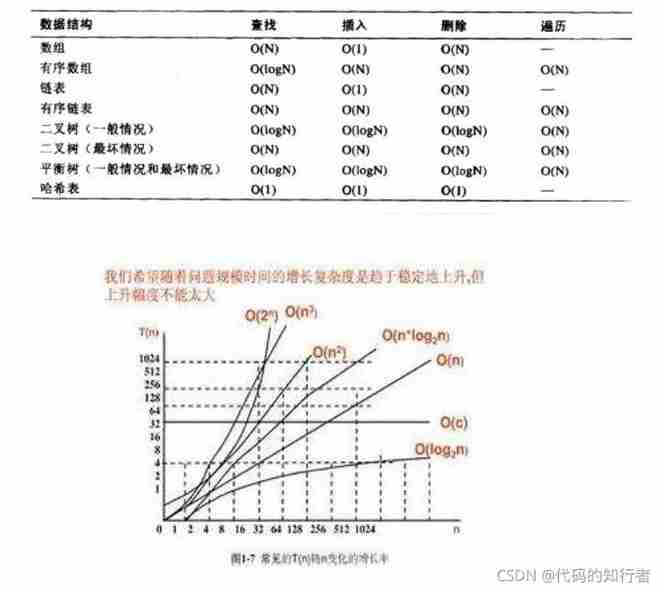
3. Mysql Index classification
3.1 Single value index
Create with the table :CREATE TABLE customer (id INT(10) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT ,customer_no VARCHAR(200),customer_name VARCHAR(200),PRIMARY KEY(id),KEY (customer_name));
Create a single value index separately :CREATE INDEX idx_customer_name ON customer(customer_name);
3.2 unique index
Concept : The value of the index column must be unique , But you can have an empty value
Created with the table :CREATE TABLE customer (id INT(10) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT ,customer_no VARCHAR(200),customer_name VARCHAR(200),PRIMARY KEY(id),KEY (customer_name),UNIQUE (customer_no));
Create a unique index :CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_customer_no ON customer(customer_no);
3.3 primary key
Concept : After setting it as the primary key, the database will automatically create an index ,innodb Index for clustering
Index with tableCREATE TABLE customer (id INT(10) UNSIGNEDAUTO_INCREMENT ,customer_no VARCHAR(200),customer_nameVARCHAR(200),PRIMARY KEY(id));
Create a separate primary key index :ALTER TABLE customer add PRIMARY KEY customer(customer_no);
Delete Create a primary key index :ALTER TABLE customer drop PRIMARY KEY ;
modify Create a primary key index :You must delete (drop) The original index , New again (add) Indexes
3.4 Composite index
Concept : That is, an index contains multiple columns
Index with table :CREATE TABLE customer (id INT(10) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT ,customer_no VARCHAR(200),customer_name VARCHAR(200),PRIMARY KEY(id),KEY (customer_name),UNIQUE (customer_name),KEY (customer_no,customer_name));
Index separately :CREATE INDEX idx_no_name ON customer(customer_no,customer_name);
3.5 Basic grammar
operation | command |
|---|---|
establish | CREATE [UNIQUE ] INDEX [indexName] ON table_name(column)) |
Delete | DROP INDEX [indexName] ON mytable; |
see | SHOW INDEX FROM table_name\G |
send use Alter command | ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_list) : This statement adds a primary key , This means that the index value must be unique , And cannot be NULL. |
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_list) This statement creates the value of the index It has to be the only one ( except NULL Outside ,NULL There may be many times ) | |
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD INDEX index_name (column_list): Add a normal index , Index values can appear multiple times . | |
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD FULLTEXT index_name (column_list): The statement specifies that the index is FULLTEXT , For full text retrieval lead . |
4. Index creation time
4.1 Suitable for index creation
- Primary key automatically creates unique index ;
- Fields that are frequently used as query criteria should be indexed
- Fields associated with other tables in the query , Index foreign key relationship
- Single key / The choice of Composite Index , Composite index is more cost-effective
- Fields sorted in the query , If the sorting field is accessed by index, the sorting speed will be greatly improved
- Statistics or grouping fields in query
4.2 Not suitable for index creation
- There are too few records
- A table or field that is frequently added, deleted, or modified
- Where The fields that are not used in the condition are not indexed
- Those with poor filtering are not suitable for indexing
5. Performance analysis
5.1 MySql Query Optimizer
1、Mysql Technical secondary schools are responsible for optimizing SELECT Statement optimizer module , The main function : By calculating the statistics collected in the analysis system , Requested for client Query Provide the best execution plan he thinks ( He thinks the best way to retrieve data , But not necessarily DBA Think it's the best , This part is the most time consuming )
2、 When the client MySQL Ask for one Query, The command parser module completes the request classification , Show the difference SELECT And forward it to MySQL Query Optimizer when ,MySQL Query Optimizer First of all, the whole Query To optimize , Deal with the budget of some constant expressions , Convert directly to constant value . Also on Query To simplify and convert the query conditions in , Such as removing some useless or obvious conditions 、 Structural adjustment has not Himt or Hint Information ( If there is ), The statistics of the object involved will be read , according to Query Write the corresponding calculation and analysis , And then come up with the final execution plan .
5.2 MySQL Common bottlenecks
- CPU:CPU When saturated, it usually occurs when data is loaded into memory or read from disk
- IO: disk I/O The bottleneck occurs when the load data is much larger than the memory capacity
- The performance bottleneck of server hardware :top,free,iostat, and vmstat To see the performance status of the system
The first 6 Chapter Explain Performance analysis
1. Concept
What can I do?
- Read order of tables
- Operation type of data read operation
- Which indexes can be used
- Which indexes are actually used
- References between tables
- How many rows per table are queried by the optimizer

2. Explain preparation
CREATE TABLE t1(id INT(10) AUTO_INCREMENT,content VARCHAR(100) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (id));CREATE TABLE t2(id INT(10) AUTO_INCREMENT,content VARCHAR(100) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (id));CREATE TABLE t3(id INT(10) AUTO_INCREMENT,content VARCHAR(100) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (id));CREATE TABLE t4(id INT(10) AUTO_INCREMENT,content VARCHAR(100) NULL , PRIMARY KEY (id));INSERT INTO t1(content) VALUES(CONCAT('t1_',FLOOR(1+RAND()*1000)));INSERT INTO t2(content) VALUES(CONCAT('t2_',FLOOR(1+RAND()*1000)));INSERT INTO t3(content) VALUES(CONCAT('t3_',FLOOR(1+RAND()*1000)));INSERT INTO t4(content) VALUES(CONCAT('t4_',FLOOR(1+RAND()*1000)));
3. id
explain select t2.*
from t1,t2,t3
where t1.id = t2.id and t1.id = t3.id
and t1.content = ''

explain select t2.*
from t2
where id = (select id
from t1
where id =(select t3.id
from t3
where t3.content = ''))
②id Different , If it's a subquery ,id The serial number of will increase ,id The higher the value, the higher the priority , The first to be executed

explain select t2.* from (
select t3.id
from t3
where t3.content = '') s1, t2
where s1.id = t2.id;

4. select_type
4.1 SIMPLE

4.2 PRIMARY

4.3 DERIVED
4.4 SUBQUERY

4.5 DEPENDENT SUBQUERY

4.6 UNCACHEABLE SUBQUREY

4.7 UNION
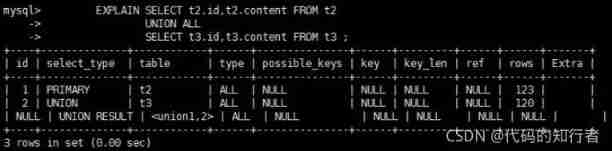
4.8 UNION RESULT
5. table
6. type
6.1 system
6.2 const
 Indicates that it is found through index once ,const For comparison primary key perhaps unique Indexes . Because only one line of data is matched , So soon
Indicates that it is found through index once ,const For comparison primary key perhaps unique Indexes . Because only one line of data is matched , So soon
6.3 eq_ref

Unique index scan , For each index key , Only one record in the table matches it . Common in primary key or unique index scan .
6.4 ref

After indexing :

6.5 range


6.6 index

6.7 all
Full Table Scan, Will traverse the entire table to find the matching rows .

6.8 index_merge

6.9 ref_or_null

6.10 index_subquery
Using indexes to associate subqueries , No more full table scans .
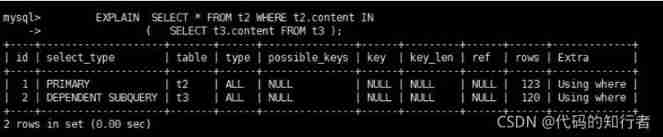

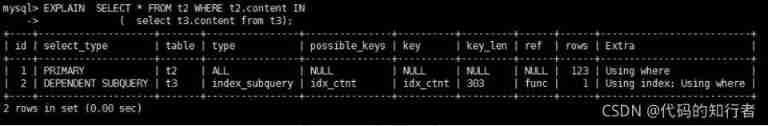 6.11 unique_subquery
6.11 unique_subquery
The join type is similar to index_subquery. Unique index in subquery .

7. possible_keys
8. key
9. key_len



10. ref
Shows which column of the index is used , If possible , It's a constant . Which columns or constants are used to find values on index columns .

11. rows
rows Columns show MySQL The number of rows that it must check to execute the query . The less, the better. !

12. Extra
12.1 Using filesort

After optimization , No more filesort The situation of :

Fields sorted in the query , If the sorting field is accessed by index, the sorting speed will be greatly improved .
12.2 Using temporary

After optimization :

12.3 Using index
12.4 Using where
12.5 Using join buffer

Connection caching is used .
12.6 impossible where

12.7 select tables optimized away

stay Myisam in :

The first 7 Chapter Batch data script
1. insert data
1.1 Create table statement
CREATE TABLE `dept` (`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`deptName` VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,`address` VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,ceo INT NULL ,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;CREATE TABLE `emp` (`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`empno` INT NOT NULL ,`name` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,`age` INT(3) DEFAULT NULL,`deptId` INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)#CONSTRAINT `fk_dept_id` FOREIGN KEY (`deptId`) REFERENCES `t_dept` (`id`)) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
1.2 Set parameters

1.3 Write random functions
1.3.1 Randomly generate strings
DELIMITER $$CREATE FUNCTION rand_string(n INT) RETURNS VARCHAR(255)BEGINDECLARE chars_str VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFJHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';DECLARE return_str VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT '';DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;WHILE i < n DOSET return_str =CONCAT(return_str,SUBSTRING(chars_str,FLOOR(1+RAND()*52),1));SET i = i + 1;END WHILE;RETURN return_str;END $$
# Used to randomly generate number to numberDELIMITER $$CREATE FUNCTION rand_num (from_num INT ,to_num INT) RETURNS INT(11)BEGINDECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;SET i = FLOOR(from_num +RAND()*(to_num -from_num+1));RETURN i;END$$
1.4 Create stored procedure
1.4.1 To create emp A stored procedure that inserts data into a table
DELIMITER $$CREATE PROCEDURE insert_emp( START INT , max_num INT )BEGINDECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;#set autocommit =0 hold autocommit Set to 0SET autocommit = 0;REPEATSET i = i + 1;
1.4.2 To create dept A stored procedure that inserts data into a table
# Execute stored procedures , Go to dept Add random data to tableDELIMITER $$CREATE PROCEDURE `insert_dept`( max_num INT )BEGINDECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;SET autocommit = 0;REPEATSET i = i + 1;INSERT INTO dept ( deptname,address,ceo ) VALUES (rand_string(8),rand_string(10),rand_num(1,500000));UNTIL i = max_numEND REPEAT;COMMIT;END$$
1.5 Calling stored procedure
1.5.1 Add data to department table
# Execute stored procedures , Go to dept Table to add 1 Ten thousand dataDELIMITER ;CALL insert_dept(10000);
1.5.2 Add data to employee table
# Execute stored procedures , Go to emp Table to add 50 Ten thousand dataDELIMITER ;CALL insert_emp(100000,500000);
1.6 Batch delete all indexes on a table
1.6.1 Delete the stored procedure of the index
DELIMITER $$CREATE PROCEDURE `proc_drop_index`(dbname VARCHAR(200),tablename VARCHAR(200))BEGINDECLARE done INT DEFAULT 0;DECLARE ct INT DEFAULT 0;DECLARE _index VARCHAR(200) DEFAULT '';DECLARE _cur CURSOR FORSELECTindex_nameFROM information_schema.STATISTICSWHEREtable_schema=dbname AND table_name=tablename AND seq_in_index=1 ANDindex_name <>'PRIMARY' ;DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND set done=2 ;OPEN _cur;FETCH_cur INTO _index;WHILE _index<>'' DOSET @str = CONCAT("drop index ",_index," on ",tablename );PREPARE sql_str FROM @str ;EXECUTE sql_str;DEALLOCATE PREPARE sql_str;SET _index='';FETCH_cur INTO _index;END WHILE;CLOSE _cur;END$$
1.6.2 Execute stored procedures
The first 8 Chapter Common index failures in single table indexes
1. Full value matching my favorite
1.1 There are the following SQL sentence
EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptid=4EXPLAIN SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptid=4 AND emp.name = 'abcd
1.2 Index

Conclusion : Full time matching my favorite is , The fields of the query can be matched in the index in order !

2. The best left prefix rule

3. Don't do any calculations on the index column
Do nothing on the index column ( Calculation 、 function 、( Automatically or Manual ) Type conversion ), It will cause index invalidation and turn to full table scan .
3.1 The function... Is used on the query column

Conclusion : There is no calculation to the left of the equal sign !
3.2 A transformation is made on the query column
create index idx_name on emp(name); |
| explain select sql_no_cache * from emp where name='30000'; |
| explain select sql_no_cache * from emp where name=30000; |

Conclusion : There is no conversion to the right of the equal sign !
4. Cannot have range query on index column
| explain SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptid=5 AND emp.name = 'abcd'; |
| explain SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptid<=5 AND emp.name = 'abcd'; |

Suggest : Put the index order of the fields that may be used for range query at the end
5. Try to use overlay index
explain SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE * FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptId=4 and name='XamgXt'; |
explain SELECT SQL_NO_CACHE age,deptId,name FROM emp WHERE emp.age=30 and deptId=4 and name='XamgXt'; |
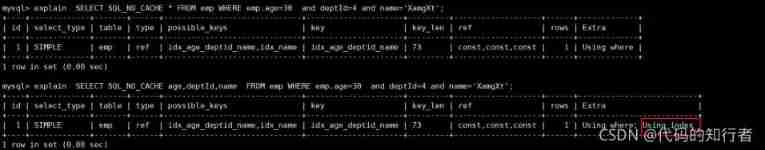
6. Use is not equal to (!= perhaps <>) When

7. Field is not null and is null

When the field is allowed to be Null Under the condition of :
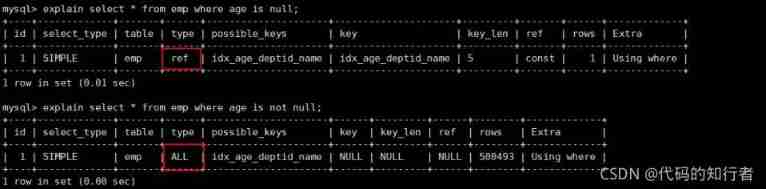 is not null No index ,is null You can use indexes .
is not null No index ,is null You can use indexes .
8. like Fuzzy matching before and after

The prefix cannot have a fuzzy match !
9. Reduce use or

Use union all perhaps union To replace :

10. practice
Where sentence | Whether the index is used |
|---|---|
where a = 3 | Y, Use to a |
where a = 3 and b = 5 | Y, Use to a,b |
where a = 3 and b = 5 and c = 4 | Y, Use to a,b,c |
where b = 3 perhaps where b = 3 and c = 4 perhaps where c = 4 | N |
where a = 3 and c = 5 | Use to a, however c Can not be ,b It's broken in the middle |
where a = 3 and b > 4 and c = 5 | Use to a and b, c Cannot be used after range ,b Broken |
where a is null and b is not null | is null Support the index however is not null I won't support it , the With a You can use index , however b Not available |
where a <> 3 | Index cannot be used |
where abs(a) =3 | Out of commission Indexes |
where a = 3 and b like 'kk%' and c = 4 | Y, Use to a,b,c |
where a = 3 and b like '%kk' and c = 4 | Y, Only for a |
where a = 3 and b like '%kk%' and c = 4 | Y, Only for a |
where a = 3 and b like 'k%kk%' and c = 4 | Y, Use to a,b,c |
11. formula
The first 9 Chapter Association query optimization
1. Create table statement
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `class` (`id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`card` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`));CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `book` (`bookid` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`card` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`bookid`));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1 + (RAND() * 20)));
2. Case study
2.1 left join

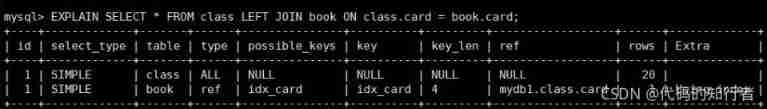

2.2 inner join
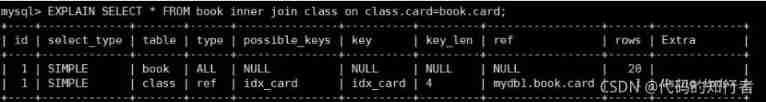
② Exchange order of two query fields , It turns out the same thing !

③ stay book In the table , Delete 9 Bar record
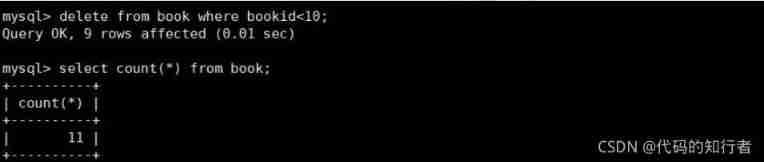
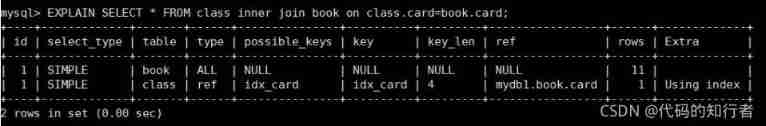
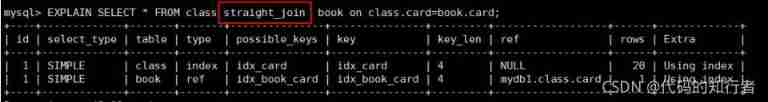 2.3 Analysis of four related query cases
2.3 Analysis of four related query cases
EXPLAIN SELECT ed.name ' figure ',c.name ' representative or leader in a certain field ' FROM(SELECT e.name,d.ceo from t_emp e LEFT JOIN t_dept d on e.deptid=d.id) edLEFT JOIN t_emp c on ed.ceo= c.id;
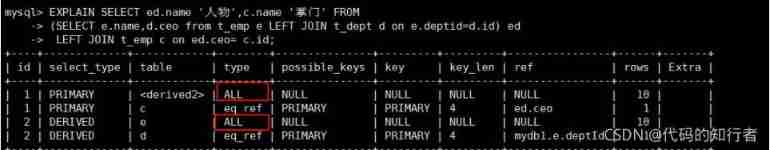
EXPLAIN SELECT e.name ' figure ',tmp.name ' representative or leader in a certain field 'FROM t_emp e LEFT JOIN (SELECT d.id did,e.name FROM t_dept d LEFT JOIN t_emp e ON d.ceo=e.id)tmpON e.deptId=tmp.did;

EXPLAIN SELECT e1.name ' figure ',e2.name ' representative or leader in a certain field 'FROM t_emp e1LEFT JOIN t_dept d on e1.deptid = d.idLEFT JOIN t_emp e2 on d.ceo = e2.id ;

Explain SELECT e2.name ' figure ',(SELECT e1.name FROM t_emp e1 where e1.id= d.ceo) ' representative or leader in a certain field 'from t_emp e2 LEFT JOIN t_dept d on e2.deptid=d.id;

Conclusion : If you can directly associate multiple tables, try to associate directly , No sub query !
The first 10 Chapter Sub query optimization
1. Case study
Take all employees who are not leaders , Group by age !
select age as ' Age ', count(*) as ' The number of ' from t_emp where id not in
(select ceo from t_dept where ceo is not null) group by age;


here , Query again :

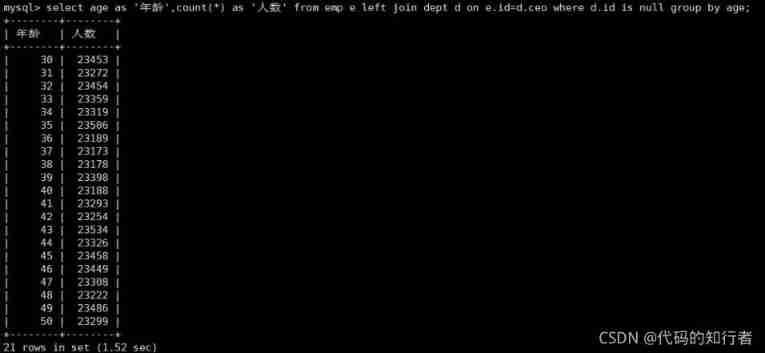
Conclusion : When judging the range , Try not to use not in and not exists, Use left join on xxx is null Instead of .
The first 11 Chapter Sorting and grouping optimization
1. No filtering, no indexing

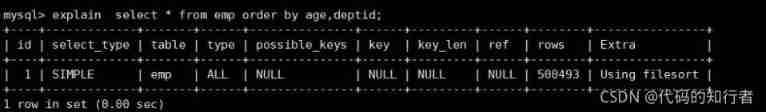
using filesort Instructions are sorted manually ! The reason is that there is no where As a filter !

Conclusion : No filtering , No index .where,limt Are equivalent to a filter condition , So you can use the index !
2. Wrong order , No sorting is required
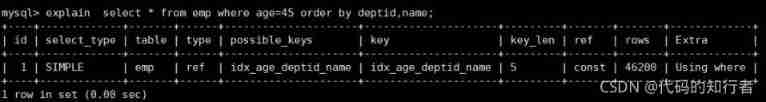
②explain select * from emp where age=45 order by deptid,empno;

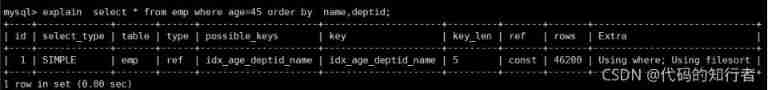

deptid Fields as filter conditions , Index not available , So sorting can't be indexed
3. In the opposite direction , No sorting is required


If the sorted field , The order is different , You need to put the difference part , Perform an inverted sequence , So you still need to sort manually !
4. Index selection
① First , eliminate emp All indexes above , Keep only the primary key index !
drop index idx_age_deptid_name on emp;
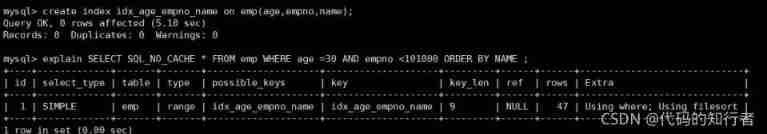



5. using filesort
5.1 mysql Sort algorithm
5.2 How to optimize
6. Use overlay index
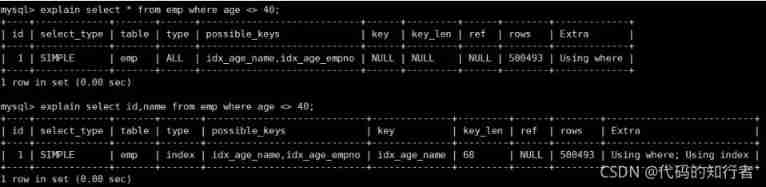
7. group by

The first 12 Chapter practice
1. Case a
select e1.name empname,e1.age empage,e2.name ceoname,e2.age ceoagefrom t_emp e1 inner join t_dept d on e1.deptid=d.idinner join t_emp e2 on d.ceo=e2.idwhere e1.age>e2.age;

Replace with a large watch , Analyze :
explain select e1.name empname,e1.age empage,e2.name ceoname,e2.age ceoage from emp e1 inner join dept d one1.deptid=d.idinner join emp e2 on d.ceo=e2.idwhere e1.age>e2.age;

two inner join The driven tables of have been indexed .
2. Case 2
select e1.name from t_emp e1inner join(select deptid,AVG(age) avgage from t_empgroup by deptid) tmpon e1.deptid=tmp.deptidwhere e1.age<tmp.avgage;

Replace with a large watch :
explain select e1.name from emp e1inner join(select deptid,AVG(age) avgage from empgroup by deptid) tmpon e1.deptid=tmp.deptidwhere e1.age<tmp.avgage;


3. Case three
select d.deptName,count(*)from t_emp e inner join t_dept don e.deptid=d.idwhere e.age>40group by d.id,d.deptNamehaving count(*)>=2

Big watch optimization :
explain select d.deptName,count(*)from emp e inner join dept don e.deptid=d.idwhere e.age>40group by d.id,d.deptNamehaving count(*)>=2


4. Case four
select d2.deptName from t_emp e inner join t_dept d2 on e.deptid=d2.idleft join t_dept d on e.id=d.ceowhere d.id is null and e.deptid is not nullgroup by d2.deptName,d2.idhaving count(*)>=2;

explain select d2.deptName from emp e inner join dept d2 on e.deptid=d2.idleft join dept d on e.id=d.ceowhere d.id is null and e.deptid is not nullgroup by d2.deptName,d2.idhaving count(*)>=2;
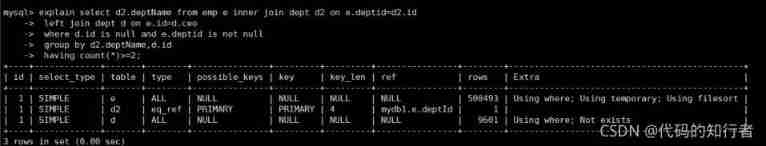

5. Case 5

Big table correlation :
explain select e.name,case when d.id is null then ' no ' else ' yes ' end ' Is it the leader ' from emp eleft join dept don e.id=d.ceo;
Optimize : stay d Tabular ceo Fields can be indexed !
6. Case 6
select d.deptName,if(avg(age)>40,' veteran ',' rookie ') from t_emp e inner join t_dept don d.id=e.deptid group by d.deptName,d.id
 Switch large tables :
Switch large tables :
explain select d.deptName,if(avg(age)>40,' veteran ',' rookie ') from dept d inner join emp eon d.id=e.deptidgroup by d.deptName,d.id


7. Case seven
select * from t_emp einner join(select deptid,max(age) maxagefrom t_empgroup by deptid) tmpon tmp.deptid=e.deptid and tmp.maxage=e.age;

Big watch optimization :
explain select * from emp einner join(select deptid,max(age) maxagefrom empgroup by deptid) tmpon tmp.deptid=e.deptid and tmp.maxage=e.age;


The first 13 Chapter Intercept query analysis
1. Slow query log
1.1 What is it?
1.2 How to use it?
SQL sentence | describe | remarks |
|---|---|---|
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%slow_query_log%'; | Check whether the slow query log is on | By default slow_query_log The value of is OFF, Indicates that slow query logs are disabled |
set global slow_query_log=1; | Open slow query log | |
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'long_query_time%'; | View slow query set threshold | Unit second |
set long_query_time=1 | Set the slow query threshold | Unit second |
[mysqld]slow_query_log=1slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.loglong_query_time=3log_output=FILE
1.2 Log analysis tool mysqldumpslow

(2) see mysqldumpslow Help for
Get the most returned recordset 10 individual SQLmysqldumpslow -s r -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.logThe most visited 10 individual SQLmysqldumpslow -s c -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.logGet the top... In chronological order 10 There are left connected query statements in the barmysqldumpslow -s t -t 10 -g "left join" /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.logIt is also recommended to use these commands in conjunction with | and more Use , Otherwise, the screen may explodemysqldumpslow -s r -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log | more
2. SHOW PROCESSLIST
1.1 What is it?
1.2 How to use it?

The first 14 Chapter A collection of tools and techniques
1.1 What is it?
1.2 effect
The first 15 Chapter Master slave copy
1.1 The fundamentals of replication

1.2 The basic principle of reproduction
1.3 The biggest problem with copying
1.4 One master one slave common configuration

The primary server is unique ID
server-id=1Enable binary logging JAVAEE Course serieslog-bin= My own local path /data/mysqlbinlog-bin=D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/data/mysqlbinSet up the database not to be copiedbinlog-ignore-db=mysqlSet up the database to be copiedbinlog-do-db= The name of the master database to be copiedSet up logbin Formatbinlog_format=STATEMENT( Default )
mysql At the beginning of master-slave replication , The slave does not inherit host data
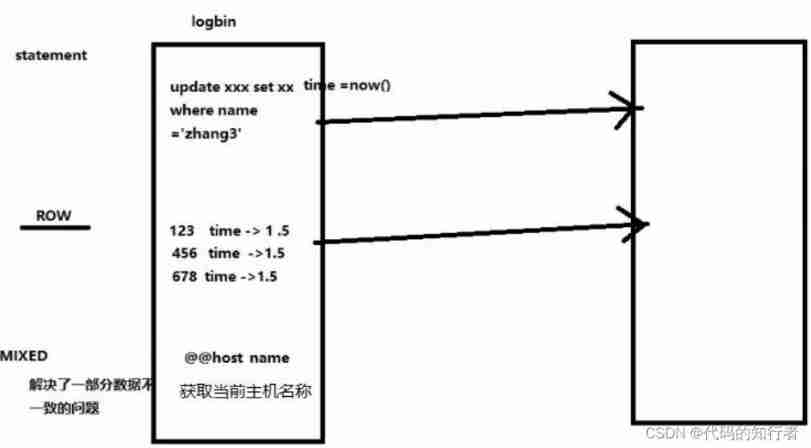
# Slave service idserver-id = 2# Be careful my.cnf There is server-id = 1# Set relay logrelay-log=mysql-relay
(5) Because the configuration file has been modified , Please check the host + All slave computers restart the background mysql service
# Create user , And authorizeGRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO ' Backup account '@' From the machine database IP' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';

(8) Inquire about master The state of , And record File and Position Value
# Inquire about master The state ofshow master status;
 Do not operate the master server after this step MYSQL, Prevent the state value of the primary server from changing
Do not operate the master server after this step MYSQL, Prevent the state value of the primary server from changing
# Inquire about master The state ofCHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST=' host IP',MASTER_USER=' Create user name ',MASTER_PASSWORD=' Created password ',MASTER_LOG_FILE='File name ',MASTER_LOG_POS=Position Numbers ;
 (10) Start copy from server
(10) Start copy from server
start slave;show slave status\G;

The following two parameters are Yes, The master-slave configuration is successful !
Slave_IO_Running: YesSlave_SQL_Running: Yes
(11) Host new library 、 new table 、insert Record , Copy from the machine
stop slave;
The first 16 Chapter MYCAT
1.1 What is it?
database middleware , It was formerly Ali's cobar
1.2 What do you do
- Read / write separation
- Data fragmentation :
Split Vertically 、 Horizontal split
vertical + Horizontal split
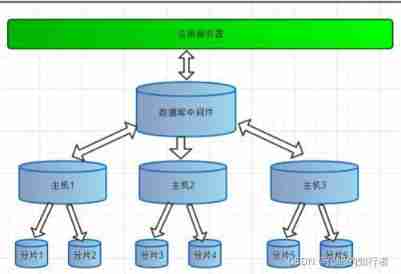
3. Multiple data source integration
1.3 MYCAT principle
“ Intercept ”:Mycat The most important verb in the principle of is “ Intercept ”, It intercepts what the user sent SQL sentence , First of all, SQL The statement does some specific analysis : Such as fragment analysis 、 Route analysis 、 Read write separation analysis 、 Cache analysis, etc , And then put this SQL Real database sent to the back end , And will return the results to do the appropriate processing , And finally back to the user .

In this way, the distributed database is decoupled from the code , The programmer doesn't notice that it's used in the background mycat still mysql.
1.4 Installing the
- Unzip the file and copy it to linux Next /usr/local/
- Three configuration files
schema.xml Define logical library , surface 、 Fragment node and so on rule.xml Define fragmentation rules
server.xml Define user and system related variables , Such as port, etc .
3. Modify before starting schema.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE mycat:schema SYSTEM "schema.dtd">
<mycat:schema xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/">
<!-- Logical library name name , checkSQLschema sqlMaxLimit Whether to add... At the end limit xxx-->
<schema name="TESTDB" checkSQLschema="false" sqlMaxLimit="100" dataNode="dn1"> </schema>
<!-- Logical library name name , dataHost Which... Is quoted dataHost database: Corresponding mysql Of database-->
<dataNode name="dn1" dataHost="localhost1" database="db1" />
<dataHost name="localhost1" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="0"
writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native" switchType="1"
slaveThreshold="100">
<heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat>
<!-- can have multi write hosts -->
<writeHost host="hostM1" url="localhost:3306" user="root"
password="123456">
</writeHost>
</dataHost>
</mycat:schema>
4. Revise server.xml
<user name="root">
<property name="password">654321</property>
<property name="schemas">TESTDB</property>
</user>
5. Start the program
Console launch : Go to mycat/bin Under the table of contents mycat console Background start : Go to mycat/bin Under the table of contents mycat start
6. An error may occur during startup
Domain name resolution failed

use vim modify /etc/hosts file , stay 127.0.0.1 Add your machine name later
 Restart network service after modification
Restart network service after modification

7. Background management window login
边栏推荐
- JobService的使用
- How to convert mindspire model to onnx format and use onnxruntime reasoning - development test
- 中国国际电子商务中心与易观分析联合发布:2021年4季度全国网络零售发展指数同比增长0.6%
- DSP online upgrade (1) -- understand the startup process of DSP chip
- Running view of program
- Eureka's timedsupersortask class (periodic task with automatic interval adjustment)
- Are you still using localstorage directly? The thinnest in the whole network: secondary encapsulation of local storage (including encryption, decryption and expiration processing)
- Unable to access gcr IO solutions
- Haplotype analysis using shapeit
- Optimisation des performances - compression, chargement et formatage des images
猜你喜欢

Talk about the multimodal project of fire

AI越进化越跟人类大脑像!Meta找到了机器的“前额叶皮层”,AI学者和神经科学家都惊了...

DSP gossip: how to save the compiled variables on the chip when the variables are defined in the code

ES复合查询工作量评估

还在直接用localStorage么?全网最细:本地存储二次封装(含加密、解密、过期处理)

Les nouveaux programmeurs optimisent une ligne de code lundi et sont exhortés à se retirer mercredi?

应用配置管理,基础原理分析

Brief introduction of quality control conditions before genotype filling

中国国际电子商务中心与易观分析联合发布:2021年4季度全国网络零售发展指数同比增长0.6%

Software architecture discussion
随机推荐
Uni app advanced creation component / native rendering [Day9]
还在直接用localStorage么?全网最细:本地存储二次封装(含加密、解密、过期处理)
Matplotlib two methods of drawing torus!
What USB driver needs to know
POI implements operation to generate word tables and operate chart data in word
Xidian AI ranked higher than Qingbei in terms of AI major, and Nantah ranked first in China in terms of Software Science in 2022
Iptables Foundation
Are you still using localstorage directly? The thinnest in the whole network: secondary encapsulation of local storage (including encryption, decryption and expiration processing)
详解连接池参数设置(边调边看)
Es composite query workload evaluation
Port occupancy
poi实现操作生成word表格和操作word中的图表数据
Original code, inverse code, complement calculation function applet; C code implementation;
One of the components of the program
Stream programming: stream support, creation, intermediate operation and terminal operation
How to convert mindspire model to onnx format and use onnxruntime reasoning - development test
wangeditor封装插件初步
The backbone of the top 100 security companies! Meichuang technology was selected into the 2022 China top 100 Digital Security Report
js正则-梳理
Odd number of characters exception
