当前位置:网站首页>[multithreading] lock strategy
[multithreading] lock strategy
2022-07-01 20:01:00 【Fly upward】
Catalog
1. Optimistic lock and pessimistic lock
2. Read / write locks and ordinary mutex locks
3. Heavyweight locks and lightweight locks
4. Hang wait lock and spin lock
5. Reentrant lock and Do not reenter the lock
7.3 CAS Implement atomic classes
8.2 Relevant interview questions
1. Optimistic lock and pessimistic lock
1) Optimism lock , That is, the probability of expected lock collision is very low .
Always assume the worst , Every time I go to get the data, I think others will modify it , So every time I get the data, I lock it , So people who want to take this data will block it until it gets the lock
for example , Even if the next epidemic comes , And don't worry about it , Life can work normally , A lot of food and supplies can be bought , No special preparation is required .( Optimism lock )
2) Pessimistic locking , That is, the probability of expected lock conflicts is very high
2. Read / write locks and ordinary mutex locks
1) For ordinary mutexes , There are only two operations : Lock and unlock
Two threads lock the same object , There will be mutual exclusion
Add read lock : If the code just reads , Just add a read lockAdd write lock : If a modification is made in the code , Just add a write lockUnlock
Between threads , There is no thread safety problem between data readers , But the writers of the data need to communicate with each other and with the readers To be mutually exclusive . If the same lock is used in both scenarios , There will be great performance loss . Therefore, read-write locks are generated .
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock Class represents a read lock . This object provides lock / unlock Method to lock and unlock .ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock Class represents a write lock . This object also provides lock / unlock The method is to enter into Row lock unlock
Between read lock and read lock , There is no mutual exclusion ( Multiple threads read a variable at the same time , There will be no thread safety issues )
Between read lock and write lock , Between write lock and write lock , To be mutually exclusive
3. Heavyweight locks and lightweight locks
CPU Provides " Atomic operation instructions ".The operating system is based on CPU Atomic instructions for , Realized mutex The mutex .JVM Based on the mutex provided by the operating system , Realized synchronized and ReentrantLock Keywords and classes .
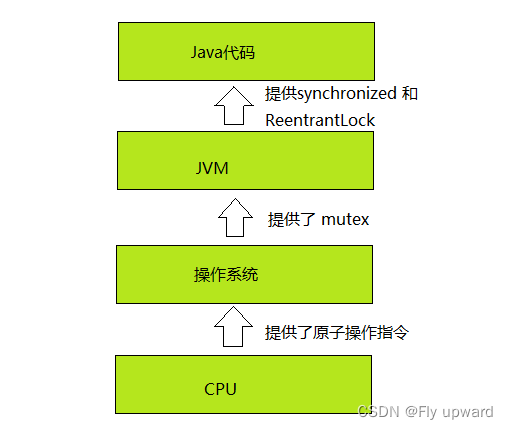
Be careful , synchronized Not just for mutex encapsulate , stay synchronized A lot of other work has been done internally
synchronized It starts with a lightweight lock . If the lock conflict is serious , Will become a heavyweight lock
2) Heavyweight lock
A large number of kernel mode user mode switchingIt's easy to trigger thread scheduling
3) Lightweight lock
A small number of kernel mode user mode switching .It is not easy to cause thread scheduling .
4) Understand user behavior vs Kernel mode
Imagine going to the bank to do business
4. Hang wait lock and spin lock
The pending lock is Heavyweight lock How to implement
advantage : Didn't give up CPU, Thread blocking and scheduling are not involved , Once the lock is released , You can get the lock at the first time .shortcoming : If the lock is held by other threads for a long time , Then it will continue to consume CPU resources . ( And the time to hang up waiting isDon't consume CPU Of
4. Fair lock and unfair lock
5. Reentrant lock and Do not reenter the lock
One thread , Lock the same lock for two consecutive times , If it will deadlock, it is a non reentrant lock , If it doesn't deadlock , It's a re-entry lock .synchronized It's a reentrant lock
6. synchronized Lock summary
1) Both an optimistic lock , It is also a pessimistic lock . ( Adaptive according to the intensity of lock competition )
2) It's not a read-write lock, it's just an ordinary mutex .
3) It's both a lightweight lock , It's also a heavyweight lock ( According to the intensity of lock competition , The adaptive )
4) The part of lightweight lock is based on spin lock . The heavyweight part is based on the pending lock
5) Not fair lock
6) Reentrant lock .
7. CAS
Let's assume that the raw data in memory V, Old expectations A, New values that need to be modified B.1. Compare A And V Whether it is equal or not .( Compare )2. If it's equal , take B write in V.( In exchange for )3. Whether the return operation is successful .
7.1 CAS Pseudo code
boolean CAS(address, expectValue, swapValue) {
if (&address == expectedValue) {
&address = swapValue;
return true;
}
return false;
}
CAS It can be regarded as an optimistic lock . ( Or it can be understood as CAS It's an implementation of optimistic lock )
7.2 CAS How did it happen
java Of CAS Take advantage of unsafe This class provides CAS operation ;unsafe Of CAS Rely on jvm For different operating systems Atomic::cmpxchg;Atomic::cmpxchg The implementation of using the assembly of CAS operation , And use cpu Hardware provided lock The mechanism guarantees its atomicity
7.3 CAS Implement atomic classes
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
// This method is equivalent to num++
num.getAndIncrement();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
// This method is equivalent to num++
num.getAndIncrement();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(num.get());
}
}
There is no thread safety problem in the above code .
be based on CAS Realized ++ operation .
This can ensure thread safety , And can compare with synchronized Efficient .
synchronized Will involve lock competition , Two threads have to wait for each other .
CAS Thread blocking and waiting are not involved
7.4 Spin lock
public class SpinLock {
private Thread owner = null;
public void lock(){
// adopt CAS See if the current lock is held by a thread .
// If the lock is already held by another thread , Then wait .
// If the lock is not held by another thread , Then put owner Set to the thread currently trying to lock .
while(!CAS(this.owner, null, Thread.currentThread())){
}
}
public void unlock (){
this.owner = null;
}
}Similar to the atomic class above , It is also realized through a loop .
Call... In the loop CAS.CAS Will compare current owner Is the value null,
If it is null Change to the current thread . It means that the current thread has got the lock .
If not null Just go back to false, Into the next loop .
The next cycle is still going on CAS operation
If the current lock is one Directly held by others , The thread currently trying to lock will be in this while Where fast
Repeat the cycle ~~~ => The spin ~~ ( Busy etc. )
Spin lock is a lightweight lock, which can also be regarded as an optimistic lock .
8. CAS Of ABA problem
hypothesis A Yes 100 deposit .,A Want to ATM take 50 Yuan . The ATM creates two threads , Execute concurrently -50 operation .We expect a thread to execute -50 success , Another thread -50 Failure .( Another thread is stuck when the machine breaks down , Press one more withdrawal , The thread is enabled , Failed to use to withdraw )
1) deposit 100. Threads 1 The current deposit value obtained is 100, Expect to update to 50; Threads 2 The current deposit value obtained is 100, Expect to update to 50.2) Threads 1 Deduction successfully executed , The deposit was changed to 50. Threads 2 Blocking waiting .3) It's the thread's turn 2 Yes , It is found that the current deposit is 50, And what I read before 100 inequality , Execution failure .Finally take it out 50
Abnormal process :
1) deposit 100. Threads 1 The current deposit value obtained is 100, Expect to update to 50; Threads 2 The current deposit value obtained is 100, Expect to update to 50.2) Threads 1 Deduction successfully executed , The deposit was changed to 50. Threads 2 Blocking waiting .3) In a thread 2 Perform before , A My friend just gave me A Transfer accounts 50, The account balance becomes 1004) It's the thread's turn 2 Yes , It is found that the current deposit is 100, And what I read before 100 identical , Perform the deduction operation againFinally take it out 100
This is the time , The deduction operation was performed twice , Namely ABA Caused by the
8.1 Solution
Give the value to be modified , Introduce version number .. stay CAS Compare the current value of the data with the old value , Also compare whether the version number meets the expectation .
CAS The operation reads the old value while , Also read the version number .When it's really revised ,If the current version number is the same as the read version number , Then modify the data , And put the version number + 1.If the current version number is higher than the read version number . The operation failed ( Think the data has been modified ).
stay Java The standard library provides AtomicStampedReference<E> class . This class can wrap a class , In-house mention It provides the version management function described above .
8.2 Relevant interview questions
Full name Compare and swap, namely " Compare and exchange ". Equivalent to the operation of an atom , Simultaneous completion " Read memory , Comparison is equal , Modify memory " These three steps . Essentially, we need CPU Support of instructions .
2) ABA How to solve the problem ?
Introduce the version number to the data to be modified . stay CAS Compare the current value of the data with the old value , Also compare whether the version number meets the expectation .If the current version number is found to be consistent with the version number read before , Just really perform the modification operation , And let the version number increase ; If you find that the current version number is larger than the version number you read before , It is considered that the operation failed .
边栏推荐
- 较真儿学源码系列-InheritableThreadLocal(逐行源码带你分析作者思路)
- fastDFS入门
- [C language] explain the usage of memset() function in detail
- Is Dao safe? Build finance encountered a malicious governance takeover and was looted!
- What if the win11 shortcut key switching input method doesn't respond? Shortcut key switching input method does not respond
- Install redis under Linux and configure the environment
- Hls4ml reports an error the board_ part definition was not found for tul. com. tw:pynq-z2:part0:1.0.
- C # joint Halcon application - Dahua camera acquisition class
- A quietly rising domestic software, low-key and powerful!
- Wechat applet realizes keyword highlighting
猜你喜欢

1592 example 1 King (sgu223 loj10170 luogu1896 increase + / provincial election -) violent thinking pressure DP 01 Backpack

【多线程】 实现单例模式 ( 饿汉、懒汉 ) 实现线程安全的单例模式 (双重效验锁)

SQL getting started plan-1-select

毕业季 | 华为专家亲授面试秘诀:如何拿到大厂高薪offer?
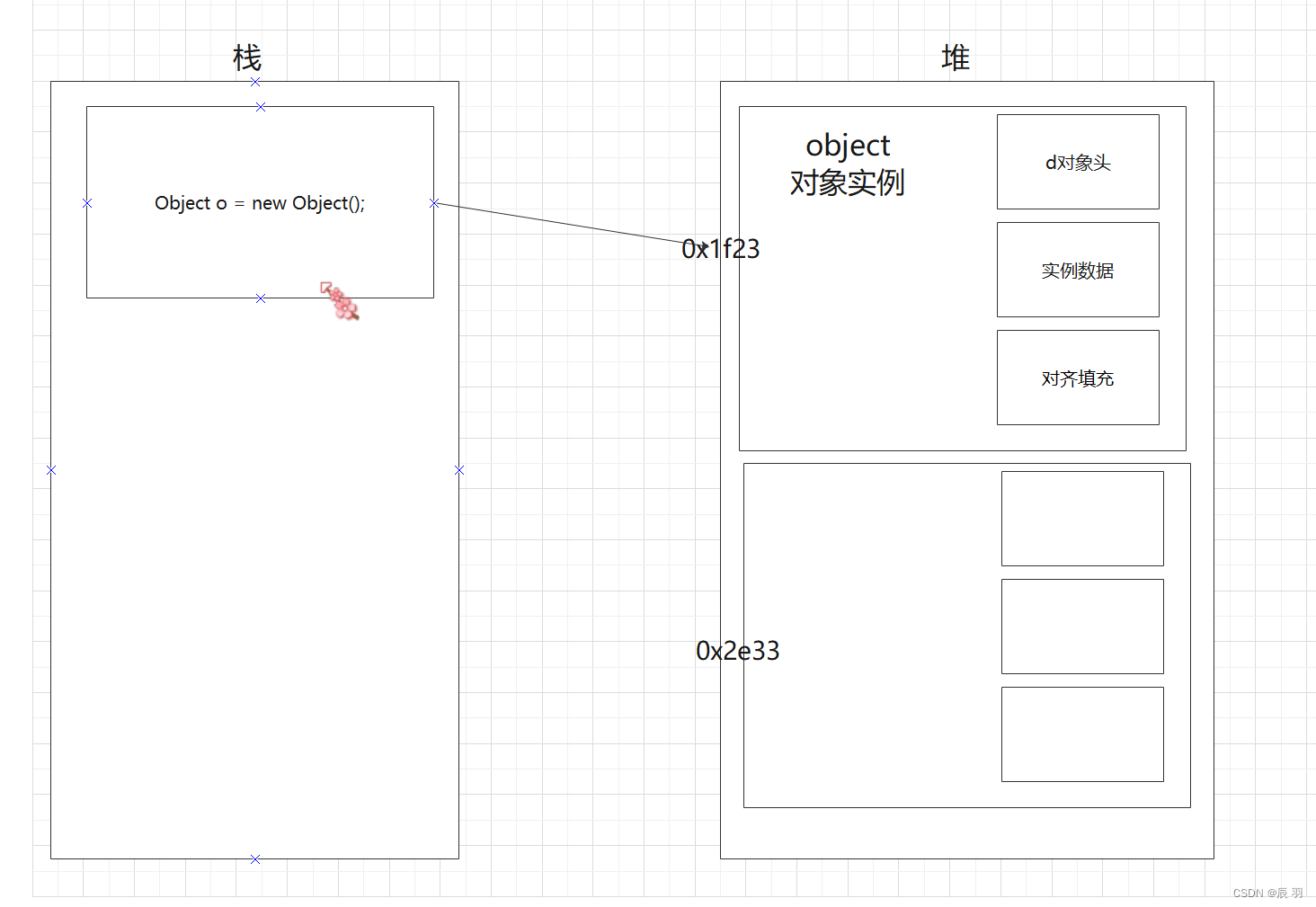
Object creation
漏洞复现-.Net-ueditor上传
STC 32位8051单片机开发实例教程 二 I/O工作模式及其配置

强大、好用、适合程序员/软件开发者的专业编辑器/笔记软件综合评测和全面推荐
JS的Proxy
![[research materials] national second-hand housing market monthly report January 2022 - Download attached](/img/c8/a205ddc2835c87efa38808cf31f59e.jpg)
[research materials] national second-hand housing market monthly report January 2022 - Download attached
随机推荐
振弦采集模块测量振弦传感器的流程步骤
Easycvr accesses the equipment through the national standard gb28181 protocol. What is the reason for the automatic streaming of the equipment?
Related concepts of cookies and sessions
Time series analysis using kibana timelion
C#聯合halcon應用——大華相機采集類
PowerDesigner设计Name和Comment 替换
开发那些事儿:EasyCVR集群设备管理页面功能展示优化
全国职业院校技能大赛网络安全“splunk“详细配置
2022/6/8-2022/6/12
Anaconda installs the virtual environment to the specified path
Problems encountered in installing MySQL in docker Ubuntu container
实例讲解将Graph Explorer搬上JupyterLab
Mo Tianlun salon | Tsinghua qiaojialin: Apache iotdb, originated from Tsinghua, builds an open source ecological road
【无标题】
EasyCVR集群视频广场页面切换时,请求流未能终止的问题优化
[exercise] HashSet
Install redis under Linux and configure the environment
#yyds干货盘点#SQL聚合查询方法总结
[untitled]
JS 之 常用内置类的使用