当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to basic use and pit closure of BigDecimal
Introduction to basic use and pit closure of BigDecimal
2022-06-11 18:27:00 【Rookie - work hard】
Preface : We often use in the development process BigDecimal To use the amount data type , Especially keep the decimal point 2 position , Improve the accuracy of scientific calculation , however BigDecimal Improper use will also lead to loss of accuracy , And double Similar situation .
One . First, let's verify the above problem , Programmer first code
/** * @author zhaoyy * @version 1.0 * @description BigDecimal Type used * @date 2022/6/9 **/
public class BigDecimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bigDecimal=new BigDecimal(66);
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
bigDecimal=new BigDecimal("6.6");
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
bigDecimal=new BigDecimal(6.6);
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
// Recommended
bigDecimal= BigDecimal.valueOf(6.6);
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
}
}
Output content :
66
6.6
6.5999999999999996447286321199499070644378662109375
6.6
The penultimate output above , There is a problem of precision loss , Recommended BigDecimal.valueOf() Method to complete the initialization value , Use less construction methods to BigDecimal assignment ,BigDecimal Constructors will call different constructor methods for different data types , You can click the open source code to understand the specific code . and valueOf() Method in use double Method to convert the type to toString Please see the following source code for details .
Source code display :
double Type construction method :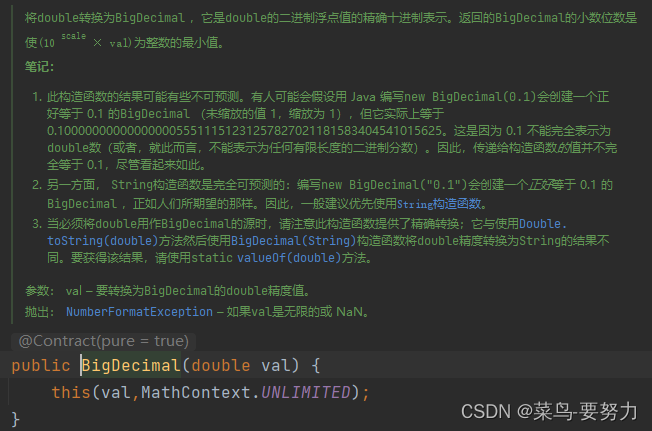

summary :
1 .BigDecimal Constructor initialization value corresponds to double,flot Type needs to consider whether it supports precision loss
2. Cause of loss of accuracy , Is that data will be converted into binary number type during data type conversion , When decimal decimal places are converted to binary, there may be an infinite loop or the length exceeding the mantissa of floating-point numbers , The problem that eventually leads to the loss of accuracy .
3. It is suggested that BigDecimal.valueOf() Try to avoid such problems
So much has been said , Let's share one BigDecimal Basic operation tool class
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/** * @author zhaoyy * @version 1.0 * @description bigDecimal Tool class * @date 2022/6/9 **/
public class BigDecimalUtils {
public static BigDecimal doubleAdd(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.add(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal floatAdd(float v1, float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v2));
return b1.add(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal doubleSub(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.subtract(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal floatSub(float v1, float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v2));
return b1.subtract(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal doubleMul(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.multiply(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal floatMul(float v1, float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v2));
return b1.multiply(b2);
}
public static BigDecimal doubleDiv(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
// Keep two decimal places ROUND_HALF_UP = rounding
return b1.divide(b2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
}
public static BigDecimal floatDiv(float v1, float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v2));
// Keep two decimal places ROUND_HALF_UP = rounding
return b1.divide(b2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
}
/** * Compare v1 v2 size * @param v1 * @param v2 * @return v1>v2 return 1 v1=v2 return 0 v1<v2 return -1 */
public static int doubleCompareTo(double v1, double v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(v2));
return b1.compareTo(b2);
}
public static int floatCompareTo(float v1, float v2) {
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v1));
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(Float.toString(v2));
return b1.compareTo(b2);
}
}
边栏推荐
- [c language] output students' names and scores in descending order of scores with structures
- 初识企业级平台
- [c language] output the average score and the student data below or equal to the average score with the structure
- MATLAB 保存imshow绘制图片到指定文件夹中的两种方法
- 使用mysql判断日期是星期几
- async导致函数结果出乎意料,改变原来代码的意图;await is only valid in async functions and the top level bodies of modules
- Sorted circular linked list
- [c language] limit the number of searches and output the maximum value found in the number of internal searches
- IEDA 底层菜单菜单简介
- Force deduction 23 questions, merging K ascending linked lists
猜你喜欢
![[golang] leetcode - 292 Nim games (Mathematics)](/img/82/54c3f6be9d08687b42cba0487380f0.png)
[golang] leetcode - 292 Nim games (Mathematics)

ISCSI详解(四)——ISCSI服务端配置实战
![[not forgetting the original intention and forging ahead] 2021 Zhongchuang Suanli new year conference and anniversary celebration](/img/ae/9a0c300f2dcb03b05d737f14b0955f.jpg)
[not forgetting the original intention and forging ahead] 2021 Zhongchuang Suanli new year conference and anniversary celebration

TR-069 protocol introduction

力扣23题,合并K个升序链表

Cryptology Summary

牛客刷题——两种排序方法
合并多棵二叉搜索树

Easycwmp source code analysis
![[C语言]用结构体把输入的指定分数范围内的学生输出](/img/40/cbd7fe5aafbaeb6237e6d257455e5e.png)
[C语言]用结构体把输入的指定分数范围内的学生输出
随机推荐
Explain AI accelerators in detail: GPU, DPU, IPU, TPU... There are infinite possibilities for AI acceleration schemes
LDPC 7 - 解码简单例子
Reading summary of nacos2.x source code
牛客刷题——求最小公倍数
论催收系统的管理子系统选型设计
01.电信_领域业务经验
关于keil中,while循环条件不成立却无法跳出的问题
async导致函数结果出乎意料,改变原来代码的意图;await is only valid in async functions and the top level bodies of modules
New work of "the father of LSTM": a new method towards self correcting neural network
[C语言]限制查找次数,输出次数内查找到的最大值
全志科技T3开发板(4核ARM Cortex-A7)——视频开发案例
[Golang]力扣Leetcode - 349. 两个数组的交集(哈希表)
[c language] compress strings and add markup characters
Apipost精妙使用技巧
Feign 共享登录信息进行请求
Is it good or not to open a stock account on the flush? Is it safe?
ISCSI详解(四)——ISCSI服务端配置实战
[C语言]压缩字符串并添加标记字符
Summary of common mysql/redis interview questions
单选按钮 文字背景同时改变