当前位置:网站首页>深度学习100例 —— 卷积神经网络(CNN)天气识别
深度学习100例 —— 卷积神经网络(CNN)天气识别
2022-08-04 10:32:00 【Ding Jiaxiong】
活动地址:CSDN21天学习挑战赛
深度学习100例——卷积神经网络(CNN)天气识别
我的环境

1. 前期准备工作
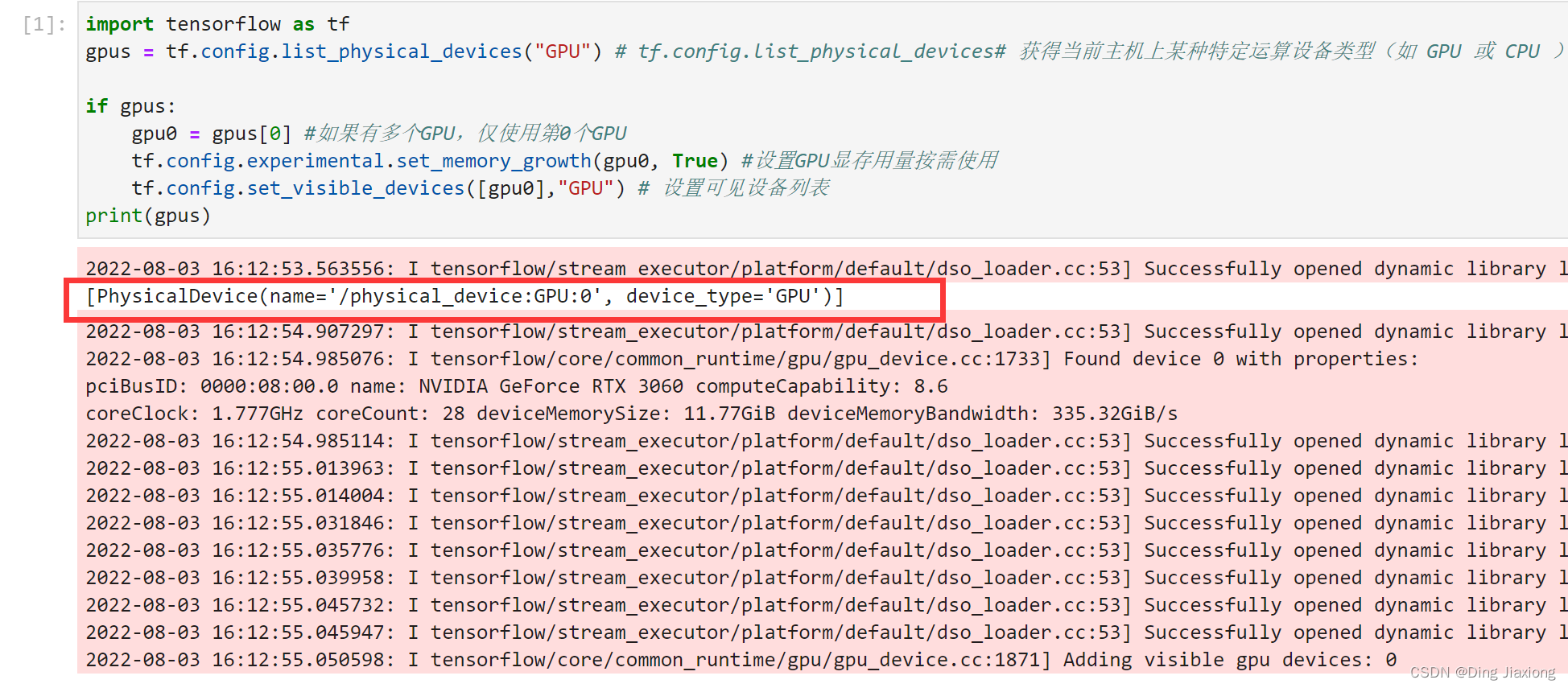
1.1 设置GPU
import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU") # tf.config.list_physical_devices# 获得当前主机上某种特定运算设备类型(如 GPU 或 CPU )的列表
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] #如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0, True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU") # 设置可见设备列表
1.2 导入数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os,PIL
# 设置随机种子尽可能使结果可以重现
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1)
# 设置随机种子尽可能使结果可以重现
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(1)
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers,models
import pathlib
1.3 查看数据
数据集中一共有cloudy、rain、shine、sunrise四类。
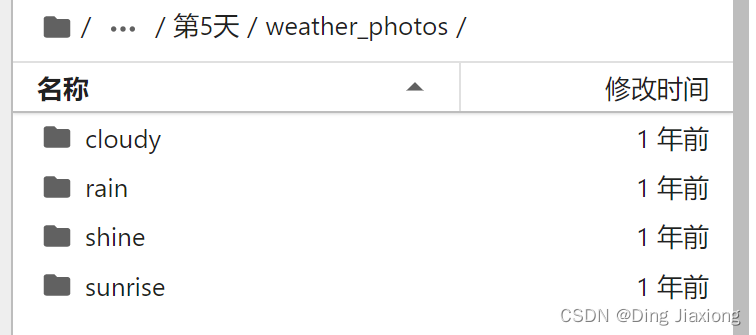
设置数据集路径及查看图片
data_dir = "第5天/weather_photos/"
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.jpg')))
print("图片总数为:",image_count)
查看sunrise的第一张图片
roses = list(data_dir.glob('sunrise/*.jpg'))
PIL.Image.open(str(roses[0]))
2. 数据预处理
2.1 加载数据
使用image dataset_from directory方法将磁盘中的数据加载到tf.data.Dataset中
batch_size = 32 # 用于控制数据批次的大小,默认32
img_height = 180 # 图片像素高度
img_width = 180 # 图片像素宽度
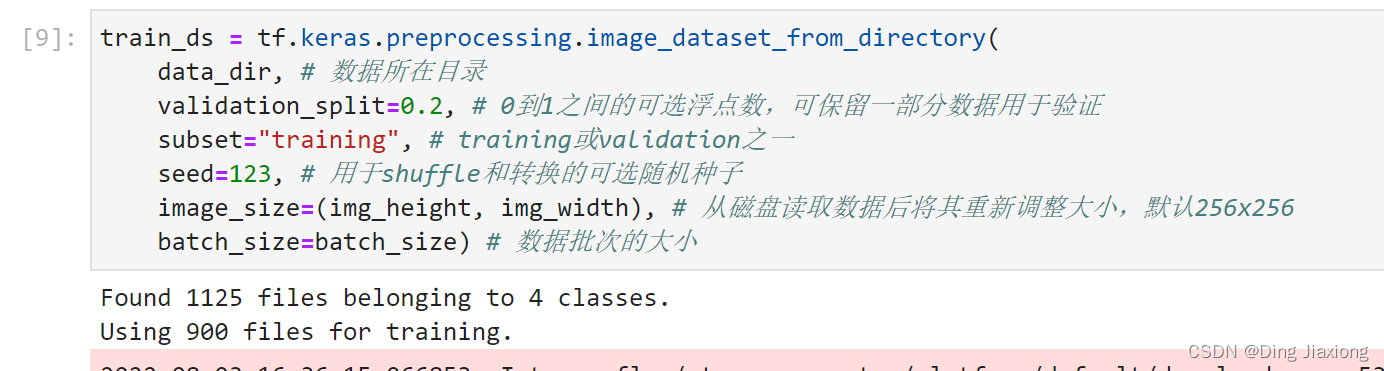
train_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir, # 数据所在目录
validation_split=0.2, # 0到1之间的可选浮点数,可保留一部分数据用于验证
subset="training", # training或validation之一
seed=123, # 用于shuffle和转换的可选随机种子
image_size=(img_height, img_width), # 从磁盘读取数据后将其重新调整大小,默认256x256
batch_size=batch_size) # 数据批次的大小
同样的设置验证数据集。
val_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="validation",
seed=123,
image_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)

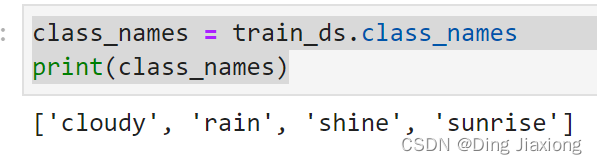
通过class_names输出数据集的标签,标签将按字母顺序对应于目录名称。
class_names = train_ds.class_names
print(class_names)
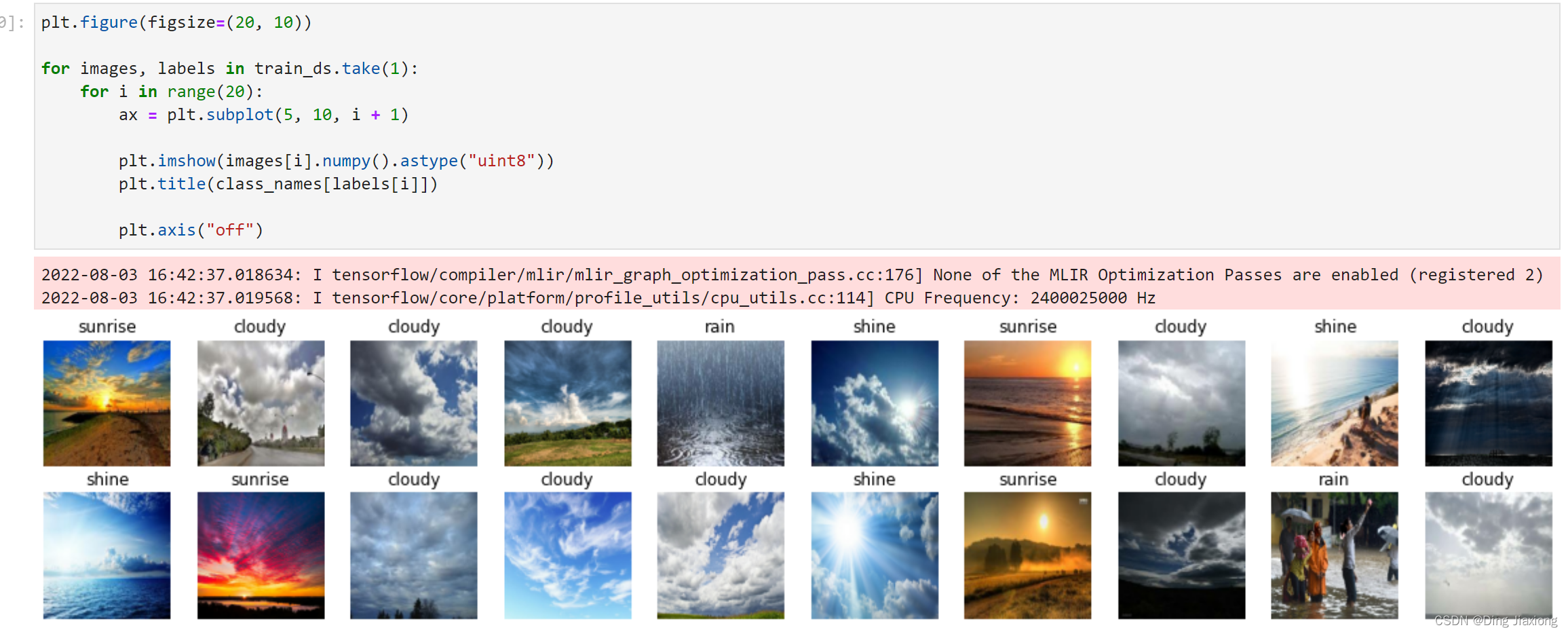
2.2 可视化数据
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
for images, labels in train_ds.take(1):
for i in range(20):
ax = plt.subplot(5, 10, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].numpy().astype("uint8"))
plt.title(class_names[labels[i]])
plt.axis("off")
2.3 检查数据
for image_batch, labels_batch in train_ds:
print(image_batch.shape)
print(labels_batch.shape)
break
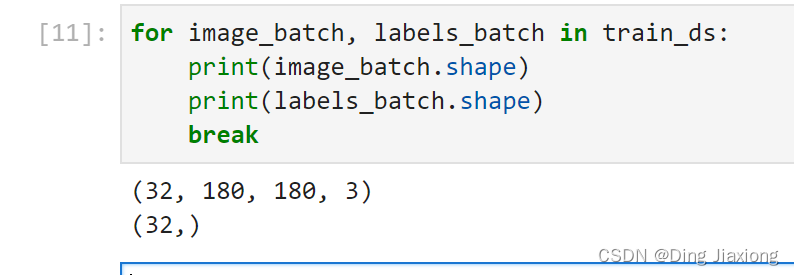
- image_batch是形状的张量(32 , 180 , 180 ,3)。3通道的180x180,32张图
- labels_batch是(32 , ) , 对应32张图片
2.4 配置数据集
shuffle():打乱数据
prefetch():预取数据,加速运行
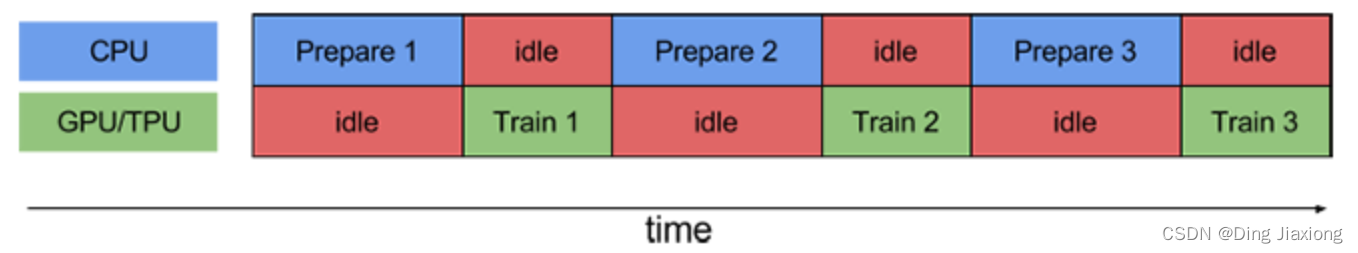
CPU正在准备数据时,加速器处于空闲状态。相反,当加速器正在训练模型时,CPU处于空闲状态。因此,训练所用的时间是CPU预处理时间和加速器训练时间的总和。prefetch()将训练步骤的预处理和模型执行过程重叠到一起。当加速器正在执行第N个训练步时,CPU正在准备第N+1步的数据。这样做不仅可以最大限度地缩短训练的单步用时〈(而不是总用时),而且可以缩短提取和转换数据所需的时间。如果不使用prefetch( ),CPU和GPU/TPU在大部分时间都处于空闲状态:
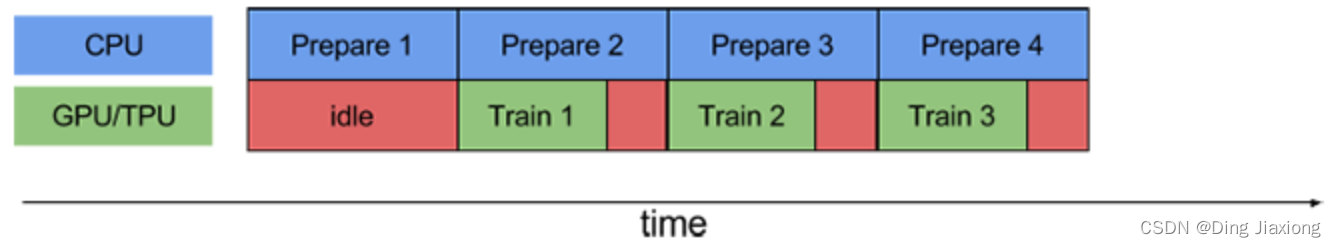
使用prefetch()可以显著减少空闲时间:
cache():将数据集缓存到内存当中,加速运行
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
train_ds = train_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
val_ds = val_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
3. 构建CNN网络
num_classes = 4
model = models.Sequential([
layers.experimental.preprocessing.Rescaling(1./255, input_shape=(img_height, img_width, 3)),
layers.Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(img_height, img_width, 3)), # 卷积层1,卷积核3*3
layers.AveragePooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层1,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层2,卷积核3*3
layers.AveragePooling2D((2, 2)), # 池化层2,2*2采样
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'), # 卷积层3,卷积核3*3
layers.Dropout(0.3),
layers.Flatten(), # Flatten层,连接卷积层与全连接层
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 全连接层,特征进一步提取
layers.Dense(num_classes) # 输出层,输出预期结果
])
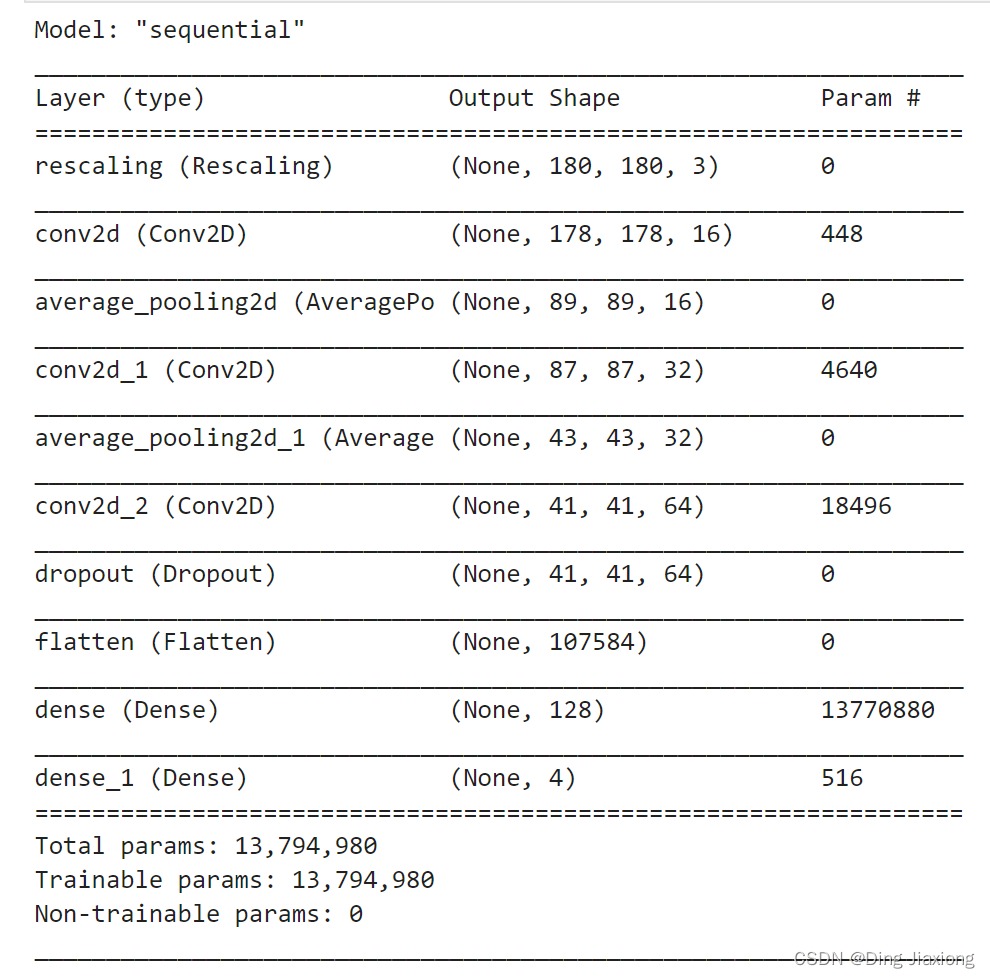
model.summary() # 打印网络结构
4. 编译模型
- 损失函数loss:用于衡量模型在训练期间的准确率
- 优化器optimizer:决定模型如何根据其看到的数据和自身的损失函数进行更新。
- 指标metrics:用于监控训练和测试步骤。
# 设置优化器
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001)
model.compile(optimizer=opt,loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),metrics=['accuracy'])
5. 训练模型
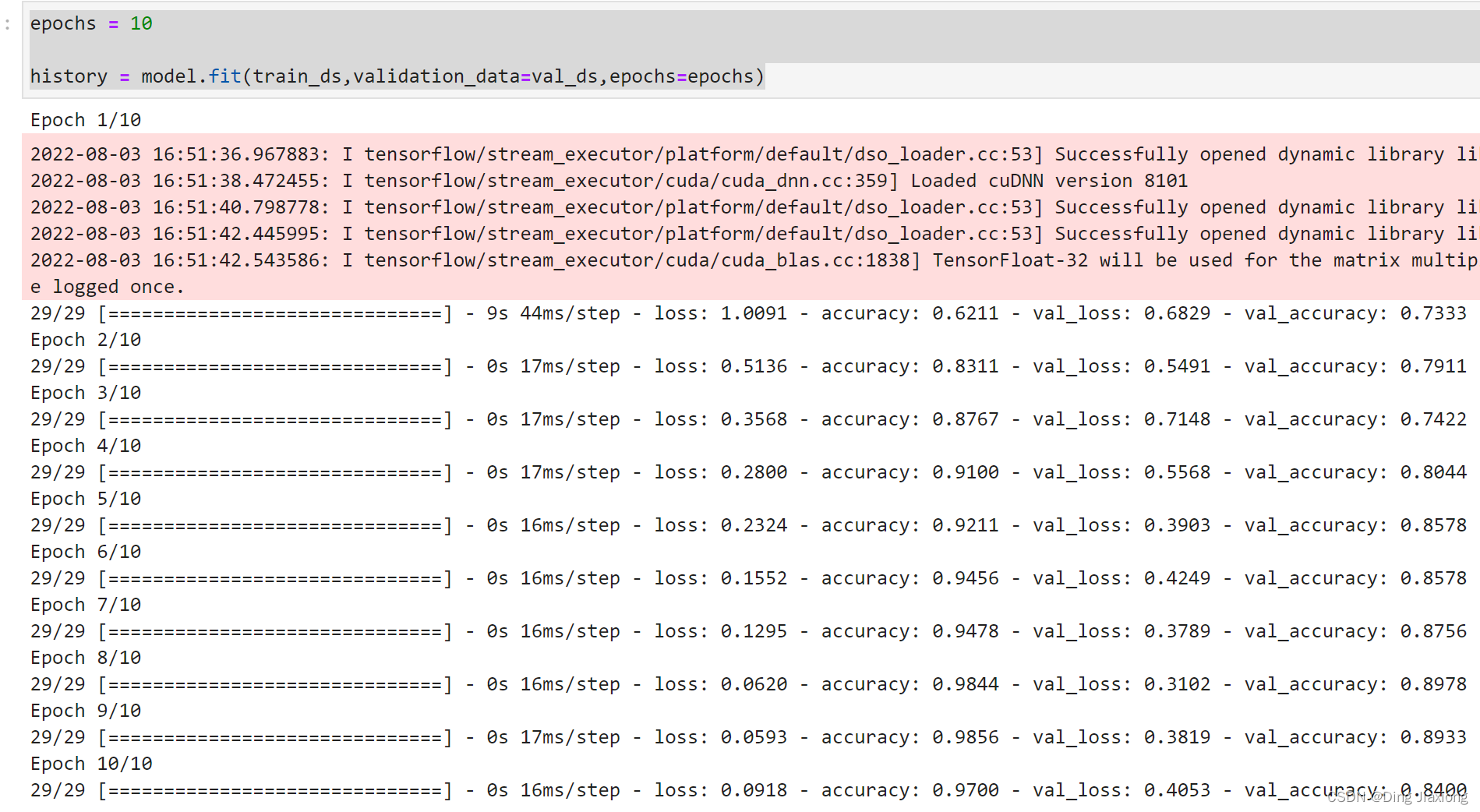
epochs = 10
history = model.fit(train_ds,validation_data=val_ds,epochs=epochs)
6. 模型评估
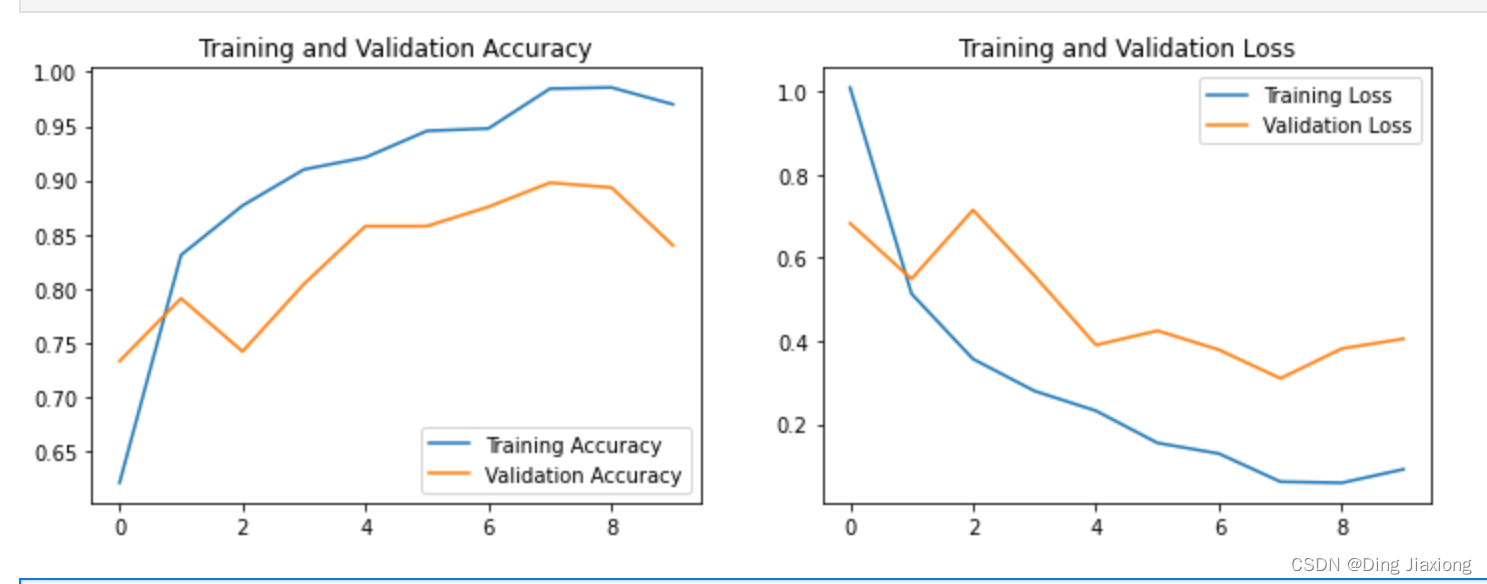
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()
边栏推荐
- Heap Sort
- 暴力破解ssh/rdp/mysql/smb服务
- 航企纠缠A350安全问题 空客主动取消飞机订单
- 【Idea系列】idea配置
- tp5+微信小程序 分片上传
- Apache Calcite 框架原理入门和生产应用
- 在 .NET MAUI 中如何更好地自定义控件
- gom登录器配置教程_谷歌浏览器如何使用谷歌搜索引擎
- Introduction to the core methods of the CompletableFuture interface
- iMeta | Baidu certification is completed, search "iMeta" directly to the publisher's homepage and submission link
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
学习在php中将特大数字转成带有千/万/亿为单位的字符串
语音社交app源码——具备哪些开发优势?
2022-08-03 第六小组 瞒春 学习笔记
一文带你了解 ESLint
Jenkins使用手册(1) —— 软件安装
Multimedia and Internet of Things technology make the version "live" 129 vinyl records "Centennial Voice"
开源一夏|ArkUI如何自定义弹窗(eTS)
iMeta | Baidu certification is completed, search "iMeta" directly to the publisher's homepage and submission link
无代码平台数字入门教程
Techwiz OLED:OLED器件的发光效率
冰蝎工具开发实现动态二进制加密WebShell
Mysql应用日志时间与系统时间相差八小时
Google Earth Engine APP ——制作上传GIF动图并添加全球矢量位置
双重for循环案例以及while循环和do while循环案例
学习在php中分析switch与ifelse的执行效率
华为云安全云脑,让企业云化运营更放心
iMeta | 德国国家肿瘤中心顾祖光发表复杂热图(ComplexHeatmap)可视化方法
用匿名函数定义函数_c语言最先执行的函数是
学习使用php把stdClass Object转array的方法整理
mysql进阶(二十六)MySQL 索引类型