当前位置:网站首页>Redis 100 million level data storage scheme hash slot partition
Redis 100 million level data storage scheme hash slot partition
2022-07-24 11:02:00 【Scattered_ step】
1~2 Billion pieces of data need to be cached , How to design this storage case ?
Single machine, single machine 100% impossible , It must be distributed storage , use redis How to land ?
The general industry has 3 Kind of solution :
The first one is : Hash remainder partition :

2 One hundred million records are 2 One hundred million k,v, We can't do it on a single machine. We have to distribute multiple machines , Suppose there is 3 Machines form a cluster , Every time a user reads or writes, he or she uses a formula :
hash(key) % N Number of machines , Calculate the hash value , It is used to determine which node the data is mapped to .
advantage :
Simple and crude , Directly effective , Just estimate the data and plan the nodes , for example 3 platform 、8 platform 、10 platform , Can guarantee a period of data support . Use Hash The algorithm makes a fixed part of the requests fall on the same server , In this way, each server will process a part of the requests ( And maintain the requested information ), Load balancing + The role of divide and rule .
shortcoming :
The originally planned node , It is troublesome to expand or shrink the capacity , Regardless of expansion or contraction , Every time the data changes, the node changes , The mapping relationship needs to be recalculated , There is no problem when the number of servers is fixed , If elastic capacity expansion or fault shutdown is required , The original mold formula will change :Hash(key)/3 Will become Hash(key) /?. At this time, the result of the remainder operation of the address will change greatly , The server obtained according to the formula will also become uncontrollable .
Some redis The machine is down , Due to the change in the number of sets , It can lead to hash Take all the remaining data and shuffle again .
The second kind : Consistent hash algorithm partition :
Uniformity Hash Algorithm background
The consistency hash algorithm 1997 Proposed by MIT in , The design goal is to solve
Distributed cache data change and mapping problem , A machine is down , The number of denominators has changed , Natural remainder is not OK 了 .
What can I do? :
Propose consistency Hash Solution .
The purpose is when the number of servers changes ,
Minimize the impact of client to server mapping
3 Big steps :
1. The algorithm constructs a consistent hash ring :
Consistent hash ring
A consistent hash algorithm must have hash Function and generate... According to the algorithm hash value , All possible hash values of this algorithm will form a full set , This set can become a hash Space [0,2^32-1], This is a linear space , But in the algorithm , We connect it end to end through appropriate logical control (0 = 2^32), This makes it logically form an annular space .
It is also in accordance with the method of taking mold , The node modeling method introduced in the previous note is to take the node ( The server ) Take the mold according to the quantity . And consistency Hash The algorithm is right 232 modulus , Simply speaking ,** Uniformity Hash The algorithm organizes the whole hash space into a virtual circle , Suppose a hash function H The value space of is 0-232-1**( That is, the hash value is a 32 Bit unsigned shaping ), The whole hash ring is shown in the figure below : The whole space is organized in a clockwise direction , The point directly above the circle represents 0,0 The first point on the right represents 1, And so on ,2、3、4、…… until 232-1, in other words 0 The first point on the left represents 232-1, 0 and 232-1 The direction coincides in zero , We put this by 232 The circle of dots is called Hash Ring .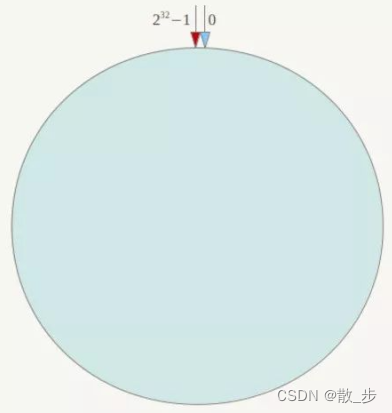
2. The server IP Node mapping :
Node mapping
Connect all nodes in the cluster IP The node is mapped to a position on the ring .
Use each server Hash Make a hash , You can choose the server IP Or the host name as a key to hash , In this way, each machine can determine its position on the hash ring . If 4 Nodes NodeA、B、C、D, after IP Hash function calculation of address (hash(ip)), Use IP The location of the address hash in the ring space is as follows :
3.key Drop key rules for server
When we need to store a kv Key to time , First calculate key Of hash value ,hash(key), Put this key Use the same function Hash Calculate the hash value and determine the position of this data on the ring , Clockwise along the ring from this position “ walk ”, The first server encountered is the server it should be located to , And store the key value pair on the node .
If we have Object A、Object B、Object C、Object D Four data objects , After hashing , The position in the ring space is as follows : According to consistency Hash Algorithm , data A Will be set to Node A On ,B Set to Node B On ,C Set to Node C On ,D Set to Node D On .
advantage :
Fault tolerance of consistent hash algorithm :
Fault tolerance
hypothesis Node C Downtime , You can see the object at this time A、B、D Not affected , Only C The object is repositioned to Node D. General , In consistency Hash In the algorithm, , If a server is not available **, Then the affected data is only from this server to the previous server in its ring space ( I.e. the first server I met when I walked in a counterclockwise direction ) Data between **, Others will not be affected . In short , Namely C Hang up , What is affected is B、C Data between , And the data will be transferred to D For storage .
Scalability of consistent hash algorithm :
Extensibility
The amount of data has increased , Need to add a node NodeX,X The position of is A and B Between , What is affected is A To X Data between , Put the A To X Enter your data into X You can go up. ,
Will not lead to hash Take all the remaining data and shuffle again .
shortcoming :
Data skew problem of consistent hash algorithm :
Hash Data skew of the ring
Uniformity Hash Algorithm in service When there are too few nodes , It is easy to be caused by uneven node distribution Data skew ( Most of the cached objects are cached on a certain server ) problem ,
For example, there are only two servers in the system :
A small summary :
In order to migrate as little data as possible when the number of nodes changes
Arrange all the storage nodes in the end Hash On the ring , Every key In the calculation Hash Later meeting Find the adjacent storage node clockwise to store .
When a node joins or exits, it only affects the node in Hash On the ring Clockwise adjacent subsequent nodes .
advantage
Adding and deleting nodes only affect the clockwise adjacent nodes in the hash ring , No impact on other nodes .
shortcoming
The distribution of data is related to the location of nodes , Because these nodes are not evenly distributed on the hash ring , Therefore, the data cannot be evenly distributed when stored .
The third kind of : Hash slot partition
1. What is it? :
The hash slot is essentially an array , Array [0,2^14 -1] formation hash slot Space .
2 Can do
Solve the problem of uniform distribution , Another layer is added between data and nodes , Call this floor Hashi trough (slot), Used to manage the relationship between data and nodes , Now it's equivalent to a slot on the node , There's data in the slot .
The groove solves the problem of granularity , It's equivalent to increasing the granularity , This makes it easy to move data .
Hash solves the mapping problem , Use key The hash value to calculate the slot , Easy data distribution .
3 How many? hash Slot
A cluster can only have 16384 Slot , Number 0-16383(0-2^14-1). These slots are allocated to all primary nodes in the cluster , The allocation strategy does not require . You can specify which numbered slots are assigned to which master node . The cluster will record the corresponding relationship between nodes and slots . After solving the relationship between node and slot , Next we need to be right key Find the hash value , Then on 16384 Remainder , What is the remainder key Fall into the corresponding slot .slot = CRC16(key) % 16384. Move data in slots , Because the number of slots is fixed , It's easier to deal with , So the problem of data mobility is solved .
Hash slot calculation :
Redis There's a built-in... In the cluster 16384 Hash slot ,redis The hash slot will be mapped to different nodes approximately equally according to the number of nodes . When need is in Redis Place one in the cluster key-value when ,redis First pair key Use crc16 The algorithm works out a result , Then get the result right 16384 Mod , So each of them key They all have a number in 0-16383 The Hashi trough between , That is, mapping to a node . The following code ,key And A 、B stay Node2, key And C Fall in the Node3 On 
边栏推荐
- Detailed explanation of Flink operation architecture
- Five application scenarios of Bluetooth module
- [dish of learning notes, dog learning C] minesweeping game
- Simply use MySQL index
- 用 Signal Processing Toolbox 软件对数据进行滤波
- Machine learning quiz (11) verification code recognition test - deep learning experiment using QT and tensorflow2
- Machine learning quiz (10) using QT and tensorflow to create cnn/fnn test environment
- Distributed lock implementation scheme (glory collection version)
- Signal processing: < three > DFT and FFT
- I admire a Google boss very much, and he left..
猜你喜欢

read_csv 报错:‘gbk‘ codec can‘t decode byte 0xb4 in position 274: illegal multibyte sequence

5个最佳WordPress广告插件

MySQL engine

西门子200smart自创库与说明

Five best WordPress advertising plug-ins

2018 arXiv | Objective-Reinforced Generative Adversarial Networks (ORGAN) for Sequence Generation Mo

Windows virtual machine security reinforcement process steps, detailed description of windows setting security policy, detailed description of win7 setting IP security policy, windows setting firewall

Zero basic learning canoe panel (3) -- static text, group box, picture box
![[AHK] AutoHotKey tutorial ①](/img/70/20f2e19e3e268ffe2f1e2956719c09.png)
[AHK] AutoHotKey tutorial ①

蓝牙模块的5大应用场景
随机推荐
零基础学习CANoe Panel(4)——按钮(Button )
Simply use MySQL index
Data visualization - White Snake 2: black snake robbery (1)
Redistribution distributed lock types
Zero basic learning canoe panel (7) -- input/output box
Tidb query SQL report runtime error: index out of range [-1] error
蓝牙技术的发展与历程
Machine learning quiz (10) using QT and tensorflow to create cnn/fnn test environment
Modbus RTU通讯协议详解与实例演示
【白帽子讲Web安全】第二章 浏览器安全
Daily three questions 7.22
MySQL engine
【直播报名】Location Cache 模块浅析及 OCP 监控、报警详解
简单使用 MySQL 索引
Capture and handling of JDBC exception sqlexception
向量化引擎对HTAP的价值与技术思考
蓝牙模块的5大应用场景
跨平台音频播放库
Machine learning quiz (11) verification code recognition test - deep learning experiment using QT and tensorflow2
cookie sessionStorage localStorage 区别