当前位置:网站首页>[secretly kill little buddy pytorch20 days -day02- example of image data modeling process]
[secretly kill little buddy pytorch20 days -day02- example of image data modeling process]
2022-07-03 20:53:00 【Can't write code】
It's today pytorch The second day of learning to punch in , come on. !!
Print the training time during the training
import os
import datetime
# Print time
def printbar():
nowtime = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print("\n"+"=========="*8 + "%s"%nowtime)
1. Prepare the data
cifar2 The data set is cifar10 A subset of a dataset , Only the first two categories are included airplane and automobile.
The training set has airplane and automobile Each picture 5000 Zhang , The test set has airplane and automobile Each picture 1000 Zhang .
cifar2 The goal of the mission is to train a model for the aircraft airplane And motor vehicles automobile Classify two kinds of pictures .
( If you need data set, please pay attention to private chat with me )
stay Pytorch There are usually two ways to build a picture data pipeline in .
The first is to use torchvision Medium datasets.ImageFolder To read the picture and then use DataLoader To load in parallel .
The second is through inheritance torch.utils.data.Dataset Implement user-defined read logic, and then use DataLoader To load in parallel .
The second method is a general method of reading user-defined data sets , You can read the picture data set , You can also read text data sets .
In this article, we introduce the first method .
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms,datasets
transform_train = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor()])
transform_valid = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor()])
ds_train = datasets.ImageFolder("cifar2/train",
transform = transform_train,target_transform= lambda t:torch.tensor([t]).float())
ds_valid = datasets.ImageFolder("cifar2/test",
transform = transform_train,target_transform= lambda t:torch.tensor([t]).float())
print(ds_train.class_to_idx)

Let's talk about it here ImageFolder
ImageFolder Suppose all files are saved in folders , Each folder stores pictures of the same category , The folder name is class name , The constructor is as follows :
ImageFolder(root, transform=None, target_transform=None, loader=default_loader)
It has four main parameters :
root: stay root Search for pictures in the specified path
transform: Yes PIL Image Conversion operation ,transform The input of is to use loader Read the return object of the picture
target_transform: Yes label Transformation
loader: How to read a picture after a given path , The default read is RGB Format PIL Image object
label It is sorted according to the folder name and saved as a dictionary , namely { Class name : Class No ( from 0 Start )}, In general, it's best to name the folder directly from 0 The starting number , This will be with ImageFolder Actually label Agreement , If not for this naming convention , Advice to see self.class_to_idx Attribute to understand label Mapping with folder name .
dl_train = DataLoader(ds_train,batch_size = 50,shuffle = True,num_workers=3)
dl_valid = DataLoader(ds_valid,batch_size = 50,shuffle = True,num_workers=3)
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
# Check out some samples
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
for i in range(9):
img,label = ds_train[i]
img = img.permute(1,2,0)
ax=plt.subplot(3,3,i+1)
ax.imshow(img.numpy())
ax.set_title("label = %d"%label.item())
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
plt.show()

2. Defining models
Use Pytorch There are usually three ways to build models :
- Use nn.Sequential Build models in a hierarchical order ,
- Inherit nn.Module Base classes build custom models ,
- Inherit nn.Module Base classes build models and assist in applying model containers (nn.Sequential,nn.ModuleList,nn.ModuleDict) encapsulate .
Choose to inherit here nn.Module Base classes build custom models .
# test AdaptiveMaxPool2d The effect of
pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
t = torch.randn(10,8,32,32)
pool(t).shape
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=32,kernel_size = 3)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size = 2,stride = 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32,out_channels=64,kernel_size = 5)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p = 0.1)
self.adaptive_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(64,32)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(32,1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.adaptive_pool(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.linear2(x)
y = self.sigmoid(x)
return y
net = Net()
print(net)

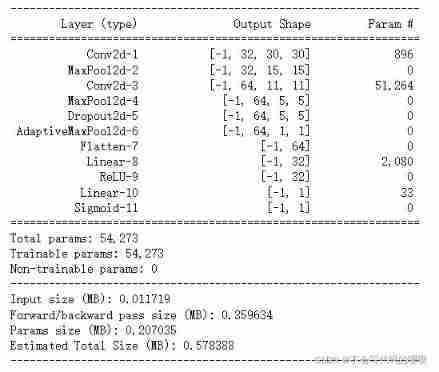
import torchkeras
torchkeras.summary(net,input_shape= (3,32,32))
3. Training models
Pytorch It usually requires the user to write a custom training cycle , The code style of the training cycle varies from person to person .
Yes 3 Class typical training cycle code style :
- Script form training cycle
- Function form training cycle
- Class form training cycle
Here we introduce a more general functional training cycle .
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
model = net
model.optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr = 0.01)
model.loss_func = torch.nn.BCELoss()
model.metric_func = lambda y_pred,y_true: roc_auc_score(y_true.data.numpy(),y_pred.data.numpy())
model.metric_name = "auc"
def train_step(model,features,labels):
# Training mode ,dropout The layer acts
model.train()
# Gradient clear
model.optimizer.zero_grad()
# Forward propagation for loss
predictions = model(features)
loss = model.loss_func(predictions,labels)
metric = model.metric_func(predictions,labels)
# Back propagation gradient
loss.backward()
model.optimizer.step()
return loss.item(),metric.item()
def valid_step(model,features,labels):
# Prediction model ,dropout The layer does not work
model.eval()
# Turn off gradient computation
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = model(features)
loss = model.loss_func(predictions,labels)
metric = model.metric_func(predictions,labels)
return loss.item(), metric.item()
# test train_step effect
features,labels = next(iter(dl_train))
train_step(model,features,labels)
Start model training
def train_model(model,epochs,dl_train,dl_valid,log_step_freq):
metric_name = model.metric_name
dfhistory = pd.DataFrame(columns = ["epoch","loss",metric_name,"val_loss","val_"+metric_name])
print("Start Training...")
nowtime = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print("=========="*8 + "%s"%nowtime)
for epoch in range(1,epochs+1):
# 1, Training cycle -------------------------------------------------
loss_sum = 0.0
metric_sum = 0.0
step = 1
for step, (features,labels) in enumerate(dl_train, 1):
loss,metric = train_step(model,features,labels)
# Print batch The level of log
loss_sum += loss
metric_sum += metric
if step%log_step_freq == 0:
print(("[step = %d] loss: %.3f, "+metric_name+": %.3f") %
(step, loss_sum/step, metric_sum/step))
# 2, Verification cycle -------------------------------------------------
val_loss_sum = 0.0
val_metric_sum = 0.0
val_step = 1
for val_step, (features,labels) in enumerate(dl_valid, 1):
val_loss,val_metric = valid_step(model,features,labels)
val_loss_sum += val_loss
val_metric_sum += val_metric
# 3, Log -------------------------------------------------
info = (epoch, loss_sum/step, metric_sum/step,
val_loss_sum/val_step, val_metric_sum/val_step)
dfhistory.loc[epoch-1] = info
# Print epoch The level of log
print(("\nEPOCH = %d, loss = %.3f,"+ metric_name + \
" = %.3f, val_loss = %.3f, "+"val_"+ metric_name+" = %.3f")
%info)
nowtime = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print("\n"+"=========="*8 + "%s"%nowtime)
print('Finished Training...')
return dfhistory

4. Model to evaluate
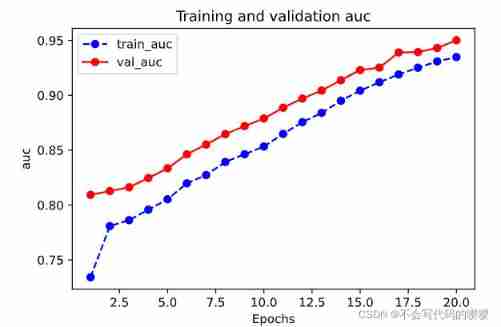
The evaluation of the model is generally to evaluate the effect on the training set and the verification set , During model training , We all keep one dfhistory Of , This is a DataFrame Structure , Inside is the change of the accuracy and loss of the model on the training set and the verification set during the training process , We can see the training of the model through visualization .
dfhistory

%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_metric(dfhistory, metric):
train_metrics = dfhistory[metric]
val_metrics = dfhistory['val_'+metric]
epochs = range(1, len(train_metrics) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, train_metrics, 'bo--')
plt.plot(epochs, val_metrics, 'ro-')
plt.title('Training and validation '+ metric)
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel(metric)
plt.legend(["train_"+metric, 'val_'+metric])
plt.show()
plot_metric(dfhistory,"loss")

plot_metric(dfhistory,"auc")
5. Using the model
def predict(model,dl):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
result = torch.cat([model.forward(t[0]) for t in dl])
return(result.data)
# Prediction probability
y_pred_probs = predict(model,dl_valid)
y_pred_probs
# Forecast category
y_pred = torch.where(y_pred_probs>0.5,
torch.ones_like(y_pred_probs),torch.zeros_like(y_pred_probs))
y_pred

6. Save the model
It is recommended to save the parameters Pytorch Model .
# Print related parameter names
print(model.state_dict().keys())

# Save model parameters
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./data/model_parameter.pkl")
net_clone = Net()
net_clone.load_state_dict(torch.load("./data/model_parameter.pkl"))
predict(net_clone,dl_valid)
边栏推荐
- Refer to some books for the distinction between blocking, non blocking and synchronous asynchronous
- Task of gradle learning
- 【leetcode】1027. Longest arithmetic sequence (dynamic programming)
- Global and Chinese market of speed limiter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Print linked list from end to end
- Etcd raft Based Consistency assurance
- XAI+网络安全?布兰登大学等最新《可解释人工智能在网络安全应用》综述,33页pdf阐述其现状、挑战、开放问题和未来方向
- Measurement fitting based on Halcon learning -- Practice [1]
- First knowledge of database
- Sort out several network request methods of JS -- get rid of callback hell
猜你喜欢
Yyds dry goods inventory TCP & UDP

How to choose cache read / write strategies in different business scenarios?
Preliminary practice of niuke.com (11)
1.5 learn to find mistakes first

In 2021, the global revenue of syphilis rapid detection kits was about US $608.1 million, and it is expected to reach US $712.9 million in 2028

运维各常用命令总结

全网都在疯传的《老板管理手册》(转)

Basic preprocessing and data enhancement of image data
2.6 formula calculation

Interval product of zhinai sauce (prefix product + inverse element)
随机推荐
How to choose cache read / write strategies in different business scenarios?
【c】 Digital bomb
In 2021, the global revenue of thick film resistors was about $1537.3 million, and it is expected to reach $2118.7 million in 2028
1.4 learn more about functions
Discussion Net legacy application transformation
Etcd 基于Raft的一致性保证
Producer consumer mode (multithreading, use of shared resources)
Line segment tree blue book explanation + classic example acwing 1275 Maximum number
Haven't expressed the artifact yet? Valentine's Day is coming. Please send her a special gift~
How to set the system volume programmatically- How to programmatically set the system volume?
Recommendation of books related to strong foundation program mathematics
一台服务器最大并发 tcp 连接数多少?65535?
Cesiumjs 2022 ^ source code interpretation [7] - Analysis of the request and loading process of 3dfiles
Apprentissage intensif - notes d'apprentissage 1 | concepts de base
同花顺开户注册安全靠谱吗?有没有风险的?
Sightseeing - statistics of the number of shortest paths + state transfer + secondary small paths
Go learning notes (4) basic types and statements (3)
淺析 Ref-NeRF
[Tang Laoshi] C -- encapsulation: member variables and access modifiers
@Scenario of transactional annotation invalidation