当前位置:网站首页>Consistency inspection and evaluation method kappa
Consistency inspection and evaluation method kappa
2022-07-27 00:44:00 【Hello, tomorrow,,】
Kappa Scoring measures the consistency between two scores . Quadratic weighting kappa It is calculated by using the scores assigned by the manual rater and the predicted scores . This indicator is from -1( The raters are completely inconsistent ) To 1( The raters are completely consistent ) Unequal .κ Is defined as :

among k It's the number of categories ,oi j and ei j They are the elements in the observation matrix and the expectation matrix .wi j The calculation is as follows :

because Cohens Kappa characteristic , Researchers must carefully explain this ratio . for example , If we consider that two pairs of raters have the same agreement percentage , But the rating ratio is different , We should know , This will greatly affect Kappa ratio . Another problem is the amount of code : As the number of code increases ,Kappa Become taller . Besides ,Kappa May be lower , Even if there is a high level of consistency , Even if the personal rating is accurate . All the above factors make Kappa Become an analyzable volatility . Use Kappa The main reason for the ratio is that we cannot get the label of the validation and test data set . Of these datasets Kappa Value is achieved by submitting our model and running code to Kaggle Obtained by the inspection system on the site . Besides , We cannot explicitly access the images in the test data set .
Generally, whether there is difference between the number of the same evaluation obtained by the model and the expectation based on possibility is analyzed , When the two models have the same number of evaluations and the number based on possibility expectation is basically the same ,kappa The value of is close to 1.
Take a chestnut , Model A And benchmark kappa:

kappa = (p0-pe) / (n-pe)
among ,P0 = Sum of observed values in diagonal cells ;pe = Sum of expected values in diagonal cells .
according to kappa The calculation method is divided into simple kappa(simple kappa) And weighting kappa(weighted kappa), weighting kappa It is divided into linear weighted kappa and quadratic weighted kappa.
weighted kappa
About linear still quadratic weighted kappa The choice of , Depending on your dataset class The significance of the difference between . For example, for fundus image recognition data ,class=0 For health ,class=4 It is very serious in the late stage of the disease , So for class=0 Predicted success 4 The punishment caused by your behavior should be far greater than class=0 Predicted success class=1 act , Use quadratic Words 0->4 The punishment is equal to 16 Times 0->1 The punishment . The following figure shows the comparison of two calculation methods of a four classification .

Python Code implementation :
#! /usr/bin/env python2.7
import numpy as np
def confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the confusion matrix between rater's ratings
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
conf_mat = [[0 for i in range(num_ratings)]
for j in range(num_ratings)]
for a, b in zip(rater_a, rater_b):
conf_mat[a - min_rating][b - min_rating] += 1
return conf_mat
def histogram(ratings, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the counts of each type of rating that a rater made
"""
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(ratings)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(ratings)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
hist_ratings = [0 for x in range(num_ratings)]
for r in ratings:
hist_ratings[r - min_rating] += 1
return hist_ratings
def quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
quadratic_weighted_kappa calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
rater_a = np.array(rater_a, dtype=int)
rater_b = np.array(rater_b, dtype=int)
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(min(rater_a), min(rater_b))
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(max(rater_a), max(rater_b))
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = pow(i - j, 2.0) / pow(num_ratings - 1, 2.0)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the linear weighted kappa
linear_weighted_kappa calculates the linear weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
linear_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = abs(i - j) / float(num_ratings - 1)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the kappa
kappa calculates the kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
if i == j:
d = 0.0
else:
d = 1.0
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=None):
"""
Calculates the mean of the quadratic
weighted kappas after applying Fisher's r-to-z transform, which is
approximately a variance-stabilizing transformation. This
transformation is undefined if one of the kappas is 1.0, so all kappa
values are capped in the range (-0.999, 0.999). The reverse
transformation is then applied before returning the result.
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas), where kappas is a vector of
kappa values
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights), where weights is a vector
of weights that is the same size as kappas. Weights are applied in the
z-space
"""
kappas = np.array(kappas, dtype=float)
if weights is None:
weights = np.ones(np.shape(kappas))
else:
weights = weights / np.mean(weights)
# ensure that kappas are in the range [-.999, .999]
kappas = np.array([min(x, .999) for x in kappas])
kappas = np.array([max(x, -.999) for x in kappas])
z = 0.5 * np.log((1 + kappas) / (1 - kappas)) * weights
z = np.mean(z)
return (np.exp(2 * z) - 1) / (np.exp(2 * z) + 1)
def weighted_mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(solution, submission):
predicted_score = submission[submission.columns[-1]].copy()
predicted_score.name = "predicted_score"
if predicted_score.index[0] == 0:
predicted_score = predicted_score[:len(solution)]
predicted_score.index = solution.index
combined = solution.join(predicted_score, how="left")
groups = combined.groupby(by="essay_set")
kappas = [quadratic_weighted_kappa(group[1]["essay_score"], group[1]["predicted_score"]) for group in groups]
weights = [group[1]["essay_weight"].irow(0) for group in groups]
return mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=weights)边栏推荐
- 关于Redis问题的二三事
- Find method of web page parsing by crawler
- 10_ Evaluate classification
- [qt] meta object system
- C language shutdown applet
- Class and object notes I
- C语言 关机小程序
- Matlab simulation of inverted pendulum control system based on qlearning reinforcement learning
- Reduced dimension mean dot product matrix multiplicative norm probability normal distribution square loss
- TypeScript(tsconfig.json)
猜你喜欢

13_ Ensemble learning and random forests

Find method of web page parsing by crawler
![[leetcode] no duplicate longest string](/img/97/bf8c9b019136ab372ce2c43cddbb2c.jpg)
[leetcode] no duplicate longest string

The company gave how to use the IP address (detailed version)

Today's 20220719 toss deeplobcut

DOM day_01(7.7) dom的介绍和核心操作

Draw impact function
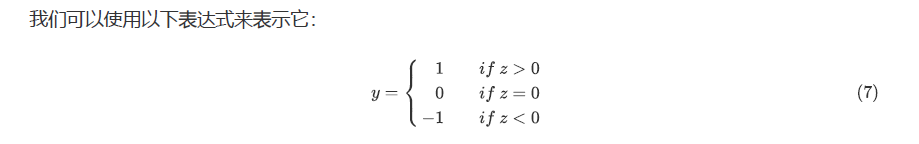
放图仓库-2(函数图像)

【3. 基础搜索与图论初识】
Drawing warehouse Tsai
随机推荐
Mysql常用函数(汇总)
Helicopter control system based on Simulink
【Codeforces Round #807 (Div 2.) A·B·C】
Request attribute in crawler
Friend友元函数以及单例模式
"Syntaxerror: future feature annotations is not defined"
【3. Vim 操作】
Matlab simulation of image reconstruction using filtered back projection method
A simple prime number program. Beginners hope that older bosses can have a look
【4.10 博弈论详解】
[2. TMUX operation]
Torch. correlation function
[Qt]元对象系统
Lt9611ux Mipi to HDMI 2.0 dual port with audio
MySQL common functions (summary)
UNET notes
【AcWing第61场周赛】
[qt] container class, iterator, foreach keyword
[LeetCode] 无重复最长字符串
【3. 基础搜索与图论初识】