当前位置:网站首页>ThreadLocal Kills 11 consecutive questions
ThreadLocal Kills 11 consecutive questions
2022-07-25 18:51:00 【InfoQ】
Preface
ThreadLocal
1. Why use ThreadLocal?
JDKsynchronizedLock Atomicity JDKThreadLocal Threads copy @Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public void add() {
threadLocal.set(1);
doSamething();
Integer integer = threadLocal.get();
}
}
2. ThreadLocal What is the principle of ?
ThreadLocalThreadLocalMappublic class ThreadLocal<T> {
...
public T get() {
// Get the current thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Get the member variables of the current thread ThreadLocalMap object
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
// according to threadLocal Objects from map In order to get Entry object
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// Get saved data
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
// Initialization data
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
// Get the data to initialize
T value = initialValue();
// Get the current thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Get the member variables of the current thread ThreadLocalMap object
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// If map Not empty
if (map != null)
// Set the initial value to map in ,key yes this, namely threadLocal object ,value Is the initial value
map.set(this, value);
else
// If map It's empty , You need to create a new map object
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
public void set(T value) {
// Get the current thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Get the member variables of the current thread ThreadLocalMap object
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// If map Not empty
if (map != null)
// Set the value to map in ,key yes this, namely threadLocal object ,value It's incoming value value
map.set(this, value);
else
// If map It's empty , You need to create a new map object
createMap(t, value);
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
...
}
...
}
ThreadLocalgetsetsetInitialValueThreadLocalMapThreadLocalMapstatic class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
...
private Entry[] table;
...
}
ThreadLocalMapEntryWeakReferenceEntryThreadLocalMapEntryEntryThreadLocalvalueThreadLocalMapThreadpublic class Thread implements Runnable {
...
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}

ThreadThreadLocalMapEntry Array EntryGC
Weak reference Strong citation 3. Why ThreadLocal do key?
ThreadLocalMapThreadLocalThreadThreadLocalThread@Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
Thread@Service
public class ThreadLocalService {
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal3 = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
Thread
ThreadThreadLocalget
4. Entry Of key Why is it designed as a weak reference ?
WeakReference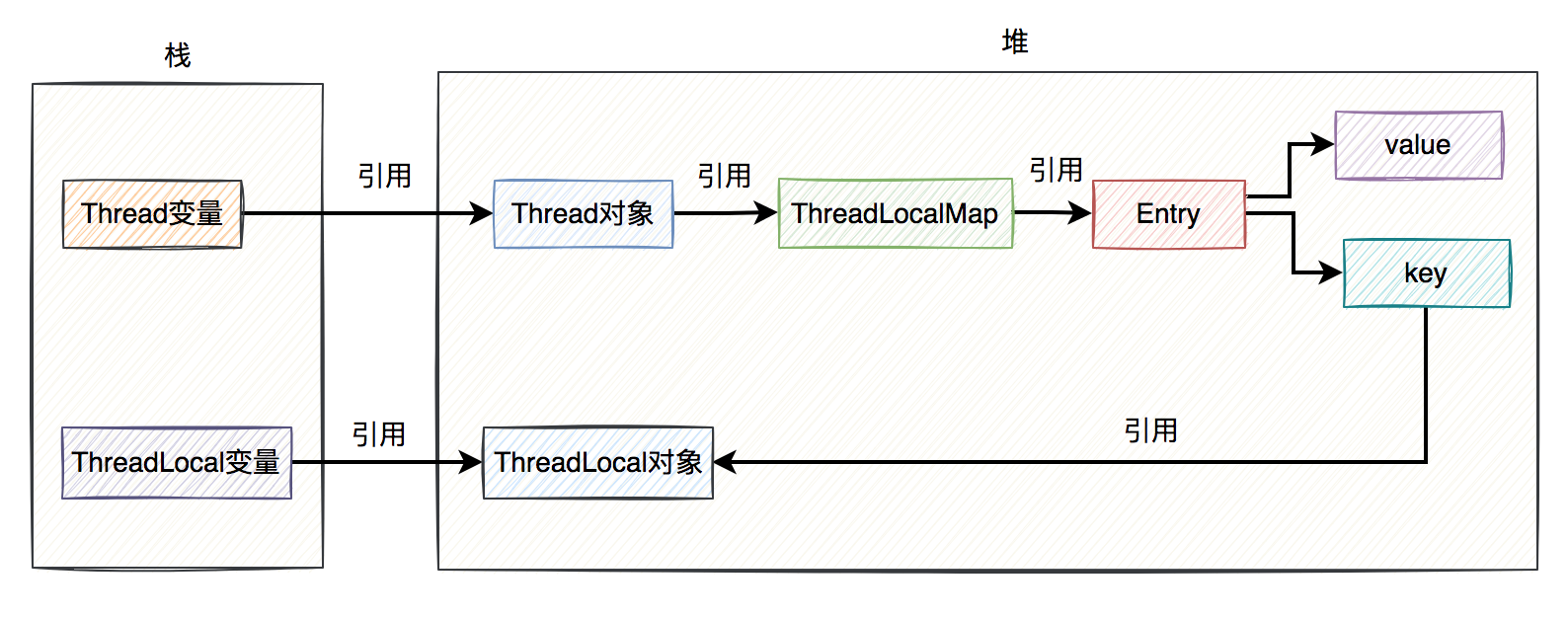
Threads Thread pool Strong reference chain GC Memory leak Weak reference Weak reference 
nullgetsetremove Null pointer exception getsetremove Memory leak - key by null Is the condition of ,ThreadLocal Variable pointing to the
null, also key Is a weak reference . If ThreadLocal The variable is not disconnected ThreadLocal A strong reference to , namely ThreadLocal The variable does not point to null,GC Just rashly quote the weak key Recycled , No, it will affect the use of normal users ?
- If at present ThreadLocal Variable pointing to the
null了 , also key Also for the null 了 , But if nothing else ThreadLocal Variable triggerget、setorremoveMethod , It can also cause memory leaks .
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakReference<Object> weakReference0 = new WeakReference<>(new Object());
System.out.println(weakReference0.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference0.get());
}
[email protected]
null
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weakReference1 = new WeakReference<>(object);
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
}
[email protected]
[email protected]
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> weakReference1 = new WeakReference<>(object);
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
object=null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference1.get());
}
[email protected]
[email protected]
null
5. ThreadLocal It will really lead to memory leakage ?
getsetremove
getsetremove Strong reference chain Memory leak 6. How to solve the memory leak problem ?
removepublic class CurrentUser {
private static final ThreadLocal<UserInfo> THREA_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal();
public static void set(UserInfo userInfo) {
THREA_LOCAL.set(userInfo);
}
public static UserInfo get() {
THREA_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void remove() {
THREA_LOCAL.remove();
}
}
public void doSamething(UserDto userDto) {
UserInfo userInfo = convert(userDto);
try{
CurrentUser.set(userInfo);
...
// Business code
UserInfo userInfo = CurrentUser.get();
...
} finally {
CurrentUser.remove();
}
}
finallyremoveremove7. ThreadLocal How to locate the data ?
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
And And modulus And operation 162hash Conflict getEntryprivate Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
// adopt hash The algorithm obtains the subscript value
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
// If at the subscript position key Just what we need to find key
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
// That means we found the data , Go straight back to
return e;
else
// Explain the appearance of hash The conflict , Keep looking back
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
getEntryAfterMissprivate Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// Judge Entry If the object is not empty , And it's going through the cycle
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// If at present Entry Of key Just what we need to find key
if (k == key)
// It shows that we really found the data this time
return e;
if (k == null)
// If key It's empty , Clean up dirty data
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
// If you still don't find the data , Then continue to look back
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
nextIndexprivate static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
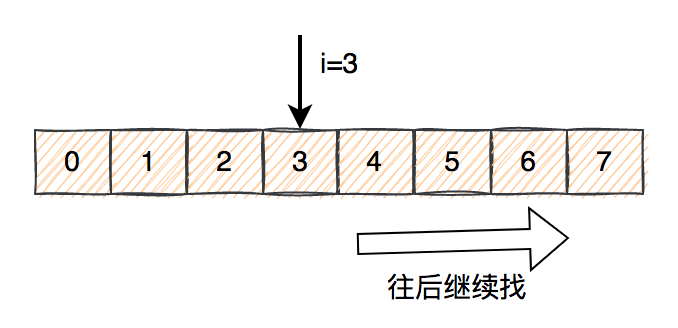

ring - adopt key Of hashCode Take the remainder and calculate a subscript .
- By subscript , Locate the concrete in the array Entry, If key Just what we need key, It means that , Then directly return the data .
- If the first 2 We didn't find the data we wanted , From the subscript position of the array , Keep looking back .
- If the first 3 Find in step key It's just what we need key, It means that , Then directly return the data .
- If you still don't find the data , Then continue to look behind . If you find the last position , Still no data found , Then start again , That is, the subscript is 0 The location of , Continue looking for data from front to back .
- Until we find the first Entry Until it's empty .
8. ThreadLocal How to expand capacity ?
16setrehashprivate void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
private void rehash() {
// Try recycling first key by null Value , Make room
expungeStaleEntries();
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
16 * 2 * 4 / 3 * 4 - 16 * 2 / 3 * 4 = 8
1/2private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
// Press 2 Times the size of the expansion
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}

- The old size + 1 = new size
- If new size Older than or equal to size Of 2/3 when , Expansion needs to be considered .
- Try to recycle before capacity expansion key by null Value , Make room .
- If it is found after recycling size Or greater than or equal to the old size Of 1/2 when , Just need real expansion .
- Press... Every time 2 Times the size of the expansion .
9. How parent and child threads share data ?
One thread public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println(" The parent thread gets data :" + threadLocal.get());
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(" The child thread gets the data :" + threadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
The parent thread gets data :6
The child thread gets the data :null
InheritableThreadLocalpublic class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InheritableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println(" The parent thread gets data :" + threadLocal.get());
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(" The child thread gets the data :" + threadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
The parent thread gets data :6
The child thread gets the data :6
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
init10. How to share data in the thread pool ?
Separate threads Thread pool private static void fun1() {
InheritableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println(" The parent thread gets data :" + threadLocal.get());
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
threadLocal.set(6);
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(" Get data from thread pool for the first time :" + threadLocal.get());
});
threadLocal.set(7);
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(" Get data from the thread pool for the second time :" + threadLocal.get());
});
}
The parent thread gets data :6
Get data from thread pool for the first time :6
Get data from the thread pool for the second time :6
TransmittableThreadLocal<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>transmittable-thread-local</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
private static void fun2() throws Exception {
TransmittableThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set(6);
System.out.println(" The parent thread gets data :" + threadLocal.get());
ExecutorService ttlExecutorService = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1));
threadLocal.set(6);
ttlExecutorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(" Get data from thread pool for the first time :" + threadLocal.get());
});
threadLocal.set(7);
ttlExecutorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(" Get data from the thread pool for the second time :" + threadLocal.get());
});
}
The parent thread gets data :6
Get data from thread pool for the first time :6
Get data from the thread pool for the second time :7
TransmittableThreadLocalTtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorServiceExecutorServiceTransmittableThreadLocalExecutorServiceTtlRunnableTtlCallableRunnablepublic void run() {
Map<TransmittableThreadLocal<?>, Object> copied = (Map)this.copiedRef.get();
if (copied != null && (!this.releaseTtlValueReferenceAfterRun || this.copiedRef.compareAndSet(copied, (Object)null))) {
Map backup = TransmittableThreadLocal.backupAndSetToCopied(copied);
try {
this.runnable.run();
} finally {
TransmittableThreadLocal.restoreBackup(backup);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("TTL value reference is released after run!");
}
}
- Put the ThreadLocal Make a backup , Then the parent class's ThreadLocal Copy it over .
- Carry out the real run Method , You can get the latest of the parent class ThreadLocal data .
- From the backed up data , Restore the ThreadLocal data .
11. ThreadLocal What are the USES ?
- stay spring Transaction , Ensure that one thread , Multiple operations of a transaction get one Connection.
- stay hiberate In the management session.
- stay JDK8 Before , In order to solve SimpleDateFormat Thread safety of .
- Get the context of the currently logged in user .
- Temporarily save permission data .
- Use MDC Save log information .
- ThreadLocal Why is the variable suggested to be defined as static Of ?
- Entry Why do arrays pass hash The algorithm calculates the subscript , Straight line addressing method , Instead of using subscript values directly ?
- What's the difference between strong references and weak references ?
- Entry Array size , Why 2 Of N Power ?
- Use InheritableThreadLocal when , If the parent thread re set value , Can the modified new value be obtained correctly in the sub thread ?
边栏推荐
- Alibaba cloud technology expert haochendong: cloud observability - problem discovery and positioning practice
- The auction house is a VC, and the first time it makes a move, it throws a Web3
- MySQL子查询篇(精选20道子查询练习题)
- Twitter acquired a public opinion war, which was turned into a child quarrel by musk
- 「Wdsr-3」蓬莱药局 题解
- rust多线程安全计数
- 请问什么是国债逆回购?安全吗?
- 淦,为什么 ““ .length !== 3 ??
- Vc/pe is running towards Qingdao
- Summer Challenge [FFH] this midsummer, a "cool" code rain!
猜你喜欢

曾拿2亿融资,昔日网红书店如今全国闭店,60家店仅剩3家

Automatic machine learning library: Tpot の learning notes

怎样设计产品帮助中心?以下几点不可忽视

VC/PE正跑向青岛
可视化模型网络连接

Process communication (Systemv communication mode: shared memory, message queue, semaphore)
韩国AI团队抄袭震动学界!1个导师带51个学生,还是抄袭惯犯

With a market value of 30billion yuan, the largest IPO in Europe in the past decade was re launched on the New York Stock Exchange

从目标检测到图像分割简要发展史
The auction house is a VC, and the first time it makes a move, it throws a Web3
随机推荐
Northeast people know sexiness best
A brief history from object detection to image segmentation
Advanced software testing - test classification
n-queens problem
With a financing of 200million yuan, the former online bookstore is now closed nationwide, with only 3 stores left in 60 stores
Powell's function of Ceres
Dachang cloud business adjustment, a new round of war turn
VC/PE正跑向青岛
With a market value of 30billion yuan, the largest IPO in Europe in the past decade was re launched on the New York Stock Exchange
淦,为什么 ““ .length !== 3 ??
Address book (I)
Vc/pe is running towards Qingdao
拍卖行作VC,第一次出手就投了个Web3
【帮助中心】为您的客户提供自助服务的核心选项
String function and memory function (2)
Register carefully! The number of applicants for these double non-governmental institutions exceeded 10000!
Ping 命令详解[通俗易懂]
Osmosis extends its cross chain footprint to poca through integration with axelar and moonbeam
"Wdsr-3" Penglai pharmaceutical Bureau solution
怎么禁止使用360浏览器(怎么才能把自带的浏览器停用)