当前位置:网站首页>Basic operation of queue (implemented in C language)
Basic operation of queue (implemented in C language)
2022-07-01 13:53:00 【Brant_ zero】
This blog brings stack's good brother —— queue .
Catalog
One 、 The concept and structure of queue
Two 、 Framework Definition of queue
3、 ... and 、 The function realization of queue
3.1 Initialization of the queue
One 、 The concept and structure of queue
queue : Data insertion is only allowed at one end , A special linear table that deletes data at the other end , The queue has fifo (First In First Out) Characteristics of . Queue entry : The end that performs the insertion operation is called A party ; Outgoing queue : The section for deleting is called Team head .
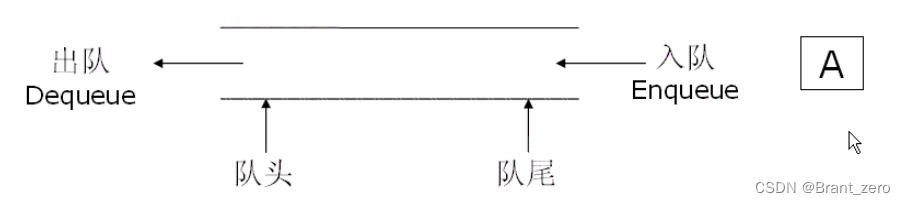
Two 、 Framework Definition of queue
Queues can also be implemented using arrays or linked lists , Using the structure of linked list to realize more , Because if you use the structure of an array , Out of the queue in the array 0 Data is displayed at the subscript , It will be less efficient .
Next, let's take a look at the basic queue operations to be implemented this time .
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq); // Initialization of the queue
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); // Destruction of queues
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); // insert data
void QueuePop(Queue* pq); // Delete data
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); // The queue is empty
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); // Queue header data
QDataType QueueBck(Queue* pq); // End of queue data
int QueueSize(Queue* pq); // The size of the queue Be careful :
The stack uses arrays , Arrays are directly accessible . And if we use linked lists to implement queues , Set a head and tail The pointer indicates the head and tail of the team , among head and tail Are ordinary single linked list node structures , So they should be set next Pointer fields and data Data fields , Only in this way can we realize the characteristics of queues .
3、 ... and 、 The function realization of queue
3.1 Initialization of the queue
It is similar to the single linked list initialization implemented before , There is no more explanation here .
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}3.2 Destruction of queues
Because it is in the form of a linked list , So we can't release space directly in whole segment like array , To use while Release each node .
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* Dest = pq->head;
while (Dest)
{
QNode* temp = Dest->next;
free(Dest);
Dest = temp;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}3.3 Queue insert data
Steps of inserting data into the queue :
① take newnode link to head Node next;② take newnode Set as new tail node .
Here we pay attention , When we initialize , We will head and tail Nodes are set to NULL, So we should make a judgment when we insert data for the first time , If (head==NULL), Then we should tail and head Set to newnode node , Only in this way can the linked list be linked normally .
The notes are very detailed , You can see that .
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
// Create a node
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
// Judge pq Is it an empty node
// If it is Will newnode Set as the first node of the current queue
// If not Will newnode link to pq Next position of
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{ // Both nodes point to newnode Indicates that there is only one element in the queue
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
//1. take newnode link to tail Behind
pq->tail->next = newnode;
//2. take newnode Replace with new tail
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}3.4 Queue delete data
As mentioned above , The queue is fifo , So we Delete data from the head of the team .
Steps of deleting data in the queue :
① preservation head The location of the next node
② Release head node
③ Set the saved node as new head.
Be careful :
① First judge that the queue cannot be empty
② If there is only one node left in the queue , We released head Node and set it to NULL, But we didn't deal with tail node , here tail Nodes become classic wild pointers . So we need to make an extra judgment when there is only one node left , namely (pq->head->next==NULL), We want to release head node , And its head and tail All are set for NULL.
The code is as follows :
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
// Make an extra judgment , Solve if there is only one node left ,pop Words lead to tail For the wild pointer
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}3.5 The queue is empty
How to judge the empty queue ?
At this time, we can only judge head Is it NULL that will do , namely (head->next==NULL);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}3.6 Take the header data
Be careful : For these operations of fetching and deleting data, we must first judge whether the queue is empty .
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}3.7 Take the tail data
QDataType QueueBck(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail ->data;
}3.8 The size of the queue
The length of linked list arrays can be calculated by calculating subscripts , So here we can only use circular calculation until cur==NULL;
int QueueSize(Queue *pq)
{
assert(pq);
int count = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}Four 、 A functional test
The same test method as the stack is used to check whether our queue implementation is successful .
Again , Queues cannot be traversed , So we also need to take out a queue header data , Then pop up the header data , Until the queue is empty .

5、 ... and 、 summary
Compared to stack , The nature of the queue is quite different from that of the stack , Similarly, the chain structure we use here is different from the form of array .
I feel that the only difficulty in implementing queues may be the flexible use of two-tier structures , Others are very similar to the implementation of stack , You can define the framework of queues , Then realize it by yourself , This is very helpful for mastering the structure , The understanding of queues will also deepen .
Okay , This blog is over , Next, after doing a few questions, you will start learning trees , A new journey , Let's learn data structure , Come on together .
边栏推荐
- Chen Yu (Aqua) - Safety - & gt; Cloud Security - & gt; Multicloud security
- 20个实用的 TypeScript 单行代码汇总
- 玩转gRPC—不同编程语言间通信
- Introduction to distributed transactions (Seata)
- 【机器学习】VAE变分自编码器学习笔记
- JVM有哪些类加载机制?
- Yan Rong looks at how to formulate a multi cloud strategy in the era of hybrid cloud
- 2022. Let me take you from getting started to mastering jetpack architecture components - lifecycle
- 3.4 data query in introduction to database system - select (single table query, connection query, nested query, set query, multi table query)
- Grafana reports an error: error= "failed to send notification to email addresses: [email protected] : 535 Error:
猜你喜欢

进入前六!博云在中国云管理软件市场销量排行持续上升

【241. 为运算表达式设计优先级】

04-Redis源码数据结构之字典

The best landing practice of cave state in an Internet ⽹⾦ financial technology enterprise

一文读懂TDengine的窗口查询功能

焱融看 | 混合云时代下,如何制定多云策略

6年技术迭代,阿里全球化出海&合规的挑战和探索

2022. Let me take you from getting started to mastering jetpack architecture components - lifecycle

【Flask】Flask启程与实现一个基于Flask的最小应用程序

面试题目总结(1) https中间人攻击,ConcurrentHashMap的原理 ,serialVersionUID常量,redis单线程,
随机推荐
Error:Kotlin: Module was compiled with an incompatible version of Kotlin. The binary version of its
【241. 为运算表达式设计优先级】
进入前六!博云在中国云管理软件市场销量排行持续上升
ArrayList capacity expansion mechanism and thread safety
Summary of interview questions (1) HTTPS man in the middle attack, the principle of concurrenthashmap, serialVersionUID constant, redis single thread,
Go整合Logrus实现日志打印
[anwangbei 2021] Rev WP
Self cultivation of open source programmers who contributed tens of millions of lines of code to shardingsphere and later became CEO
Leetcode question 1: sum of two numbers (3 languages)
Fiori applications are shared through the enhancement of adaptation project
C language ordering management system
Kongsong (Xintong Institute) - cloud security capacity building and trend in the digital era
SAP 智能机器人流程自动化(iRPA)解决方案分享
8 best practices to protect your IAC security!
Error:Kotlin: Module was compiled with an incompatible version of Kotlin. The binary version of its
Applet - applet chart Library (F2 chart Library)
04 redis source code data structure dictionary
陈宇(Aqua)-安全-&gt;云安全-&gt;多云安全
洞态在某互联⽹⾦融科技企业的最佳落地实践
使用net core 6 c# 的 NPOI 包,读取excel..xlsx单元格内的图片,并存储到指定服务器