当前位置:网站首页>转--拿来即用:分享一个检查内存泄漏的小工具
转--拿来即用:分享一个检查内存泄漏的小工具
2022-07-01 21:50:00 【worthsen】
【原创声明】
如果觉得文章不错,请转发、分享给您的朋友
我会把十多年嵌入式开发中的项目实战经验进行总结、分享,相信不会让你失望的!
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明,必须在文章中给出原文连接。
<article class="baidu_pl">
<div id="article_content" class="article_content clearfix">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/blogv2/dist/mdeditor/css/editerView/ck_htmledit_views-163de54645.css">
<div id="content_views" class="htmledit_views">
<p><span style="color:#ffbb66;"><strong>【功能描述】</strong></span></p>
【功能描述】
在嵌入式系统应用程序开发过程中,内存泄漏是一个很严重也很头疼的问题。 当然了,有很多的专业工具软件来检查内存泄漏,我用的比较多的是memwatch, valgrind。
这些工具主要是在开发过程中用来检查内存泄漏。但是,如果所有的程序都开发完成,开始集成测试时,仍然发现系统资源存在持续减少的情况,那么该如何处理呢?
这里提供的小工具就是用来处理这种情况的:可以监控你怀疑的、可能存在内存泄漏的那些进程使用的系统资源。
特别是当一个系统是由多个人来开发的、由多个进程来组成的情况,如果存在资源泄漏的情况,你说应该首先怀疑谁呢?应该让谁先去检查自己的程序是否有问题呢?扯皮往往就发生了,小伙伴之间的隔阂也就在潜意识中埋下了种子。
此时,监控程序输出的数据最管用!

【测试环境】
1. x86系统
我是在 Ubuntu16.04 下测试的,使用系统自带 gcc 编译器。
2.嵌入式系统
只需要把编译器换成对应的交叉编译器即可。
【代码下载】
1.网盘
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1yNrjQ6var8xokAJWEsFYFw
passwd:uqbh
/**
* @brief: 这个小工具用来监控系统中一些进程的资源使用情况,
* 可以用来检查程序中是否存在内存泄露。
*
* @author: 微信 captain5780
* @email: [email protected]
*
* @note: ./memory_trace <进程名称1> <进程名称2> <进程名称3>
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#define TRACE_ITEM_NUM 4
#define PROCESS_MAX 20
#define PROCESS_NAME_LEN 128
#define BUF_LEN 512
// 需要监控的资源名称
char *TraceItem[TRACE_ITEM_NUM] =
{"VmSize", "VmRSS", "VmStk", "VmData"};
// 保存需要监控的进程名称
char *ProcessList[PROCESS_MAX];
// 打印消息,在实际项目中可以利用 zlog 等日志工具来记录到文件系统中。
static void log_msg(const char *msg)
{
printf("%s", msg);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// 检查最大监控的进程个数
if (argc >= PROCESS_MAX) {
printf("too many process \n");
exit(-1);
}
// 提取命令行参数传入的进程名称,保存在 ProcessList 中。
int i, k, count;
for (i = 0, count = 0; i < argc - 1; i++) {
count++;
ProcessList[i] = (char *)malloc(PROCESS_NAME_LEN);
memset(ProcessList[i], 0, PROCESS_NAME_LEN);
sprintf(ProcessList[i], "%s", argv[i + 1]);
}
time_t rawtime;
struct tm *timeinfo;
char *buf = (char *)malloc(BUF_LEN);
while (1) {
// 记录当前的时间
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN);
sprintf(buf, "\n[%02d:%02d:%02d] \n",
timeinfo->tm_hour,
timeinfo->tm_min,
timeinfo->tm_sec);
log_msg(buf);
// 此for循环用于获取监控进程的资源占用情况
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN);
sprintf(buf, "[%s] \n", ProcessList[i]);
log_msg(buf);
for (k = 0; k < TRACE_ITEM_NUM; k++) {
memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN);
// 获取进程ID号: 执行系统命令,然后读取输出结果。
sprintf(buf,
"ps -aux | grep %s | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'",
ProcessList[i]);
FILE *fp = popen(buf, "r");
if (NULL == fp) {
printf("popen failed! \n");
continue;
}
char line[128] = { 0 };
fgets(line, 128, fp);
int len = strlen(line);
if (*(line + len - 1) == '\n')
*(line + len - 1) = 0;
pclose(fp);
// 根据进程ID号,获取该进程的堆栈信息。
memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN);
sprintf(buf,
"cat /proc/%s/status | grep %s | grep -v grep",
line, TraceItem[k]);
fp = popen(buf, "r");
if (NULL == fp) {
printf("popen failed! \n");
continue;
}
fgets(line, 128, fp);
pclose(fp);
log_msg(line); // 记录到日志
}
}
// 获取系统的空闲资源信息
memset(buf, 0, BUF_LEN);
sprintf(buf, "free | grep Mem: | grep -v grep");
FILE *fp = popen(buf, "r");
if (NULL == fp) {
printf("popen failed! \n");
continue;
}
char line[128] = { 0 };
fgets(line, 128, fp);
pclose(fp);
log_msg(line);
sleep(5); // 间隔一段时间
}
// 释放 malloc 分配的堆空间
free(buf);
for (i = 0; i < PROCESS_MAX; i++) {
if (ProcessList[i])
free(ProcessList[i]);
}
return 0;
}
3.打印输出
这个工具的功能其实很简单,就是调用系统指令来监控进程占用的系统资源情况。
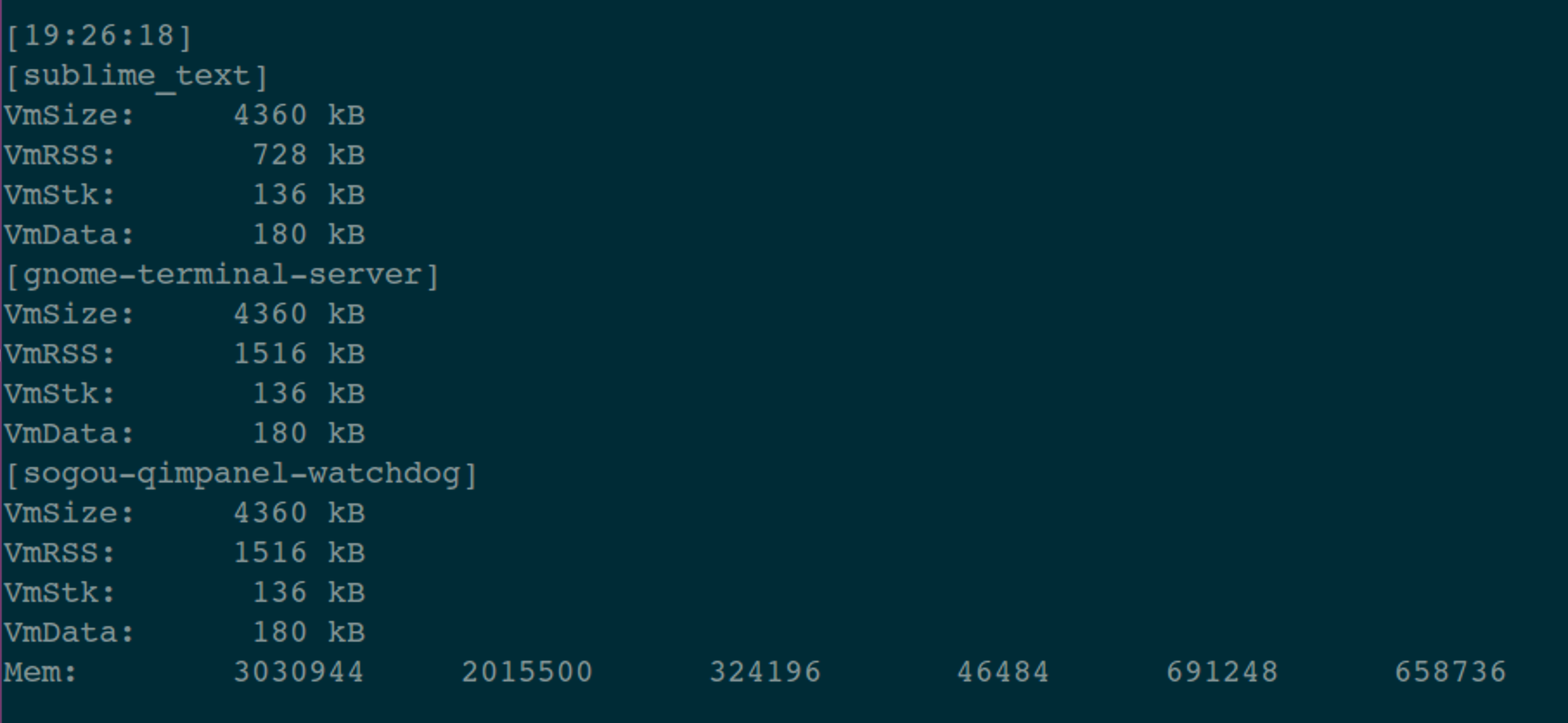
具体来说就是持续输出:/proc/[pid]/status 的内容。这个文件中有4个关键指标,这里简单列出,具体含义可以搜索一下。
VmSize(KB): 进程使用的虚拟内存大小。
VmRSS(KB): 进程中驻留在物理内存的一部分,没有交换到硬盘。
VmStk(KB): 进程使用的栈的大小。
VmData(KB): 进程数据段的大小。
【为什么写这个小工具】
之前写过一个物联网网关产品,其中包括3个大的模块,而且是由不同的人负责的,要命的是:这3个人一个在日本,一个在台湾,还有一个就是我们。
在集成测试时发现系统资源存在持续减少的情况,而且找不到规律。因为各进程之间的交互比较多,也许只是在触发了某些特定的执行逻辑时,才可能发生内存泄漏等情况。
为了找出罪魁祸首,于是写了这个小工具。执行了大概2天的时间,很快就定位到了问题的源头。
【你可能会遇到的问题】
1. 系统指令
程序中使用到了几个系统指令:proc, grep, awk, free。
这些指令在不同的嵌入式系统中的输出格式可能会有所不同,如果直接运行这个工具的输出有问题,那么就需要把代码中的指令解析部分调整一下。
2.如何调整
例如:代码中利用这条指令来根据 进程名称 得到 进程ID:ps -aux | grep %s | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}’
对于ps指令,在你的系统中也许不需要 -aux 属性。
对于 awk 指令,在你的系统中提取的自带也许是'{print $1}’。
实践出真知!

【END】
1.这是原创文章,请尊重版权。如需转载,请保留全部内容并注明来源。如果方便的话,请联系我确认。
2.文章中如有错误,或者希望交流、探讨相关内容,非常欢迎联系我。
3.邮箱:[email protected]
4.公众号:IOT物联网小镇
边栏推荐
- internal field separator
- el-input文本域字数限制,超过显示变红并禁止输入
- RestTemplate 远程调用工具类
- # CutefishOS系统~
- MySQL MHA high availability configuration and failover
- SAP ui5 application development tutorial 104 - multi select support for SAP ui5 table controls and how to use code to select multiple table row items at a time
- 小红书Scheme跳转到指定页面
- 【日常训练】326. 3 的幂
- MySQL stored procedure
- 固定资产管理子系统报表分为什么大类,包括哪些科目
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
pytorch训练自己网络后可视化特征图谱的代码
Arlo's thinking after confusion
牛客月赛-分组求对数和
MySQL stored procedure
Ffmpeg learning notes
分享一个一年经历两次裁员的程序员的一些感触
园区全光技术选型-中篇
Slope compensation
Wechat open platform scanning code login [easy to understand]
MySQL view exercise
internal field separator
Fully annotated SSM framework construction
数字货币:影响深远的创新
redis配置文件中常用配置详解[通俗易懂]
How to write a performance test plan
旅游管理系统
Pytorch sharpening chapter | argmax and argmin functions
【扫盲】机器学习图像处理中的深层/浅层、局部/全局特征
Single step debugging analysis of rxjs observable of operator
447-哔哩哔哩面经1









![[untitled]](/img/60/9a56e8b00c386779be13308515b24f.png)