当前位置:网站首页>Convex optimization notes
Convex optimization notes
2022-06-23 19:07:00 【Bachuan Xiaoxiaosheng】
Simple convex optimization notes
Convex functions and convex sets
- The region above the convex function is a convex set
- The region above the function is a convex set , Then the function is convex
convex set
aggregate C C C The line segments between any two points are in the set C C C in , It's called a collection C C C For convex sets
∀ x 1 , x 2 ∈ C , θ ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] be θ x 1 + ( 1 − θ ) x 2 ∈ C \forall x_{1},x_{2}\in C, \theta\in[0,1]\\ be \theta x_{1}+(1-\theta)x_{2}\in C ∀x1,x2∈C,θ∈[0,1] be θx1+(1−θ)x2∈C
expand
∀ x 1 , . . . , x k ∈ C , θ i ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] And ∑ θ i = 1 be ∑ θ i x i ∈ C \forall x_{1},...,x_{k}\in C, \theta_{i}\in[0,1] And \sum\theta_{i}=1\\ be \sum\theta_{i}x_{i}\in C ∀x1,...,xk∈C,θi∈[0,1] And ∑θi=1 be ∑θixi∈C
A convex polygon is a convex set , Boundary missing is not a convex set
Hyperplane and half space
hyperplane
{ x ∣ a T x = b } \{x|a^{T}x=b\} { x∣aTx=b}
Half space
{ x ∣ a T x ≤ b } { x ∣ a T x ≥ b } \{x|a^{T}x\leq b\}\\ \{x|a^{T}x\geq b\} { x∣aTx≤b}{ x∣aTx≥b}

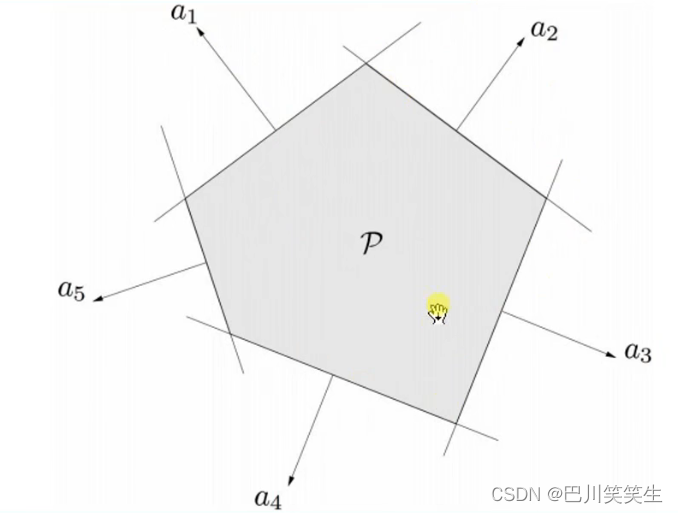
Polyhedron
A polyhedron is the intersection of a finite half space and a hyperplane
P = { x ∣ a j T x ≤ b j , c i T x = d i } P=\{x|a_{j}^{T}x\leq b_{j},c_{i}^{T}x=d_{i}\} P={ x∣ajTx≤bj,ciTx=di}
Affine set ( Such as hyperplane , A straight line ), ray , Line segment , Half spaces are polyhedrons
A polyhedron is a convex set
A bounded polyhedron is called a polyhedron
Keep convexity operation
- Set intersection operation

Proof of definition
- Affine transformation
- Telescopic
- translation
- Projection
f ( x ) = A x + b , A ∈ R m × n , b ∈ R m f : R n → R m f ( S ) = { f ( x ) ∣ x ∈ S } S by Convex Set → f ( S ) by Convex Set f ( S ) by Convex Set → S by Convex Set f(x)=Ax+b,A\in R^{m\times n},b\in R^{m}\\ f:R^{n}\rightarrow R^{m} \quad f(S)=\{f(x)|x\in S\}\\ S For convex sets \rightarrow f(S) For convex sets \\ f(S) For convex sets \rightarrow S For convex sets \\ f(x)=Ax+b,A∈Rm×n,b∈Rmf:Rn→Rmf(S)={ f(x)∣x∈S}S by Convex Set →f(S) by Convex Set f(S) by Convex Set →S by Convex Set
- Perspective transformation
The perspective function scales the vector ( standard ) Let the components of the last dimension be discarded together
P : R n + 1 → R n , P ( z , t ) = z / t P:R^{n+1}\rightarrow R^{n}, P(z,t)=z/t P:Rn+1→Rn,P(z,t)=z/t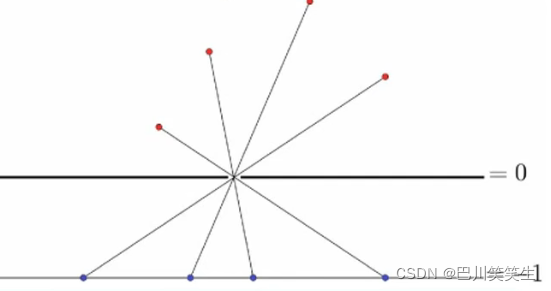
- Projective transformation ( Linear fractional transformation )
Compound of perspective and affine
g : R n → R n + 1 g ( x ) = [ A c T ] x + [ b d ] A ∈ R m × n , b ∈ R m , c ∈ R n , d ∈ R g:R^{n}\rightarrow R^{n+1}\\ g(x)=\begin{bmatrix} A\\ c^{T} \end{bmatrix}x+ \begin{bmatrix} b \\ d \end{bmatrix}\\ A\in R^{m\times n},b\in R^{m},c\in R^{n},d\in R g:Rn→Rn+1g(x)=[AcT]x+[bd]A∈Rm×n,b∈Rm,c∈Rn,d∈R
Definition f f f Is a linear fractional function
f ( x ) = ( A x + b ) c T x + d d o m f = { x ∣ c T x + d > 0 } f(x)=\frac{(Ax+b)}{c^{T}x+d}\\ dom f=\{x|c^{T}x+d>0\} f(x)=cTx+d(Ax+b)domf={ x∣cTx+d>0}
if c = 0 , d > 0 c=0,d>0 c=0,d>0 be f f f Is an ordinary affine function
Split hyperplane
set up C C C and D D D For two disjoint convex sets , Then there is a hyperplane P P P, P P P Can be C C C and D D D Separate
∀ x ∈ C , a T x ≤ b And ∀ x ∈ D , a T x ≥ b \forall x\in C,a^{T}x\leq b And \forall x\in D,a^{T}x\geq b ∀x∈C,aTx≤b And ∀x∈D,aTx≥b
Note that you can take the equal sign

Converse proposition
If two convex sets C C C and D D D The divided hyperplane exists , C C C and D D D Disjoint is a false proposition
Strengthen the conditions
If at least one of the two convex sets is open , Then if and only if there is a split hyperplane , They don't intersect
Split hyperplane construction
distance
The distance between two sets is the shortest distance between two sets
structure
Make a distance perpendicular to
Supporting hyperplanes
A collection of C C C, x 0 x_{0} x0 by C C C Points on the border . If exist a ≠ 0 a\neq 0 a=0, Satisfied with any x ∈ C x\in C x∈C, There are a T x ≤ a T x 0 a^{T}x\leq a^{T}x_{0} aTx≤aTx0 establish , Is called hyperplane { x ∣ a T x = a T x 0 } \{x|a^{T}x=a^{T}x_{0}\} { x∣aTx=aTx0} For collection C C C At point x 0 x_{0} x0 Support hyperplane at
There is a supporting hyperplane at any point on the boundary of a convex set
conversely , If a closed non hollow ( The inner point is not empty ) aggregate , There is a supporting hyperplane at any point on the boundary , Then the set is convex
Convex function
If the function f f f Domain of definition d o m f dom f domf For convex sets , And meet
∀ x , y ∈ d o m f , 0 ≤ θ ≤ 1 Yes f ( θ x + ( 1 − θ ) y ) ≤ θ f ( θ ) + ( 1 − θ ) f ( y ) \forall x,y\in domf,0\leq\theta\leq1 Yes f(\theta x+(1-\theta)y)\leq \theta f(\theta)+(1-\theta)f(y) ∀x,y∈domf,0≤θ≤1 Yes f(θx+(1−θ)y)≤θf(θ)+(1−θ)f(y)
First order differentiable
if f f f First order differentiable , The function f f f Is a convex function if and only if f f f The domain of definition d o m f dom f domf Is a convex set and
∀ x , y ∈ d o m f , f ( y ) ≥ f ( x ) + ▽ f ( x ) T ( y − x ) \forall x,y\in dom f,f(y)\geq f(x)+\bigtriangledown f(x)^{T}(y-x) ∀x,y∈domf,f(y)≥f(x)+▽f(x)T(y−x)
For convex functions , The essence of the first-order Taylor approximation is the global estimation of the function
On the contrary, if a function's first-order Taylor approximation is always its global estimation , Then the function is convex
Second order differentiability
If the function f f f Second order differentiability , The function f f f Is a convex function if and only if d o m f dom f domf For convex sets , And
▽ 2 f ( x ) ≻ = 0 \bigtriangledown^{2}f(x)\succ =0 ▽2f(x)≻=0
if f f f For a function of one variable , The above formula indicates that the second derivative is greater than or equal to 0 0 0
if f f f Is a multivariate function , The above formula represents the positive semidefinite of the second derivative Hessian matrix
Example
- e a x e^{ax} eax
- x a , x ∈ R + , a ≥ 1 or a ≤ 0 x^{a},x\in R_{+},a\geq1 or a\leq 0 xa,x∈R+,a≥1 or a≤0
- − l o g x -logx −logx
- x l o g x xlogx xlogx
- ∣ ∣ x ∣ ∣ p ||x||_{p} ∣∣x∣∣p
- m a x ( x 1 , . . . , x n ) max(x_{1},...,x_{n}) max(x1,...,xn)
- x 2 / a , a > 0 x^{2}/a,a>0 x2/a,a>0
- l o g ( e x 1 + . . . + e x n ) log(e^{x_{1}+...+e^{x_{n}}}) log(ex1+...+exn)
Shangjing map

function f f f The image is defined as { ( x , f ( x ) ) ∣ x ∈ d o m f } \{(x,f(x))|x\in dom f\} { (x,f(x))∣x∈domf}
function f f f The context map of is defined as
e p i f = { ( x , t ) ∣ x ∈ d o m f , f ( x ) ≤ t } epif=\{(x,t)|x\in domf,f(x)\leq t\} epif={ (x,t)∣x∈domf,f(x)≤t}
Convex functions and convex sets
A function is a convex function , If and only if its context graph is a convex set
A function is a concave function , If and only if its set is subconvex
h y p o f = { ( x , t ) ∣ t ≤ f ( x ) } hypo f=\{(x,t)|t\leq f(x)\} hypof={ (x,t)∣t≤f(x)}
Jason inequality
f f f Is a convex function
f ( θ x + ( 1 − θ ) y ) ≤ θ f ( x ) f(\theta x+(1-\theta)y)\leq\theta f(x) f(θx+(1−θ)y)≤θf(x)
if θ 1 . . . θ k ≥ 0 , θ 1 + . . . + θ k = 1 be f ( θ 1 x 1 + . . . + θ k x k ) ≤ θ 1 f ( x 1 ) + . . . + θ k f ( x k ) if \theta_{1}...\theta_{k}\geq 0,\theta_{1}+...+\theta_{k}=1\\ be f(\theta_{1}x_{1}+...+\theta_{k}x_{k})\leq\theta_{1}f(x_{1})+...+\theta_{k}f(x_{k}) if θ1...θk≥0,θ1+...+θk=1 be f(θ1x1+...+θkxk)≤θ1f(x1)+...+θkf(xk)
if p ( x ) ≥ 0 stay S ⊆ d o m f , ∫ S p ( x ) d x = 1 be f ( ∫ S p ( x ) x d x ) ≤ ∫ S f ( x ) p ( x ) d x or f ( E x ) ≤ E ( f ( x ) ) if p(x)\geq 0 stay S\subseteq domf,\int_{S}p(x)dx=1 \\ be f(\int_{S}p(x)xdx)\leq \int_{S}f(x)p(x)dx\\ or f(Ex)\leq E(f(x)) if p(x)≥0 stay S⊆domf,∫Sp(x)dx=1 be f(∫Sp(x)xdx)≤∫Sf(x)p(x)dx or f(Ex)≤E(f(x))
It can be proved by Jason inequality
D ( p ∣ ∣ q ) = ∑ p ( x ) l o g p ( x ) q ( x ) = E p ( x ) l o g p ( x ) q ( x ) ≥ 0 D(p||q)=\sum p(x)log \frac{p(x)}{q(x)}=E_{p(x)}log\frac{p(x)}{q(x)}\geq 0 D(p∣∣q)=∑p(x)logq(x)p(x)=Ep(x)logq(x)p(x)≥0
wait
Operators that preserve the convexity of functions
- Nonnegative weighted sum
f ( x ) = w 1 f 1 ( x ) + . . . + w n f n ( x ) f(x)=w_{1}f_{1}(x)+...+w_{n}f_{n}(x) f(x)=w1f1(x)+...+wnfn(x) - Compound with affine function
g ( x ) = f ( A x + b ) g(x)=f(Ax+b) g(x)=f(Ax+b) - Point by point maximum , Pointwise supremum
f ( x ) = m a x ( f 1 ( x ) , . . . , f n ( x ) ) f ( x ) = sup y ∈ A g ( x , y ) f(x)=max(f_{1}(x),...,f_{n}(x))\\ f(x)=\sup_{y\in A}g(x,y) f(x)=max(f1(x),...,fn(x))f(x)=y∈Asupg(x,y)
The pointwise supremum function of the function corresponds to the intersection of the boundary graph on the function
Convex optimization
The basic form of optimization problem
most Small turn f 0 ( x ) , x ∈ R n No etc. type about beam f i ( x ) ≤ 0 , i = 1... m etc. type about beam h i ( x ) = 0 , j = 1... p nothing about beam optimal turn m = p = 0 To minimize the f_{0}(x),x\in R^{n}\\ Inequality constraints f_{i}(x)\leq 0,i=1...m\\ Equality constraints h_{i}(x)=0,j=1...p\\ Unconstrained optimization m=p=0 most Small turn f0(x),x∈Rn No etc. type about beam fi(x)≤0,i=1...m etc. type about beam hi(x)=0,j=1...p nothing about beam optimal turn m=p=0
optimal turn ask topic Of Domain D = ⋂ i = 1 m d o m f i ∩ ⋂ j = 1 p d o m h j can That's ok spot ( Explain ) x ∈ D And full foot about beam strip Pieces of can That's ok Domain , the Yes can That's ok spot Set close Domain of optimization problem D=\bigcap_{i=1}^{m} domf_{i} \cap \bigcap_{j=1}^{p}domh_{j} \\ It's possible ( Explain )x\in D And meet the constraints \\ The feasible region , Set of all feasible points optimal turn ask topic Of Domain D=i=1⋂mdomfi∩j=1⋂pdomhj can That's ok spot ( Explain )x∈D And full foot about beam strip Pieces of can That's ok Domain , the Yes can That's ok spot Set close
most optimal turn value p ∗ = i n f { f 0 ( x ) ∣ f i ( x ) ≤ 0 , i = 1... m , h j ( x ) = 0 , j = 1... p } most optimal turn Explain p ∗ = f 0 ( x ∗ ) Optimization value p^{*}=inf\{f_{0}(x)|f_{i}(x)\leq0,i=1...m,h_{j}(x)=0,j=1...p\}\\ Optimal solution p^{*}=f_{0}(x^{*}) most optimal turn value p∗=inf{ f0(x)∣fi(x)≤0,i=1...m,hj(x)=0,j=1...p} most optimal turn Explain p∗=f0(x∗)
The basic form of convex optimization problem
f i ( x ) by Convex Letter Count h j ( x ) by Imitation shoot Letter Count f_{i}(x) Is a convex function \\ h_{j}(x) For affine functions fi(x) by Convex Letter Count hj(x) by Imitation shoot Letter Count
Important nature
- The feasible region is a convex set
- The local optimal solution is the global optimal solution
The dual problem
Lagrange function
L ( x , λ , υ ) = f 0 ( x ) + ∑ λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ υ j h j ( x ) L(x,\lambda,\upsilon)=f_{0}(x)+\sum \lambda_{i}f_{i}(x)+\sum\upsilon _{j}h_{j}(x) L(x,λ,υ)=f0(x)+∑λifi(x)+∑υjhj(x)
To fix x x x, Lagrange function L ( x , λ , υ ) L(x,\lambda,\upsilon ) L(x,λ,υ) For about λ \lambda λ and υ \upsilon υ The affine function of
Lagrange dual function
g ( λ , υ ) = inf x ∈ D L ( x , λ , υ ) = inf x ∈ D ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ λ i f i ( x ) + ∑ υ j h j ( x ) ) if nothing Next indeed world set The righteous g ( λ , υ ) = − ∞ g(\lambda,\upsilon)=\inf_{x\in D}L(x,\lambda,\upsilon)=\inf_{x\in D}(f_{0}(x)+\sum \lambda_{i}f_{i}(x)+\sum\upsilon _{j}h_{j}(x))\\ If there is no infimum definition g(\lambda,\upsilon)=-\infty g(λ,υ)=x∈DinfL(x,λ,υ)=x∈Dinf(f0(x)+∑λifi(x)+∑υjhj(x)) if nothing Next indeed world set The righteous g(λ,υ)=−∞
By definition, there are : Yes ∀ λ ≥ 0 , ∀ υ \forall \lambda\geq 0,\forall\upsilon ∀λ≥0,∀υ, The original optimization problem has the optimal value p ∗ p^{*} p∗, be
g ( λ , υ ) ≤ p ∗ g(\lambda,\upsilon)\leq p^{*} g(λ,υ)≤p∗
further , Lagrange dual function is concave function 
hypothesis x 0 x_{0} x0 Is not workable , There is f i ( x ) > 0 f_{i}(x)>0 fi(x)>0, select λ i → ∞ \lambda_{i}\rightarrow\infty λi→∞, For other multipliers λ i = 0 , j ≠ i \lambda_{i}=0,j\neq i λi=0,j=i
hypothesis x 0 x_{0} x0 feasible , Then there are f i ( x ) ≤ 0 , i = 1... m f_{i}(x)\leq 0,i=1...m fi(x)≤0,i=1...m, Make λ i = 0 , i = 1... m \lambda_{i}=0,i=1...m λi=0,i=1...m
Yes
sup λ ≥ 0 L ( x , λ ) = sup λ ≥ 0 ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ λ i f i ( x ) ) = { f 0 ( x ) , f i ( x ) < 0 ∞ , o t h e r \sup_{\lambda\geq 0}L(x,\lambda)=\sup_{\lambda\geq 0}(f_{0}(x)+\sum\lambda_{i}f_{i}(x))= \left\{\begin{matrix} f_{0}(x),f_{i}(x)<0 \\ \infty,other \end{matrix}\right. λ≥0supL(x,λ)=λ≥0sup(f0(x)+∑λifi(x))={ f0(x),fi(x)<0∞,other
The original problem is inf x f 0 ( x ) \inf_{x} f_{0}(x) infxf0(x) Turn into inf x sup λ ≥ 0 L ( x , λ ) \inf_{x} \sup_{\lambda\geq 0}L(x,\lambda) infxsupλ≥0L(x,λ)
The dual problem is to find the maximum value of the dual function , namely
sup λ ≥ 0 inf x L ( x , λ ) \sup_{\lambda\geq0}\inf_{x}L(x,\lambda) λ≥0supxinfL(x,λ)
and
sup λ ≥ 0 inf x L ( x , λ ) ≤ inf x sup λ ≥ 0 L ( x , λ ) \sup_{\lambda\geq0}\inf_{x}L(x,\lambda)\leq\inf_{x}\sup_{\lambda\geq0}L(x,\lambda) λ≥0supxinfL(x,λ)≤xinfλ≥0supL(x,λ)
Strong dual condition
The maximum value of the dual function is the minimum value of the original problem
f 0 ( x ∗ ) = g ( λ ∗ + υ ∗ ) = inf x ( f 0 ( x ) + ∑ λ i ∗ f i ( x ) + ∑ υ j ∗ h j ( x ) ) ≤ f 0 ( x ∗ ) + ∑ λ i ∗ f i ( x x ) + ∑ υ j ∗ h j ( x ∗ ) ≤ f 0 ( x ∗ ) f_{0}(x^{*})=g(\lambda^{*}+\upsilon^{*})\\ =\inf_{x}(f_{0}(x)+\sum \lambda_{i}^{*}f_{i}(x)+\sum\upsilon _{j}^{*}h_{j}(x))\\ \leq f_{0}(x^{*})+\sum \lambda_{i}^{*}f_{i}(x^{x})+\sum\upsilon _{j}^{*}h_{j}(x^{*})\\ \leq f_{0}(x^{*}) f0(x∗)=g(λ∗+υ∗)=xinf(f0(x)+∑λi∗fi(x)+∑υj∗hj(x))≤f0(x∗)+∑λi∗fi(xx)+∑υj∗hj(x∗)≤f0(x∗)
Conditions
f i ( x ∗ ) ≤ 0 h i ( x ∗ ) = 0 λ i ∗ ≥ 0 λ i ∗ f i ( x ∗ ) = 0 i = 1... m ▽ f 0 ( x ∗ ) + ∑ λ i ∗ ▽ f i ( x x ) + ∑ υ j ∗ ▽ h j ( x ∗ ) = 0 f_{i}(x^{*})\leq 0\\ h_{i}(x^{*})= 0\\ \lambda_{i}^{*}\geq 0\\ \lambda_{i}^{*}f_{i}(x^{*})= 0\\ i=1...m\\ \bigtriangledown f_{0}(x^{*})+\sum \lambda_{i}^{*}\bigtriangledown f_{i}(x^{x})+\sum\upsilon _{j}^{*}\bigtriangledown h_{j}(x^{*})=0 fi(x∗)≤0hi(x∗)=0λi∗≥0λi∗fi(x∗)=0i=1...m▽f0(x∗)+∑λi∗▽fi(xx)+∑υj∗▽hj(x∗)=0
边栏推荐
- IOT platform construction equipment, with source code
- 今年,安徽母基金大爆发
- 元宇宙大杀器来了!小扎祭出4款VR头显,挑战视觉图灵测试
- 从零开发小程序和公众号【第一期】
- Une fois que le port série de Jerry est réglé, le Code aléatoire est imprimé, et le cristal interne n'est pas étalonné [chapitre]
- 矩阵分析笔记(二)
- [noi 2014] 15. Syndrome de difficulté à se lever [binaire]
- CV-全连接神经网络
- Stream流的使用
- Browser cross domain
猜你喜欢

Js25 topic

vPROM笔记
![When Jerry's serial port is set up, it prints garbled code, and the internal crystal oscillator is not calibrated [chapter]](/img/6d/96b3326a201bf17d436c1af7834232.png)
When Jerry's serial port is set up, it prints garbled code, and the internal crystal oscillator is not calibrated [chapter]

STM32 (VIII) -- PWM output

Yaxiang spice listed on Shenzhen Stock Exchange: with a market value of 4billion, Dinglong Bohui and Yongyao investment are shareholders

微机原理第八章笔记整理
![[noi 2014] 15. Syndrome de difficulté à se lever [binaire]](/img/3a/12e9b2566d3ca3330a3cc6c5eaf135.png)
[noi 2014] 15. Syndrome de difficulté à se lever [binaire]

函數的定義和函數的參數

吃顿饭的时间,学会simulink之BLDC基本原理

Basic knowledge of penetration test
随机推荐
Definition and model of indicators (complex indicators)
IOT platform construction equipment, with source code
Use of stream streams
Noah fortune passed the hearing: with an annual revenue of 4.3 billion yuan, Wang Jingbo has 49% voting rights, and Sequoia is a shareholder
Jerry's seamless looping [chapter]
Jerry added an input capture channel [chapter]
涂鸦智能通过聆讯:拟回归香港上市 腾讯是重要股东
Définition de la fonction et paramètres de la fonction
【云动向】华为云云商店品牌全新发布 4大亮点都在这儿
Borui data attends Alibaba cloud observable technology summit, and digital experience management drives sustainable development
高级计网笔记(三)
Jerry's adding timer interrupt [chapter]
杰理之播 MP3 提示音功能【篇】
机器学习工作岗位
Requirements and precautions for applying for multi domain SSL certificate
8、AI医生案例
矩阵分析笔记(二)
【NOI2014】15. Difficult to get up syndrome [binary]
Shunted Self-Attention | 源于 PvT又高于PvT,解决小目标问题的ViT方法
Function definition and function parameters
