当前位置:网站首页>[foundation of deep learning] learning of neural network (4)
[foundation of deep learning] learning of neural network (4)
2022-06-12 11:48:00 【Programmer Xiao Li】
Based on the previous study , We have learned some key points in neural network learning , Let's finally review the steps of learning .
The steps of learning
1. minibatch
From the training data , Select partial data , constitute mini-batch, We have set the goal of mini-batch Minimize the cost of .
2. Calculate the gradient value
In order to find the optimal weight parameter , We need the partial derivative of the weight according to the cost function ( gradient ), The method of gradient descent is continuously used to obtain the minimum cost function .
3. Update the weight according to the gradient
According to the calculated gradient , Keep learning along the descending gradient 、 Adjust the weight , In order to reach the optimal value .
Take two-layer neural network as an example , Briefly describe the learning process ( single batch Training steps )
1. Guide pack
# For file operations
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
# The previously defined function
from common.functions import *
# Gradient descent function
from common.gradient import numerical_gradient2. initialization
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, weight_init_std=0.01):
# Initialization weight
self.params = {}
# The first layer of weight
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
# The first layer is offset
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
# Second layer weight
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
# The second layer is offset
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
Here on the first floor 、 The weight of the second layer initializes the weight matrix according to the normal distribution , The offset matrix is initialized directly to 0
3. Forward propagation
def predict(self, x):
# The weight
W1, W2 = self.params['W1'], self.paraams['W2']
# bias
b1, b2 = self.params['b1'], self.params['b2']
# first floor , Calculate the weight and input the opportunity and add offset
a1 = np.dot(x, W1) + b1
# Calculate the activated value
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
# The second floor , Calculate the weight and input the opportunity and add offset
a2 = np.dot(z1, W2) + b2
# softmax Activate category
y = softmax(a2)
return y4. Use the cross entropy function to calculate the cost
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return cross_entropy_error(y, t)5. Gradient calculation
# x: input data , t: Monitoring data
def numerical_gradient(self, x, t):
loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
grads['W1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W1'])
grads['b1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b1'])
grads['W2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W2'])
grads['b2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b2'])
return grads6. Accuracy statistics
def accuracy(self, x, t):
# Output
y = self.predict(x)
# Which tag is output
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
# Real label
t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
# Accuracy calculation
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
introduce mini-batch( Group training )
mini-batch It is simply to divide the large amount of data into small amounts of data and execute them for many times :
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
from two_layer_net import TwoLayerNet
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_ laobel = True)
# Test error
train_loss_list = []
# Hyperparameters
# The number of iterations ( The number of times the gradient drops )
iters_num = 10000
# Training data size
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
# Batch size
batch_size = 100
# Learning rate
learning_rate = 0.1
# Initialize the network , Input layer 784=28*28, Middle layer 50, Output layer 10
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10)
# iteration 10000 Time
for i in range(iters_num):
# obtain mini-batch(100 In groups )
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
# Calculate the gradient
grad = network.numerical_gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
# Update parameters
for key in ('W1', 'b1', 'W2', 'b2'):
network.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
# Record the learning process
loss = network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)

We found that , As the number of iterations increases , The value of the cost function decreases gradually , This shows that learning is effective .
Calculation of accuracy ( Effect check )
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
from two_layer_net import TwoLayerNet
# Load data
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_ laobel = True)
# cost
train_loss_list = []
# Training accuracy
train_acc_list = []
# Test accuracy
test_acc_list = []
# Average each epoch Number of repetitions of
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
# Hyperparameters
iters_num = 10000
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10)
for i in range(iters_num):
# obtain mini-batch
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
# Calculate the gradient
grad = network.numerical_gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
# Update parameters
for key in ('W1', 'b1', 'W2', 'b2'):
network.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
loss = network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
# Calculate each epoch The recognition accuracy of
if i % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = network.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
test_acc = network.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
print("train acc, test acc | " + str(train_acc) + ", " + str(test_acc))Epoch The concept of : We think batch The size is 100 Of mini-batch, loop 600 Time , will ” Traverse “ Again 100*600=60000( Training data size ), We put 600 It is called one time epoch.

As the number of iterations increases , The accuracy has been continuously improved , The accuracy of the testing machine and the training set is basically the same , Indicates that no fitting has occurred .
thus , The learning process of deep learning is over .
边栏推荐
- MySQL lock leak detection and defect filling
- Summary of rosbridge use cases_ Chapter 26 opening multiple rosbridge service listening ports on the same server
- Differences among various cross compiling tools of arm
- Socket implements TCP communication flow
- Simple solution of regular expression
- VirtualBox virtual machine shut down due to abnormal system. The virtual machine startup item is missing
- 35. search insertion position
- 視頻分類的類間和類內關系——正則化
- UML系列文章(30)体系结构建模---制品图
- SSL引入原因及加密步骤
猜你喜欢

Simple solution of regular expression

Byte order - how to judge the big end and the small end
Deep learning and CV tutorial (14) | image segmentation (FCN, segnet, u-net, pspnet, deeplab, refinenet)

UML系列文章(30)体系结构建模---制品图

Humans want to have money, power, beauty, eternal life and happiness... But turtles only want to be a turtle

TinyMCE realizes automatic uploading of pasted pictures

JS to load and display Excel files

Unlimited growth, we will all go to the future | the 15th anniversary of the founding of InfoQ China

C# 35. 选择默认网卡
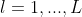
視頻分類的類間和類內關系——正則化
随机推荐
ioremap
The first thing with a server
Video JS library uses custom components
标品和非标品如何选品,选品的重要性,店铺怎样布局
Logrotate log rotation method create and copyruncate principles
Golang Foundation (6)
manuscript手稿格式准备
邻居子系统之邻居项状态更新
[the 11th national competition of Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer]
TinyMCE series (III) introduction to common TinyMCE APIs
正则表达式 | 浅解
你需要社交媒体二维码的21个理由
Index in MySQL show index from XXX the meaning of each parameter
Humans want to have money, power, beauty, eternal life and happiness... But turtles only want to be a turtle
Unlimited growth, we will all go to the future | the 15th anniversary of the founding of InfoQ China
Spark common encapsulation classes
K52. Chapter 1: installing kubernetes v1.22 based on kubeadm -- cluster deployment
Byte order (network / host) conversion
MySQL45讲 01 | 基础架构:一条SQL查询语句是如何执行的?
C# 36. DataGridView行号