当前位置:网站首页>One article solves all search backtracking problems of Jianzhi offer
One article solves all search backtracking problems of Jianzhi offer
2022-06-25 18:14:00 【[email protected]】
List of articles
- 1. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - I. Print binary tree from top to bottom
- 2. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - II. Print binary tree from top to bottom II
- 3. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - III. Print binary tree from top to bottom III
- 4. The finger of the sword Offer 26. The substructure of a tree
- 5. The finger of the sword Offer 27. Image of binary tree
- 6. The finger of the sword Offer 28. Symmetric binary tree
- 7. The finger of the sword Offer 12. Path in matrix
- 8. The finger of the sword Offer 13. The range of motion of the robot
- 9. The finger of the sword Offer 34. The path of a value in a binary tree
- 10. The finger of the sword Offer 36. Binary search tree and double linked list
- 11. The finger of the sword Offer 54. The second of binary search tree k Big node
- 12. The finger of the sword Offer 64. seek 1+2+…+n
- 13. The finger of the sword Offer 68 - I. The nearest common ancestor of a binary search tree
- 14. The finger of the sword Offer 68 - II. The nearest common ancestor of a binary tree
- 15. The finger of the sword Offer 37. Serialize binary tree
- 16. The finger of the sword Offer 38. Arrangement of strings
- 17. The finger of the sword Offer 55 - I. The depth of the binary tree
- 18. The finger of the sword Offer 55 - II. Balanced binary trees
1. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - I. Print binary tree from top to bottom
The finger of the sword Offer 32 - I. Print binary tree from top to bottom

Ideas : Use queue Just go through the hierarchy
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return new int[0];//root by null when , return []
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node=q.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)
q.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
q.add(node.right);
}
int ans[]=new int[list.size()];
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)
{
ans[i]=list.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
//O(n) BFS Need to cycle N Time
//O(n/2) When the number is a balanced binary tree , At most n/2 Nodes in the queue
2. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - II. Print binary tree from top to bottom II
The finger of the sword Offer 32 - II. Print binary tree from top to bottom II

Ideas : Use queues for hierarchical traversal , However, the nodes of each layer should be regarded as a list recorded , That is, each layer needs to be traversed separately internally
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)
return list;
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int size=q.size();
List<Integer> level=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)// Go through each layer
{
TreeNode node=q.pop();
level.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
q.offer(node.right);
}
list.add(level);
}
return list;
}
}
//O(n) BFS Need to cycle N Time
//O(n/2) When the number is a balanced binary tree , At most n/2 Nodes in the queue
3. The finger of the sword Offer 32 - III. Print binary tree from top to bottom III
The finger of the sword Offer 32 - III. Print binary tree from top to bottom III
Ideas : Use queues for hierarchical traversal , The order of adding is different for each layer , The first 1 Layers are added from left to right , The first 2 Columns are added from right to left … You can set a layer number , Odd layer positive order addition , Even columns are added in reverse order
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)
return list;
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
int levelNum=1;// The layer number is initialized to 1
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int size=q.size();
// Use here LinkedList Easy to add nodes upside down
LinkedList<Integer> level=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)// Go through each layer
{
TreeNode node=q.pop();
if(levelNum%2!=0)// Odd number layer Follow to add
level.addLast(node.val);
else// Even layers Add... Upside down
level.addFirst(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
q.offer(node.right);
}
list.add(level);
levelNum++;
}
return list;
}
}
4. The finger of the sword Offer 26. The substructure of a tree
The finger of the sword Offer 26. The substructure of a tree

Ideas : Traversing the tree A Each node of a, Then judge by a Whether there is a subtree and B equally , If it is the same, it returns true, Otherwise, continue to judge , Distributed in a Start the comparison between the left and right child nodes of , If the tree A The traversal has not returned yet true, shows B No A The subtree of ; In the process of comparison , If the tree B The traversal has not returned yet false shows B yes A A subtree of , You need two functions , One isSubstructue() Used for depth traversal , One judge Used to determine whether the subtree of the current node starts with B equally
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
// As long as there is a tree for null, Just go back to false
if(A==null||B==null)
return false;
// Here are not three judge, Because what we need is a preorder traversal (dfs), If
// There is no substructure at the beginning of the current node , The next time starts with the left child node of the current node
// Compare again , Then the left child node
return judge(A,B)||isSubStructure(A.left,B)||isSubStructure(A.right,B);
}
boolean judge(TreeNode A,TreeNode B)
{
if(B==null)//B The tree traversal has not returned yet false That is the true First judge B Whether the tree has been traversed
return true;
if(A==null)//A The tree is traversed ,B The tree has not been traversed yet
return false;
if(A.val!=B.val)// The current nodes are not equal
return false;
// The current node is equal Then compare the values of the left child node and the right child node
return judge(A.left,B.left)&&judge(A.right,B.right);
}
}
//O(MN) M yes A The number of nodes N yes B The number of nodes Traverse A need O(M) about A Each node of the needs to call recur Use O(N)
//O(M)
5. The finger of the sword Offer 27. Image of binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 27. Image of binary tree

Ideas 1: Use recursive depth search , Exchange nodes from bottom to top
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return null;
TreeNode tmp=root.left;
root.left=mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right=mirrorTree(tmp);
return root;
}
}
//O(N)
//O(N)
Ideas 2: Use the auxiliary queue hierarchy to traverse , Exchange nodes from top to bottom
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return null;
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node=q.pop();
if(node.left!=null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
q.offer(node.right);
TreeNode tmp=node.left;
node.left=node.right;
node.right=tmp;
}
return root;
}
}
//O(N)
//O(N)
6. The finger of the sword Offer 28. Symmetric binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 28. Symmetric binary tree

Ideas : Recursion , Judge the left node of the current node L And right node R, If it is a symmetric binary tree , Then there are L.val==R.val L.left.val==R.right.val L.right.val==R.left.val, Comparison function judge In recursion
The termination condition is :
- L R Also for null That is, it crosses the leaf node at the same time Return at this time true
- L R Not crossing leaf nodes at the same time , return false
- The two are not null, But the current value is different return false
- dissatisfaction 1-3 If the recursion termination condition of (A Left comparison B Right A Right comparison B Left )
Time complexity :O(n) n Is the number of nodes Judge a pair of nodes at a time At most n/2 Time
Spatial complexity :O(n)
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
// If the tree is empty, it will directly return true
if(root==null)
return true;
return judge(root.left,root.right);
}
boolean judge(TreeNode leftTree,TreeNode rightTree)
{
// The left and right subtrees reach the leaf node at the same time , Explain symmetry
if(leftTree==null&&rightTree==null)
return true;
// Left and right subtrees do not reach leaf nodes at the same time , Explain asymmetry
if(leftTree==null||rightTree==null)
return false;
// Returns if the value of a node is different false
if(leftTree.val!=rightTree.val)
return false;
// The current node is the same, but the left and right subtrees have not been traversed Continue traversing
return judge(leftTree.left,rightTree.right) &&judge(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
}
7. The finger of the sword Offer 12. Path in matrix
The finger of the sword Offer 12. Path in matrix

Ideas : Deep search , The starting position of the search is m*n individual , Pay attention to the search function dfs Termination conditions in , Be careful : A grid cannot be accessed more than once in a search , So you need to set it to ’\0’ To indicate that you have visited , When the search is over, you can \0 Restore to the original characters ( Of course, you can also use another tag to access the array , But it will increase the space overhead )
Time complexity O(3 K ^K KMN) : In the worst case , We need to traverse the matrix with a length of K All schemes of string , The time complexity is O(3 K ^K K); Common matrix MN A starting point , The time complexity is O(MN) .
Calculation of number of schemes : Set the string length to K , Each character in the search has up 、 Next 、 Left 、 You can choose from the four right directions , Give up looking back ( Last character ) The direction of , be left over 333 A choice , Therefore, the complexity of the number of schemes is O(3^K)Spatial complexity O(K) : The depth of recursion in the search process does not exceed K , Therefore, the stack space used by the system due to function calls is occupied O(K) ( Because after the function returns , Stack space for system calls will be freed ). In the worst case K=MN , The recursion depth is MN , At this point, the system stack uses O(MN) Extra space
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
int m=board.length;
int n=board[0].length;
int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(dfs(board,word,i,j,index))//m*n Starting position
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char [][] board,String word,int i,int j,int index)
{
if(i<0||i>=board.length||j>=board[0].length||j<0||board[i][j]!=word.charAt(index))// Stop looking for conditions
return false;
if(index==word.length()-1)// The match is successful
return true;
board[i][j]='\0';// take (i,j) The location is marked as visited
boolean ans= dfs(board,word,i+1,j,index+1)||dfs(board,word,i,j+1,index+1)|| dfs(board,word,i-1,j,index+1)|| dfs(board,word,i,j-1,index+1);// Continue searching up, down, left and right , One for true that will do Don't write alone , This will not play the role of short circuit or
board[i][j]=word.charAt(index);// Restore tag
return ans;
}
}
8. The finger of the sword Offer 13. The range of motion of the robot
The finger of the sword Offer 13. The range of motion of the robot

Ideas : Deep search , It's similar to the last question , But it's a little different , There is only one starting point for this topic , Since there is only one search and access, there is no need to access again , Therefore, there is no need to restore
class Solution {
int count=0;
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
// Tag array Judge (i,j) Whether the location has been accessed
boolean visited[][]=new boolean[m][n];
dfs(0,0,m,n,k,visited);// There is only one starting position (0,0)
return count;
}
public void dfs(int i,int j,int m,int n,int k,boolean[][] visited)
{
if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||visited[i][j]==true||calNum(i,j)>k)
return;// Termination conditions
count++;
visited[i][j]=true;//(i,j) The location has been visited
dfs(i+1,j,m,n,k,visited);// Go down
dfs(i-1,j,m,n,k,visited);// Go up
dfs(i,j+1,m,n,k,visited);// turn right
dfs(i,j-1,m,n,k,visited);// Walk towards
//visited[i][j] No need to restore Because only one search There is only one starting position
}
public int calNum(int i,int j)
{
//i,j All are 1 Digits or two digits
int ans=i/10+i%10+j/10+j%10;// Calculate the sum of digits
return ans;
}
}
//O(mn)
//O(mn)
9. The finger of the sword Offer 34. The path of a value in a binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 34. The path of a value in a binary tree

Ideas : Depth-first search , For a tree, it is also a preorder traversal , When traversing, determine whether the leaf node and whether the path sum is equal to target
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root,target,list);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int target, List<Integer> list)
{
if(root==null)
return;
list.add(root.val); // Add the current node
// Conform to the node values and =target And it's a leaf node
if(target==root.val&&root.left==null&&root.right==null)
{
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(list));// Must use new Create a new
}
dfs(root.left,target-root.val,list);// Traverse left subtree
dfs(root.right,target-root.val,list);// Traversal right subtree
list.remove(list.size()-1);// The sum of the paths is not equal to target
// Path recovery : You need to delete the newly added element before backtracking
}
}
10. The finger of the sword Offer 36. Binary search tree and double linked list
The finger of the sword Offer 36. Binary search tree and double linked list 

Ideas :
- Ascending order is required And it's a binary search tree , Therefore, the middle order traversal can be adopted
- When building the reference relationship between adjacent nodes , Set the precursor node
preAnd the current nodecur, Not only should we buildpre.right = cur, You should also buildcur.left = pre- Set the chain header node
headAnd tail nodestail, Should be builthead.left = tailandtail.right = head
class Solution {
Node head,pre;// The default value is null
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null)//root If it is empty, it will return to otherwise head by null head.left A null pointer exception will occur
return null;
dfs(root);
// The title requires head to tail connection head Finally point to the head pre Pointing tail
head.left=pre;//head The left pointer of points to pre Caudal node
pre.right=head;//pre The right pointer of points to head Head node
return head;// Return head pointer
}
public void dfs(Node cur)
{
if(cur==null)
return;// Recursion end condition
dfs(cur.left);// In the sequence traversal : Left root right
if(pre==null)//pre It's empty explain cur Point to the first node
head=cur;// therefore head Point to the head node
else//pre Not empty explain cur It points to a non head node pre Point to the previous node
pre.right=cur;// The right pointer of the previous node points to the current node
cur.left=pre;// The left pointer of the current node points to the previous node
pre=cur;// Save the current node It is used for lower level recursive creation
dfs(cur.right);
}
}
//O(n) n Is the number of nodes in the binary tree
//O(n)
11. The finger of the sword Offer 54. The second of binary search tree k Big node
The finger of the sword Offer 54. The second of binary search tree k Big node

Ideas : Because it's a binary search tree , The middle order traversal is followed by ascending , The last element is the largest , The topic requires that k Big , That is, the penultimate number after the middle order traversal K Elements , For convenience , According to
Right root leftGet an inverse sequence of middle order traversal , This is the positive number K Elements , In the process of traversal, we make K–,K==0 It means that the... Was found K Big nodes
class Solution {
int ans,k;//k Should be set to member variable
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k=k;
inOrderReverse(root);
return ans;
}
public void inOrderReverse(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return;
// Medium order ascending order : Left root right Middle and reverse order : Right root left
inOrderReverse(root.right);// Right root left
k--;// Count minus one
if(k==0)// Traverse to the k Big nodes , That is, the second in reverse order k Nodes
{
ans=root.val;
return;
}
inOrderReverse(root.left);
}
}
//O(n) In the worst case A binary tree degenerates into a linked list with only right child nodes
//O(n)
12. The finger of the sword Offer 64. seek 1+2+…+n
The finger of the sword Offer 64. seek 1+2+…+n

Ideas : utilize && Short circuit to achieve if The function of judgment
class Solution {
int sum;
public int sumNums(int n) {
//x It doesn't make any sense Just to form a Boolean expression
//n If =0 Words hinder sumNums(n-1) You won't go in amount to 1 individual if Judge
boolean x=(n>0)&&(sumNums(n-1)>0);
sum+=n;
return sum;
}
}
//O(n)
//O(n)
13. The finger of the sword Offer 68 - I. The nearest common ancestor of a binary search tree
The finger of the sword Offer 68 - I. The nearest common ancestor of a binary search tree 
Ideas : Using the properties of binary search tree , The left child node < The root node < The specific solution of the right child node can be iterative or recursive
// iteration
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while(root!=null)
{
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val)//p q In the present root In the left subtree of the node
root=root.left;
else if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val)//p q In the present root In the right subtree of the node
root=root.right;
else//p q The node is located at root In the left and right subtrees of the node explain root Is the nearest public node
break;
}
}
}
// recursive
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root.val>p.val&&root.val>q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
else if(root.val<p.val&&root.val<q.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
return root;
}
}
14. The finger of the sword Offer 68 - II. The nearest common ancestor of a binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 68 - II. The nearest common ancestor of a binary tree

Ideas : if root yes p,q The nearest common ancestor of a node , It can only be the following 3 One of the three situations :
- p,q be located root In the left and right subtrees
- root=p,q be located root In the left or right subtree of
- root=q,p be located root In the left or right subtree of
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null)// If the tree is empty , Go straight back to null
return null;
if(root==p||root==q)// If p and q One of them is equal to root Of , Then their nearest common ancestor is root( A node can also be its own ancestor )
return root;
// Recursively traverses the left subtree , Just find it in the left subtree p or q, Return to whoever you find first
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
// Recursively traverses the right subtree , Just find it in the right subtree p or q, Return to whoever you find first
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left==null&&right==null)
return null;
// If in the left subtree p and q Can't find , be p and q It must all be in the right subtree , The first traversal in the right subtree is the nearest common ancestor ( A node can also be its own ancestor )
if(left==null)
return right;
// If in the right subtree p and q Can't find , be p and q It must be all in the left subtree , The first traversal in the left subtree is the nearest common ancestor ( A node can also be its own ancestor )
if(right==null)//left!=null&&right!=null explain root It's the nearest public node
return left;
return root;
}
}
//O(n)
//O(n)
15. The finger of the sword Offer 37. Serialize binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 37. Serialize binary tree 
Ideas : Use BFS or DFS One thing to note is that you need to fill in the empty nodes of the binary tree , Make the binary tree representation complete
DFS Serialized sequence :1,2,#,#,3,4,#,#,5,#,#,
BFS Serialized sequence :1,2,3,#,#,4,5,#,#,#,#,
//DFS
public class Codec {
String SEP=",";// Separator representation
String NULL="#";// A null pointer means
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
serialize(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
public void serialize(TreeNode root,StringBuilder sb)
{
if(root==null)
{
sb.append(NULL).append(SEP);
return;
}
// The former sequence traversal
sb.append(root.val).append(SEP);
serialize(root.left,sb);
serialize(root.right,sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String str[]=data.split(SEP);
LinkedList<String> nodes=new LinkedList<>();
for(String s:str)
{
nodes.addLast(s);
}
return deserialize(nodes);
}
public TreeNode deserialize(LinkedList<String> nodes)
{
String firstNode=nodes.removeFirst();// The first node of the preamble
if(firstNode.equals(NULL))// At present nodes The element in is null
return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(firstNode));
root.left=deserialize(nodes);
root.right=deserialize(nodes);
return root;
}
}
//O(n)
//O(n)
class Codec {
public:
char SEP=',';
string null_ptr="#";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
string str;
serialize(root,str);
return str;
}
void serialize(TreeNode* root,string &str) {
if(root==NULL)
{
str+=(null_ptr+SEP);
return;
}
str+=to_string(root->val)+SEP;//c++ Integer in cannot be added directly to string First convert an integer to a string
serialize(root->left,str);
serialize(root->right,str);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
list<string> nodes;
string s;
for(int i=0;i<data.size();i++)
{
if(data[i]==SEP)
{
nodes.push_back(s);
s.clear();
}
else
{
s+=data[i];
}
}
return deserialize(nodes);
}
TreeNode* deserialize(list<string> &nodes)
{
string s=nodes.front();
nodes.pop_front();
if(s==null_ptr)
return NULL;//c++ The null pointer in is NULL Java Medium null
TreeNode *node=new TreeNode(stoi(s));//stoi In the header file <cstring> in
node->left=deserialize(nodes);
node->right=deserialize(nodes);
return node;
}
};
//BFS
public class Codec {
String SEP=",";// Separator representation
String NULL="#";// A null pointer means
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return "";
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
Queue<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node=q.poll();
if(node!=null)
{
sb.append(node.val).append(SEP);
q.offer(node.left);
q.offer(node.right);
}
else
sb.append(NULL).append(SEP);
}
// sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length());// Delete the last comma
return sb.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data)
{
if(data.equals(""))
return null;// Empty tree
//substring(1,data.length()-1) Remove the head and tail []
String val[]=data.split(SEP);
Queue<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[0]));
q.offer(root);
int i=1;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode node=q.poll();
if(!val[i].equals(NULL))
{
node.left=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[i]));
q.offer(node.left);
}
i++;
if(!val[i].equals(NULL))
{
node.right=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val[i]));
q.offer(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
//O(n)
//O(n)
16. The finger of the sword Offer 38. Arrangement of strings
The finger of the sword Offer 38. Arrangement of strings

Ideas : In exchange for , to flash back
class Solution {
ArrayList<String> lists=new ArrayList<>();
char c[];
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c=s.toCharArray();
backtrack(0);
return lists.toArray(new String[lists.size()]);
}
public void backtrack(int x)
{
if(x==c.length-1)
{
lists.add(String.valueOf(c));
return;
}
ArrayList<Character> list=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=x;i<c.length;i++)
{
if(list.contains(c[i]))// Determine whether the element to be added is included
continue;
// If s="aab" We just need to fix the first one a Encounter No 2 individual a Just skip
list.add(c[i]);
swap(i,x);
backtrack(x+1);
swap(x,i);
}
}
// Exchange to achieve full permutation
public void swap(int x,int i)
{
char tmp=c[i];
c[i]=c[x];
c[x]=tmp;
}
}
17. The finger of the sword Offer 55 - I. The depth of the binary tree
The finger of the sword Offer 55 - I. The depth of the binary tree 
Ideas 1:DFS
Time complexity :O(n)
Spatial complexity :O(n)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
Ideas 2: BFS
Time complexity :O(n)
Spatial complexity :O(n)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
int depth=0;
LinkedList<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int sz=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
TreeNode node=q.poll();
if(node.left!=null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
q.offer(node.right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}
18. The finger of the sword Offer 55 - II. Balanced binary trees
The finger of the sword Offer 55 - II. Balanced binary trees

Ideas : A method for solving the maximum depth of binary tree by using the previous problem , For each node , Judge whether the maximum height difference between the left and right subtrees of the node is greater than 1
Time complexity : Worst case nlogn n Is the number of nodes in a binary tree For a full binary tree , The number of nodes in each layer is logn, And on each floor maxDepth The time complexity of the operation of is n
Spatial complexity :O(n) In the worst case, the binary tree degenerates into a linked list
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return true;
if(Math.abs(maxDepth(root.left)-maxDepth(root.right))>1)
return false;
return isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
版权声明
本文为[[email protected]]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/02/202202190532337521.html
边栏推荐
- Introduction to microservices
- 解析数仓lazyagg查询重写优化
- 喜报|海泰方圆通过CMMI-3资质认证,研发能力获国际认可
- 深度学习网路模型
- 解决nvprof 报错ERR_NVGPUCTRPERM - The user does not have permission to profile on the target device.
- Qinheng ch583 USB custom hid debugging record
- 篇5:VS2017搭建QT5.9.9开发环境
- Optimization of lazyagg query rewriting in parsing data warehouse
- Getting started with kotlin (20) several common dialog boxes
- About Equilibrium - Simplified bottleneck model
猜你喜欢
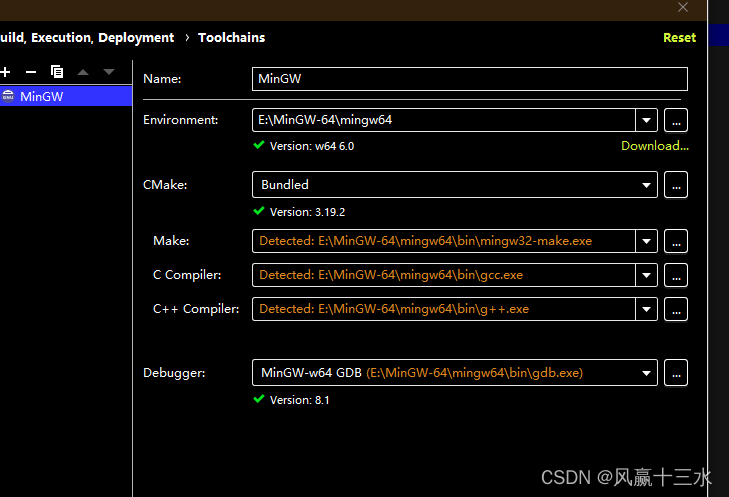
Article 6:clion:toolchains are not configured configure disable profile

The Stackies 2022:32个营销技术栈入选

Install spark + run Scala related projects with commands + crontab scheduled execution

Virtual machine class loading mechanism
Uncover ges super large scale graph computing engine hyg: Graph Segmentation

What is an operator?
158_ Model_ Power Bi uses DAX + SVG to open up almost all possibilities for making business charts
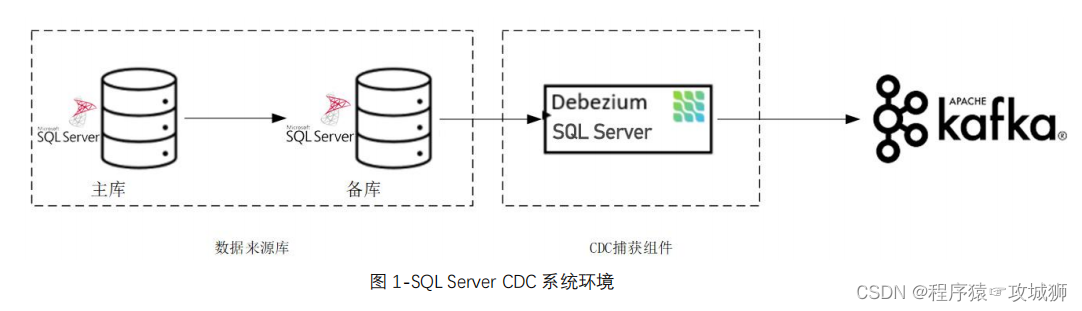
SQL Server real time backup library requirements

Introduction to microservices

SDN系统方法 | 10. SDN的未来
随机推荐
Indexes
Fixed frequency and voltage regulation scheme of Qi v1.2.4 protocol
Uncover ges super large scale graph computing engine hyg: Graph Segmentation
What is an operator?
Essential characteristics of convolution operation +textcnn text classification
Chapter 4:win10 installing mingw64
沁恒CH583 USB 自定义HID调试记录
Introduction to microservices
力扣每日一题-第27天-561.数组拆分Ⅰ
Is it safe for a securities company to open an account with the lowest handling fee among the top ten
Good news | Haitai Fangyuan has passed the cmmi-3 qualification certification, and its R & D capability has been internationally recognized
Redis trend - NVM memory
【日常记录】——对BigDecimal除法运算时遇到的Bug
How to open a stock account? Is it safe to open a securities account
微信小程序报错:request:fail url not in domain list
什么是泛型以及在集合中泛型的使用[通俗易懂]
哈希竞猜游戏系统开发如何开发?哈希竞猜游戏系统开发应用详情案例及源码
.NET Worker Service 如何优雅退出
ACY100油烟浓度在线监控仪针对饮食业厨房油烟排放
深度学习网路模型