当前位置:网站首页>C language - Introduction - Foundation - grammar - process control (VII)
C language - Introduction - Foundation - grammar - process control (VII)
2022-07-04 19:47:00 【Hu Anmin】
The basic concept of process control
By default, after the program runs , The system will execute each line of code in the program from top to bottom in writing order . But this is not
Meet all our development needs , In order to facilitate us to control the running process of the program ,C Language provides 3 A process control structure , Different process control structures can realize different operation processes . this 3 The two process structures are Sequential structure 、 Selection structure 、 Loop structure Basically, if computers can work like people, then process control is the core , No process control , There is no such thing as all current software , Simply put, the switch of your electric light is controlled by the process
Sequential structure
Execute from top to bottom according to the writing order of the code , That's not enough , All fools know 
Selection structure
Judge the given condition , Then decide the execution code according to the judgment result 

C The language provides two choice structures , Namely if and switch
Selection structure if
if
If the expression is true , Execute statement block 1, Otherwise, do not execute

#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age=25;
if (age >= 18) {
// true
printf(" Open the network card \n"); // perform
}
printf(" Buy cigarettes \n");
return 0;
}
if else
If the expression is true , Then execute the statement block 1, Otherwise, execute the statement block 2 ,else Can't get away from if Use alone 
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age=11;
if (age > 18) {
//false
printf(" Open the network card \n");
} else {
printf(" Call parents to drive \n"); // perform
}
printf(" Buy cigarettes \n");
return 0;
}
if else if
- If " expression 1" It's true , execute " Sentence block 1", Otherwise, judgment " expression 2", If it's true , perform " Sentence block 2", Otherwise, judge again " expression 3", If it's true , perform " Sentence block 3", When the expression 1、2、3 Are not satisfied , Will execute the last else sentence
- In many braces , Only the contents in one brace will be executed
- Only all the previous additions are not satisfied , Will execute else What's in braces

#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age=11;
if(age>40){
// false
printf(" Give me your room card ");
}else if(age>25){
printf(" Give me your business card ");
}else if(age>18){
printf(" To network card ");
}else{
printf(" Give the good man a card "); // perform
}
printf(" Buy cigarettes \n");
return 0;
}
if nesting
if You can continue to nest if, else You can also continue to nest if
if Be careful
Any value is true or false 
When if else When there is only one statement after , if else The following braces can be omitted ( Not recommended )
When if else When the following braces are omitted , else Will automatically contact the nearest one if matching 
If if else The braces are omitted , Then you can't define variables later 

Selection structure switch
because if else if It's not simple enough , therefore switch And that's what happened , He followed if else if Complement each other .switch Provides point-to-point judgment , It is more efficient than if Just look at the matching pattern in the figure below quickly

You can see from the picture above ,if It takes a layer of judgment , and switch It only needs one judgment to directly locate the target , So in , A large number of single condition scenarios that need to be judged are multi-purpose switch however switch Can't replace if, because switch The judgment condition is relatively simple 
Calculation " expression " Value , One by one " Constant expression " Value is compared with , When " expression " The value of is related to a " Constant expression " When the values of are equal , That is, execute the following statements , Then jump out switch sentence If " expression " The value of is the same as all case After " Constant expression " Are not the same , execute default The following sentence
Example 
Be careful :
- switch Condition expression must be of type integer , Or it can be promoted to an integer value (char、short) , Otherwise, the editor reports an error
- case The value of can only be a constant , And it must also be an integer , Or it can be promoted to an integer value (char、short)
- case The values of the following constant expressions cannot be the same
- case Then you want to define variables , Must give case Add braces
case 1:{ Code } - switch As long as any one of them case matching , All the others case and default It's going to fail . So if case and default There is no break There will be penetration problems
- switch in default It can be omitted
- switch in default You don't have to write to the end , No matter where you put it, you'll wait for all case Will not be executed until they do not match ( Except for penetration problems )
if and Switch transformation
it seems if and switch Can achieve the same function , So when do we use... In enterprise development if, When to use
switch Well ?
- if else if Multiplex selection for range
- switch It is for point-to-point selection
For example, judge whether the data entered by the user is greater than 100

From above 2 You can see from the picture if and switch In what environment ( Compare size and range using if, Judgment is equal to using switch …)
Loop structure
C The language provides three loop structures , Namely while、dowhile and for Loop structure is a very important structure in program . Its characteristics are , When a given condition holds , Executing a program segment repeatedly , Until the conditions don't hold . The given condition is called " The loop condition ", A program segment that is executed repeatedly is called " The loop body "
If you don't understand through the above figure , such as : You get up to eat in the morning and then go to work , Dinner after work in the evening , sleep , It's like this again and again every day , This is the cycle , Then you might say I can take a vacation , Then this is the condition judgment in the cycle process , So this is the computer program , Loops are particularly important in computers , Some automated scripts and automated programs are ok , It can be executed automatically without human control , This is the main reason why computers improve human efficiency , If there is no cycle, all tasks need to be performed manually one by one
Loop structure while

Several conditions constituting the cyclic structure
- Cycle control conditions ( Main basis for cycle exit , To control when the loop exits )
- The loop body ( Code snippets that are executed repeatedly during the loop )
- A statement that can end a loop ( Increasing 、 Decline 、 really 、 Fake wait , It can make the cycle condition false and exit the cycle )

while Circular execution flow
- First of all, we will judge " Cycle control conditions " Is it true , If false, skip directly to the end of the loop statement
- If " Cycle control conditions " It's true , Perform a loop body , Then judge again " Cycle control conditions " Is it true , For real, continue
- Execution loop body , Jump out of loop for false
- Repeat the above operation , until " Cycle control conditions " Until it's false

#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int count = 0;
while (count < 3) {
printf(" bullets ~ Beep, beep, beep \n");
count++;
}
printf(" Loop execution complete \n");
return 0;
}
- Judge whether the cycle control condition is true , here 0 < 3 It's true
- Execute the code in the loop body , Print " bullets "
- perform " A statement that can end a loop " count = 1
- Judge whether the cycle control condition is true again , here 1 < 3 It's true
- Execute the code in the loop body , Print " bullets "
- perform " A statement that can end a loop " count = 2
- Judge whether the cycle control condition is true again , here 2 < 3 It's true
- Execute the code in the loop body , Print " bullets "
- perform " A statement that can end a loop " count = 3
- Judge whether the cycle control condition is true again , here 3 < 3 For false , Skip loop statements
- Execute the code after the loop statement , Print " Loop execution complete "
while Cycling considerations :
- Any value is true or false 0(false),1(true) , If the condition is always true, Then there will be an endless cycle ( Use... Depending on the situation )
- When while When there is only one statement after ,while The following braces can be omitted ( Not recommended )
- If while The braces are omitted , Then you can't define variables later ( Not recommended )
- The simplest dead cycle
while (1);( Not recommended )
Loop structure do while

do while and while In fact, it's almost , That is, the condition is judged after the execution of the loop body , That is, the worst loop body will also be executed once

Example 
do-while Circular execution flow
- In the first place while Whether the conditions in are true , It will be executed once " The loop body "
- After executing a loop body , Then judge again while Is the condition in true , If true, continue to execute the loop body , Jump out of loop for false
- Repeat the above operation , until " Cycle control conditions " Until it's false
Application scenarios ( Do it first , And then in the validation )
while and do…while Application scenarios
- In most cases while and dowhile interchangeable , So it works while Just use while
- In any case, you need to execute the loop body first , Only use do…while
do...whileOnce proposed to abolish , But it's useful for input checking
Loop structure for


#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf(" bullets ~ Beep, beep, beep \n");
}
return 0;
}
for Circular execution flow
- First, execute " Initialization expression ", And throughout the cycle , The initialization expression will be executed only once
- Then judge " Loop condition expression " Is it true , Execute the statement in the loop body for true
- After the loop body is executed , And then it will execute " Operation expression after loop ", Then judge whether the condition is true again , It's true
- Continue to execute the loop body , Jump out of loop for false
- Repeat the process , Until the conditions are not established for loop
for Cycle considerations and while almost
- while What can be done for Can do it , So it can be used in development for Just use for, because for More flexible , And contrast while Come on for Save more memory space
- If the value of the initialization expression , Need to be used after the cycle , Then use while , If the value of the initialization expression , You don't need to use... After the loop , Then use for
- stay for Loop initializes the variables defined in the expression , Only in for After the loop {} Medium visit
- The simplest dead cycle
for(;;);
Four big jumps
C The language provides four jump statements , Namely return、break、continue、goto ,break:
break
End current operation , Applicable only switch And circular structure 

break matters needing attention :
- break Leave the scope of application (for , switch), Existence is meaningless
- In a multi-level cycle , One break The statement just jumps out one level
- break There can be no statements below , Because it can't be implemented
continue
End the cycle , Enter the next cycle , Only applicable to circular structure 
goto
This is a topic that is not worth discussing ,goto It destroys the structured programming process , It will make the program level unclear , And it is not easy to read. , So be careful , goto sentence , Jump can only be implemented in this function , Can't jump across functions . But he is very efficient when jumping out of multiple cycles 


return
End current function , Return the result to the caller , The return type of the premise function is not void , There can be more than one in the same function return, But in the end, only those that meet the conditions will be returned , If all conditions are met , Then only the first one will be returned
grammar : return expression | value 

More specific details need to be used when learning functions , Here you can know first
Nesting of loops
There are other cyclic structures in the cyclic body of the cyclic structure , We call it loop nesting , Generally speaking, one cycle solves linear problems , The double cycle and triple cycle can solve the plane and three-dimensional problems
Be careful :
- Generally, the nesting of loops should not exceed three layers , Otherwise, it's hard to maintain , Disaster.
- The number of times the outer loop is executed * The number of times the inner loop is executed is the total number of times the inner loop is executed
- In multiple loops , If possible , The longest loop should be placed on the innermost layer , The shortest cycle is on the outermost layer , In order to reduce CPU The number of times that the cyclic layer is cut across





边栏推荐
- Introduction to polyfit software
- Explicit random number
- BCG 使用之CBCGPTabWnd控件(相当于MFC TabControl)
- 西门子HMI下载时提示缺少面板映像解决方案
- Lenovo explains in detail the green smart city digital twin platform for the first time to solve the difficulties of urban dual carbon upgrading
- SSRS筛选器的IN运算(即包含于)用法
- @Data source connection pool exhaustion caused by transactional abuse
- 多表操作-外连接查询
- Socket programming demo II
- Kotlin inheritance
猜你喜欢
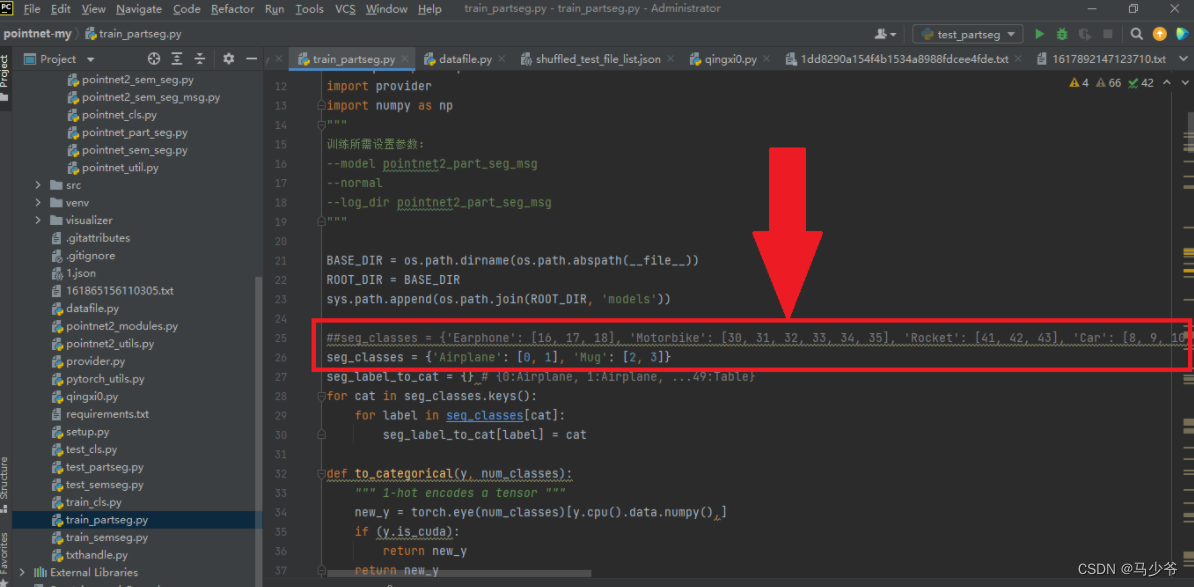
Pointnet/Pointnet++点云数据集处理并训练

Lm10 cosine wave homeopathic grid strategy

92. (cesium chapter) cesium building layering

TCP两次挥手,你见过吗?那四次握手呢?

Mysql database basic operation -ddl | dark horse programmer

黑马程序员-软件测试--09阶段2-linux和数据库-31-43修改文件权限字母发的说明,-查找链接修改文件,查找文件命令,链接文件,压缩解压方式,vi编辑器基本使用,
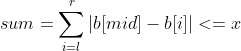
Abc229 summary (connected component count of the longest continuous character graph in the interval)
Some thoughts on whether the judgment point is located in the contour
牛客小白月赛7 谁是神箭手

Hough transform Hough transform principle
随机推荐
【毕业季】绿蚁新醅酒,红泥小火炉。晚来天欲雪,能饮一杯无?
TCP两次挥手,你见过吗?那四次握手呢?
Opencv functions and methods related to binary threshold processing are summarized for comparison and use
Siemens HMI download prompts lack of panel image solution
c# .net mvc 使用百度Ueditor富文本框上传文件(图片,视频等)
FPGA timing constraint sharing 01_ Brief description of the four steps
Dark horse programmer - software testing - 09 stage 2-linux and database -31-43 instructions issued by modifying the file permission letter, - find the link to modify the file, find the file command,
Chrome开发工具:VMxxx文件是什么鬼
安徽 中安在线文旅频道推出“跟着小编游安徽”系列融媒体产品
Niuke Xiaobai monthly race 7 I new Microsoft Office Word document
1007 maximum subsequence sum (25 points) (PAT class a)
多表操作-内连接查询
在线SQL转Excel(xls/xlsx)工具
HDU 1097 A hard puzzle
Is it safe to open an account at Great Wall Securities? How to open an account when buying stocks
Add namespace declaration
数据集划分
Cbcgptabwnd control used by BCG (equivalent to MFC TabControl)
“只跑一趟”,小区装维任务主动推荐探索
Cbcgpprogressdlg progress bar used by BCG

