当前位置:网站首页>CANN算子:利用迭代器高效实现Tensor数据切割分块处理
CANN算子:利用迭代器高效实现Tensor数据切割分块处理
2022-07-04 18:34:00 【InfoQ】
任务场景及目标
常规方案:
准备知识及分析
1.步长
2.迭代器
template <typename T>
class PositionIterator {
public:
PositionIterator(){};
~PositionIterator(){};
PositionIterator(std::vector<T> stt, std::vector<T> sh) {
if (stt.size() != sh.size()) {
PositionIterator();
} else {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < sh.size(); i++) {
if (stt[i] >= sh[i]) {
PositionIterator();
}
}
pos_ = stt;
shape_ = sh;
}
}
PositionIterator operator++() {
pos_[shape_.size() - 1] += 1;
for (unsigned int i = shape_.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (pos_[i] / shape_[i] != 0) {
pos_[i - 1] += pos_[i] / shape_[i];
pos_[i] = pos_[i] % shape_[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
bool End() {
if (pos_[0] != shape_[0]) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
std::vector<T> GetPos() { return pos_; }
std::vector<T> GetShape() { return shape_; }
private:
std::vector<T> pos_;
std::vector<T> shape_;
};Diagonal算子的实现
template <typename T>
uint32_t DiagonalCpuKernel::DoComputeType(CpuKernelContext &ctx,
const int64_t &offset,
const int64_t &dim1,
const int64_t &dim2) {
// Get the inuput and output
Tensor *input_x = ctx.Input(0);
Tensor *y = ctx.Output(0);
// Get some information of input
auto x_shape = input_x->GetTensorShape();
std::vector<int64_t> x_shape_ = x_shape->GetDimSizes();
const int64_t x_dim = x_shape->GetDims();
auto dataptr = reinterpret_cast<T *>(ctx.Input(0)->GetData());
auto y_dataptr = reinterpret_cast<T *>(y->GetData());
// Compute
// 首先计算出对角线元素个数
int64_t dsize = OffsetSize(offset, dim1, dim2, x_shape_);
// 生成输入Tensor的步长向量x_stride
std::vector<int64_t> x_stride = ConstructStride<int64_t>(x_shape_);
// 分情况讨论,2维和大于2维的情况
if (x_dim != N2) {
//set the vx_shape and vx_stride
// 生成x_shape和x_stride中除去dim1和dim2对应值的vx_shape与vx_stride
std::vector<int64_t> vx_shape, vx_stride;
for (unsigned int tmp_dim = 0; tmp_dim < x_shape_.size(); tmp_dim++) {
if (tmp_dim != dim1 && tmp_dim != dim2) {
vx_shape.push_back(x_shape_[tmp_dim]);
vx_stride.push_back(x_stride[tmp_dim]);
}
}
// set the y_shape, y_stride, vy_stride
// 生成输出Tensor的形状及步长向量:y_shape和y_stride
std::vector<int64_t> y_shape = vx_shape;
y_shape.push_back(dsize);
std::vector<int64_t> y_stride =
ConstructStride<int64_t>(y_shape);
// 生成输出Tensor的出去最后一维的步长向量:vy_stride
std::vector<int64_t> vy_stride = y_stride;
vy_stride.pop_back();
// 读取对角数据
std::vector<int64_t> v_start(vx_shape.size(), 0);
for (PositionIterator<int64_t> myiter(v_start, vx_shape); !myiter.End();
++myiter) {
// 利用迭代器确定除dim1和dim2维度的位置坐标
auto p = myiter.GetPos();
// 通过步长向量和位置坐标计算出输入和输出的基础位置值base_pos1和outbase_pos
int64_t base_pos1 = MulSum<int64_t>(p, vx_stride);
int64_t outbase_pos = MulSum<int64_t>(p, vy_stride);
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; i++) {
// 结合前面计算出的基础位置值,对dim1和dim2对应维度确定对角元素位置,并赋值给输出数据地址(get_data涉及对上对角还是下对角取元素,不影响对迭代器作用的理解)
int64_t base_pos2 = i * (x_stride[dim1] + x_stride[dim2]);
int64_t arr[N2] = {x_stride[dim1], x_stride[dim2]};
y_dataptr[outbase_pos + i] =
get_data(base_pos1 + base_pos2, offset, arr, dataptr);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; i++) {
int64_t base_pos = i * (x_stride[dim1] + x_stride[dim2]);
int64_t arr[N2] = {x_stride[dim1], x_stride[dim2]};
y_dataptr[i] = get_data(base_pos, offset, arr, dataptr);
}
}
return KERNEL_STATUS_OK;
}迭代器的其他用法
for (position_iterator<int64_t> mit(v_start, v_shape); !mit.end(); ++mit) {
auto p = mit.get_pos();
int axis_len = input_shape_[tmp_axis];
std::vector<ValueIndex<T>> data_(axis_len);
int base_pos = mul_sum<int64_t>(p, v_stride);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < axis_len; i++) {
data_[i].value = x_dataptr[base_pos + i * input_stride[tmp_axis]];
data_[i].index = i;
}
std::vector<std::vector<T1>> data_;
for (int64_t i = 0; i < dim0; i++) {
std::vector<T1> tmp_v1;
for (PositionIterator<int64_t> mit(v_start, v_shape); !mit.End(); ++mit) {
auto pos = mit.GetPos();
tmp_v1.push_back(
x_dataptr[MulSum<int64_t>(pos, v_stride) + i * input_stride[axis]]);
}
data_.push_back(tmp_v1);
}边栏推荐
- Find the nth power of 2
- HDU 6440 2018 Chinese college student program design network competition
- HDU 1372 & POJ 2243 Knight Moves(广度优先搜索)
- Add namespace declaration
- FTP, SFTP file transfer
- Stream流
- 1011 World Cup betting (20 points) (pat a)
- To sort out messy header files, I use include what you use
- 1008 Elevator(20 分)(PAT甲级)
- Shell programming core technology "four"
猜你喜欢

English grammar_ Noun - use
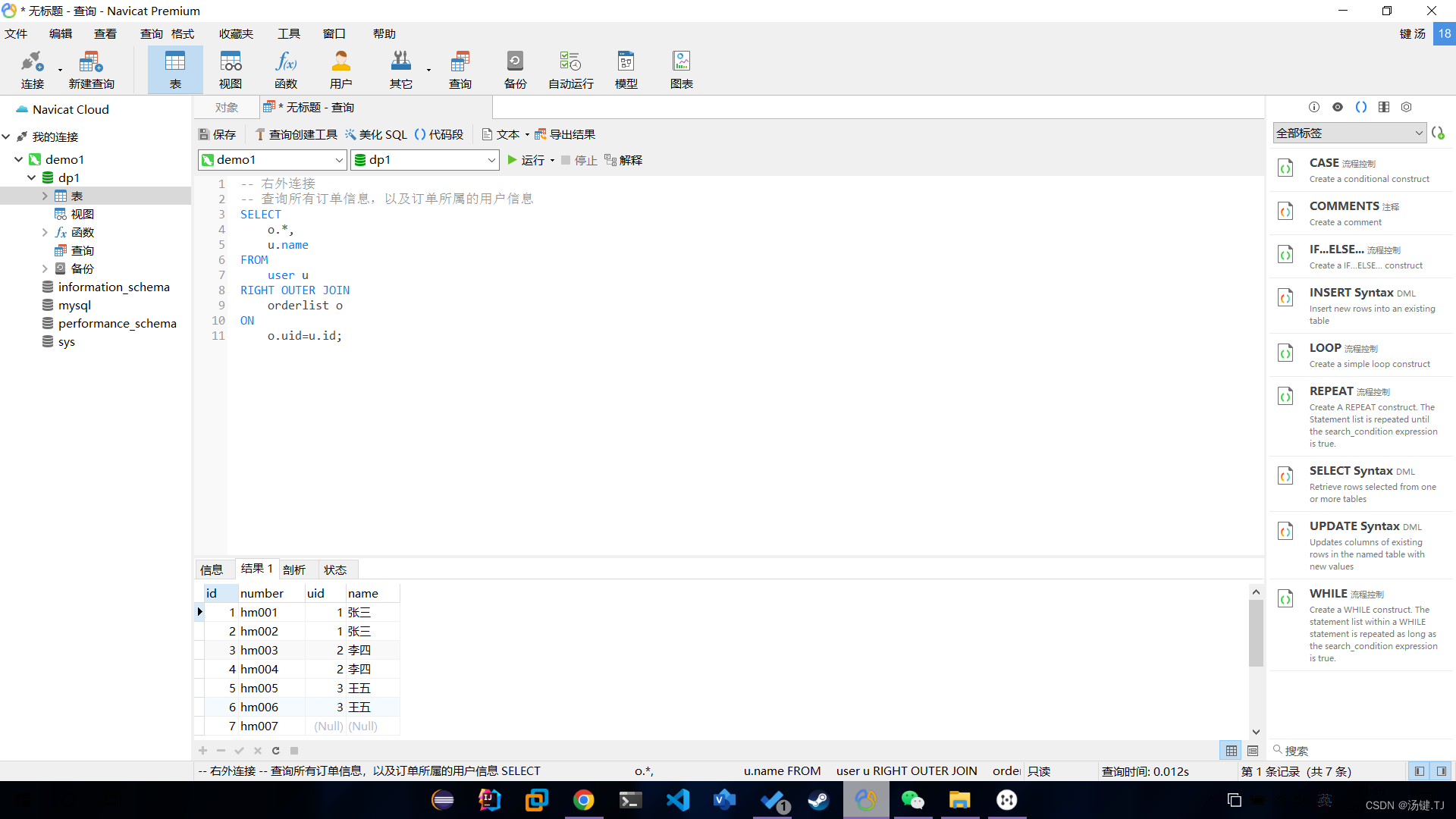
Multi table operation - external connection query

Lenovo explains in detail the green smart city digital twin platform for the first time to solve the difficulties of urban dual carbon upgrading

Comment utiliser async awati asynchrone Task Handling au lieu de backgroundworker?

PolyFit软件介绍
BCG 使用之CBCGPProgressDlg进度条使用

C语言-入门-基础-语法-流程控制(七)
ACM组合计数入门
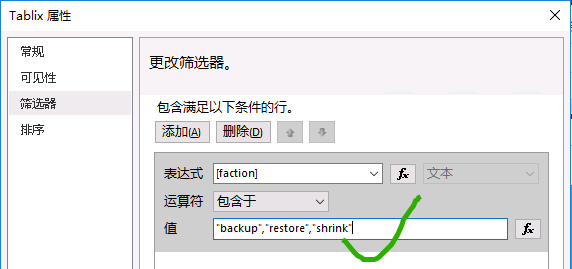
SSRS筛选器的IN运算(即包含于)用法

Hough transform Hough transform principle
随机推荐
Pointnet/Pointnet++点云数据集处理并训练
SSRS筛选器的IN运算(即包含于)用法
Educational Codeforces Round 22 E. Army Creation
1009 product of polynomials (25 points) (PAT class a)
BCG 使用之CBCGPProgressDlgCtrl进度条使用
What should we pay attention to when doing social media marketing? Here is the success secret of shopline sellers!
求2的n次方
Comment utiliser async awati asynchrone Task Handling au lieu de backgroundworker?
BCG 使用之CBCGPTabWnd控件(相当于MFC TabControl)
1002. A+B for Polynomials (25)(PAT甲级)
QT realizes interface sliding switching effect
The explain statement in MySQL queries whether SQL is indexed, and several types in extra collate and summarize
Functional interface
MySQL数据库基本操作-DDL | 黑马程序员
C语言-入门-基础-语法-流程控制(七)
需求开发思考
1007 maximum subsequence sum (25 points) (PAT class a)
HMM隐马尔可夫模型最详细讲解与代码实现
如何使用Async-Awati异步任务处理代替BackgroundWorker?
矩阵翻转(数组模拟)