当前位置:网站首页>Talk about the implementation principle of @autowired
Talk about the implementation principle of @autowired
2022-06-23 08:27:00 【Young and】
@Autowired Use
Constructor injection
public Class Outer {
private Inner inner;
@Autowired
public Outer(Inner inner) {
this.inner = inner;
}
}
Attribute injection
public Class Outer {
@Autowired
private Inner inner;
}
Methods to inject
public Class Outer {
private Inner inner;
public Inner getInner() {
return inner;
}
@Autowired
public void setInner(Inner inner) {
this.inner = inner;
}
}
At present, most of the code uses the 2、 The first 3 Kind of . The first 1 Plant in bean Complete when instantiating , And the first 2、 The first 3 The implementation principle of each kind is the same , Complete when the attribute is populated . This article will introduce the second and third implementation principles
Before we start , If we design it ourselves @Autowired, How should we achieve ? I think it's simple
- Find... By reflection bean Of class Under all the notes @Autowired Fields and methods for
- Get field , adopt getBean( Field ) Get the corresponding bean, And then call... Through reflection field Of set take bean Inject
@Autowired Source code analysis
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor class
This category is @Autowired Implementation class of , First preview the class methods

Find a real opportunity to intervene bean The creation of can only be a post processor , For post-processing are 3 A way , One of them is obsolete , Namely postProcessMergedBeanDefinition、postProcessProperties Post processing , Let's take another look at this 2 The specific code of the method
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter
implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, BeanFactoryAware {
...
@Override
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// 1. seek bean All of them are @Autowired Properties of annotations , And encapsulate the attributes into InjectedElement type
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
...
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
// 1. Find through @Autowired Attribute or method of annotation
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 2. Inject
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
...
}
It is the same as our guess , First, find out all the comments @Autowired Property or method , Then inject , Of course postProcessMergedBeanDefinition The post processor call must be in postProcessProperties Previous , Here we review spring bean The creation process of .
2 Processors I have marked in yellow

*1.* * Find all @Autowired*
// seek bean All of them are @Autowired Properties of annotations , And encapsulate the attributes into InjectedElement type
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
// Get cached key value , General with beanName do key
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
// From the cache metadata
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
// testing metadata Need to update
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
// adopt clazz class , Find all @Autowired Property or method , And encapsulate it into InjectionMetadata type
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
// take metadata Join the cache
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
You can see spring Still using cache to improve performance , Keep track of the core code buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz)
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
// see clazz Is there a Autowired annotation
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
// Here we need to pay attention to AutowiredFieldElement,AutowiredMethodElement All inherited InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement
// Therefore, this list can store the annotated attributes and annotated methods
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
// 1. adopt do while loop , Recursively look for the directly inherited parent class @Autowired
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
// 2. By reflection , Get all properties ,doWithLocalFields The following anonymous methods are applied to each attribute in a loop
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
// Judge the present field Whether the attribute contains @Autowired Annotations
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
// Returns the modifier of the property in the class , If it is equal to static Constant , Throw an exception ,@Autowired Annotations on static attributes are not allowed
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
// @Autowired Yes required attribute , obtain required Value , The default is true
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
// 3. take field Encapsulated into InjectedElement, And add it to the collection , It's used here AutowiredFieldElement
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
// 4. @Autowired It can be annotated on the method
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
// 5. Encapsulate the method into InjectedElement, And add it to the collection , It's used here AutowiredMethodElement
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
// Return the directly inherited parent class
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
// If the parent class is not empty, the parent class's @Autowired Properties or methods are also found
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
// 6. new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements), Generate all the found properties or methods to be injected metadata return
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
- Outer layer
do … while …The loop of is used to recursively find the parent class@AutowiredProperties or methods - Get all attributes through reflection and verify whether each attribute is
@Autowiredannotation - Will find the containing
@AutowiredAnnotated filed Encapsulated intoAutowiredFieldElement, Add to list - Loop through the annotations on the method
- Encapsulate the found method into
AutowiredMethodElement, And add it to the list
There is a special point to emphasize here ,InjectedElement By AutowiredFieldElement、AutowiredMethodElement Inherited , They all have their own inject function , Implement respective injection . So change ArrayList elements Is to have 2 There are two types of properties
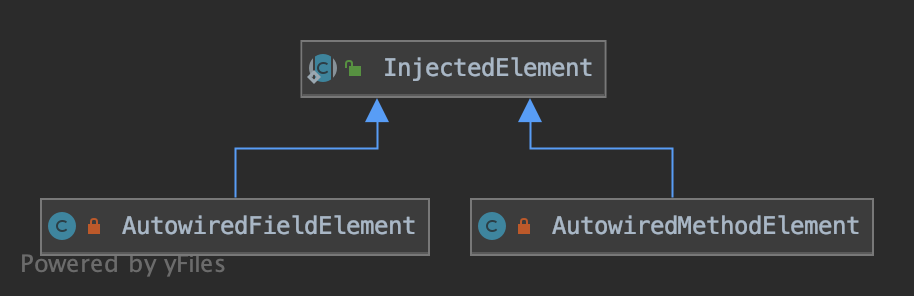
- A list of all elements found and clazz Generate as a parameter metadata The data returned
2. Inject
// Inject
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// Get all the elements that need to be injected
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
// The element of the iteration is not empty
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
// Cyclic injection , It could be here AutowiredFieldElement Or maybe AutowiredMethodElement, So called inject yes 2 A different way
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
utilize for loop , Traverse what we just found elements list , For injection .
There is a special reminder on it , there element It could be AutowiredFieldElement type 、 or AutowiredMethodElement type . Each represents @Autowired Comment on attribute 、 And the annotation on the method 2 Two different elements . So they call element.inject(target, beanName, pvs); It's different
2.1 Field injection (AutowiredFieldElement)
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
// Wrapper class for injection , Wrapping constructor parameters , Method parameter or field
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
// Set up class
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
// Need to be automatically injected beanNames, It is only possible here = 1, Method injection is possible for multiple
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();// Get type converter
try {
// adopt beanFactory Get the value of the property , For example, you need to call getBean("b") Get the dependent attribute singleton , And through automatic transformation to the required type
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
// Registration dependence ,
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
// Because it's attribute Injection , So it's only possible here to be equal to 1
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
// The current cache value
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
// By reflection , take value The value is set to bean in
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
Most of the above work is being done to be injected bean And type conversion , If you go further, you can spring Ioc Say it again , But the core is still getBean( Field ) Get the corresponding bean… Here we are concerned with the core statement , This is the 2 sentence
if (value != null) {
// By reflection , take value The value is set to bean in
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
spring By way of reflection , call field Of set Inject attributes
2.2 Methods to inject (AutowiredMethodElement)
private class AutowiredMethodElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
// @Autowired Mark on the method
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
// With cache
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
// No cache , Get all the parameters of the method directly
int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();
arguments = new Object[argumentCount];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];
Set<String> autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(argumentCount);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
// Loop all parameters
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
// adopt beanFactory, Get generation injected bean, And type conversion
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (arguments != null) {
DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, arguments.length);
// Registration dependence
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeans);
// If the number of automatic injections = Number of parameters , Cache
if (autowiredBeans.size() == argumentCount) {
Iterator<String> it = autowiredBeans.iterator();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
String autowiredBeanName = it.next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {
// cache
cachedMethodArguments[i] = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i]);
}
}
}
// Caching method
this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;
}
else {
this.cachedMethodArguments = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
// Reflection calls injection methods , Will get all the bean As a parameter
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
}
The biggest difference between this and attribute injection is ,@Autowired Comment on method , Methods can have multiple parameters , So here we need to get one by one through the loop , And get bean In the same way as above , The essence is through getBean obtain .
The core statement is 2 sentence
// Reflection calls injection methods , Will get all the bean As a parameter
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
Unlike attribute Injection , When @Autowired Comment on method , For example, we annotate in setter On the way , Then you only need to call this directly setter Method to pass in the parameter array , That is to use invoke Trigger method , The process of specific attribute assignment is in setter Method is written by the user
边栏推荐
- How to start Jupiter notebook in CONDA virtual environment
- 9 ways in which network security may change in 2022
- Map interface and its sub implementation classes
- PHP serialization and deserialization CTF
- 论文阅读【Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset】
- 词性家族
- Analysis of JMeter pressure measurement results
- 给你的win10装一个wget
- Data assets are king, analyzing the relationship between enterprise digital transformation and data asset management
- 坑爹的“敬业福”:支付宝春晚红包技术大爆发
猜你喜欢

目标检测中的多尺度特征结合方式

为什么用生长型神经气体网络(GNG)?

坑爹的“敬业福”:支付宝春晚红包技术大爆发

十多年前的入职第一天

Self organizing map neural network (SOM)

Vulnhub | DC: 3 |【实战】

Data assets are king, analyzing the relationship between enterprise digital transformation and data asset management

“方脸老师”董宇辉再回应热度下降:把农产品直播做好让农民受益 考虑去支教

Which one is better for rendering renderings? 2022 latest measured data (IV)

看了5本书,我总结出财富自由的这些理论
随机推荐
Huawei ECS EIP cannot be pinged
如何评价代码质量
Pyspark on HPC (Continued): reasonable partition processing and consolidated output of a single file
Install a WGet for your win10
Arclayoutview: implementation of an arc layout
4-绘制椭圆、使用定时器
Dongyuhui, the "square face teacher", responded that the popularity was declining: do a good job of live broadcasting of agricultural products to benefit farmers and consider supporting education
[cross border e-commerce solutions] lighthouse will be used for pure IP expansion of new business - continuous efforts!
C restart application
PHP serialization and deserialization CTF
How to mine keywords and improve user experience before website construction?
The kernel fails to shut down when the easygbs program stops. How should I optimize it? [code attached]
Deep learning ----- convolution (conv2d) bottom layer
odoo项目 发送信息到微信公众号或企业微信的做法
C print zoom
What are open source software, free software, copyleft and CC? Can't you tell them clearly?
Vulnhub | dc: 3 | [actual combat]
最常用的5中流ETL模式
坑爹的“敬业福”:支付宝春晚红包技术大爆发
ThreadPoolExecutor线程池实现原理与源码解析