当前位置:网站首页>The use of DDR3 (Naive) in Xilinx VIVADO (2) Read and write design
The use of DDR3 (Naive) in Xilinx VIVADO (2) Read and write design
2022-08-04 11:13:00 【chylinne】
1、概述
本文基于 Xilinx VIVADO 2018.3 调用的 DDR3 IP 核(Memory Interface Generator, MIG 7 Series),针对 Xilinx 定义的 app 接口(Naive),Design the read-write module state machine,并用 Verilog 进行实现.
2、Read and write state machine design
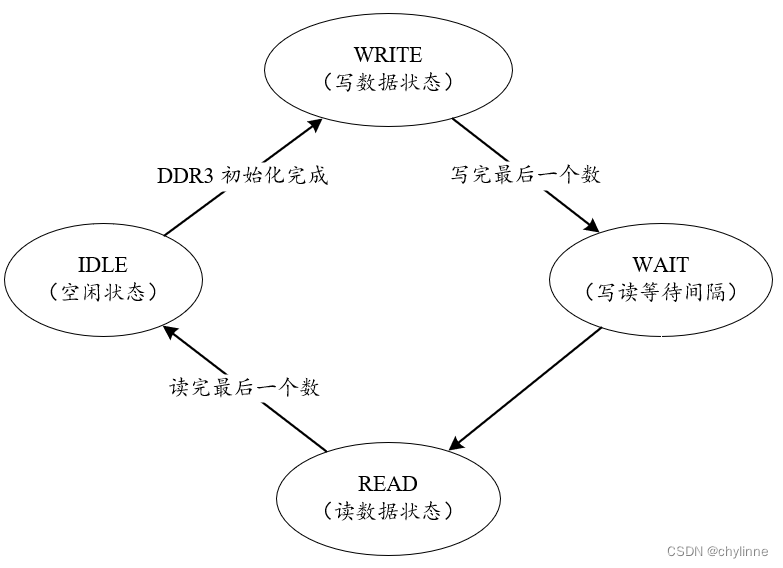
The function we designed the read-write test module is expected to achieve:
(1)Write a certain amount of data(可设置,默认 512 个)到 DDR3,Write address from 0 开始.
(2)从地址 0 Write before starting to read DDR3 的数据,Simultaneous judgment reading、Whether the write data is consistent.
(3)Cycle through the previous two steps,即写、读、写、读 ......
因此,状态机很简单,我们可以设置如下 4 个状态,Its state transition rules are shown in the figure above.
IDLE:初始状态,等 MIG IP After the core initialization is completed, it jumps to the write data state WRITE.
WRITE:写数据状态,in this state MIG IP The core writes a certain amount of data(测试为 512 个).When the last data is written,Synchronous jump to wait state WAIT.
WAIT:过渡状态,Only one clock cycle is maintained.
READ:读数据状态,In this state from MIG IP The core reads a certain amount of data(测试为 512 个).when the last data is read,Synchronously jump to the initial state IDLE.Start a new round of writing、读过程.
上一篇文章说到,在 Xilinx 定义的 app 接口(Naive)模式下,DDR3 There are three scenarios when writing data,This test uses the scenario where the write command and the write data occur on the same clock cycle,This will make coding much easier,But a little bit of efficiency is sacrificed accordingly(不会造成多大的影响).
3、代码实现
The complete read-write module test code is as follows:
module ddr3_rw # (
parameter integer WR_LEN = 512,
parameter integer DATA_WIDTH = 128, //8 times 16 equals 128 bits
parameter integer ADDR_WIDTH = 28
)(
input ui_clk,
input ui_clk_sync_rst ,
input init_calib_complete,
input app_rdy,
input app_wdf_rdy,
input app_rd_data_valid,
input [DATA_WIDTH - 1:0] app_rd_data,
output reg [ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0] app_addr,
output app_en,
output app_wdf_wren,
output app_wdf_end,
output [2:0] app_cmd,
output reg [DATA_WIDTH - 1:0] app_wdf_data,
output reg error_flag
);
localparam IDLE = 4'b0001;
localparam WRITE = 4'b0010;
localparam WAIT = 4'b0100;
localparam READ = 4'b1000;
reg [3:0] cur_state;
reg [3:0] next_state;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0] rd_addr_cnt;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0] wr_addr_cnt;
reg [ADDR_WIDTH - 1:0] rd_cnt;
wire error;
wire rst_n;
wire wr_proc;
wire wr_last;
wire rd_addr_last;
assign rst_n = ~ui_clk_sync_rst;
assign app_en = app_rdy && ((cur_state == WRITE && app_wdf_rdy) || cur_state == READ);
assign app_wdf_wren = (cur_state == WRITE) && wr_proc;
assign app_wdf_end = app_wdf_wren;
assign app_cmd = (cur_state == READ) ? 3'd1 :3'd0;
assign wr_proc = ~app_cmd && app_rdy && app_wdf_rdy;
assign wr_last = app_wdf_wren && (wr_addr_cnt == WR_LEN - 1) ;
assign rd_addr_last = (rd_addr_cnt == WR_LEN - 1) && app_rdy && app_cmd;
always @(posedge ui_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(~rst_n)
cur_state <= IDLE;
else
cur_state <= next_state;
end
always @(*)
begin
if(~rst_n)
next_state = IDLE;
else
case(cur_state)
IDLE:
if(init_calib_complete)
next_state = WRITE;
else
next_state = IDLE;
WRITE:
if(wr_last)
next_state = WAIT;
else
next_state = WRITE;
WAIT:
next_state = READ;
READ:
if(rd_addr_last)
next_state = IDLE;
else
next_state = READ;
default:;
endcase
end
always @(posedge ui_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(~rst_n)
begin
app_wdf_data <= 0;
wr_addr_cnt <= 0;
rd_addr_cnt <= 0;
app_addr <= 0;
end
else
case(cur_state)
IDLE:begin
app_wdf_data <= 0;
wr_addr_cnt <= 0;
rd_addr_cnt <= 0;
app_addr <= 0;
end
WRITE:begin
if(wr_proc)begin
app_wdf_data <= app_wdf_data + 1;
wr_addr_cnt <= wr_addr_cnt + 1;
app_addr <= app_addr + 8;
end
else begin
app_wdf_data <= app_wdf_data;
wr_addr_cnt <= wr_addr_cnt;
app_addr <= app_addr;
end
end
WAIT:begin
rd_addr_cnt <= 0;
app_addr <= 0;
end
READ:begin
if(app_rdy)begin
rd_addr_cnt <= rd_addr_cnt + 1'd1;
app_addr <= app_addr + 8;
end
else begin
rd_addr_cnt <= rd_addr_cnt;
app_addr <= app_addr;
end
end
default:begin
app_wdf_data <= 0;
wr_addr_cnt <= 0;
rd_addr_cnt <= 0;
app_addr <= 0;
end
endcase
end
assign error = (app_rd_data_valid && (rd_cnt!=app_rd_data));
always @(posedge ui_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(~rst_n)
error_flag <= 0;
else if(error)
error_flag <= 1;
end
always @(posedge ui_clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if(~rst_n)
rd_cnt <= 0;
else if(app_rd_data_valid && rd_cnt == WR_LEN - 1)
rd_cnt <= 0;
else if (app_rd_data_valid )
rd_cnt <= rd_cnt + 1;
end
endmodule边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
123
tp5+微信小程序 分片上传
Advanced transcriptome analysis and R data visualization hot registration (2022.10)
遍历Map的四种方法
*iframe*
开源一夏|ArkUI如何自定义弹窗(eTS)
iMeta | German National Cancer Center Gu Zuguang published a complex heatmap visualization method
What is the principle of thermal imaging temperature measurement?Do you know?
图文手把手教程--ESP32 MQTT对接EMQX本地服务器(VSCODE+ESP-IDF)
MySql数据库入门的基本操作
入门MySql表的增删查改
使用.NET简单实现一个Redis的高性能克隆版(二)
什么是终端特权管理
知网网站地址更换
命令模式(Command)
Mysql——》类型转换符binary
Graphical Hands-on Tutorial--ESP32 One-Key Network Configuration (Smartconfig, Airkiss)
上帝空间——全球首个基于Web3.0的艺术协议创意平台,拓宽多元艺术融合边界
MySQL 45 讲 | 10 MySQL为什么有时候会选错索引?
强烈推荐一款优秀且通用的后台管理系统