当前位置:网站首页>How MySQL works - Chapter 14
How MySQL works - Chapter 14
2022-06-24 18:13:00 【Laugh at the common people while drinking】
This chapter focuses on How to use Yes sql Statement changes The way , To improve query performance .
We call this method query rewriting .
This optimization should be based on relational algebra . Of course I forgot all my relational algebra ..
14.1
This section deals with conditional simplification .
Remove parentheses

Constant passing
a = 5 and b > a
Can be optimized to a = 5 and b > 5
Remove useless conditions
(a < 1 and b = b) or (a = 6 or 5 != 5)
Can be reduced to
a < 1 or a = 6
Expression evaluation
a = 5+1 Can be reduced to a = 6
If there are function calls , such as abs(a) > 5, Can not be simplified
HAVING and WHERE Merge
If... Does not appear in the query statement sum max This kind of aggregate function and group by Clause , The query optimizer puts having Clause and where Clauses are merged .
Constant table detection
First, let's talk about the constant table , There are two possibilities for constant tables , or There is only one record in the table , Not even a single record , or Use primary key equivalence matching or unique secondary index column equivalence matching as search criteria to query tables .
When the constant table is detected , First Execute constant table query , Then replace all the conditions related to the table in the statement with constants , Finally, the query cost of other tables is analyzed .
There is a problem , If there is no record in the table , It's a constant table . How do we know before we query ? After all, I haven't visited yet ? The answer is through statistics . and InnoDB The statistical values recorded in the table are inaccurate , So this only applies to MyISAM Equal engine .
14.2
This section deals with the elimination of external connections .
Before the start , First, we need to draw out the table to be used for a while .
CREATE TABLE t1 (
m1 int,
n1 char(1)
) Engine=InnoDB, CHARSET=utf-8;
CREATE TABLE t2 (
m2 int,
n2 char(1)
) Engine=InnoDB, CHARSET=utf-8;

The difference between internal and external connections is , If no match is found on Clause filter condition records , For external connections , The records in the driver table will be added to the result set , The driven table part uses null fill . For internal connections , The records of the drive table will be discarded .
Take this example 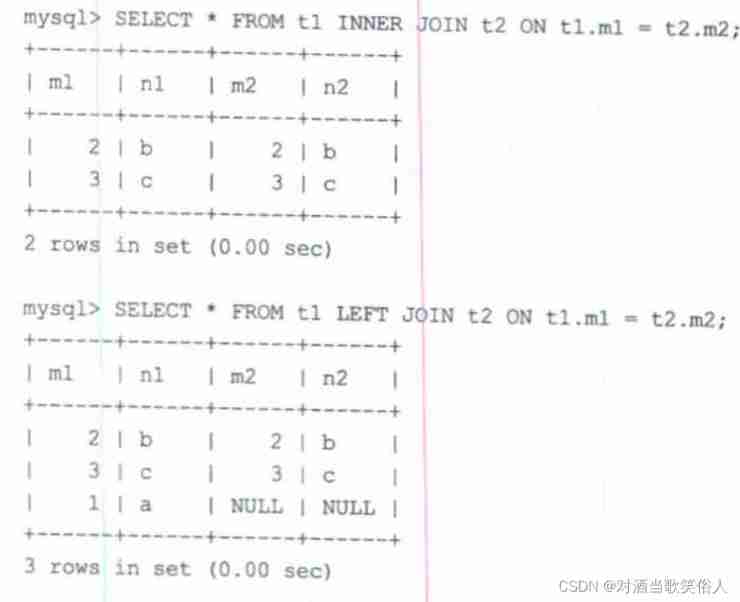
therefore , As long as we use where sentence Just kill the redundant driver table records , For example, specify... In the search criteria “ The column of the driven table is not null”, Then the extra records from the external connection will be excluded . The outer connection can be transformed into the inner connection .

Of course , There are many ways , You can also specify t2.m2 = 2, In a word, it is OK to exclude the extra records of external connections .
14.3
This section is the largest part of this chapter , Sub query optimization .
There can also be another query statement at a certain position in a query statement , The query that appears in a certain position of a query statement is called a subquery .
Subquery location
Select In the sentence

This is also called a query list
stay from In the sentence

Here, the subquery is treated as a table .as t It means to give the watch another name t.
stay where/on Clause
select * from t1 where m1 in (select m2 from t2);
stay order/group by clause
It doesn't make sense
Sub query classification
There are two sub query classification methods .
One is to query by the returned result set , The other is to partition the molecular query according to the relationship with the outer query .
Query by the returned result set area
Scalar subquery

A subquery that returns only a single value is a scalar subquery
Line sub query
A subquery that returns only one record
Column query
Query a column of data , However, this column should contain multiple data , Otherwise, it is a scalar subquery
Table sub query
Return multi row and multi column results
Segment the molecular query in relation to the outer query
- Uncorrelated subqueries : Subqueries can be run independently to produce results , Does not depend on the value of the outer query .
- Correlation subquery : The execution of subqueries depends on the outer results
An example of a related subquery
SELECT • FROM t1 WHERE m1 IN (SELECT m2 FROM t2 WHERE n1 = n2);
n1 Is the value of the outer query
Use of subqueries in Boolean expressions
Subqueries are generally used in the following scenarios in Boolean expressions :
Use =、>、<、>=、<>、!=、<=> As an operator of Boolean expression
The general syntax format is as follows
Operands The operator ( Subquery )
The operand can be a column name , Constant , Or more complex expressions . It can even be another subquery ( A subquery can only be a scalar subquery or a row subquery ).
for example :
[NOT] IN/ANY/ALL/SOME Subquery
For column subqueries and table subqueries , It contains many records , So it can't be used directly = Those operators are connected .
We use it IN/ANY/ALL/SOME To judge .ANY and SOME Express the same meaning .
- Operands [NOT] IN ( Subquery ): Simple and easy to understand , No explanation.
- ANY/SOME: Operands The operator ANY/SOME ( Subquery ) , Examples are as follows
select * from t1 where m1 > any(select m2 from t2);
- ALL: Operands The operator ALL( Subquery ): and ANY Is essentially the same , The difference is semantics
EXISTS
[NOT] EXISTS ( Subquery )
exists It is used to determine whether there are records in the result set of sub queries , Don't care what the record is .
Sub query syntax considerations
- Must be enclosed in parentheses
- stay SELECT The subquery in clause must be a scalar subquery
- You need to make sure it's scalar / Row subquery , It can be used limit 1 To limit the number of records
- If the subquery is preceded by [NOT] IN/ANY/ALL/SOME when , Subquery cannot contain limit sentence
- You cannot query a table while adding, deleting, or modifying records in the table
Execution method of subquery
Also use the previous single_table surface .
CREATE TABLE single_table (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
key1 VARCHAR(100),
key2 INT,
key3 VARCHAR(100),
key_part1 VARCHAR(100),
key_part2 VARCHAR(100),
key_part3 VARCHAR(100),
common_field VARCHAR(100),
PRIMARY KEY (id),
KEY idx_key1 (key1),
UNIQUE KEY uk_key2 (key2),
KEY idx_key3 (key3),
KEY idx_key_part(key_part1, key_part2, key_part3)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARSET=utf8;
There are 10000 A record , And there are two separate bodies , One is called s1, One is called s2.
Simple thinking
Simple thinking is the simplest and most direct thinking .
If it is an unrelated subquery , Then execute the subquery first , Then take the subquery result as the parameter of the outer query .
If it is a related subquery , First, extract a record from the result set of the outer query , Take the record to determine the parameters of the subquery , Then execute the subquery , Keep repeating .
It doesn't look like a problem . Of course , In fact, there are many optimizations .
Scalar subquery 、 How the row subquery is executed
There is no optimization in this case , Just plain thinking .
IN Sub query optimization
Materialization and materialization table
If you follow the simple idea IN Subquery ( In the case of unrelated subqueries ), You may face the following problems :
- The result set is too big , Memory explosion
- Affect outer queries , such as :
- Cannot use index effectively , You can only scan the whole table
- testing IN Is the expression TRUE Spend too much time
To optimize this seed query , The designer writes the results of the subquery to the temporary table .
The columns in the temporary table are the columns found by the sub query . Besides , Records will be de duplicated .
The de duplication operation can first reduce the space consumption .
If the subquery result set is small , You can use memory based temporary tables , And build a hash index
In this way, you can quickly judge whether a value is in the temporary table .O(1).
If the subquery result set is large , Disk based temporary tables , And establish B+ Tree index
The process of saving a result set to a temporary table is called Physicochemical . We call the temporary table that holds the result set Physicochemical table .
because B+ Trees / Hash help , Judge whether a value is very fast in the table .
Physicochemical meter transfer connection
Because the result set becomes a table , Therefore, the query statement is equivalent to the original table and materialized table Make internal connections .
We can make use of what we have said before Cost based optimization To choose a reasonable driver 、 Driven relationship . The core idea is that small tables drive large tables , Try to make the index work when connecting .
Subquery to half join
Although it's very good to transfer to physicochemical table . But the designer also thought Do you want to avoid materialization , Directly transfer the subquery to the connection Well ?
Think about this sql:
select * from s1 where key1 in (select common_field from s2 where key3 = 'a');
Is it right?
select * from s1 inner join s2 on s1.key1 = s2.common_field where s2.key3 = 'a';
It's like ?
these two items. sql It's really similar . The main problem is that the result set of subqueries is de duplicated ,common_field Value is unique .
And the inner connection , The same commo_field( Don't consider key3='a’ This matter ) value , May put s1 A record in is put into the result set many times . So these two sql Is incomplete .
So it's happening Half a connection This concept : about s1 A record in the table , We only care about s2 Whether there are matching records in the table , It doesn't care how many records match . The final result set is reserved for s1 part .
If you don't understand what a semi connection is , Just understand one thing , We must find a way to give s2 De duplication of values in
Semi - join itself is just a concept , The outside is useless .MySQL How to realize this semi connection ?
Table pullout
Because the core idea is to s2 De duplication of records in , Therefore, when all the columns of the sub query have primary keys / When the index is unique , Subqueries can be eliminated directly , Convert to inner connection ( This is the example above ).
The unique index ensures that the result is de duplicated .
Duplicate Weedout
We set up a system about s1 Temporary table of primary key . In the temporary table s1 The primary key should also be indexed to maintain uniqueness .
Every time we want to add a record to the result set , all First, check whether the primary key value corresponding to this record exists in the temporary table . If the primary key exists in the temporary table , I don 't want to insert . Otherwise, insert the primary key value into the temporary table , Add the record to the result set .
In a word , It is to use the primary key found by the outer query to remove duplicates .
LooseScan
Remember the core idea duplicate removal . If our subquery has indexes on the columns to be queried , Then we can take those trains ( The direct index covers , It must be fast ) The index of . Because the index itself can help sort , So for each value , Just take the first record , Use the first record to match the record of the driven table .
Here's an example :
select * from s1
where key3 in (select key1 from s2 where key1 > 'a' and key1 < 'b');
s2 There are key1 The index of .
That is to say, only the first record is accessed to remove the duplicate .
Semi connected physicochemical
It means that if it is inconvenient to remove the weight of the half connection , If not, materialize it directly ·· The physicochemical table itself is de duplicated .
First Match
The whole is based on simple ideas ( The related sub query part ) go . Take one record at a time to match the records in the result set of the sub query . The key point is that if the match is successful , Then directly add to the result set , This record will no longer match .
Use the analogy of two-layer cycle , If you succeed , The outer loop is direct continue.
In fact, that is Loose Scan In turn, . Use the outer table as the driving table .
A subquery cannot be converted to a semi join
In some cases , Subqueries cannot become semi - join .
For example, the subquery and other conditions are separated by OR Connected to 、 Outside the subquery is NOT IN Instead of IN、 The subquery contains GROUP BY/ HAVING / Aggregation function 、 The subquery contains union Etc., etc. .
For the untranslatable , You can use the following methods
Physicochemical : Note that the materialized table here cannot be connected to the table of the outer loop . Otherwise, it is half connected ······ It's just that after the materialization, the judgment is very fast , After all, you can have hash indexes .
hold IN Switch to EXISTS

This rule is quite general , Except for some special cases , For example, an outer expression or an inner expression involves NULL When . Because it does not contain IS NULL In case of operation , If an operand is NULL, The result of the expression is also NULL. and EXISTS The result must be TRUE/FALSE, This sum NULL Dissimilarity .fortunately , Usually subqueries are in where or on in ,where or on Indistinguishes NULL and FALSE.
So why do you sometimes put in convert to EXISTS Well ? Because the conversion is more likely to use the index .
For example 
convert to 
stay 5.5 Version before , In fact, there is no semi connection and materialization , It's all converted into EXISTS, This makes better use of the index .
ANY/ALL Sub query optimization
Unrelated subqueries can put ANY or ALL Eliminate , Become a function call .
[NOT] EXISTS Execution of subquery
In fact, it is a simple method
Optimization of derived tables

The subquery in this bracket is a derived table .
For derived tables , Can also be optimized . The most intuitive thing is materialization , Not much said .
Be careful , Materialization is inert . Like this sql, First from s2 Take a record , The derived table is generated only when matching . If s2 Not in it key2=1 The record of , It doesn't generate .
Another possibility is to eliminate derived tables directly .
select * from (select * from s1 where key1 = 'a') as derived_s1;
select * from s1 where key1 = a
The upper and lower statements are equivalent , So the derived table is really unnecessary .
Another example is the above 
This statement , Derived tables can be merged with outer queries .
Of course , It is not always possible to merge derived tables with outer queries . For example, there are various functions 、group by ah 、having ah 、limit ah 、union ah 、limit ah 、distinct ah 、 The subquery is nested with a subquery, and so on …
边栏推荐
- Number of occurrences of numbers in the array (medium difficulty)
- How can an enterprise successfully complete cloud migration?
- Open up the construction of enterprise digital procurement, and establish a new and efficient service mode for raw material enterprises
- Comparison of similarities and differences between easynvr video edge computing gateway and easynvr software versions
- Noi Mathematics: solution of quadratic congruence equation
- Provide secure and convenient Oracle solutions for smart contract developers
- The country has made a move! Launch network security review on HowNet
- Conditional competition overview
- 03. Tencent cloud IOT device side learning -- overview of mqtt control package
- Selection (033) - what is the output of the following code?
猜你喜欢
Mariana Trench, Facebook's open source code analysis tool
![[untitled]](/img/ab/066923f1aa1e8dd8dcc572cb60a25d.jpg)
[untitled]
An analysis of the comments on the TV series Douban by procedural apes
Cloud service selection of enterprises: comparative analysis of SaaS, PAAS and IAAs

On software requirement analysis

Digital transformation informatization data planning and technology planning
![[NLP] 3 papers on how Stanford team builds a better chat AI](/img/f1/1c2ff31a728152395618800600df45.jpg)
[NLP] 3 papers on how Stanford team builds a better chat AI
About swagger

How to decompile APK files

How to start cloud native application development
随机推荐
Millions of dollars worth of NFT were stolen in the attack, and Google issued an emergency warning to 3.2 billion users worldwide | February 21 global network security hotspot
Go collaboration and pipeline to realize asynchronous batch consumption scheduling task
1. Leveldb getting started
Business leaders compete for CIO roles
股票网上开户安全吗?应该怎么办理?
Application service access configuration parameters
2. Leveldb design principle -- LSM
Three years of bug free, tips for improving code quality
[MySQL practice] binlog, a sharp tool for problem analysis
Litamin: SLAM Based on geometric approximation of normal distribution
Error reported after NPM I
Project Management Guide: tips, strategies and specific practices
腾讯云荣获“可信云技术最佳实践-虚拟化”
How does the video platform import the old database into the new database?
How to use rdbtools to analyze redis large keys
Go language GC implementation principle and source code analysis
Ten excellent business process automation tools for small businesses
[North Asia data recovery]_ mdb_ catalog. Mongodb database data recovery case in case of WT file corruption
Eight recommended microservice testing tools
Three indicators to help you measure the effectiveness of digital transformation

