当前位置:网站首页>Summary of four parameter adjustment methods for machine learning
Summary of four parameter adjustment methods for machine learning
2022-06-25 15:14:00 【m0_ sixty-one million eight hundred and ninety-nine thousand on】
Introduce
Wikipedia says ,“Hyperparameter optimization or tuning Is to select the best set of learning algorithms hyperparameters The problem of ”.
This article is reproduced in Collection | Summary of four parameter adjustment methods for machine learning
ML One of the most difficult parts of the workflow is to find the best hyperparameters for the model .ML The performance of the model is directly related to the hyperparameters . The better the parameters are tuned , The better the model is . Tuning metaparameters can be very tedious and difficult , It's more of an art than a science .
Hyperparameters
Hyperparameters are parameters used to control the behavior of algorithms when modeling . These parameters cannot be obtained from routine training . Before training the model , You need to assign values to them .

A simple list of hyperparameters
Catalog
1. Traditional manual search
In the traditional tuning process , We manually check the set of random hyperparameters by training algorithms , And choose the best parameter set that meets our goal .
Let's look at the code :
#importing required libraries
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold , cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
wine = load_wine()
X = wine.data
y = wine.target
#splitting the data into train and test set
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.3,random_state = 14)
#declaring parameters grid
k_value = list(range(2,11))
algorithm = ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute']
scores = []
best_comb = []
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5)
#hyperparameter tunning
for algo in algorithm:
for k in k_value:
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k,algorithm=algo)
results = cross_val_score(knn,X_train,y_train,cv = kfold)
print(f'Score:{round(results.mean(),4)} with algo = {algo} , K = {k}')
scores.append(results.mean())
best_comb.append((k,algo))
best_param = best_comb[scores.index(max(scores))]
print(f'\nThe Best Score : {max(scores)}')
print(f"['algorithm': {best_param[1]} ,'n_neighbors': {best_param[0]}]")
shortcoming :
There is no way to ensure the best combination of parameters .
It's a process of trial and error , therefore , It's very time consuming .
2. The grid search
Grid search is a basic super parameter optimization technology . It's similar to manual tuning , Build a model for each permutation of all given hyperparametric values specified in the grid , Evaluate and select the best model . Consider the example above , Two of these parameters k_value =[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] & algorithm =[ auto , ball_tree , kd_tree ,brute ], In this case , In total, it builds 9*4 = 36 Different models .

Let's see sklearn Of GridSearchCV How it works :
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
grid = GridSearchCV(knn,grid_param,cv = 5)
grid.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
grid.best_params_
#Score achieved with best parameter combination
grid.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
grid.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
grid.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
shortcoming :
Because it tries every combination of the hyperparameters , According to the score of cross validation, the best combination was selected , This makes GridsearchCV Very slow .
3. Random search
The motivation for using random search instead of grid search is , in many instances , All the hyperparameters may not be equally important . Random search random selection of parameter combinations from a hyperparametric space , Parameters from n_iter Given a fixed number of iterations, choose . Experimental proof , The result of random search is better than that of grid search .
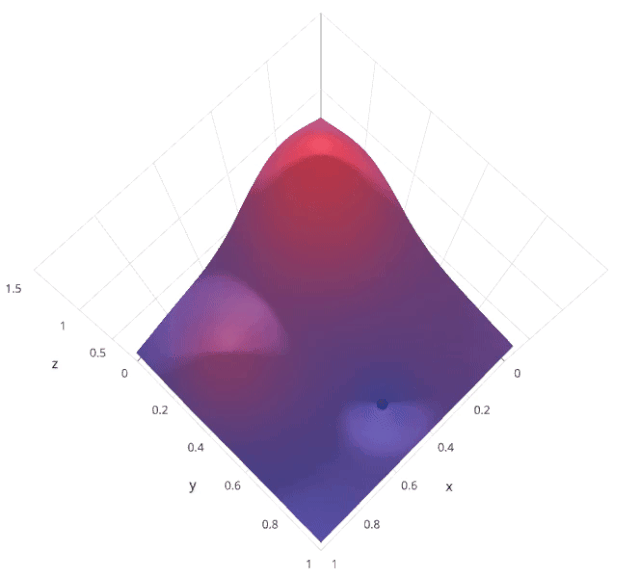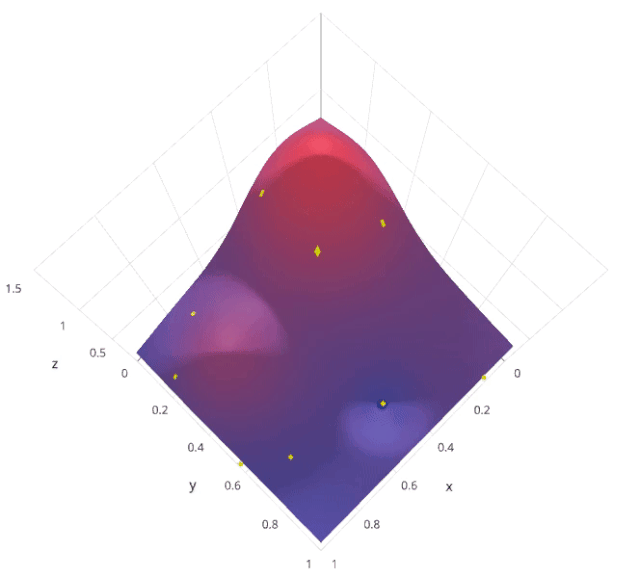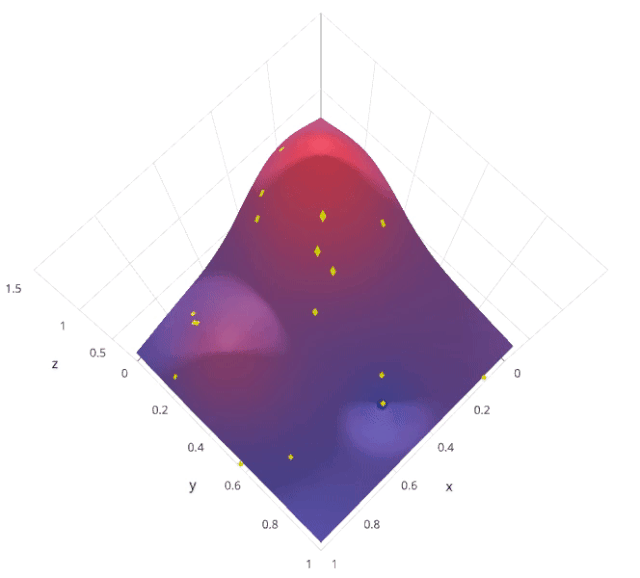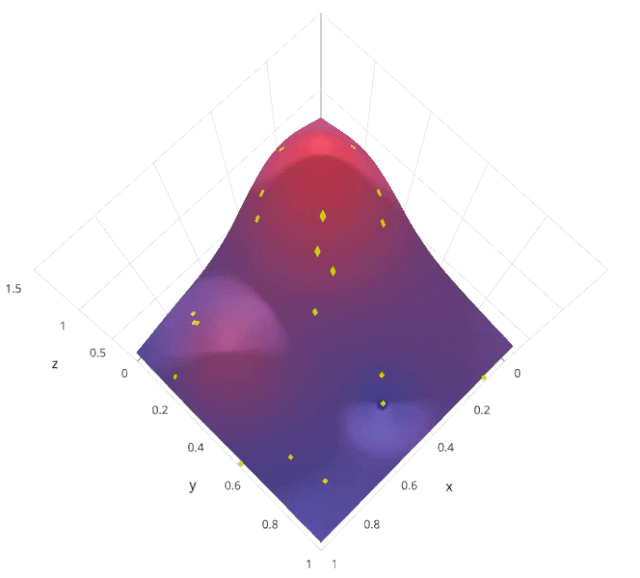
Let's understand sklearn Of RandomizedSearchCV How it works :
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
rand_ser = RandomizedSearchCV(knn,grid_param,n_iter=10)
rand_ser.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
rand_ser.best_params_
#score achieved with best parameter combination
rand_ser.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
rand_ser.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
rand_ser.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
shortcoming :
The problem with random search is that it cannot guarantee the best combination of parameters .
4. Bayesian search
Bayesian Optimization belongs to a class of optimization algorithms , It's called sequential model-based optimization (SMBO) Algorithm . These algorithms use previous pairs of losses f The observation of , To determine the next ( The optimal ) Spot sampling f. The algorithm can be summarized as follows .
Use the points previously evaluated X 1:n, Calculate the loss f A posteriori expectation of .
At a new point X Sampling loss of f, To maximize f Some of the ways to expect . This method specifies f Which areas of the domain are most suitable for sampling .
Repeat these steps , Until some convergence criteria are satisfied .

Let's use it scikit- optimization Of BayesSearchCV To understand the .
Installation: pip install scikit-optimize
from skopt import BayesSearchCV
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# parameter ranges are specified by one of below
from skopt.space import Real, Categorical, Integer
knn = KNeighborsClassifier()
#defining hyper-parameter grid
grid_param = { 'n_neighbors' : list(range(2,11)) ,
'algorithm' : ['auto','ball_tree','kd_tree','brute'] }
#initializing Bayesian Search
Bayes = BayesSearchCV(knn , grid_param , n_iter=30 , random_state=14)
Bayes.fit(X_train,y_train)
#best parameter combination
Bayes.best_params_
#score achieved with best parameter combination
Bayes.best_score_
#all combinations of hyperparameters
Bayes.cv_results_['params']
#average scores of cross-validation
Bayes.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
Another similar library for Bayesian search is bayesian-optimization.
Installation: pip install bayesian-optimization
shortcoming :
To be in 2 Dimension or 3 It takes more than ten samples to get a good surrogate surface in the search space of dimension , Increasing the dimension of the search space requires more samples .
summary
There is always a trade-off between the guarantee of determining the best combination of parameters and the calculation time . If the hyperparametric space ( Number of super parameters ) A very large , Then a random search is used to find a potential combination of the parameters , Then use the grid search in that area ( Potential combinations of hyperparameters ) Select the best feature .
边栏推荐
- Core mode and immediate rendering mode of OpenGL
- Power automatic test system nsat-8000, accurate, high-speed and reliable power test equipment
- If multiple signals point to the same slot function, you want to know which signal is triggered.
- QT loading third-party library basic operation
- Qmake uses toplevel or topbuilddir
- Explanation of dev/mapper
- JS select all exercise
- 55 specific ways to improve program design (2)
- From 408 to independent proposition, 211 to postgraduate entrance examination of Guizhou University
- 15 -- k points closest to the origin
猜你喜欢

Open a restaurant

Arithmetic operations and expressions
Solution of push code failure in idea

GDB debugging
Js- get the mouse coordinates and follow them

Time stamp calculation and audio-visual synchronization of TS stream combined video by ffmpeg protocol concat

搭建极简GB28181 网守和网关服务器,建立AI推理和3d服务场景,然后开源代码(一)

Gif动画怎么在线制作?快试试这款gif在线制作工具

Design and implementation of thread pool

QT set process startup and self startup
随机推荐
Review of arrays and pointers triggered by a topic
Custom structure type
多张动图怎样合成一张gif?仅需三步快速生成gif动画图片
3. Sequential structure multiple choice questions
Character encoding minutes
System Verilog - thread
Basic knowledge of pointer
What moment makes you think there is a bug in the world?
Brain tree (I)
电源自动测试系统NSAT-8000,精准高速可靠的电源测试设备
Time stamp calculation and audio-visual synchronization of TS stream combined video by ffmpeg protocol concat
Qcodeeditor - QT based code editor
Yolov3 spp Darknet version to caffemodel and then to OM model
One question per day, a classic simulation question
Function of getinstance() method
搭建极简GB28181 网守和网关服务器,建立AI推理和3d服务场景,然后开源代码(一)
Std:: vector minutes
Mining procedure processing
New title of PTA
Arithmetic operations and expressions