当前位置:网站首页>MySQL create and manage tables
MySQL create and manage tables
2022-06-23 14:51:00 【Chen Yixin】
Catalog
1.1 A procedure for storing data
2. Create and manage databases
2.2.1 View all current databases
2.2.3 View the database currently in use
2.2.4 View all tables under the specified library
2.2.5 View database creation information
2.3.1 Change the database character set
1. Basic knowledge of
1.1 A procedure for storing data
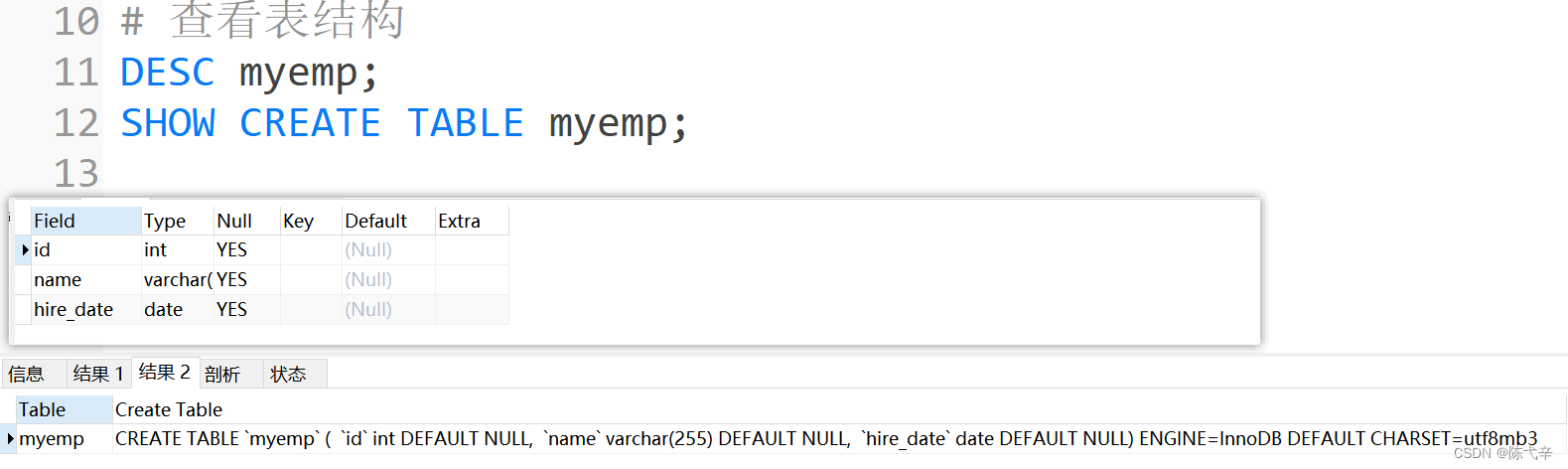
Storing data is the first step in processing data . Only by storing the data correctly , We can carry out effective processing and Analysis . otherwise , It can only be a mess , Do not know how to start .that , How can we put all kinds of business-related 、 Complex data , Orderly 、 Store it efficiently ? stay MySQL in , A complete data stored procedure has a total of 4 Step , Create a database 、 Acknowledgement field 、 Create data table 、 insert data .
We need to create a database first , Instead of creating a data table directly ?Because from the level of system architecture ,MySQL The order of database system from large to small is database server 、 database 、 Data sheet 、 Data table Rows and columns .MySQL The database server was previously installed . therefore , Let's start by creating a database .1.2 Identifier naming rules
1. Database name 、 The table name must not exceed 30 Characters , Variable names are limited to 29 individual2. Must contain only A–Z, a–z, 0–9, _ common 63 Characters3. Database name 、 Table name 、 Do not include spaces in object names such as field names4. The same MySQL In software , The database cannot have the same name ; In the same library , A watch cannot have the same name ; In the same table , The field cannot have the same name5. You must ensure that your field has no and reserved words 、 Database systems or common methods conflict . If you insist on using , Please be there. SQL Use in statement `( mark of emphasis ) Lead up6. Keep field names and types consistent : When naming fields and specifying data types for them, be sure to ensure consistency , If the data type is an integer in a table , Then don't turn into character in another table1.3 MySQL Data types in
type
Examples of types
Integer types
TINYINT、SMALLINT、MEDIUMINT、INT( or INTEGER)、BIGINT
Floating point type
FLOAT、DOUBLE
Fixed point number type
DECIMAL
A type of
BIT
Date time type
YEAR、TIME、DATE、DATETIME、TIMESTAMP
Text string type
CHAR、VARCHAR、TINYTEXT、TEXT、MEDIUMTEXT、LONGTEXT
Enumeration type
ENUM
Collection types
SET
Binary string type
BINARY、VARBINARY、TINYBLOB、BLOB、MEDIUMBLOB、LONGBLOB
JSON type
JSON object 、JSON Array
Spatial data types
Single value :GEOMETRY、POINT、LINESTRING、POLYGON;
aggregate :MULTIPOINT、MULTILINESTRING、MULTIPOLYGON、GEOMETRYCOLLECTION
among , Several common types are introduced as follows :
data type
describe
INT
from -2^31 To 2^31-1 The integer data of . The storage size is 4 Bytes
CHAR(size)
Fixed length character data . If not specified , The default is 1 Characters , Maximum length 255
VARCHAR(size)
Variable length character data , Save according to the actual length of the string , Length... Must be specified
FLOAT(M,D)
Single precision , Occupy 4 Bytes ,M= Integer bit + Decimal places ,D= Decimal places . D<=M<=255,0<=D<=30, Default M+D<=6
DOUBLE(M,D)
Double precision , Occupy 8 Bytes ,D<=M<=255,0<=D<=30, Default M+D<=15
DECIMAL(M,D)
High precision decimal , Occupy M+2 Bytes ,D<=M<=65,0<=D<=30, The maximum value range is related to DOUBLE identical .
DATE
Date data , Format 'YYYY-MM-DD'
BLOB
Long text data in binary form , Up to 4G
TEXT
Long text data , Up to 4G
2. Create and manage databases
2.1 Create database
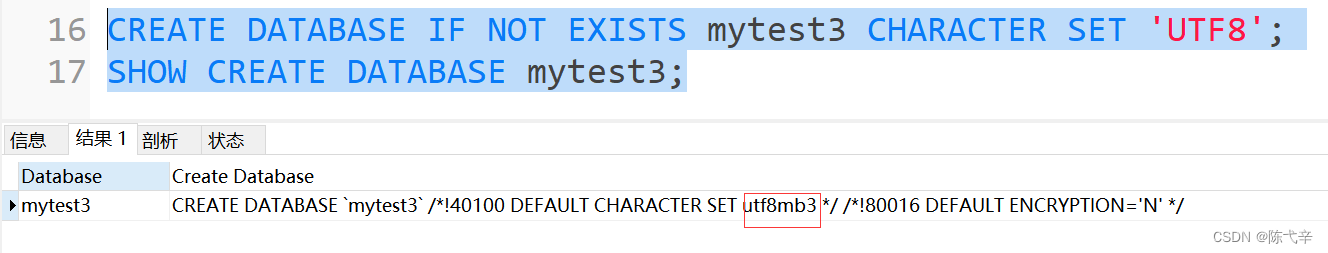
The way 1: Create databaseCREATE DATABASE Database name ;The way 2: Create database and specify character setCREATE DATABASE Database name CHARACTER SET Character set ;
The way 3: Determine whether the database already exists , If it does not exist, create the database ( recommend )CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Database name ;
2.2 Using a database
2.2.1 View all current databases
grammar :
SHOW DATABASES; # There is one S, Representing multiple databases2.2.2 Use / Switch database
grammar :
USE Database name ;
2.2.3 View the database currently in use
grammar :
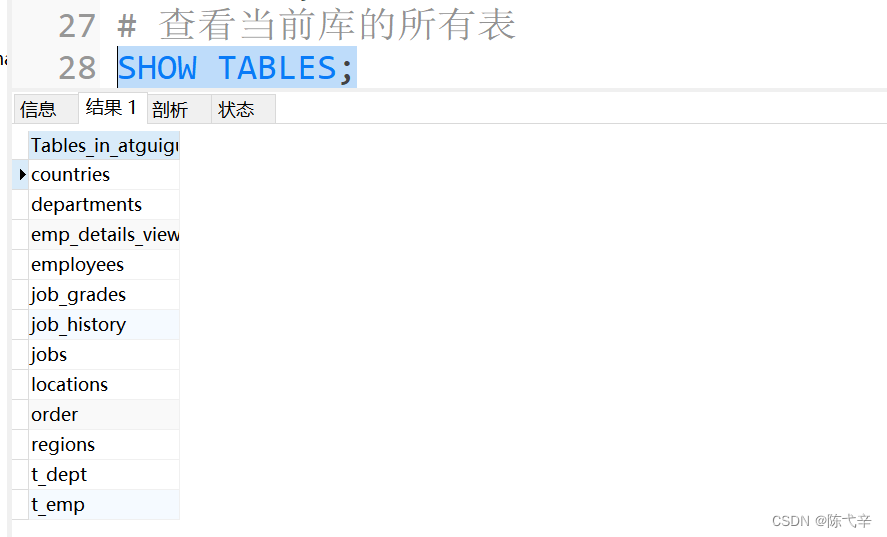
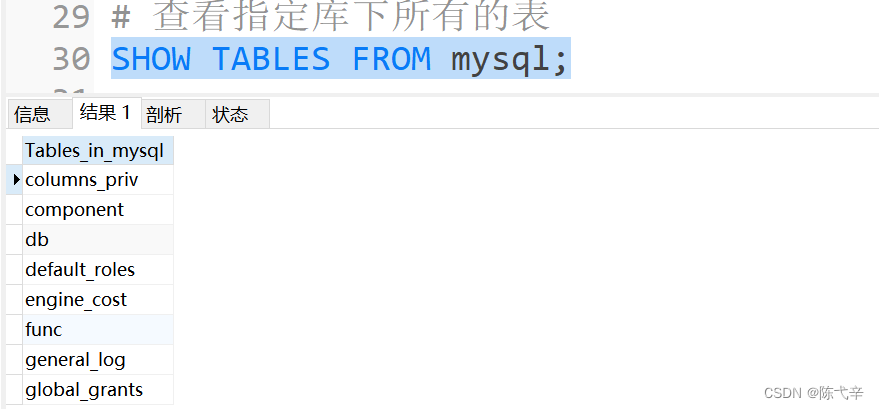
SELECT DATABASE(); # One used mysql Global functions in2.2.4 View the table under the specified library
grammar :
SHOW TABLES 【FROM Database name 】; # see 【 Specify... In the database 】 All tables
SHOW TABLE Table name 【FROM Database name 】;# see 【 Specify... In the database 】 Designated table
2.2.5 View database creation information
grammar :
SHOW CREATE DATABASE Database name ;perhaps :SHOW CREATE DATABASE Database name \G2.3 modify the database
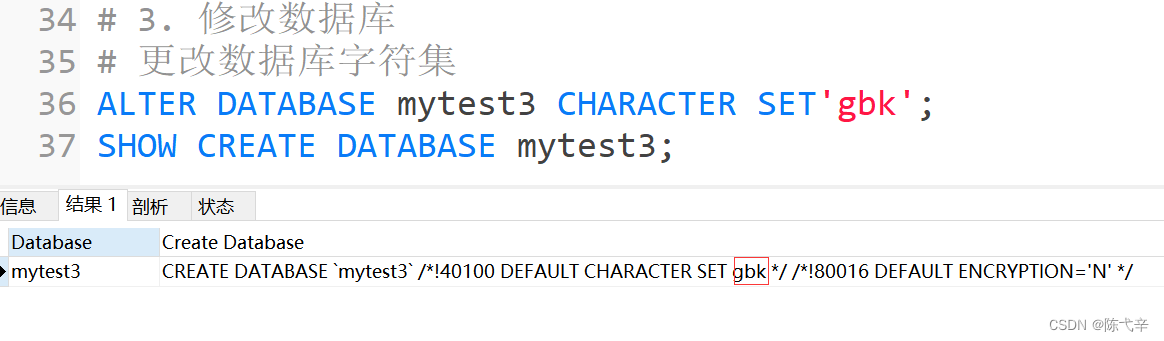
2.3.1 Change the database character set
grammar :
ALTER DATABASE Database name CHARACTER SET Character set ; # such as :gbk、utf8 etc.Be careful :DATABASE You can't change your name . Some visualization tools can be renamed , It's building a new library , Copy all tables to the new library , Delete the old library again .2.4 Delete database
The way 1: Delete the specified database , If the database does not exist , False report .DROP DATABASE Database name ;The way 2: Delete the specified database ( recommend )DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS Database name , If the database does not exist , It ends silently , No mistake. .3. Create table
3.1 How it was created 1
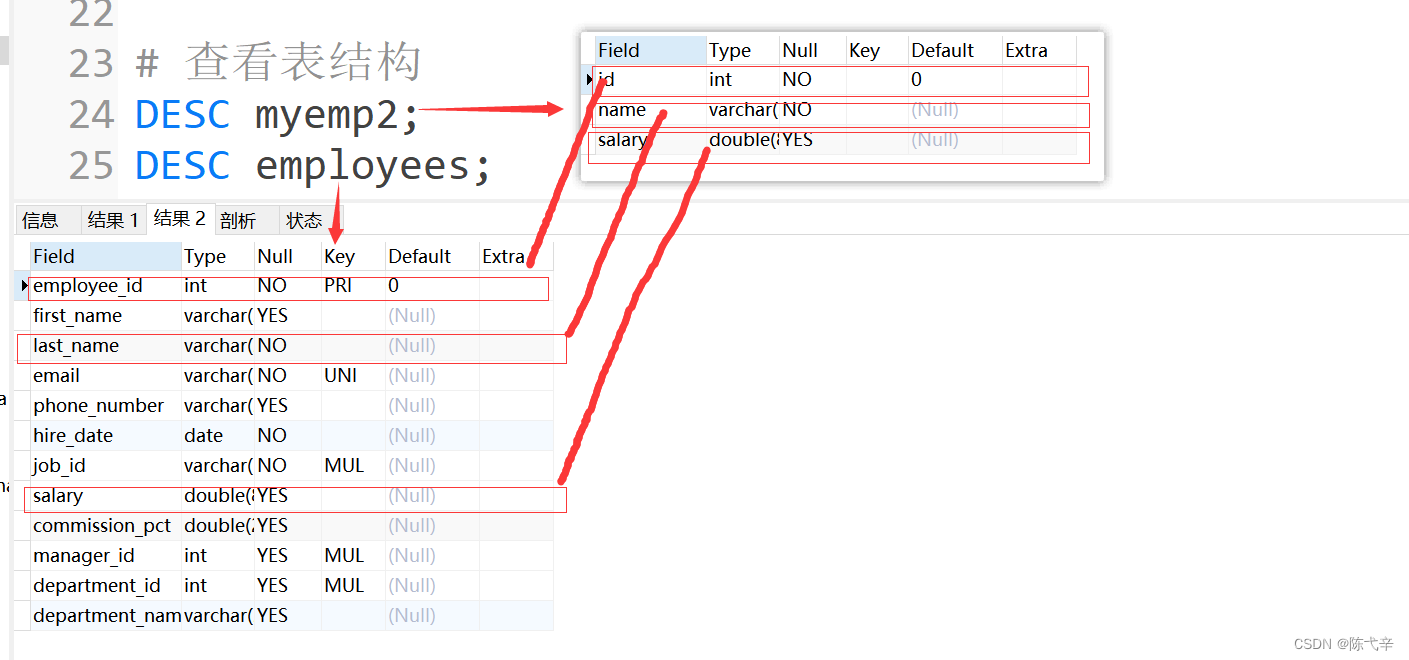
Must have :1.CREATE TABLE jurisdiction2. Storage spaceGrammar format :CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] Table name (Field 1, data type [ constraint condition ] [ The default value is ],Field 2, data type [ constraint condition ] [ The default value is ],Field 3, data type [ constraint condition ] [ The default value is ],……[ Table constraints ]);Combined with the IF NOT EXISTS keyword , said : If the data table to be created does not exist in the current database , Then create a data table ;If the data table to be created already exists in the current database , The table creation statement is ignored , No longer create data table .Must specify :1. Table name2. Name ( Or field name ), data type , lengthOptional designation :1. constraint condition2. The default value is
notes :1.MySQL When executing the table creation statement , take id The type of the field is set to int(11), there 11 It's actually int Type specifies the display width , The default display width is 11. You can also specify the display width of data when creating a data table .2. stay MySQL 8.x In the version , No longer recommended as INT Type specifies the display length , This syntax may be removed in future versions .
3.2 How it was created 2
Use AS subquery Options , Combine creating tables with inserting dataThe specified column should correspond to the column in the subquery one by oneDefine columns by column names and default values
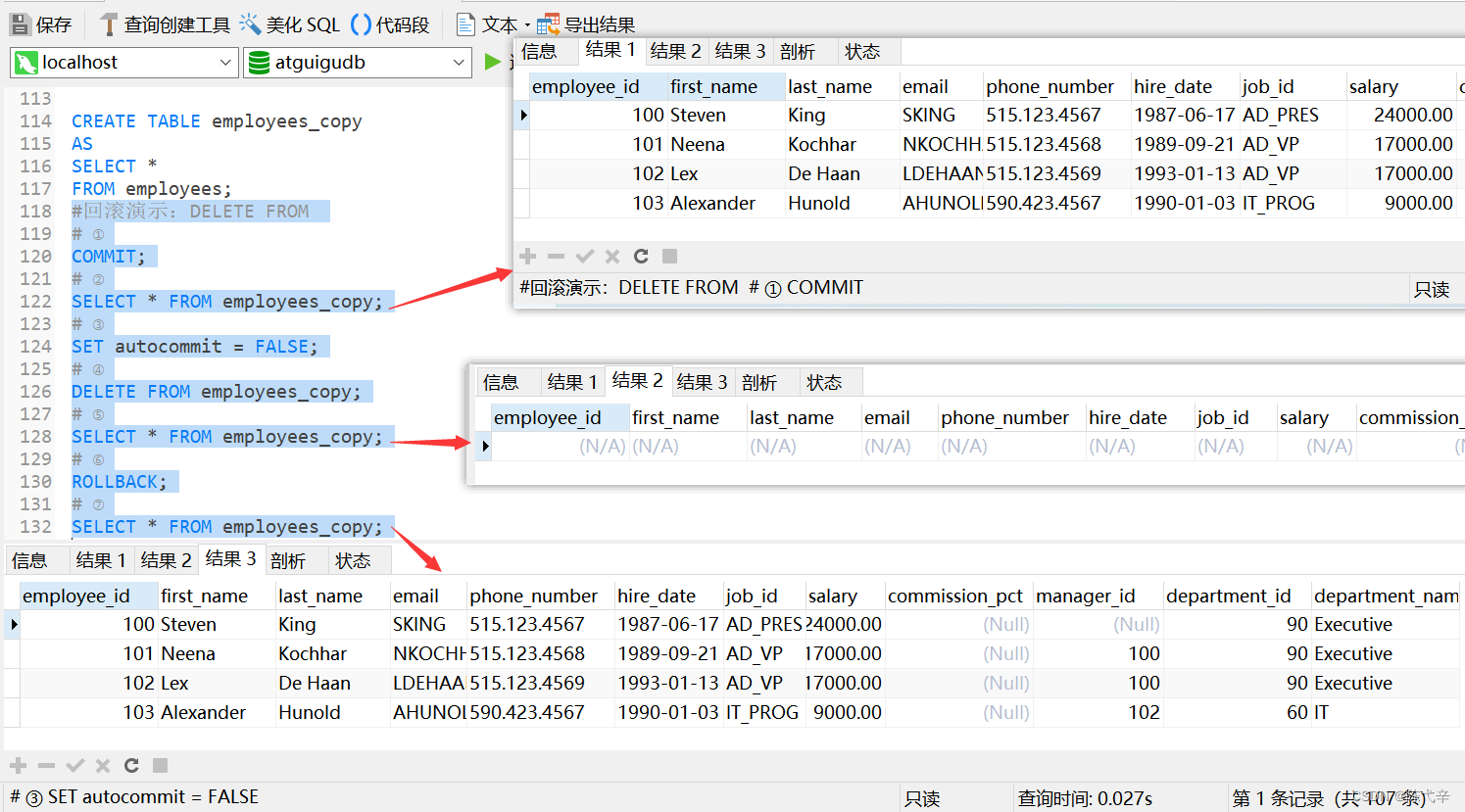
3.2.1 practice 1: Create a table emplooyees_copy, Realize to employees Replication of tables , Including data
3.2.2 practice 2: Create a table emplooyees_blank, Realize to employees Replication of tables , Excluding data
4. Modify table
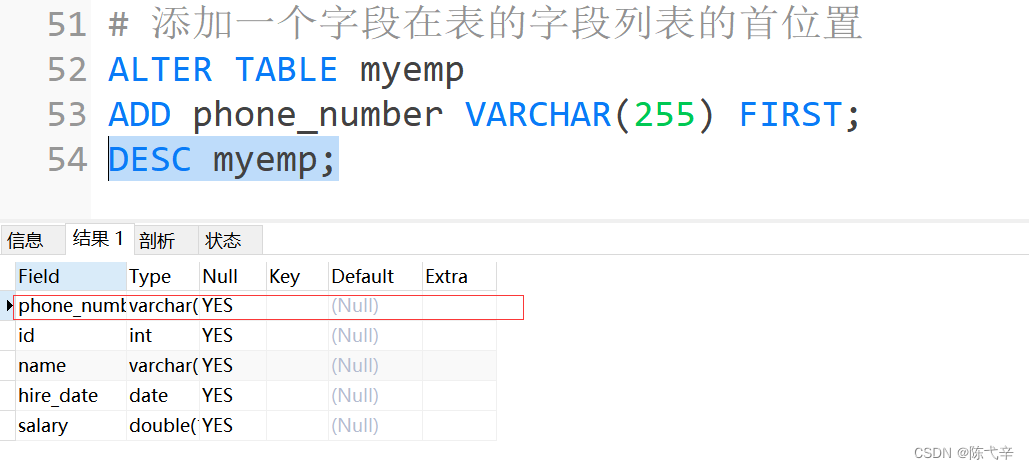
Modifying a table means modifying the structure of a data table that already exists in the database .Use ALTER TABLE Statement can realize :1. Add columns to existing tables2. Modify columns in existing tables3. Delete columns from existing tables4. Rename columns in an existing table4.1 Append a column
The syntax is as follows :ALTER TABLE Table name ADD 【COLUMN】 Field name Field type 【FIRST|AFTER Field name 】;
4.2 Modify a column
You can modify the data type , length 、 Default values and locationsModify field data type 、 length 、 The default value is 、 The syntax format of the location is as follows :ALTER TABLE Table nameMODIFY 【COLUMN】 Field name 1 Field type 【DEFAULT The default value is 】【FIRST|AFTER Field name 2】;
4.3 Rename a column
Use CHANGE old_column new_column dataType Clause renames the column .The syntax is as follows :ALTER TABLE Table name CHANGE 【column】 Name New column names New data types ;
4.4 Delete a column
The syntax format of deleting a field in the table is as follows :ALTER TABLE Table name DROP 【COLUMN】 Field name ;
5. rename table
Mode one : Use RENAMEGrammar format :
REMANE TABLE Table name
TO The new name of the table ;
Mode two : Use ALTER
Grammar format :
ALTER TABLE Table name
RENAME 【TO】 The new name of the table ;
6. Delete table
stay MySQL in , When a data sheet No association with any other data table when , Can be Delete the current data table directly .Data and structures are deletedAll running related transactions are committedAll relevant indexes are deletedDROP TABLE Statement cannot be rolled back ( That is, it cannot be undone . If you delete it, you can't find it back , Unless there is a backup )Grammar format :DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] Data sheet 1 [, Data sheet 2, …, Data sheet n];
IF EXISTS Means : If the corresponding data table exists in the current database , Delete the data table ; If there is no... In the current database In the corresponding data sheet , Delete statement is ignored , No longer delete the data table .7. Clear the table
7.1 TRUNCATE TABLE sentence
TRUNCATE TABLE language sentence :1. Delete all data in the table , Keep the table structure2. Free the storage space of the tableGrammar format :TRUNCATE TABLE Table name ;7.2 DELETE FROM sentence :
Grammar format :DELETE FROM Table name ;( You can add filter conditions , It means deleting some data )7.3 contrast TRUNCATE TABLE And DELETE FROM
7.3.1 contrast TRUNCATE TABLE And DELETE FROM
The same thing : All data in the table can be deleted , While preserving the data structureDifference :TRUNCATE TABLE: Once you do this , Delete all table data . meanwhile , Data cannot be rolled backDELETE FROM: Once you do this , All table data can be deleted ( No where). meanwhile , dataRollback is possibleexplain :1.TRUNCATE TABLE Than DELETE Fast , It also uses less system and transaction log resources , but TRUNCATE nothing Transaction without triggering TRIGGER, Possible accidents , so This statement is not recommended in development code .2.TRUNCATE TABLE In function and without WHERE Clause DELETE Same statement .7.3.2 DCL Medium COMMIT and ROLLBACK expand
COMMIT : Submit data . Once you do this , The data is permanently stored in the database , Means that the data is notYou can roll back .ROLLBACK : Once you do this , Data rollback can be realized . Roll back to the last COMMIT after .7.3.3 DDL And DML explain
1.DDL Once the operation is performed , You can't roll back . Instructions SET autocommit = FALSE Yes DDL Operation failure ( Because at the end of execution DDL After the operation , This must be done COMMIT. And this COMMIT The operation is not affected bySET autocommit = FALSE Affected )2.DML Default operation of , Once executed , It cannot be rolled back . however , If in execution DML Before , Yes SET autocommit = FALSE , The rollback can be realized by executing the operation .7.3.4 TRUNCATE TABLE And DELETE FROM Roll back the demo
边栏推荐
- 5分钟快速上线Web应用和API(Vercel)
- [in depth understanding of tcapulusdb technology] tcapulusdb business data backup
- Technology creates value and teaches you how to collect wool
- Penetration test - right raising topic
- 2022 college entrance examination quarterly essay winners announced
- 巴比特 | 元宇宙每日必读:Meta、微软等科技巨头成立元宇宙标准论坛组织,华为、阿里加入,英伟达高管称欢迎来自加密世界的参与者...
- [digital signal processing] linear time invariant system LTI (judge whether a system is a "non time variant" system | case 2)
- AI intelligent robot saves us time and effort
- 建议自查!MySQL驱动Bug引发的事务不回滚问题,也许你正面临该风险!
- 【深入理解TcaplusDB技术】TcaplusDB导入数据
猜你喜欢

阿里 Seata 新版本终于解决了 TCC 模式的幂等、悬挂和空回滚问题

【DataHub】LinkedIn DataHub学习笔记

分布式数据库使用逻辑卷管理存储之扩容

Ie mode of selenium edge

raspberry pi安装 wiringpi

Babbitt | metauniverse daily must read: meta, Microsoft and other technology giants set up the metauniverse Standards Forum. Huawei and Alibaba joined. NVIDIA executives said that they welcomed partic

2021-05-22

一款自动生成单元测试的 IDEA 插件

乐高宣布涨价,炒家更嗨皮了

Instructions for laravel8 Beanstalk
随机推荐
[in depth understanding of tcapulusdb technology] tcapulusdb construction data
MySQL高级语句二
等保備案是什麼意思?應該去哪裏辦理備案?
渗透测试-提权专题
Selenium Edge的IE模式
2021-06-07
2021-05-08
Penetration test - right raising topic
Teach you how to build Tencent cloud server (explanation with pictures and pictures)
Illustration of ONEFLOW's learning rate adjustment strategy
LEGO announces price increase, speculators are more excited
ai智能机器人让我们工作省时省力
Win10 64位系统如何安装SQL server2008r2的DTS组件?
Test article
2021-04-15
MySQL高级语句一
Error 1079 when starting a service: the account of this service is different from that of other services running on the same process
[digital signal processing] linear time invariant system LTI (judge whether a system is a "non time variant" system | case 2)
2021-05-08
Technology creates value and teaches you how to collect wool