当前位置:网站首页>[JS] - [array, stack, queue, linked list basics] - Notes
[JS] - [array, stack, queue, linked list basics] - Notes
2022-06-24 23:17:00 【Interesting learning】
【js】-【 Array 】- note
Statement : This note is based on the Nuggets brochure , If you want to learn more details , Please move https://juejin.cn/book/6844733800300150797
1 Array
1.1 One dimensional creation
const arr = []
const arr = new Array()
Specify the length
const arr = new Array(7)
Create a length determination 、 At the same time, the value of each element is also determined by the array
const arr = (new Array(7)).fill(1)
1.2 One dimensional traversal
forloop
// Gets the length of the array
const len = arr.length
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
// Output the element value of the array , Output the current index
console.log(arr[i], i)
}
forEachMethod
arr.forEach((item, index)=> {
// Output the element value of the array , Output the current index
console.log(item, index)
})
mapMethod
On the basis of traversal “ Reprocessing ”
const newArr = arr.map((item, index)=> {
// Output the element value of the array , Output the current index
console.log(item, index)
// Add... To the current element value 1
return item+1
})
map To return a new array , The value of each element in the array is based on its existing element value +1 After the results of the
1.3 Two dimensional array
Initialize a two-dimensional array
const len = arr.length
for(let i=0;i<len;i++) {
// Initialize each pit of the array as an array
arr[i] = []
}
1.4 Two dimensional array traversal
# Cache the length of the external array
const outerLen = arr.length
for(let i=0;i<outerLen;i++) {
# The length of the internal array of the cache
const innerLen = arr[i].length
for(let j=0;j<innerLen;j++) {
# The value of the output array , The index of the output array `const arr = [1,2]
arr.push(3) // [1,2,3]`
console.log(arr[i][j],i,j)
}
}
2 Array addition and deletion methods
2.1 Add element to array
unshiftMethod - Add elements to the head of the array
const arr = [1,2]
arr.unshift(0) # [0,1,2]
pushMethod - Add elements to the end of the array
const arr = [1,2]
arr.push(3) # [1,2,3]
spliceMethod - Add elements anywhere in the array
const arr = [1,2]
arr.splice(1,0,3) # [1,3,2]
The first input parameter is the starting index value , The second input parameter indicates the number of elements to be deleted from the starting index , The third parameter is the incoming value
2.2 Delete elements from array
- shift Method - Delete the elements at the head of the array
const arr = [1,2,3]
arr.shift() # [2,3]
- pop Method - Delete the elements at the end of the array
const arr = [1,2,3]
arr.pop() # [1,2]
- splice Method - Delete elements anywhere in the array
const arr = [1,2,3]
arr.splice(1,1) # [1, 3]
3 Stack 、 queue
The implementation of stack and queue generally depends on array
The difference between the two is , Their respective pairs of arrays Add or delete The operation has different restrictions .
3.1 Stack
Only adding elements from the tail is allowed
Only elements are allowed to be taken from the tail
// The initial state , The stack is empty
const stack = []
// Stacking process
stack.push(' Northeast big board ')
stack.push(' Cornetto ')
stack.push(' Chilez ')
stack.push(' Ice factory ')
stack.push(' Bright milk brick ')
// Stack out process , Execute only when the stack is not empty
while(stack.length) {
// Simply access the top element of the stack ( Don't stack )
const top = stack[stack.length-1]
console.log(' Now the ice cream is ', top)
// Push the top element out of the stack
stack.pop()
}
// The stack is empty
stack // []
3.2 queue
Only push and shift Complete the addition and deletion of “ Array ”
const queue = []
queue.push(' Little book one sister ')
queue.push(' Little book second sister ')
queue.push(' Little book third sister ')
while(queue.length) {
// Simply access the team head element ( Not out of the team )
const top = queue[0]
console.log(top,' Take the meal ')
// Remove the team head element from the team
queue.shift()
}
// Team space
queue // []
4 Linked list
In the list , The name of the data unit is “ node ”, And the distribution of nodes and nodes , Can be discrete in memory .
To access any element in the linked list , We all have to start from the starting point , One by one next, Access to the target node . To ensure that the starting point is reachable , We sometimes set a head Pointer to point to the starting position of the linked list :
- Create linked list node , You need a constructor :
function ListNode(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
- Use the constructor to create a node
const node = new ListNode(1)
node.next = new ListNode(2)
Data field value is 1,next The node data field value is 2
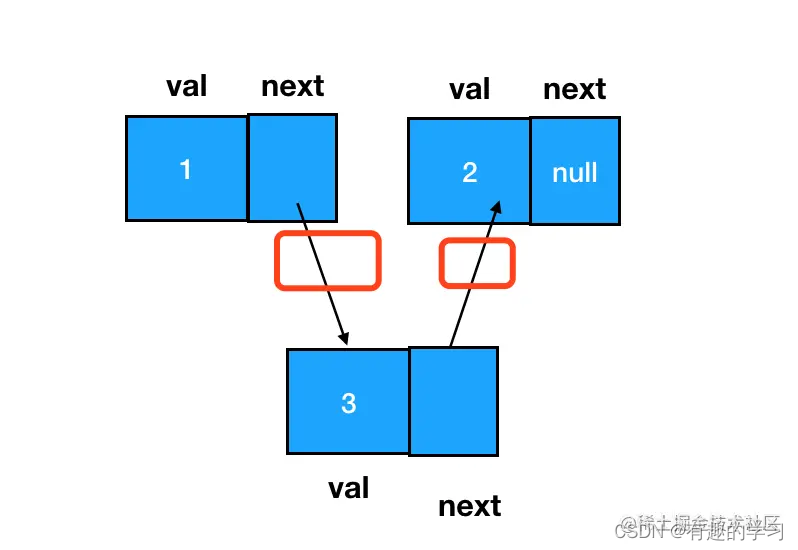
3. Insert a new node between any two nodes
What we need to change is Precursor node and Target node Of next Pointer to
# If the target node does not exist , So remember to create it manually
const node3 = new ListNode(3)
# hold node3 Of next Pointer to node2( namely node1.next)
node3.next = node1.next
# hold node1 Of next Pointer to node3
node1.next = node3
- Deletion of linked list elements
Directly let its precursor node node1 Of next The pointer jumps over it 、 Point to node3 In the subsequent
node1.next = node3.next
You can use only one pointer , This pointer is used to locate the precursor node of the target node .
// utilize node1 You can go to node3
const target = node1.next
node1.next = target.next
Relative to arrays , Linked lists have an obvious advantage , Adding and deleting elements does not require moving redundant elements
In the list , Just make it clear that you want to insert / Delete target location , The complexity of the add / delete operation is constant , Expressed as O(1).
however Linked list There is also a drawback : When we try to read a particular ( The first i individual ) The linked list node of , You must traverse the entire linked list to find it , Expressed as O(n).
But in Array in , We access the index directly 、 You can do it in one step , The complexity of this operation will be downgraded to a constant level O(1)
Insertion of linked list / Delete more efficiently , And the access efficiency is low ; The access efficiency of array is high , The insertion efficiency is low
边栏推荐
- Case analysis: using "measurement" to improve enterprise R & D efficiency | ones talk
- Financial management [2]
- Dig deep into MySQL - resolve the clustered index / secondary index / federated index of InnoDB storage engine
- Blogs personal blog test point (manual test)
- Building Survey [3]
- JD 618 conference tablet ranking list announced that the new dark horse brand staff will compete for the top three, learning from Huawei, the leader of domestic products
- Notes for laravel model
- Laravel user authorization
- 372. 棋盘覆盖
- Epics record reference 3 -- fields common to all records
猜你喜欢

【nvm】
对抗训练理论分析:自适应步长快速对抗训练
Concurrent shared model management
Theoretical analysis of countermeasure training: adaptive step size fast countermeasure training

docker安装mysql-简单无坑

并发之共享模型管程

01_SpingBoot 框架入门

【js】-【栈、队-应用】-学习笔记
Blogs personal blog project details (servlet implementation)

Canvas to add watermark to pictures
随机推荐
【js】-【字符串-应用】- 学习笔记
监听 Markdown 文件并热更新 Next.js 页面
laravel 验证器的使用
01_ Getting started with the spingboot framework
OpenSSL SSL_read: Connection was reset, errno 10054
07_ Springboot for restful style
Super detailed cookie addition, deletion, modification and query
Accounting standards for business enterprises application [5]
基本数据类型
Building Survey [3]
laravel学习笔记
JD 618 conference tablet ranking list announced that the new dark horse brand staff will compete for the top three, learning from Huawei, the leader of domestic products
golang convert json string to map
【js】-【数组、栈、队列、链表基础】-笔记
Construction equipment [6]
Financial management [2]
Dig deep into MySQL - resolve the non clustered index of MyISAM storage engine
OpenSSL SSL_ read: Connection was reset, errno 10054
冒泡排序
Attention, postgraduate candidates! They are the easiest scams to get caught during the preparation period?!