当前位置:网站首页>Risc-v tool chain compilation notes
Risc-v tool chain compilation notes
2022-07-27 02:26:00 【Time Flies Fang】
Catalog
Preface
RISC-V The instruction set has the advantage of being simplified due to its open source , At present, it is more and more widely used in the industry . This article is based on an open source project hummingbird E200 RISC-V SoC For example , Analyze and sort out the test method and process of self-test cases in this project , I hope I can give you the same inquiry learning RISC-V Some help from my friends .
One 、E200 RV Tool chain file structure
E200 The tool chain of is placed in riscv-tests Under the folder , The tool chain under this folder can put assembly instructions (.S file ) Compiled into binary files ( Store in genreated Under the folder ), The compilation process will also include stay /env And /isa/macros The following macro definitions reuse some standard assemblers 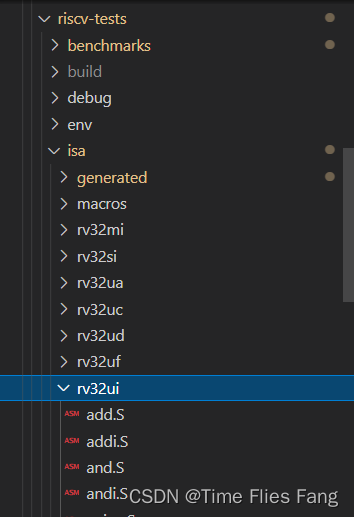
Two 、addi.S assembler
This section is to addi.S, Take the immediate addition instruction as an example , analysis e200 SoC Test method of self-test case , This can also help you understand the mapping process from software to hardware .
1. Source code
#*****************************************************************************
# addi.S
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Test addi instruction.
#
#include "riscv_test.h"
#include "test_macros.h"
RVTEST_RV64U
RVTEST_CODE_BEGIN
#-------------------------------------------------------------
# Arithmetic tests
#-------------------------------------------------------------
TEST_IMM_OP( 2, addi, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x000 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 3, addi, 0x00000002, 0x00000001, 0x001 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 4, addi, 0x0000000a, 0x00000003, 0x007 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 5, addi, 0xfffffffffffff800, 0x0000000000000000, 0x800 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 6, addi, 0xffffffff80000000, 0xffffffff80000000, 0x000 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 7, addi, 0xffffffff7ffff800, 0xffffffff80000000, 0x800 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 8, addi, 0x00000000000007ff, 0x00000000, 0x7ff );
TEST_IMM_OP( 9, addi, 0x000000007fffffff, 0x7fffffff, 0x000 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 10, addi, 0x00000000800007fe, 0x7fffffff, 0x7ff );
TEST_IMM_OP( 11, addi, 0xffffffff800007ff, 0xffffffff80000000, 0x7ff );
TEST_IMM_OP( 12, addi, 0x000000007ffff7ff, 0x000000007fffffff, 0x800 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 13, addi, 0xffffffffffffffff, 0x0000000000000000, 0xfff );
TEST_IMM_OP( 14, addi, 0x0000000000000000, 0xffffffffffffffff, 0x001 );
TEST_IMM_OP( 15, addi, 0xfffffffffffffffe, 0xffffffffffffffff, 0xfff );
TEST_IMM_OP( 16, addi, 0x0000000080000000, 0x7fffffff, 0x001 );
2. the definition
We can see from the source code that , In assembly language include 了 riscv_test.h and test_macros.h Two documents , stay riscv_test.h The code in mainly defines SoC Start code of , When the top-level assembly calls RVTEST_CODE_BEGIN When a macro is defined , Replace with the following code ( excerpts )
You can see , The startup code is mainly for SoC It's abnormal , Interrupt and other mechanisms for initialization settings , This part will be analyzed in detail if there is a chance to learn later . For all self-test cases , This part of the code is the same .
stay test_macros.h In file , It defines some test functions of self-test cases , With addi.S For example ,TEST_IMM_OP It's just one. test_macros.h Macro definition in , The relevant code is :
#define TEST_CASE( testnum, testreg, correctval, code... ) \ test_ ## testnum: \ code; \ li x29, MASK_XLEN(correctval); \ li TESTNUM, testnum; \ bne testreg, x29, fail;
//......
#define TEST_IMM_OP( testnum, inst, result, val1, imm ) \ TEST_CASE( testnum, x30, result, \ li x1, MASK_XLEN(val1); \ inst x30, x1, SEXT_IMM(imm); \ )
We use :
TEST_IMM_OP( 4, addi, 0x0000000a, 0x00000003, 0x007 );
Take this code as an example , Functionally , This is the fourth test instruction (testnum), What we tested was addi Instructions (inst), The right result is 0xa(result), Operands and immediate numbers (val1, imm) Respectively 0x3 and 0x7. that , At the assembly instruction level , Or on the hardware scale , How to verify this “3+7=10” The test is correct ?
Let's see test_macros.h Macro definition in , If the relevant macro definitions are all converted into assembly code , The assembly code of this test function can be written as :
li x1, 0x3;
addi x30, x1, 0x7;
li x29, 0xa;
li TESTNUM, 4;
bne x30, x29, fail;
After simplification and analysis , The above assembly code is already very simple ,li stay RV Is load immediate (load immediate) It means ,bne yes RV Branch jump instruction in , When the values stored in two registers are not equal, the program counter (PC) Jump . The function of the above code is to store the operation results in x30 In the register , Store the correct results in x29 In the register , And judge whether the values of the two registers are equal .
To verify whether our analysis is correct , We can also enter the file structure /isa/generated in , Find out .dump A file with a suffix , This part of the file is also called disassembly file , You can open it directly with a text editor , You can disassemble the binary files compiled by the tool chain into assembly language , To help developers see whether the compiler works properly , Find the disassembly code of this part as :
//rv32ui-p-addi.dump
8000027e <test_4>:
8000027e: 408d li ra,3
80000280: 00708f13 addi t5,ra,7
80000284: 4ea9 li t4,10
80000286: 4191 li gp,4
80000288: 1ddf1763 bne t5,t4,80000456 <fail>
The leftmost column of the above code is the instruction address , The middle column is 16 Instruction content of base , The rightmost column is disassembly code , You can see that the compiler has reallocated the address space and the naming character , But the specific functions are consistent with our analysis
summary
It is important to explore the process from software to hardware from the top down , It can help us understand the design and verification process of processors . In the future, I will continue to go deeper with e200 Hummingbird SoC Take the framework as an example to summarize and sort out the workflow of software and hardware collaboration .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

睡不着时闭眼躺着,到底有没有用?

(prefix and / thinking) codeforces round 806 (Div. 4) F Yet Another Problem About Pairs Satisfying an Inequality

HCIP-第四天-OSPF路由协议

【洋哥带你玩转线性表(四)——链式队列】

What is the principle of synchronized lock escalation in multithreading?
【洋哥带你玩转线性表(三)——双向链表】

First acquaintance with C language (1)

在有序数组找具体某个数字

Hcip bidirectional republication and routing strategy

多点双向重发布和路由策略-拓扑实验
随机推荐
js中的数组方法和循环
RS-485 bus communication application
Prompt to leave the page
今天浅讲一下转义字符【萌新版】
HCIP-第四天-OSPF路由协议
睡不着时闭眼躺着,到底有没有用?
Plato Farm有望通过Elephant Swap,进一步向外拓展生态
Timer interrupt experiment
HandsomeForum学习论坛
Introduction to STM32 lesson 1
Lora光照传感器节点数据采集
Record the star user of handsomeblog
JUC concurrent programming
【C语言程序设计】分支结构
C language - assignment operator, compound assignment operator, self increasing and self decreasing operator, comma operator, conditional operator, goto statement, comment
(prefix and / thinking) codeforces round 806 (Div. 4) F Yet Another Problem About Pairs Satisfying an Inequality
Hcip OSPF comprehensive experiment
Interesting C language
C language -- while statement, dowhile statement, for loop and loop structure, break statement and continue statement
Lecture 3 - GPIO input / output library function usage and related routines