当前位置:网站首页>C mapster object mapper learning
C mapster object mapper learning
2022-06-22 02:35:00 【Cook, sister】
install Mapster
PM> Install-Package Mapster
perhaps dotnet add package Mapster
Define the entity
Purpose : Use Mapster Realization User To UserDto Mapping
public class User
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string Sex { get; set; }
public string like { get; set; }
}
public class UserDto
{
public string name { get; set; }
public int UserAge { get; set; }
public string UserSex { get; set; }
public string like { get; set; }
}
Easy to use
/*
* By default , No configuration required ,Mapster It will match according to the same name of two entity fields
* On the first call , Configuration will be cached , The second time, it will fetch... From the cache , To improve performance
*/
var user = new User();
var dto = user.Adapt<UserDto>();// Map to a new object
user.Adapt(dto);// Mapping based on the target object
// Be careful :Adapt The configuration used by the extension method is `TypeAdapterConfig.GlobalSettings`
Mapster To configure (TypeAdapterConfig)
You can use it directly Mapster Built in global static configuration TypeAdapterConfig.GlobalSettings
, You can also instantiate a configuration new TypeAdapterConfig()
Instantiation is recommended , Yes TypeAdapterConfig Mapping configuration .
notes :Mapster The default matching rule is to map between the same field names .
Mode one
Directly in TypeAdapterConfig Configure the mapping relationship of objects
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
// Mapping rule
config.ForType<User, UserDto>()
.Map(dest => dest.UserAge, src => src.Age)
.Map(dest => dest.UserSex, src => src.Sex);
var mapper = new Mapper(config);// Be sure to mapper Set as single instance
var user = new User{Name = "xiaowang",Age = 18,Sex = "boy"};
var dto = mapper.Map<UserDto>(user);
The field has a pre suffix , have access to NameMatchingStrategy.ConvertDestinationMemberName
Replace the target field name , Make it the same as the source field name .
There are also ways to replace source fields NameMatchingStrategy.ConvertSourceMemberName
Be careful : If one
ForType
Define multipleNameMatchingStrategy
, The rules defined later will overwrite the rules defined earlier , So only the last defined rules will take effect
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
// Use
config.ForType<User, UserDto>()
.NameMatchingStrategy(NameMatchingStrategy.ConvertDestinationMemberName(dest => dest.Replace("User", "")));
Mode two
How to use the interface , Need to achieve IRegister
// Implementation interface IRegister
public class UserDtoRegister : IRegister
{
public void Register(TypeAdapterConfig config)
{
config.ForType<User,UserDto>()
Map(dest => dest.UserAge, src => src.Age);
//...
}
}
// Instantiation Mapper
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
//var config = TypeAdapterConfig.GlobalSettings;
// Only to be given IRegister Assembly name ,Mapster Will automatically identify IRegister, Perform configuration injection .
config.Scan(" Assembly name 1"," Assembly name 2");
var mapper = new Mapper(config);// Be sure to set to single instance
Ignore fields
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
// Mapping rule
config.ForType<User, UserDto>()
.Map(dest => dest.UserAge, src => src.Age)
.Map(dest => dest.UserSex, src => src.Sex);
.IgnoreNullValues(true)// Ignore null mapping
.Ignore(dest => dest.UserAge)// Ignore specified fields
.IgnoreAttribute(typeof(DataMemberAttribute))// Ignore fields for specified properties
.NameMatchingStrategy(NameMatchingStrategy.IgnoreCase)// Ignore the case of field names
.IgnoreNonMapped(true);// Ignore all fields except those configured above
config.ForType<User,UserDto>()
.IgnoreMember((member, side) => !member.Type.Namespace.StartsWith("System"));// Implement more granular ignore rules
member
and side
They correspond to each other IMemberModel
and MemberSide
, Here I post the corresponding source code .
// Contains information about the mapping type
public interface IMemberModel
{
Type Type { get; }
string Name { get; }
object? Info { get; }
AccessModifier SetterModifier { get; }
AccessModifier AccessModifier { get; }
IEnumerable<object> GetCustomAttributes(bool inherit);
}
// Identifies whether the current source type or target type
public enum MemberSide
{
Source = 0,
Destination = 1
}
Branch (Fork)
Mapster Of Fork The function allows us to define local mapping rules , And the branch does not compile repeatedly , There is no need to consider performance issues .
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
var mapper = new Mapper(config);
var user = new User{Name = "xiaowang",Age = 18,Sex = "boy"};
var dto = mapper.From(user).ForkConfig(forked =>
{
// This branch rule , Will not compile repeatedly , Only valid in this statement , Does not affect the config Configuration of
forked.ForType<User, UserDto>().Map(dest => dest.name, src => src.Name);
})
.AdaptToType<UserDto>();// Map to a new object
dto = mapper.From(user).ForkConfig(forked =>
{
forked.ForType<User, UserDto>().Map(dest => dest.name, src => src.Name);
})
.AdaptTo(new UserDto());// Mapping based on the target object
NewConfig Method
NewConfig Method allows us to create a new configuration between two types , If the mapping relationship has been configured before the two types , be NewConfig Method overrides the previous configuration
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
config.ForType<User,UserDto>().Map(dest => dest.UserAge, src => src.Age);
//...
// Cover User and UserDto Previous configuration
config.NewConfig<User,UserDto>().Map(dest=>dest.UserAge,src=>100);
// Expanding knowledge : Cover Mapster Default static configuration
TypeAdapterConfig<User,UserDto>.NewConfig().Default.NameMatchingStrategy(NameMatchingStrategy.IgnoreCase);
Pass parameters at runtime
Allow the runtime to pass in data , Intervene in the mapping process
var config = new TypeAdapterConfig();
config.ForType<User, UserDto>()
.Map(dest => dest.name, src => MapContext.Current.Parameters["userName"]);// Configure runtime parameters
var mapper = new Mapper(config);
// Incoming data when using
var user = new User();
var dto = mapper.From(user).BuildAdapter().AddParameters("userName","xiaowang").AdaptToType<UserDto>();
Other knowledge points
We try not to configure the mapping rules between entities to TypeAdapterConfig.GlobalSettings
( The default configuration ). As the business grows , It is difficult to balance all businesses in one configuration , Possible travel conflicts , Relatively complex business , You can create a new TypeAdapterConfig
, Or use config.Clone()
Can easily copy a configuration . Global configuration can put some simple configuration items , for example : Ignore case when mapping .
Be careful :Adapt The extension method uses
TypeAdapterConfig.GlobalSettings
Tips
Adapt The use of extension methods
Dictionary<string,object> dict = new User().Adapt<Dictionary<string,object>>();//object To Dictionary Transformation
string s = 123.Adapt<string>(); //equal to 123.ToString();
int i = "123".Adapt<int>(); //equal to int.Parse("123");
Before and after intercepting the mapping
BeforeMapping
Methods and AfterMapping
//BeforeMapping Before the mapping is executed
config.ForType<User, UserDto>().BeforeMapping((src, dest) =>
{
src.Age = 100;
dest.UserAge = src.Age + 10;
});
//AfterMapping After the mapping is executed
//...
For more tips, see the official documentation :GitHub - MapsterMapper/Mapster: A fast, fun and stimulating object to object Mapper
边栏推荐
- EMC整改小技巧
- How to apply PMP project management knowledge?
- Wechat applet film and television comment exchange platform system graduation design completion (6) opening defense ppt
- Minecraft 1.18.2 生化8 模组 1.3版本 物品3D化+更加复杂村庄
- 【3.整数与浮点数二分】
- DAST black box vulnerability scanner part 4: scanning performance
- EMC Radiation Emission rectification - principle Case Analysis
- 最新发布:Neo4j 图数据科学 GDS 2.0 和 AuraDS GA
- rt_thread线程管理
- Qt程序怎么实现选中ListWidget中的某一行为默认选中
猜你喜欢
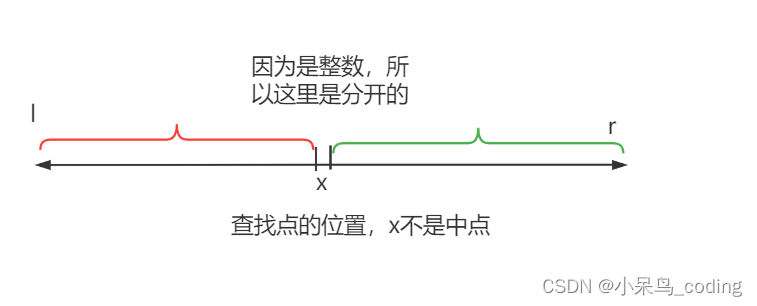
【3.整数与浮点数二分】
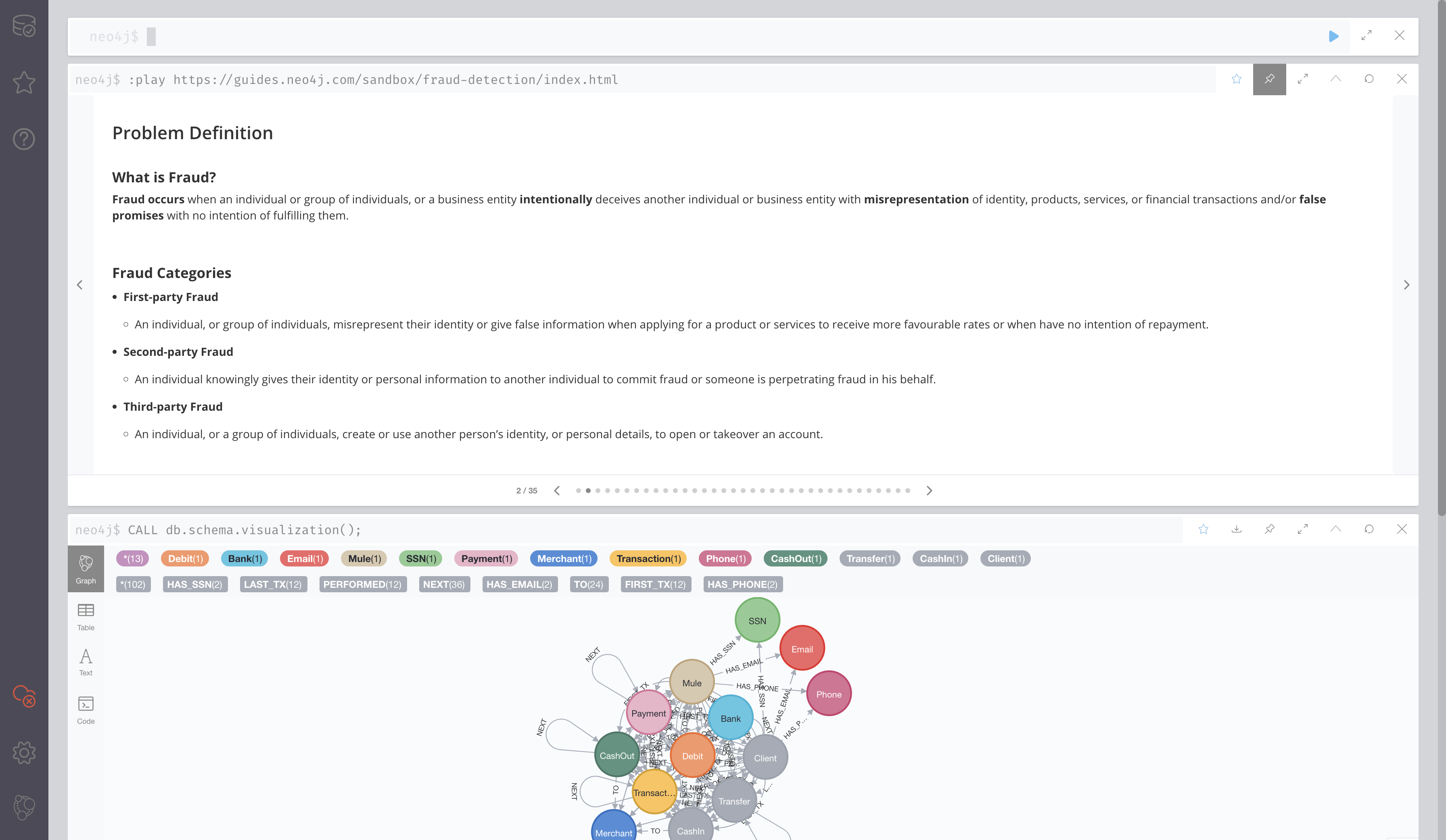
使用 Neo4j 沙箱学习 Neo4j 图数据科学 GDS

Wechat applet film and television comment exchange platform system graduation design (2) applet function
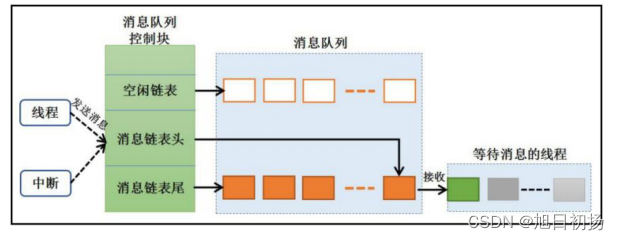
rt_ Message queue of thread
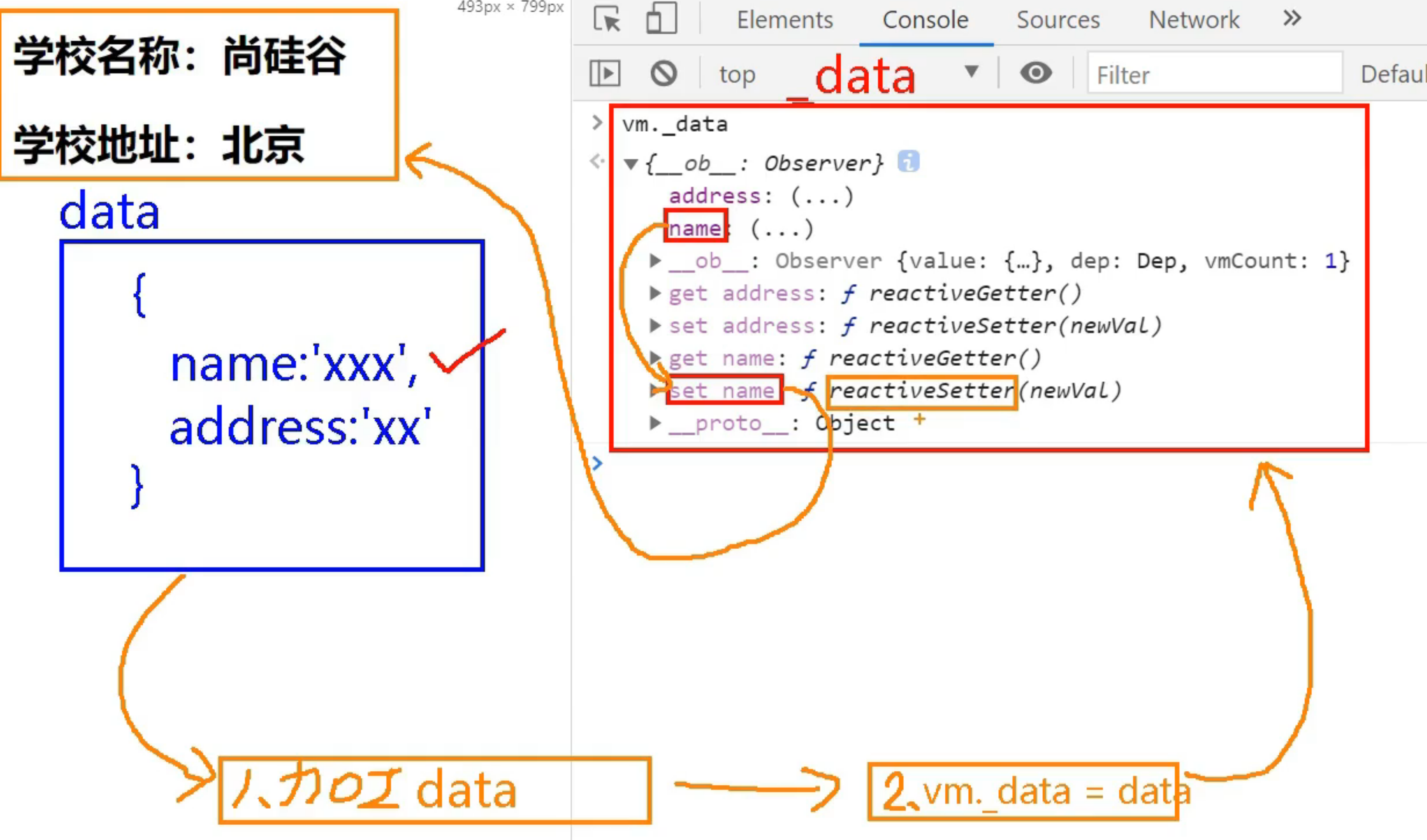
Atguigu---- list rendering

微信小程序影视评论交流平台系统毕业设计毕设(6)开题答辩PPT

In 2022, the number of mobile banking users in Q1 will reach 650million, and ESG personal financial product innovation will be strengthened

Review of mathematical knowledge: triple integral

On Monday, I asked the meaning of the | -leaf attribute?

Wechat applet film and television comment exchange platform system graduation design completion (6) opening defense ppt
随机推荐
Show you how to distinguish several kinds of parallelism
Word document to markdown document?
Zap grammar sugar
国产品牌OPPO官方最新出品!这份PPT报告!真刷新我对它认知了
How does the QT program implement the default selection of a behavior in the selected listwidget
rt_thread的消息队列
Flash back when GoLand starts
智翔金泰冲刺科创板:年营收3919万亏损超3亿 拟募资40亿
Graphconnect 2022 at a glance
华阳智能冲刺深交所:拟募资4亿 复星惟盈是股东
Get to know unity3d (project structure, third-party plug-in of probuilder)
微信小程序影视评论交流平台系统毕业设计毕设(2)小程序功能
import和require在浏览器和node环境下的实现差异
Return to Chengdu to start my software testing career
Wechat applet film and television comment exchange platform system graduation design (3) background function
Matlab learning notes (5) import and export of MATLAB data
使用 OKR 进行 HR 数字化转型
EMC radiation emission rectification - principle case analysis
How to use tensorboard add_ histogram
Informer有什么